Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1268-1276.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.06.011
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
A neural regulation mechanism of head electroacupuncture on brain network of patients with stroke related sleep disorders
ZHANG Boyang1, ZHOU Yang2, FENG Liyuan3, SUI Dan4, HE Lei5, TONG Dan6, WANG Ruoyu3, SUI Xue7, SONG Jing3, WANG Dongyan3( )
)
- 1 Rehabilitation Department, Wuxi Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuxi 214000, China
2 Imaging Department, Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, Harbin 150000, China
3 Acu-Moxi Department III, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150000, China
4 Rehabilitation Department B, Second Hospital of Harbin, Harbin 150000, China
5 Acu-Moxi Department, Lianyungang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lianyungang 222000,China
6 Integrated TCM and Western Medicine Department, Suzhou Dushu lake hospital, Suzhou 215000, China
7 Internal Medicine Department, Zhaozhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Daqing 163000, China
-
Received:2023-09-23Accepted:2024-01-10Online:2024-12-15Published:2024-11-12 -
Contact:Prof. WANG Dongyan, Acu-Moxi Department Ⅲ, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150000, China. doctwdy@163.com Telephone: +86-18646026767 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China Project: the Study of Central Mechanism of Electroacupuncture on Sishencong (EX-HN1) Improving Sleep Architecture and Neurocognitive Function Using Electroencephalogram-Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging(81774426);Major Scientific Research Project of Wuxi Health Commission: Clinical Study of Intelligent Hand Rehabilitation Training System for Nerve Function Reconstruction of Patients with Hand Dysfunction after Cerebral Infarction(Z202121)
Cite this article
ZHANG Boyang, ZHOU Yang, FENG Liyuan, SUI Dan, HE Lei, TONG Dan, WANG Ruoyu, SUI Xue, SONG Jing, WANG Dongyan. A neural regulation mechanism of head electroacupuncture on brain network of patients with stroke related sleep disorders[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1268-1276.
share this article
| Scale | SA group (n = 33) | EA group (n = 34) | F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSQI | 13.7±2.0 | 14.6±2.7 | 2.87 | 0.095 |
| MoCA_B | 19.5±4.3 | 19.6±4.0 | 0.02 | 0.897 |
| SAS | 48.6±6.6 | 48.1±5.7 | 0.09 | 0.759 |
| SDS | 53.2±7.6 | 52.4±7.8 | 0.16 | 0.690 |
Table 1 Scale scores comparing EA and SA groups before treatment ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Scale | SA group (n = 33) | EA group (n = 34) | F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSQI | 13.7±2.0 | 14.6±2.7 | 2.87 | 0.095 |
