Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 830-838.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240515.006
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Acupuncture improves the live birth of patients with repeated implantation failure: a retrospective cohort study
SUN Junjian1,2, XIE Henghui3, LI Huanhuan4, TIAN Xiangming4, FANG Yigong5( ), ZHOU Wenhui4(
), ZHOU Wenhui4( )
)
- 1 Medical Center for Human Reproduction, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100020, China
2 Department of Gynecology, Beijing First Hospital of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Beijing 100026, China
3 Department of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100020, China
4 Medical Center for Human Reproduction, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100020, China
5 Institute of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2024-11-18Accepted:2024-03-14Online:2024-08-15Published:2024-05-15 -
Contact:Prof. FANG Yigong, Institute of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China.fangyigong@163.com Telephone: +86-10-64014411; Prof. ZHOU Wenhui, Medical Center for Human Reproduction, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100020, China.wenhuizhbjcy@126.com Telephone: +86-10-85231423
Cite this article
SUN Junjian, XIE Henghui, LI Huanhuan, TIAN Xiangming, FANG Yigong, ZHOU Wenhui. Acupuncture improves the live birth of patients with repeated implantation failure: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 830-838.
share this article
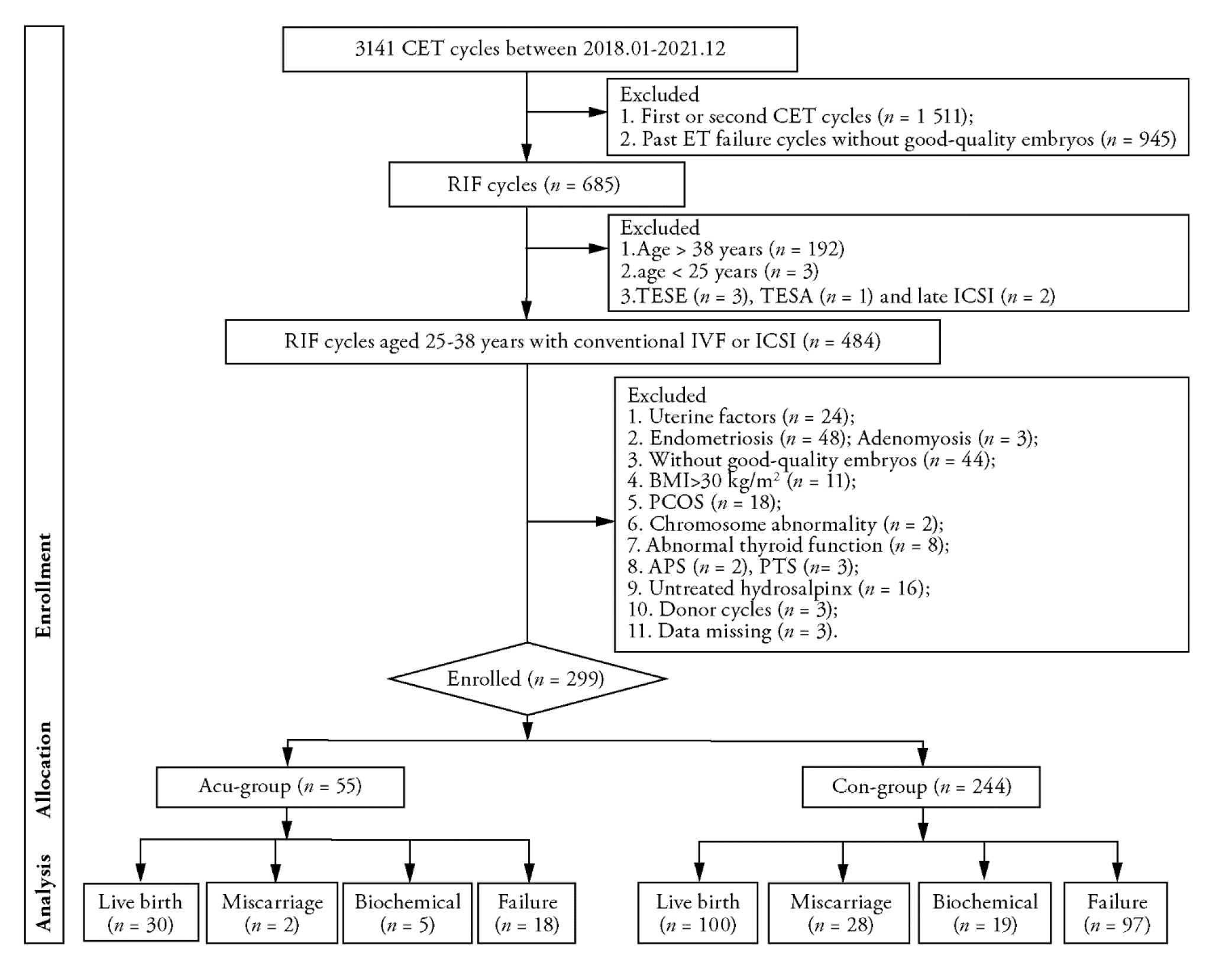
Figure 1 Flow chart IVF: in vitro fertilization; ICSI: intracytoplasmic sperm injection; CET: cryo-thawed embryo transfer; ET: embryo transfer; TESE: testicular sperm extraction; TESA: testicular sperm aspiration; RIF: repeated implantation failure; BMI: body mass index; PCOS: polycystic ovary syndrome; APS: Antiphospholipid syndrome; PTS: Pre-thrombolic state.
