Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 468-477.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240402.001
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Acupotomy alleviates knee osteoarthritis in rabbit by regulating chondrocyte mitophagy via Pink1-Parkin pathway
ZHU Wenting1, GUO Changqing2( ), DU Mei2, MA Yunxuan2, CUI Yongqi2, CHEN Xilin2, GUO Changqing3
), DU Mei2, MA Yunxuan2, CUI Yongqi2, CHEN Xilin2, GUO Changqing3
- 1 the Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
2 School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
3 Department of Medical Technology, Shijiazhuang Medical College, Hebei 050599, China
-
Received:2023-08-11Accepted:2023-12-19Online:2024-06-15Published:2024-04-02 -
Contact:Mrs. GUO Changqing, Shijiazhuang Medical College, Hebei 050599, China.925499172@qq.com Telephone: +86-311-82517626 -
Supported by:Key Project of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine: to Investigate the Effect of Acupotomy Mechanics on Oxidative Injury of Rabbit Chondrocytes with Knee Osteoarthritis Based on Mitophagy Mediated by Pink1/Parkin Signaling Pathway(2020-JYB-ZDGG-059);National Natural Science Foundation of China: to Investigate the Mechanism of Acupotomy "Regulating Tendon and Treating Bone" in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis based on the Vascularization of Hypoxic Cartilage Mediated by Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1alpha/ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Pathway(82074523)
Cite this article
ZHU Wenting, GUO Changqing, DU Mei, MA Yunxuan, CUI Yongqi, CHEN Xilin, GUO Changqing. Acupotomy alleviates knee osteoarthritis in rabbit by regulating chondrocyte mitophagy via Pink1-Parkin pathway[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 468-477.
share this article
| Item | Group | n | Before intervention | After intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROM | CON | 6 | 141.2±2.1 | 140.7±3.5 |
| KOA | 6 | 31.2±6.5a | 53.2±10.0a | |
| Acu | 6 | 40.3±4.6a | 97.3±12.5ab | |
| Lequesne MG | CON | 6 | 0.0±0.0 | 0.0±0.0 |
| KOA | 6 | 7.3±0.5 | 6.5±1.0 | |
| Acu | 6 | 7.3±0.8 | 3.3±0.8b |
Table 1 Behavioral assessment of rabbits from the 3 groups (scores, $\bar{x} \pm s$)
| Item | Group | n | Before intervention | After intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROM | CON | 6 | 141.2±2.1 | 140.7±3.5 |
| KOA | 6 | 31.2±6.5a | 53.2±10.0a | |
| Acu | 6 | 40.3±4.6a | 97.3±12.5ab | |
| Lequesne MG | CON | 6 | 0.0±0.0 | 0.0±0.0 |
| KOA | 6 | 7.3±0.5 | 6.5±1.0 | |
| Acu | 6 | 7.3±0.8 | 3.3±0.8b |

Figure 1 Cartilage degeneration under microscope A: safranin O-fast green staining of the knee cartilage (× 200); A1: CON group; A2: KOA group; A3: Acu group; B: Col-Ⅱ immunofluorescence staining in knee cartilage (× 200); B1-B3: CON group; B4-B6: KOA group; B7-B9: Acu group; C: analysis of the Mankin score; D: analysis of the Col-Ⅱ fluorescence intensity. CON group: no modelling or no intervention; KOA group: 6 weeks of modeling followed by no intervention; Acu group: 6 weeks of modeling followed by acupotomy intervention for 4 weeks. Col-Ⅱ: type Ⅱ collagen; CON: control; KOA: knee osteoarthritis; Acu: acupotomy. The data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). Compared with the CON group, aP < 0.01; compared with the KOA group, bP < 0.01.
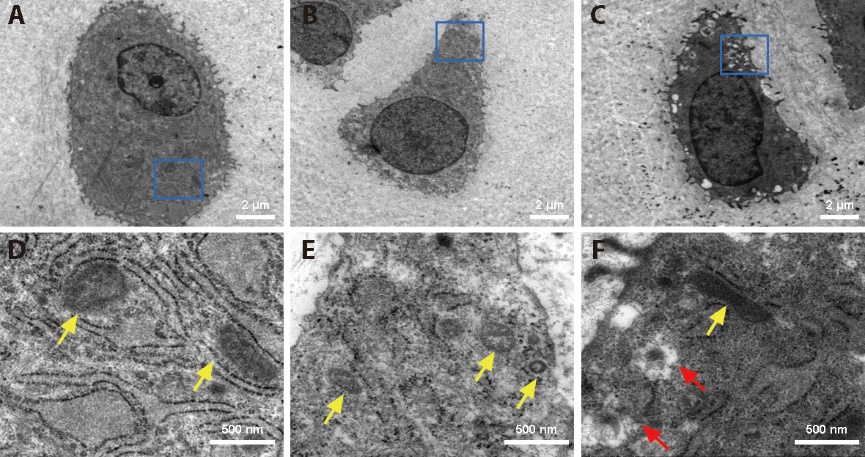
Figure 2 Ultramicrostructure of chondrocyte mitochondria A, B, C: chondrocytes at low magnification (× 1200); D, E, F: chondrocytes at high magnification (× 8000); A, D: CON group; B, E: KOA group; C, F: Acu group; CON group: no modeling or no intervention; KOA group: 6 weeks of modeling followed by no intervention; Acu group: 6 weeks of modeling followed by acupotomy intervention for 4 weeks. The yellow arrow indicates mitochondria; the red arrow indicates mitochondrial autophagosomal vesicles.