| MoCA_B | 19.5±4.3 | 19.6±4.0 | 0.02 | 0.897 |
| SAS | 48.6±6.6 | 48.1±5.7 | 0.09 | 0.759 |
| SDS | 53.2±7.6 | 52.4±7.8 | 0.16 | 0.690 |
| Scale | SA group (n = 33) | EA group (n = 34) | F value | P value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD | MD | |||||
| PSQI | 12.2±1.5 | -1.42 | 7.1±2.4 | -7.59 | 109.98 | <0.001 |
| MoCA_B | 21.9±2.8 | 2.36 | 26.1±2.2 | 6.41 | 45.79 | <0.001 |
| SAS | 45.2±5.3 | -3.37 | 40.0±5.1 | -8.14 | 16.79 | <0.001 |
| SDS | 50.0±6.4 | -3.19 | 43.8±5.8 | -8.60 | 17.09 | <0.001 |
Table 2 Scale scores comparing EA and SA groups after treatment
| Scale | SA group (n = 33) | EA group (n = 34) | F value | P value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD | MD | |||||
| PSQI | 12.2±1.5 | -1.42 | 7.1±2.4 | -7.59 | 109.98 | <0.001 |
| MoCA_B | 21.9±2.8 | 2.36 | 26.1±2.2 | 6.41 | 45.79 | <0.001 |
| SAS | 45.2±5.3 | -3.37 | 40.0±5.1 | -8.14 | 16.79 | <0.001 |
| SDS | 50.0±6.4 | -3.19 | 43.8±5.8 | -8.60 | 17.09 | <0.001 |
| Scales | Time | SA group (n = 33) | EA group (n = 34) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F value | P value | F value | P value | |||||
| PSQI | Pre | 13.7±2.0 | 10.66 | 0.002 | 14.6±2.7 | 311.67 | <0.001 | |
| Post | 12.2±1.5 | 7.1±2.4 | ||||||
| MoCA_B | Pre | 19.5±4.3 | 26.88 | <0.001 | 19.6±4.0 | 203.77 | <0.001 | |
| Post | 21.9±2.8 | 26.1±2.2 | ||||||
| SAS | Pre | 48.6±6.6 | 13.42 | 0.001 | 48.1±5.7 | 80.58 | <0.001 | |
| Post | 45.2±5.3 | 40.0±5.1 | ||||||
| SDS | Pre | 53.2±7.6 | 11.67 | 0.001 | 52.4±7.8 | 87.45 | <0.001 | |
| Post | 50.0±6.4 | 43.8 ± 5.8 | ||||||
Table 3 Scale scores comparing pre- and post-treatment within EA and SA groups
| Scales | Time | SA group (n = 33) | EA group (n = 34) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F value | P value | F value | P value | |||||
| PSQI | Pre | 13.7±2.0 | 10.66 | 0.002 | 14.6±2.7 | 311.67 | <0.001 | |
| Post | 12.2±1.5 | 7.1±2.4 | ||||||
| MoCA_B | Pre | 19.5±4.3 | 26.88 | <0.001 | 19.6±4.0 | 203.77 | <0.001 | |
| Post | 21.9±2.8 | 26.1±2.2 | ||||||
| SAS | Pre | 48.6±6.6 | 13.42 | 0.001 | 48.1±5.7 | 80.58 | <0.001 | |
| Post | 45.2±5.3 | 40.0±5.1 | ||||||
| SDS | Pre | 53.2±7.6 | 11.67 | 0.001 | 52.4±7.8 | 87.45 | <0.001 | |
| Post | 50.0±6.4 | 43.8 ± 5.8 | ||||||

Figure 1 Main FC enhanced areas of DMN in the EA group before treatment FC: functional connectivity; DMN: default mode network; EA: electroacupuncture group.
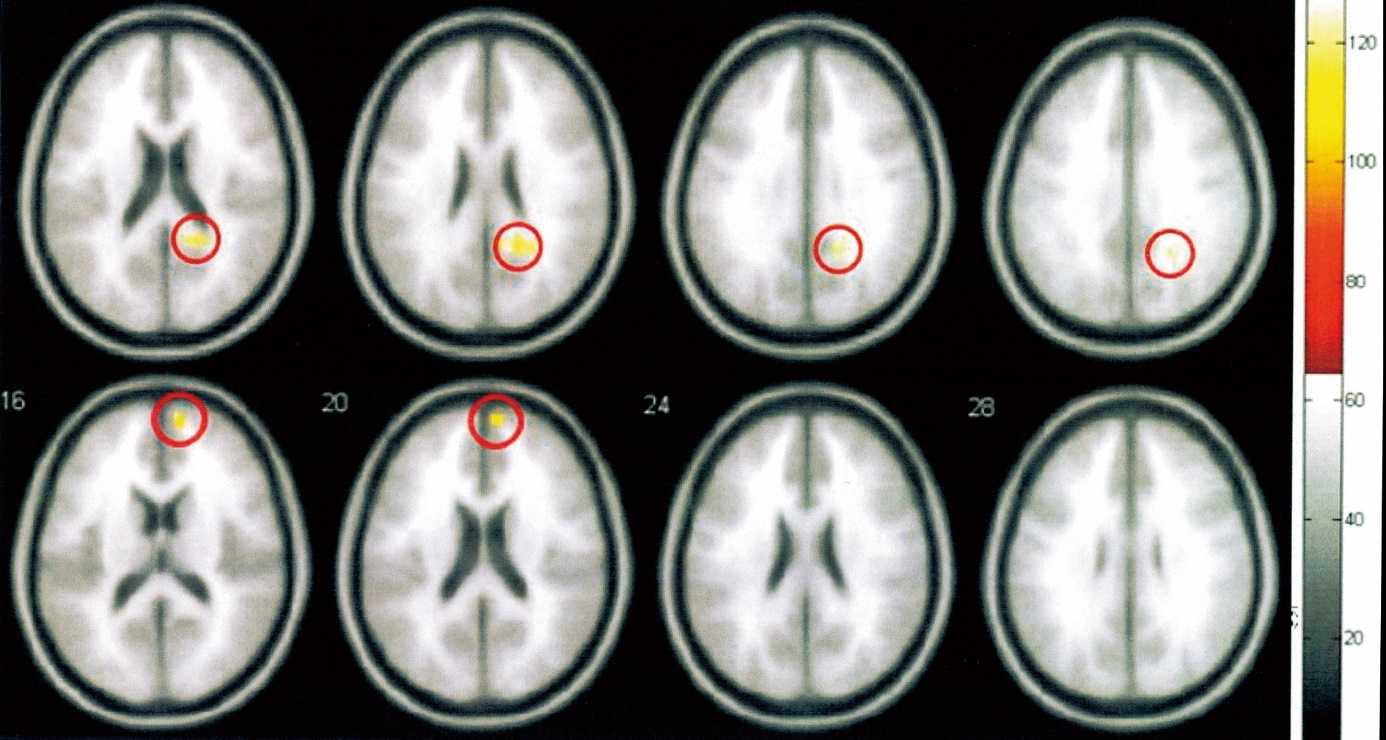
Figure 2 Main FC weakened areas of DMN in the EA group after treatment FC: functional connectivity; DMN: default mode network; EA: electroacupuncture group.