| Characteristic | Acu (n = 55) | Con (n = 244) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at OPU (years) | 33.0 (30.0-36.0) | 33.0 (30.0-35.8) | 0.519 |
| Age during ET (years) | 34.0 (30.0-37.0) | 33.0 (31.0-36.0) | 0.701 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.2 ± 0.4 | 22.1 ± 0.2 | 0.854 |
| Basal FSH (IU/L) | 7.1 (5.8-8.5) | 6.3 (5.4-7.7) | 0.030 |
| Basal E2 (pg/mL) | 47.2 ± 2.1 | 50.2 ± 1.6 | 0.480 |
| Antral follicle count | 12.0 (10.0-15.0) | 14.0 (10.0-19.0) | 0.034 |
| Causes of infertility [(n) %] Female Male Mixes Unexplained | (27) 49.1 (1) 1.8 (16) 29.1 (11) 20.0 | (136) 55.7 (15) 6.1 (40) 16.4 (53) 21.7 | 0.114 |
| Infertility type [(n) %] Primary Secondary | (39) 70.9 (16) 29.1 | (158) 64.8 (86) 35.2 | 0.384 |
| No. of ET-failure cycles [(n) %] Twice Three times More than three times | (42) 76.4 (8) 14.5 (5) 9.1 | (153) 62.7 (61) 25.0 (30) 12.3 | 0.149 |
Table 1 Baseline clinical information of patients according to acupuncture therapy
| Characteristic | Acu (n = 55) | Con (n = 244) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at OPU (years) | 33.0 (30.0-36.0) | 33.0 (30.0-35.8) | 0.519 |
| Age during ET (years) | 34.0 (30.0-37.0) | 33.0 (31.0-36.0) | 0.701 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.2 ± 0.4 | 22.1 ± 0.2 | 0.854 |
| Basal FSH (IU/L) | 7.1 (5.8-8.5) | 6.3 (5.4-7.7) | 0.030 |
| Basal E2 (pg/mL) | 47.2 ± 2.1 | 50.2 ± 1.6 | 0.480 |
| Antral follicle count | 12.0 (10.0-15.0) | 14.0 (10.0-19.0) | 0.034 |
| Causes of infertility [(n) %] Female Male Mixes Unexplained | (27) 49.1 (1) 1.8 (16) 29.1 (11) 20.0 | (136) 55.7 (15) 6.1 (40) 16.4 (53) 21.7 | 0.114 |
| Infertility type [(n) %] Primary Secondary | (39) 70.9 (16) 29.1 | (158) 64.8 (86) 35.2 | 0.384 |
| No. of ET-failure cycles [(n) %] Twice Three times More than three times | (42) 76.4 (8) 14.5 (5) 9.1 | (153) 62.7 (61) 25.0 (30) 12.3 | 0.149 |
| Characteristic | Acu (n = 55) | Con (n = 244) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transformation a E2 (pg/mL) | 400.2 (240.3-667.2) | 322.5 (215.6-899.5) | 0.440 |
| LH (IU/L) | 4.6 (0.5-12.6) | 7.7 (1.2-14.9) | 0.062 |
| P (ng/mL) | 0.3 (0.2-0.4) | 0.4 (0.2-0.6) | 0.006 |
| Phase of embryos transferred [(n) %] Day 3 Day 3 + Day5-6 D5/D6 | (31) 56.4 (4) 7.3 (20) 36.4 | (87) 35.7 (13) 5.3 (144) 59.0 | 0.010 |
| No. of embryos transferred [(n) %] 1 2 | (16) 29.1 (39) 70.9 | (98) 40.2 (146) 59.8 | 0.127 |
| No. of High-quality embryos [(n) %] 1 2 | (28) 50.9 (27) 49.1 | (104) 42.6 (140) 57.4 | 0.167 |