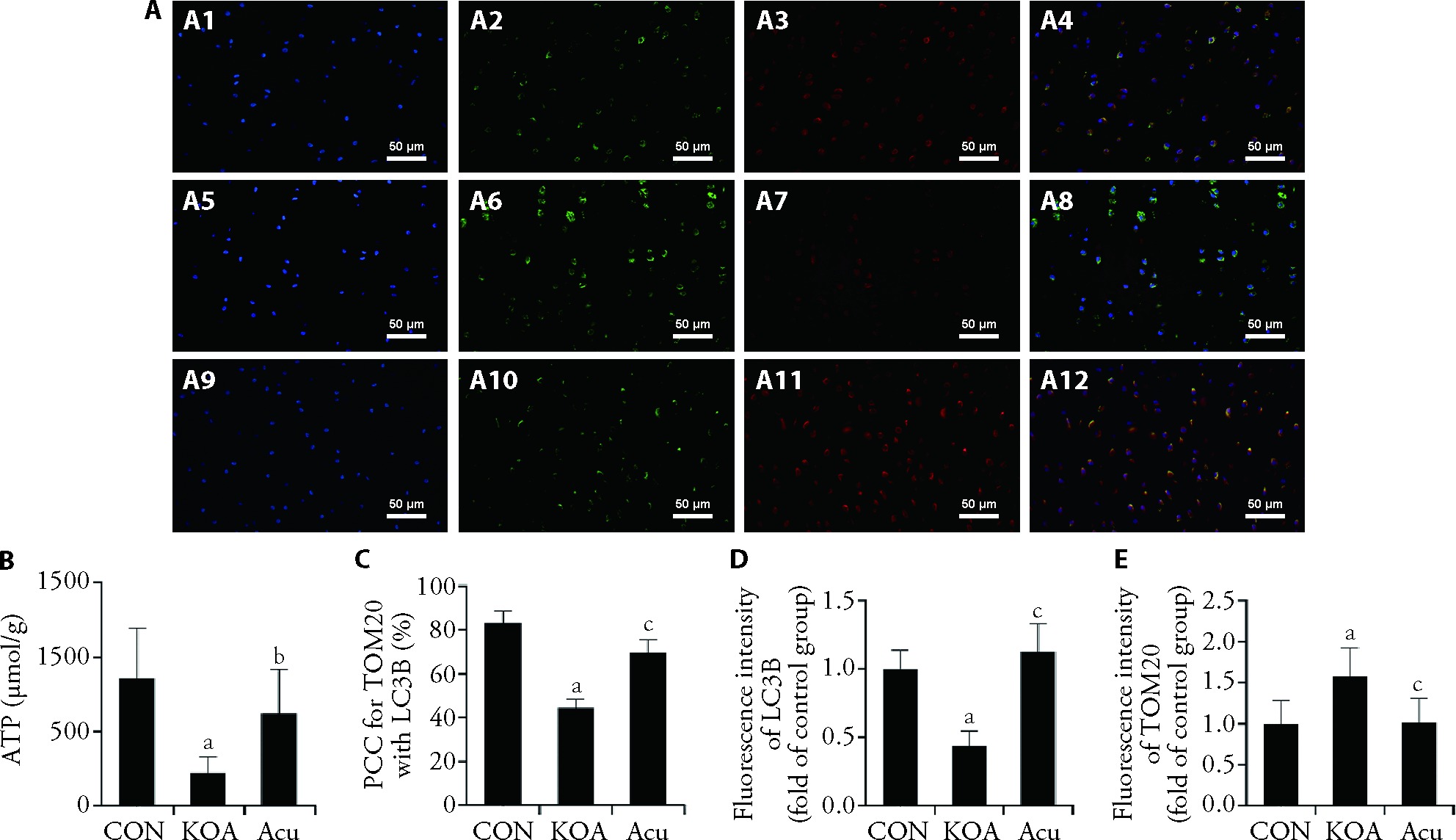
Figure 3 Immunofluorescence staining of mitophagy and mitochondrial function A: double immunofluorescence staining for TOM20 and LC3B (× 400); A1, A2, A3, A4: CON group; A5, A6, A7, A8: KOA group; A9, A10, A11, A12: Acu group; A1, A5, A9: DAPI staining; A2, A6, A10: TOM20 staining; A3, A7, A11: LC3B staining; A4, A8, A12: merge of TOM20 and LC3B staining; B: level of ATP; C: colocalization coefficient; D, E: analysis of TOM20 and LC3B fluorescence intensity. CON group: no modeling or no intervention; KOA group: 6 weeks of modeling followed by no intervention; Acu group: 6 weeks of modeling followed by acupotomy intervention for 4 weeks. ATP: adenosine triphosphate; PCC: Pearson's correlation coefficient; TOM20: translocase of the outer membrane 20; LC3B: microtubule-associated protein-1 light chain-3B; CON: control; KOA: knee osteoarthritis; Acu: acupotomy; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. The data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). aP < 0.01 compared with the control group; bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01, compared with the KOA group.