Figure 3 Main FC enhanced areas of CCN in the EA group after treatment FC: functional connectivity; CCN: cognitive control network EA: electroacupuncture group.
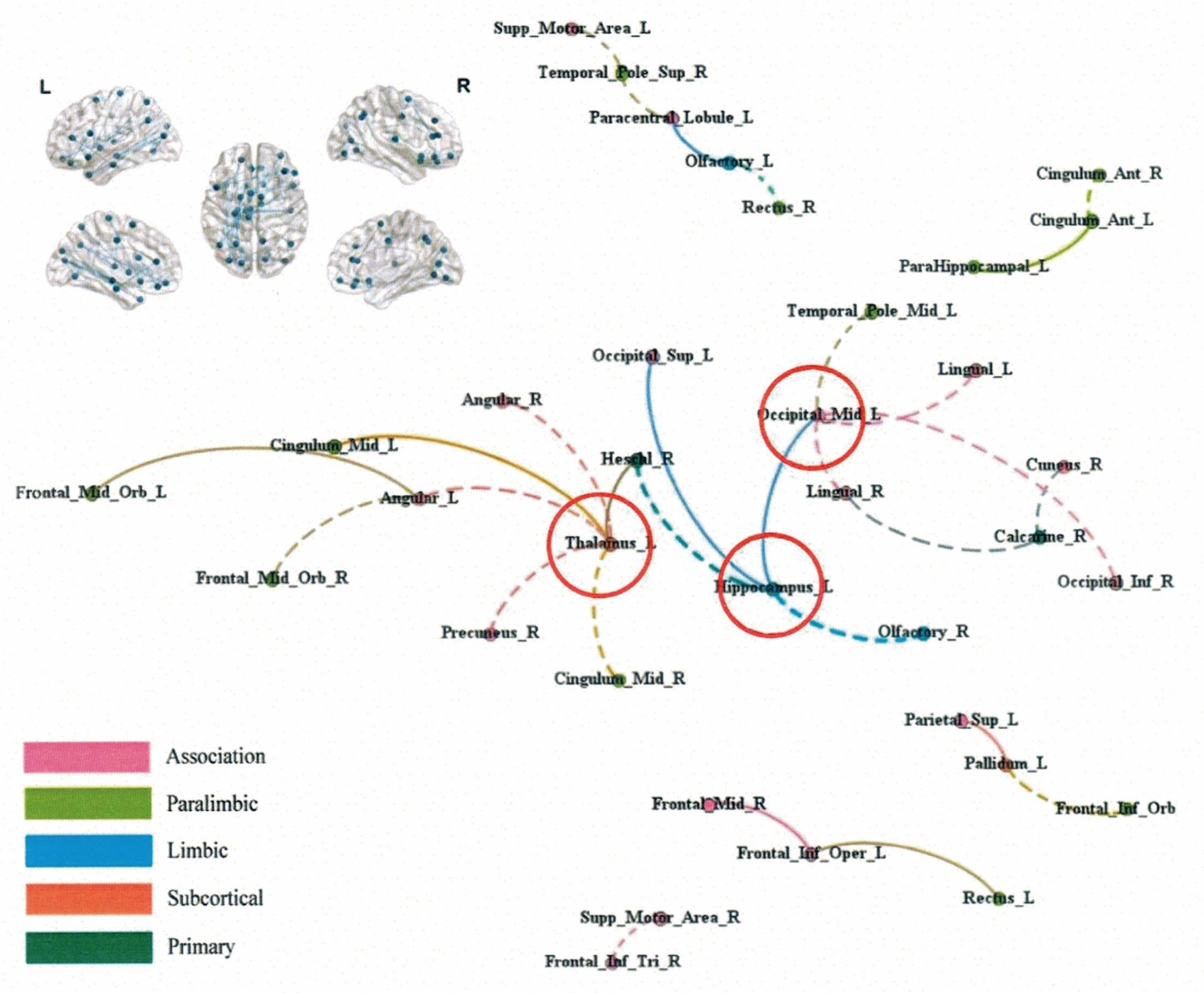
Figure 4 Plane visualization of the significant results of continuous edges analysis in the EA group after treatment EA: electroacupuncture group. The Thalamus.L, Hippocampus.L, and Occipital.mid.L were the key nodes.