| Endometrium morphology [(n) %] A A- A-B B | (28) 50.9 (12) 21.8 (9) 16.4 (6) 10.9 | (140) 57.4 (57) 23.4 (25) 10.2 (22) 9.0 | 0.563 |
| Endometrial preparation [(n) %] Natural cycle HRT cycle Stimulated cycle Endometrium thickness (mm)a | (8) 14.5 (43) 78.2 (4) 7.3 9.48±0.245 | (41) 16.8 (179) 73.4 (24) 9.8 9.58±0.130 | 0.771 0.983 |
| Fertilization method [(n) %] half ICSI IVF | (9) 16.4 (8) 14.5 (38) 69.1 | (24) 9.8 (32) 13.1 (188) 77.0 | 0.471 |
Table 2 Characteristics of patients during CET divided by acupuncture therapy
| Characteristic | Acu (n = 55) | Con (n = 244) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transformation a E2 (pg/mL) | 400.2 (240.3-667.2) | 322.5 (215.6-899.5) | 0.440 |
| LH (IU/L) | 4.6 (0.5-12.6) | 7.7 (1.2-14.9) | 0.062 |
| P (ng/mL) | 0.3 (0.2-0.4) | 0.4 (0.2-0.6) | 0.006 |
| Phase of embryos transferred [(n) %] Day 3 Day 3 + Day5-6 D5/D6 | (31) 56.4 (4) 7.3 (20) 36.4 | (87) 35.7 (13) 5.3 (144) 59.0 | 0.010 |
| No. of embryos transferred [(n) %] 1 2 | (16) 29.1 (39) 70.9 | (98) 40.2 (146) 59.8 | 0.127 |
| No. of High-quality embryos [(n) %] 1 2 | (28) 50.9 (27) 49.1 | (104) 42.6 (140) 57.4 | 0.167 |
| Endometrium morphology [(n) %] A A- A-B B | (28) 50.9 (12) 21.8 (9) 16.4 (6) 10.9 | (140) 57.4 (57) 23.4 (25) 10.2 (22) 9.0 | 0.563 |
| Endometrial preparation [(n) %] Natural cycle HRT cycle Stimulated cycle Endometrium thickness (mm)a | (8) 14.5 (43) 78.2 (4) 7.3 9.48±0.245 | (41) 16.8 (179) 73.4 (24) 9.8 9.58±0.130 | 0.771 0.983 |
| Fertilization method [(n) %] half ICSI IVF | (9) 16.4 (8) 14.5 (38) 69.1 | (24) 9.8 (32) 13.1 (188) 77.0 | 0.471 |
| Outcome | Acu | Con | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | Rough Adjusteda OR (95% CI) | Fine Adjustedb OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Live birth Ongoing pregnancy | 54.5 (30/55) 56.4 (31/55) | 41.0 (100/244) 43.0 (105/244) | 1.073 (1.008, 1.144) 1.069 (1.004, 1.139) | 1.103 (1.028, 1.183) 1.100 (1.025, 1.179) | 1.105 (1.029, 1.187) 1.100 (1.025, 1.181) |
| Clinical pregnancy | 58.2 (32/55) | 52.5 (128/244) | 1.041 (0.981, 1.105) | 1.063 (0.996, 1.135) | 1.065 (0.997, 1.138) |
| Implantation rate | 41.5 (39/94) | 40.8 (159/390) | 1.041 (0.976, 1.110) | 1.067 (0.994, 1.146) | 1.070 (0.996, 1.149) |
| Biochemical | 9.1 (5/55) | 7.8 (19/244) | 0.992 (0.893, 1.102) | 0.999 (0.904, 1.103) | 1.002 (0.903, 1.112) |
| Miscarriage | 3.6 (2/55) | 11.5 (28/244) | 0.768 (0.535, 1.101) | 0.776 (0.548, 1.099) | 0.778 (0.551, 1.099) |