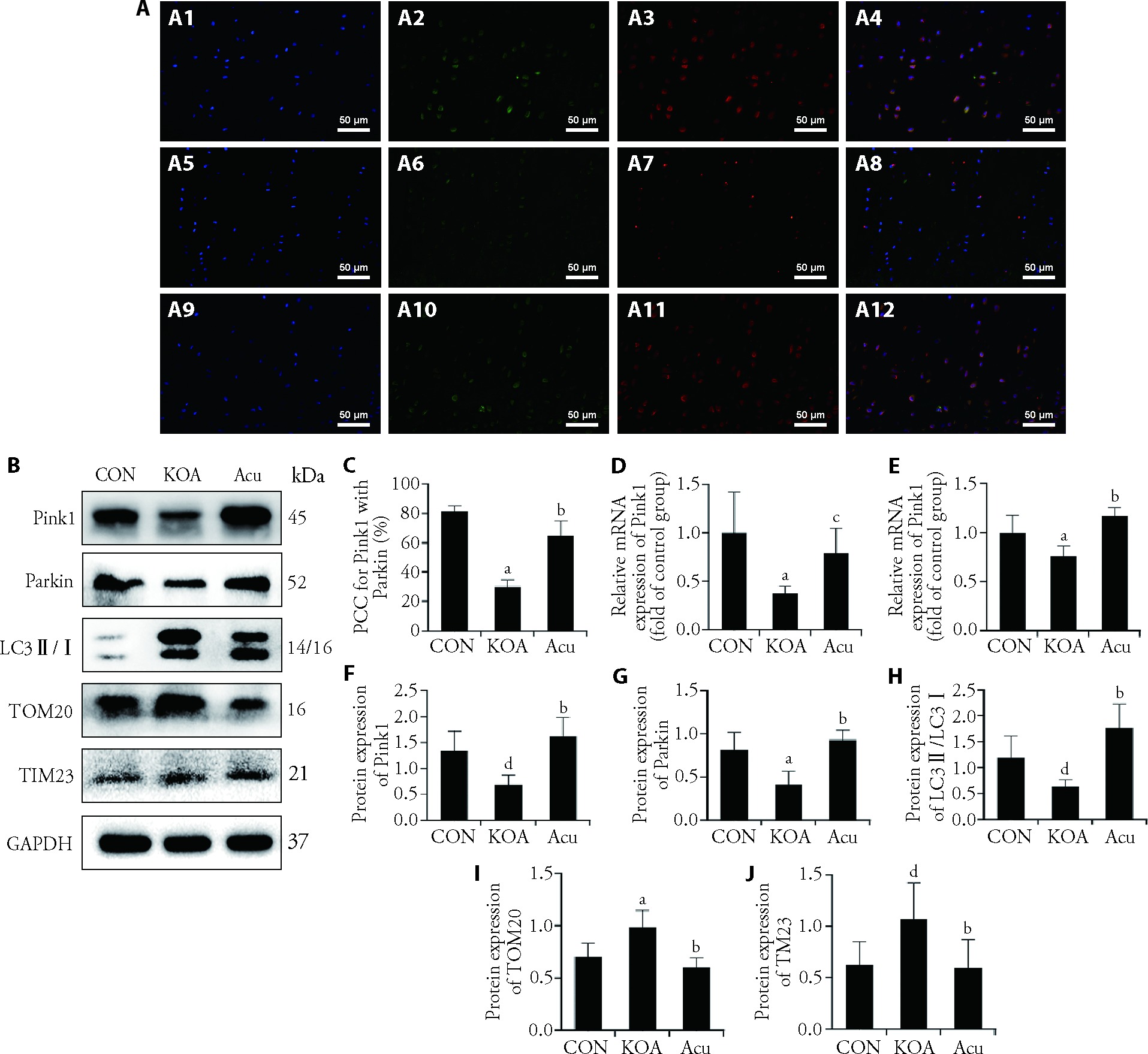
Figure 4 Expression of factors associated with the Pink1-Parkin pathway A: double immunofluorescence staining for Pink1 and Parkin (× 400); A-1A4: CON group; A5-A8: KOA group; A9-A12: Acu group; A1, A5, A9: DAPI staining; A2, A6, A10: Pink1 staining; A3, A7, A11: Parkin staining; A4, A8, A12: merge of Pink1 and Parkin staining; B: Pink1, Parkin, LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ, TOM20 and TIM23 expression was detected by Western blot analyses. C: colocalization coefficient; D: mRNA expression of Pink1; E: mRNA expression of Parkin; F: Western blotting analysis of Pink1 expression; G: Western blotting analysis of Parkin expression; H: Western blotting analysis of LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ expression; I: Western blotting analysis of TOM20 expression; J: Western blotting analysis of TIM23 expression. CON group: no modeling or no intervention; KOA group: 6 weeks of modeling followed by no intervention; Acu group: 6 weeks of modeling followed by acupotomy intervention for 4 weeks. PCC: Pearson's correlation coefficient; Pink1: PTEN-induced putative kinase 1; LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ: microtubule-associated protein-1 light chain-3Ⅱ/Ⅰ; TOM20: translocase of the outer membrane 20; TIM23: translocase of the inner membrane 23; CON: control; KOA: knee osteoarthritis; Acu: acupotomy; DAPI: 4', 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; PTEN: phosphatase and Tensin Homolog. The data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). aP < 0.01 and dP < 0.01 compared with the control group; bP < 0.01 and cP < 0.05, compared with the KOA group.
| 1. |
Long H, Liu Q, Yin H, et al. Prevalence trends of site-specific osteoarthritis from 1990 to 2019: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. Arthritis Rheumatol 2022; 74: 1172-83.
DOI URL |
| 2. |