| 1. |
Hepburn M, Bollu PC, French B, Sahota P. Sleep medicine: stroke and sleep. Mo Med 2018; 115: 527-32.
PMID |
| 2. | Baylan S, Griffiths S, Grant N, Broomfield NM, Evans JJ, Gardani M. Incidence and prevalence of post-stroke insomnia: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev 2020; 49: 101222. |
| 3. |
Das J, G K R. Post stroke depression: the sequelae of cerebral stroke. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2018; 90: 104-14.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Cai W, Mueller C, Li YJ, Shen WD, Stewart R. Post stroke depression and risk of stroke recurrence and mortality: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev 2019; 50: 102-9.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Johansson U, Nilsson AÖ, Falkdal AH, von Koch L, Hellman T, Eriksson G. The delivery of the ReWork-Stroke program: a process evaluation. Work 2021; 70: 467-78.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Manconi M, Ferri R, Miano S, et al. Sleep architecture in insomniacs with severe benzodiazepine abuse. Clin Neurophysiol 2017; 128: 875-81.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Alessi C, Vitiello MV. Insomnia (primary) in older people: non-drug treatments. BMJ Clin Evid 2015; 2015: 2302. |
| 8. | Hou Z, Sun Z, Sun S. Impacts of the repetitive transcranial acupuncture stimulation on the content of serum orexin: A in patients with post-stroke insomnia. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2018; 38: 1039-42. |
| 9. | Yeung WF, Chung KF, Zhang SP, Yap TG, Law AC. Electro-acupuncture for primary insomnia: a randomized controlled trial. Sleep 2009; 32: 1039-47. |
| 10. | Gao H. International Classification of Sleep Disorders (3): Diagnostic criteria for a chronic insomnia disorder. Shijie Shui Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018; 5: 555-7. |
| 11. | Wang LD, Liu JM, Yang Y, Peng B, Wang YL. Stroke prevention and treatment in China still faces great challenges- guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke in China 2018; Zhong Guo Xun Huan Za Zhi 2019, 34: 105-19. |
| 12. | Geriatric Neurology Group of Geriatric Medicine Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Expert recommendations on the process of diagnosis and treatment of cognitive disorders in Chinese elderly. Zhong Hua Lao Nian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2014; 33: 817-25. |
| 13. |
Napadow V, Makris N, Liu J, Kettner NW, Kwong KK, Hui KK. Effects of electroacupuncture versus manual acupuncture on the human brain as measured by fMRI. Hum Brain Mapp 2005; 24: 193-205.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Yang HY, Wang DY, Dong X, He L, Lu SY, Jiao ML. Status of placebo acupuncture control research. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2020; 40: 337-41. |
| 15. | Szucs D, Ioannidis JP. Sample size evolution in neuroimaging research: an evaluation of highly-cited studies (1990-2012) and of latest practices (2017-2018) in high-impact journals. Neuroimage 2020; 221: 117164. |
| 16. |
Kundu P, Voon V, Balchandani P, Lombardo MV, Poser BA, Bandettini PA. Multi-echo fMRI: a review of applications in fMRI denoising and analysis of BOLD signals. Neuroimage 2017; 154: 59-80.