| GW at birth (weeks) Normal, 37+ Preterm, < 37 | 93.3 (28/30) 6.7 (2/30) | 88.0 (88/100) 12.0 (12/100) | 1.00 1.139 (0.898, 1.444) | 1.00 1.138 (0.891, 1.453) | 1.00 1.145 (0.882, 1.486) |
| Multiple births Single birth | 23.3 (7/30) 76.7 (23/30) | 24.0 (24/100) 76.0 (76/100) | 1.00 0.973 (0.893, 1.060) | 1.00 0.965 (0.876, 1.064) | 1.00 0.963 (0.861, 1.079) |
| Birth weight (kg) Normal, 2.5-4.0 Abnormal | 73.0 (27/37) 27.0 (10/37) | 78.2 (97/124) 21.8 (27/124) | 1.00 0.963 (0.900, 1.030) | 1.00 0.940 (0.873, 1.011) | 1.00 0.929 (0.860, 1.004) |
| Sex of baby Male Female | 67.6 (25/37) 32.4 (12/37) | 50.8 (63/124) 49.2 (61/124) | 1.00 1.032 (0.960, 1.110) | 1.00 0.961 (0.896, 1.032) | 1.00 1.027 (0.954, 1.106) |
| Delivery way Vaginal CS | 23.3 (7/30) 76.7 (23/30) | 24.0 (24/100) 76.0 (76/100) | 1.00 1.022 (0.957, 1.093) | 1.00 1.019 (0.951, 1.092) | 1.00 1.039 (0.963, 1.120) |
Table 3 Clinical pregnancy outcomes and perinatal outcomes of patients grouped by acupuncture therapy [(%) n]
| Outcome | Acu | Con | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | Rough Adjusteda OR (95% CI) | Fine Adjustedb OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Live birth Ongoing pregnancy | 54.5 (30/55) 56.4 (31/55) | 41.0 (100/244) 43.0 (105/244) | 1.073 (1.008, 1.144) 1.069 (1.004, 1.139) | 1.103 (1.028, 1.183) 1.100 (1.025, 1.179) | 1.105 (1.029, 1.187) 1.100 (1.025, 1.181) |
| Clinical pregnancy | 58.2 (32/55) | 52.5 (128/244) | 1.041 (0.981, 1.105) | 1.063 (0.996, 1.135) | 1.065 (0.997, 1.138) |
| Implantation rate | 41.5 (39/94) | 40.8 (159/390) | 1.041 (0.976, 1.110) | 1.067 (0.994, 1.146) | 1.070 (0.996, 1.149) |
| Biochemical | 9.1 (5/55) | 7.8 (19/244) | 0.992 (0.893, 1.102) | 0.999 (0.904, 1.103) | 1.002 (0.903, 1.112) |
| Miscarriage | 3.6 (2/55) | 11.5 (28/244) | 0.768 (0.535, 1.101) | 0.776 (0.548, 1.099) | 0.778 (0.551, 1.099) |
| GW at birth (weeks) Normal, 37+ Preterm, < 37 | 93.3 (28/30) 6.7 (2/30) | 88.0 (88/100) 12.0 (12/100) | 1.00 1.139 (0.898, 1.444) | 1.00 1.138 (0.891, 1.453) | 1.00 1.145 (0.882, 1.486) |
| Multiple births Single birth | 23.3 (7/30) 76.7 (23/30) | 24.0 (24/100) 76.0 (76/100) | 1.00 0.973 (0.893, 1.060) | 1.00 0.965 (0.876, 1.064) | 1.00 0.963 (0.861, 1.079) |
| Birth weight (kg) Normal, 2.5-4.0 Abnormal | 73.0 (27/37) 27.0 (10/37) | 78.2 (97/124) 21.8 (27/124) | 1.00 0.963 (0.900, 1.030) | 1.00 0.940 (0.873, 1.011) | 1.00 0.929 (0.860, 1.004) |