DOI PMID |
| 17. |
Chai Y, Sheng J, Men W, Fan Y, Wu B, Gao JH. MR imaging of oscillatory magnetic field changes: progressing from phantom to human. Magn Reson Imaging 2017; 36: 167-74.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Cao J, Ai M, Chen X, Chen J, Wang W, Kuang L. Altered resting-state functional network connectivity is associated with suicide attempt in young depressed patients. Psychiatry Res 2020; 285: 112713. |
| 19. | Shuai XX, Kong XC, Zou Y, Wang SQ, Wang YH. Global functional network connectivity disturbances in parkinson's disease with mild cognitive impairment by resting-state fMRI. Curr Med Sci 2020; 40: 1057-66. |
| 20. | Boespflug EL, Iliff JJ. The emerging relationship between interstitial fluid-cerebrospinal fluid exchange, amyloid-β, and sleep. Biol Psychiatry 2018; 83: 328-36. |
| 21. |
Lemche E, Giampietro VP, Brammer MJ, Surguladze SA, Williams SC, Phillips ML. Somatization severity associated with postero-medial complex structures. Sci Rep 2013; 3: 1032.
DOI PMID |
| 22. | Fan X, Song Y, Ma F. The physiological function of cingulate cortex and its role in the mechanism of tinnitus. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2020; 34: 1141-44. |
| 23. |
Enatsu R, Bulacio J, Nair DR, Bingaman W, Najm I, Gonzalez-Martinez J. Posterior cingulate epilepsy: clinical and neurophysiological analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2014; 85: 44-50.
DOI PMID |
| 24. | Mohamed IS, Otsubo H, Shroff M, Donner E, Drake J, Snead OC. Magnetoencephalography and diffusion tensor imaging in gelastic seizures secondary to a cingulate gyrus lesion. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2007; 109: 182-7. |
| 25. | Lin YJ, Kung YY, Kuo WJ, et al. Effect of acupuncture 'dose' on modulation of the default mode network of the brain. Acupunct Med 2016; 34: 425-32. |
| 26. | Luna B, Thulborn KR, Strojwas MH, et al. Dorsal cortical regions subserving visually guided saccades in humans: an fMRI study. Cereb Cortex 1998; 8: 40-7. |
| 27. |
Castelhano J, Duarte IC, Ferreira C, Duraes J, Madeira H, Castelo-Branco M. The role of the insula in intuitive expert bug detection in computer code: an fMRI study. Brain Imaging Behav 2019; 13: 623-37.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Marques DR, Gomes AA, Caetano G, Castelo-Branco M. Insomnia disorder and brain's default-mode network. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2018; 18: 45. |
| 29. |
Ismaylova E, Di Sante J, Gouin JP, et al. Associations between daily mood states and brain gray matter volume, resting-state functional connectivity and task-based activity in healthy adults. Front Hum Neurosci 2018; 12: 168.
DOI PMID |
| 30. | Xue JY, Xu JY, Huang Mao, et al. Scalp acupuncture Yikang therapy on Baihui (GV20), Sishencong (EX-HN1), Zhisanzhen, Niesanzhen improves neurobehavior in young rats with cerebral palsy through Notch signaling pathwa. J Tradit Chin Med 2023; 43: 337-42. |
| 31. | Liu H, Chen L, Zhang G, et al. Scalp acupuncture enhances the functional connectivity of visual and cognitive-motor function network of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020; 2020: 8836794. |
| 32. |
Kim KK, Karunanayaka P, Privitera MD, Holland SK, Szaflarski JP. Semantic association investigated with functional MRI and independent component analysis. Epilepsy Behav 2011; 20: 613-22.
DOI PMID |
| 33. |
Sala-Llonch R, Palacios EM, Junqué C, Bargalló N, Vendrell P. Functional networks and structural connectivity of visuospatial and visuoperceptual working memory. Front Hum Neurosci 2015; 9: 340.
DOI PMID |
| 34. |
Hecht D. Depression and the hyperactive right-hemisphere. Neurosci Res 2010; 68: 77-87.
DOI PMID |
| 35. | Mantovani A, Lisanby SH, Pieraccini F, Ulivelli M, Castrogiovanni P, Rossi S. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in the treatment of panic disorder (PD) with comorbid major depression. J Affect Disord 2007; 102: 277-80. |
| 36. | Wang YQ, Li R, Zhang MQ, Zhang Z, Qu WM, Huang ZL. The neurobiological mechanisms and treatments of REM sleep disturbances in depression. Curr Neuropharmacol 2015; 13: 543-53. |
| 37. |
Kouros CD, Keller PS, Martín-Piñón O, El-Sheikh M. Bidirectional associations between nightly sleep and daily happiness and negative mood in adolescents. Child Dev 2022; 93: e547-62.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Chen LM, Sun JF, Guo CL, et al. Preliminary single-arm study of brain effects during transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation treatment of recurrent depression by resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging. J Tradit Chin Med 2022; 42: 818-24.