| Sex of baby Male Female | 67.6 (25/37) 32.4 (12/37) | 50.8 (63/124) 49.2 (61/124) | 1.00 1.032 (0.960, 1.110) | 1.00 0.961 (0.896, 1.032) | 1.00 1.027 (0.954, 1.106) |
| Delivery way Vaginal CS | 23.3 (7/30) 76.7 (23/30) | 24.0 (24/100) 76.0 (76/100) | 1.00 1.022 (0.957, 1.093) | 1.00 1.019 (0.951, 1.092) | 1.00 1.039 (0.963, 1.120) |
| Item | Ongoing pregnancya | Live birtha | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine adjusted OR (95% CI) | P value | Fine adjusted OR (95% CI) | P value | |
| Acupuncture | 1.100 (1.025, 1.181) | 0.008 | 1.105 (1.029, 1.187) | 0.006 |
| Age at OPU (years) | 0.889 (0.823, 0.962) | 0.003 | 0.907 (0.839, 0.980) | 0.014 |
| AFC | 1.029 (0.992, 1.067) | 0.126 | 1.022 (0.985, 1.060) | 0.246 |
| Basal FSH | 1.069 (0.960, 1.191) | 0.225 | 1.084 (0.973, 1.209) | 0.144 |
| No. of high-quality ET | 1.347 (0.781, 2.324) | 0.284 | 1.561 (0.897, 2.717) | 0.115 |
| Embryo stage (blastocyst) | 1.468 (1.082, 1.992) | 0.014 | 1.604 (1.174, 2.190) | 0.003 |
| P on transformation day | 0.471 (0.215, 1.033) | 0.060 | 0.411 (0.178, 0.948) | 0.037 |
| LH on transformation day | 1.022 (1.000, 1.043) | 0.046 | 1.026 (1.004, 1.048) | 0.019 |
| Endometrium (mm) | 1.131 (0.997, 1.283) | 0.056 | 1.141 (1.005, 1.296) | 0.042 |
Table 4 Association of acupuncture therapy with pregnancy outcome by multivariate logistic regression analysis
| Item | Ongoing pregnancya | Live birtha | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine adjusted OR (95% CI) | P value | Fine adjusted OR (95% CI) | P value | |
| Acupuncture | 1.100 (1.025, 1.181) | 0.008 | 1.105 (1.029, 1.187) | 0.006 |
| Age at OPU (years) | 0.889 (0.823, 0.962) | 0.003 | 0.907 (0.839, 0.980) | 0.014 |
| AFC | 1.029 (0.992, 1.067) | 0.126 | 1.022 (0.985, 1.060) | 0.246 |
| Basal FSH | 1.069 (0.960, 1.191) | 0.225 | 1.084 (0.973, 1.209) | 0.144 |
| No. of high-quality ET | 1.347 (0.781, 2.324) | 0.284 | 1.561 (0.897, 2.717) | 0.115 |
| Embryo stage (blastocyst) | 1.468 (1.082, 1.992) | 0.014 | 1.604 (1.174, 2.190) | 0.003 |
| P on transformation day | 0.471 (0.215, 1.033) | 0.060 | 0.411 (0.178, 0.948) | 0.037 |
| LH on transformation day | 1.022 (1.000, 1.043) | 0.046 | 1.026 (1.004, 1.048) | 0.019 |
| Endometrium (mm) | 1.131 (0.997, 1.283) | 0.056 | 1.141 (1.005, 1.296) | 0.042 |
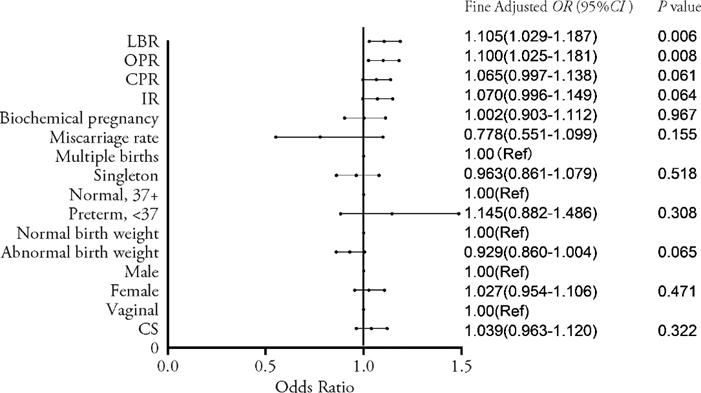
Figure 2 Forest plot of the effect of acupuncture on pregnancy outcome LBR: live birth rate; OPR: ongoing pregnancy rate; CPR: clinical pregnancy rate; IR: implantation rate; CS: cesarean section; OR: odds ratio.
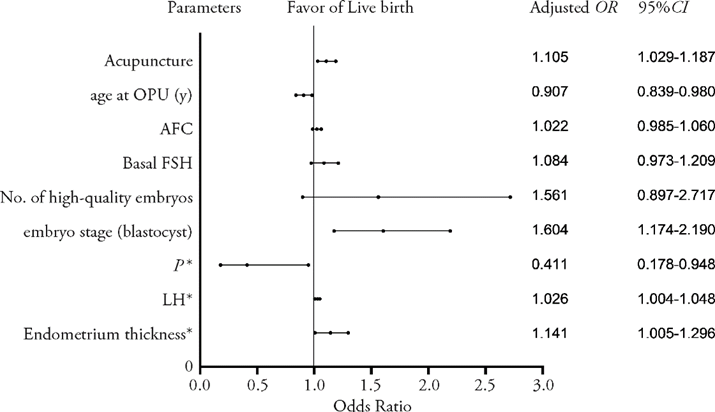
Figure 3 Favor of live birth OPU: oocyte pick-up; AFC: total antral follicle count; FSH: follicular stimulation hormone; P: progesterone; LH: luteinizing hormone; P: progesterone; LH: Luteinizing hormone; *: on endometrium-transformation day; OR: odds ratio.
| 1. |
Szamatowicz M. The role and place of the assisted reproductive technology (ART) in treatment of infertility. Ginekologia Polska 2007; 78: 175-9.
PMID |
| 2. |
Somigliana E, Vigano P, Busnell A, Paffoni A, Vegetti W, Vercellini P. Repeated implantation failure at the crossroad between statistics, clinics and over-diagnosis. Reprod Biomed Online 2018; 36: 32-8.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Li R, Shi YH, Li D. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of recurrent implantation failure. Natl Med J China 2023; 103: 89-100. |
| 4. |
Coughlan C, Ledger W, Wang Q, et al. Recurrent implantation failure: definition and management. Reprod Biomed Online 2014; 28: 14-38.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Inhorn MC, Patrizio P. Infertility around the globe: new thinking on gender, reproductive technologies and global movements in the 21st century. Hum Reprod Update 2015; 21: 411-26.
DOI PMID |
| 6. | Reig A, Franasiak J, Scott RT Jr, Seli E. The impact of age beyond ploidy: outcome data from 8175 euploid single embryo transfers. J Assist Reprod Genet 2020; 37: 595-602. |
| 7. |
Pirtea P, De Ziegler D, Tao X, et al. Rate of true recurrent implantation failure is low: results of three successive frozen euploid single embryo transfers. Fertil Steril 2021; 115: 45-53.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Hanson B, Osman E, Kim TJ, et al. A multicenter, prospective, blinded, nonselection study evaluating the predictive value of an aneuploid diagnosis using a targeted next-generation sequencing-based preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy assay and impact of biopsy. Fertil Steril 2021; 115: 627-37.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Liu X, Ma D, Wang W, et al. Intrauterine administration of human chorionic gonadotropin improves the live birth rates of patients with repeated implantation failure in frozen-thawed blastocyst transfer cycles by increasing the percentage of peripheral regulatory T cells. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2019; 299: 1165-72.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Li J, Mo S, Chen Y. The effect of G-CSF on infertile women undergoing IVF treatment: a Meta-analysis. Syst Biol Reprod Med 2017; 63: 239-47.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Bassil R, Casper R, Samara N, et al. Does the endometrial receptivity array really provide personalized embryo transfer? J Assist Reprod Genet 2018; 35: 1301-5. |
| 12. | Zhao ZQ. Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog Neurobiol 2008; 85: 355-75. |
| 13. |
Silberstein M. Do acupuncture meridians exist? Correlation with referred itch (mitempfindung) stimulus and referral points. Acupunct Med 2012; 30: 17-20.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Kuo TC, Lin CW, Ho FM. The soreness and numbness effect of acupuncture on skin blood flow. Am J Chin Med 2004; 32: 117-29. |
| 15. | Lee BC, Ogay V, Kim KW, Lee Y, Lee JK, Soh KS. Acupuncture muscle channel in the subcutaneous layer of rat skin. J Acupunct Meridian Stud 2008; 1: 13-9. |
| 16. | Li NC, Li MY, Chen B, Guo Y. A new perspective of acupuncture: the interaction among three networks leads to neutralization. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019; 2019: 2326867. |
| 17. | Xue HM, Li YM, Chen YT, et al. Effect of staging treatment of Tongyuan acupuncture on pregnancy outcome in patients with recurrent implantation failure of thin endometrium type. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2021; 41: 1338-42. |
| 18. |
Paulus WE, Zhang M, Strehler E, El-Danasouri I, Sterzik K. Influence of acupuncture on the pregnancy rate in patients who undergo assisted reproduction therapy. Fertil Steril 2002; 77: 721-4.
PMID |
| 19. |
Prapas Y, Prapas N, Jones EE, et al. The window for embryo transfer in oocyte donation cycles depends on the duration of progesterone therapy. Hum Reprod 1998; 13: 720-3.