DOI |
| [1] | XU Yingshan, WU Chunxiao, YU Wei, GUO Hongji, LU Liming, XU Nenggui, TANG Chunzhi. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 859-870. |
| [2] | ZHANG Fang, YAN Cuina, WENG Zhijun, WU Luyi, QI Li, ZHAO Min, XIN Yuhu, WU Huangan, LIU Huirong. Regulatory role of electroacupuncture on satellite glial cell activity in the colon and dorsal root ganglion of rats with irritable bowel syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 981-990. |
| [3] | CHEN Yonglin, OUYANG Ling, MENG Lingling, WU Bufan, PENG Rou, LIU Sitong, HOU Dan, WANG Yaling, JING Xinyue, LU Shengfeng, FU Shuping. Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 734-744. |
| [4] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [5] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [6] | SUN Qianhui, CHENG Kai, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, WU Xiaoling, XU Chang, QIU Xinghua, GAO Xiaofeng, LIU Daonan, YANG Qirui. Effect of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) at different time points on myocardial ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 113-121. |
| [7] | DU Zhongheng, CONG Wenjie, TANG Kejing, ZHENG Qiqi, SONG Zhiwei, CHEN Yong, YANG Su, ZHANG Chunwu, YE Tianshen. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) in mice with collagen-induced arthritis leads to adenosine A2A receptor-mediated alteration of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1103-1109. |
| [8] | JIANG Jianzhen, ZHANG Xin, LUO Zhenguo, SU Chengguo, ZHOU Haiyan, JIANG Yuqing, XIAO Xianjun, CHEN Yunfei, ZHU Jun. Efficacy of electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36) and Xuanzhong (GB39) on synovial angiogenesis in rats with adjuvant arthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 955-962. |
| [9] | LI Zhihao, HAN Wenjun, SONG Xiuling, LI Yan, CHEN Yuelai. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zhongji (CV3), Guanyuan (CV4), and bilateral Dahe (KI12) attenuates inflammation in rats with chronic nonbacterial prostatitis induced by estradiol through inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 963-972. |
| [10] | DING Luobin, WANG Huajun, LI Yao, LI Jia, LI Ling, GAO Yangping, GUAN Jian, GENG Weiqiang. Electroacupuncture stimulating Neixiyan (EX-LE5) and Dubi (ST35) alleviates osteoarthritis in rats induced by anterior cruciate ligament transaction via affecting DNA methylation regulated transcription of miR-146a and miR-140-5p [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 983-990. |
| [11] | SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, WANG Yuhang, XIN Chen, GU Dongmei, SUN Jianhua, PEI Lixia. Electroacupuncture alleviates water avoidance stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by improving intestinal barrier functions and suppressing the expression of inflammatory cytokines [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 494-500. |
| [12] | HAN Rui, CHANG Junzhao, LIU Qianqian, LIU Haitao, LI Junwei. Efficacy of electroacupunture at Zusanli (ST36) on jumping-injured muscle based on transcriptome sequencing and genes analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 322-328. |
| [13] | Minh Duc Nguyen, Thanh Van Tran, Quoc Vinh Nguyen, Ninh Khac Nguyen, Son Truong Vu, Luu Trong Nguyen, Linh Vu Phuong Dang. Effectiveness on post-stroke hemiplegia in patients: electroacupuncture plus cycling vs electroacupuncture alone [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 352-358. |
| [14] | XU Chang, LI Na, WU Xiaoling, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, SUN Qianhui, SHI Tianyu, CHAI Yemao, PANG Dandan, CHENG Kai. Effect of electroacupuncture on inflammatory signal expression in local tissues of rats with chronic pelvic pain syndrome based on purinergic 2X7 receptor/NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 signal pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 965-971. |
| [15] | SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, ZHAO Tingting, WANG Yuhang, PEI Lixia, SUN Jianhua. Electroacupuncture at Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) alleviates stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by modulating gut microbiota and corticotropin-releasing factor [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 732-740. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