PMID |
| 20. | Gui J, Xiong F, Yang W, Li J, Huang G. Effects of acupuncture on LIF and IL-12 in rats of implantation failure. Am J Reprod Immunol 2012; 67: 383-90. |
| 21. | Gao W, Tang X, Chen Z, et al. Effects of acupuncture on CCL2 and CXCL 8 expression and the subset of uNK cells in rats with embryo implantation failure. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013; 2013:12. |
| 22. |
Gardner DK, Lane M, Stevens J, Schlenker T, Schoolcraft WB. Blastocyst score affects implantation and pregnancy outcome: towards a single blastocyst transfer. Fertil Steril 2000; 73: 1155-8.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
Chu D, Fu L, Zhou W, Li Y. Effects of different open cryo-carriers on embryo survival and clinical outcome in frozen embryo transfer cycle patients. Syst Biol Reprod Med 2018; 64: 138-45.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Zhou W, Fu L, Sha W, Chu D, Li Y. Relationship of polar bodies morphology to embryo quality and pregnancy outcome. Zygote 2016; 24: 401-7.
DOI PMID |
| 25. | Zhou W, Chu D, Sha W, Fu L, Li Y. Effects of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor supplementation in culture medium on embryo quality and pregnancy outcome of women aged over 35 years. J Assist Reprod Genet 2016; 33: 39-47. |
| 26. | Qu D, Tian X, Ding L, Li Y, Zhou W. Impacts of Cyclosporin A on clinical pregnancy outcomes of patients with a history of unexplained transfer failure: a retrospective cohort study. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2021; 19: 44. |
| 27. | Huang LX, Zhao JS, Han Z, Wang XT, Li D. Nomenclature and location of acupuncture points: GB/T 12346-2006. Beijing: Chinese Standards Press; 2006: 9-39. |
| 28. | Gardner DK, Schoolcraft WB. Culture and transfer of human blastocysts. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 1999; 11: 307-11. |
| 29. |
Penzias AS. Recurrent IVF failure: other factors. Fertil Steril 2012; 97: 1033-8.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Santillán I, Lozano I, Illán J, et al. Where and when should natural killer cells be tested in women with repeated implantation failure? J Reprod Immunol 2015; 108: 142-8.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Lessey BA, Young SL. What exactly is endometrial receptivity? Fertil Steril 2019; 111: 611-7.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Zhang JY (Ming dynasty). Jing Yue Quan Shu. Beijing. People's Medical Publishing House, 2017: 44-53. |
| 33. | Huang DM, Huang GY, Lu FE, Stefan D, Andreas N, Robert G. Acupuncture for infertility: is it an effective therapy? Chin J Integr Med 2011; 17: 386-95. |
| 34. | Djaali W, Abdurrohim K, Helianthi DR. Management of acupuncture as adjuvant therapy for in vitro fertilization. Med Acupunct 2019; 31: 361-5. |
| 35. | Sun ZG. Effect of intracavitary shortwave physiotherapy combined with acupuncture on endometrial receptivity in vitro fertilization and embryo transplantation. J Tradit Chin Med 2012; 22: 1927-9. |
| 36. | Qi Y, Wang X, Hou S, Wu Z, Xu X, Pang C. Intracavitary physiotherapy combined with acupuncture mediated AMPK/ mTOR signalling to improve endometrial receptivity in patients with thin endometrium. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2022; 277: 32-41. |
| 37. | Wang YR. The effect of acupuncture at different time points on the pregnancy rate of frozen-thawed embryo transfer (Doctor’s thesis). Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2021: 63-81. |
| 38. | Yan J, Qin Y, Zhao H, et al. Live birth with OR without preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy. N Engl J Med 2021; 385: 2047-58. |
| 39. | Kucherov A, Fazzari M, Lieman H, Ball GD, Doody K, Jindal S. PGT-A is associated with reduced cumulative live birth rate in first reported IVF stimulation cycles age ≤ 40: an analysis of 133 494 autologous cycles reported to SART CORS. J Assist Reprod Genet 2023; 40: 137-49. |
| 40. |
Roelens C, Blockeel C. Impact of different endometrial preparation protocols before frozen embryo transfer on pregnancy outcomes: a review. Fertil Steril 2022; 118: 820-7.
DOI PMID |
| 41. | Ghobara T, Gelbaya TA, Ayeleke RO. Cycle regimens for frozen-thawed embryo transfer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017; 7: CD003414. |
| 42. |
Tanos V, Friedler S, Zajicek G, Neiger M, Lewin A, Schenker JG. The impact of endometrial preparation on implantation following cryopreserved-thawed-embryo transfer. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1996; 41: 227-31.
PMID |
| 43. | Yarali H, Polat M, Mumusoglu S, Yarali I, Bozdag G. Preparation of endometrium for frozen embryo replacement cycles: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Assist Reprod Genet 2016; 33: 1287-304. |
| 44. | Eleftheriadou A, Francis A, Wilcox M, Jayaprakasan K. Frozen blastocyst embryo transfer: comparison of protocols and factors influencing outcome. J Clin Med 2022; 11: 737. |
| 45. |
Zhou B, Wang Z, Dou Q, et al. Long-term outcomes of esophageal and gastric cancer patients with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: a two-center propensity score-matched cohort study. J Transl Int Med 2023; 11: 234-45.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | LI Zhongzheng, ZHAO Yadan, Ma Weigang, Zhang Yonglong, XU Zhifang, XI Qiang, LI Yanqi, QIN Siru, ZHANG Zichen, WANG Songtao, ZHAO Xue, LIU Yangyang, GUO Yi, GUO Yongming. Adenosine triphosphate mediates the pain tolerance effect of manual acupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) in mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 660-669. |
| [2] | YAN Jing, FENG Huimin, QIU Fang, WANG Haijun, YIN Luyun, JIN Xiaofei, ZHAO Jiyu, WANG Hongyang, YAN Xiaoqin. Effect on serum metabolomics of rats with premature ovarian insufficiency by Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 722-733. |
| [3] | CHEN Yonglin, OUYANG Ling, MENG Lingling, WU Bufan, PENG Rou, LIU Sitong, HOU Dan, WANG Yaling, JING Xinyue, LU Shengfeng, FU Shuping. Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 734-744. |
| [4] | ZHU Wenting, GUO Changqing, DU Mei, MA Yunxuan, CUI Yongqi, CHEN Xilin, GUO Changqing. Acupotomy alleviates knee osteoarthritis in rabbit by regulating chondrocyte mitophagy via Pink1-Parkin pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 468-477. |
| [5] | YU Wenxi, TANG Lina, LI Hongtao, WANG Yonggang, SHEN Zan. Neiguan (PC6) acupoint stimulation for preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: a cost-effective supplement in guideline-inconsistent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting prophylaxis subgroup [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 581-585. |
| [6] | WANG Dingyue, YU Yana, WANG Yiyuan, ZHANG Zhen. Musculoskeletal ultrasound to evaluate the efficacy of acupuncture: a review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 629-632. |
| [7] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xinchang, HUANG Zheng, HUANG Peiyan, YANG Mengning, ZHANG Zhihui, NI Guangxia. Mechanism of acupuncture in attenuating cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury based on nuclear receptor coactivator 4 mediated ferritinophagy [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 345-352. |
| [9] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [10] | SUN Qianhui, CHENG Kai, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, WU Xiaoling, XU Chang, QIU Xinghua, GAO Xiaofeng, LIU Daonan, YANG Qirui. Effect of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) at different time points on myocardial ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 113-121. |
| [11] | LIU Tingting, LIU Tongou, LIU Mingfu. Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture in treatment of pregnancy-related symptoms: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 16-26. |
| [12] | YANG Yi, YE Huijun, ZHENG Huiling, JIN Lihua. Clinical observation on 90 cases of primary dysmenorrhea treated by buccal acupuncture therapy: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 172-181. |
| [13] | LI Menghan, WANG Yu, RAN Dawei, YANG Xinming, DENG Shizhe, SHI Lei, MENG Zhihong. Effects of anterior sciatic nerve acupuncture on lower limb paralysis after cerebral infarction: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 205-211. |
| [14] | DU Zhongheng, CONG Wenjie, TANG Kejing, ZHENG Qiqi, SONG Zhiwei, CHEN Yong, YANG Su, ZHANG Chunwu, YE Tianshen. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) in mice with collagen-induced arthritis leads to adenosine A2A receptor-mediated alteration of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1103-1109. |
| [15] | QIN Xihui, PANG Jianli, XIONG Guan, FENG Jie. Bo′s abdominal acupuncture improves disordered metabolism in obese type 2 diabetic rats through regulating fibroblast growth factor 21 and its related adipokines [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1200-1208. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