He Y, Wu Z, Xu L, et al. The role of SIRT3-mediated mitochondrial homeostasis in osteoarthritis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2020; 77: 3729-43.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Liu HY, Chang CF, Lu CC, et al. The role of mitochondrial metabolism, AMPK-SIRT mediated pathway, LncRNA and MicroRNA in osteoarthritis. Biomedicines 2022; 10: 1477.
DOI URL |
| 4. |
Bolduc JA, Collins JA, Loeser RF. Reactive oxygen species, aging and articular cartilage homeostasis. Free Radic Biol Med 2019; 132: 73-82.
DOI URL |
| 5. |
Lemasters JJ. Selective mitochondrial autophagy, or mitophagy, as a targeted defense against oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. Rejuvenation Res 2005; 8: 3-5.
DOI URL |
| 6. |
Zeng Z, Zhou X, Wang Y, et al. Mitophagy-a new target of bone disease. Biomolecules 2022; 12: 1420.
DOI URL |
| 7. | Ding Z, Chang J, Huang W, et al. Inhibition of chondrocyte mitochondrial autophagy increased the expression of MMP-1 and MMP-13. Anhui Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2018; 53: 600-4. |
| 8. |
Sun K, Jing X, Guo J, Yao X, Guo F. Mitophagy in degenerative joint diseases. Autophagy 2021; 17: 2082-92.
DOI URL |
| 9. |
Wang C, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Liu J, Yao Z, Zhang C. Protective effects of metformin against osteoarthritis through upregulation of SIRT3-mediated PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy in primary chondrocytes. Biosci Trends 2019; 12: 605-12.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Ansari MY, Khan NM, Ahmad I, Haqqi TM. Parkin clearance of dysfunctional mitochondria regulates ROS levels and increases survival of human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2018; 26: 1087-97.
DOI URL |
| 11. |
Huang LW, Huang TC, Hu YC, et al. Zinc protects chondrocytes from monosodium iodoacetate-induced damage by enhancing ATP and mitophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020; 521: 50-6.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Felson DT. Osteoarthritis as a disease of mechanics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013; 21: 10-5.
DOI URL |
| 13. |
Kong DC, Zheng TS, Zhang M, et al. Static mechanical stress induces apoptosis in rat endplate chondrocytes through MAPK and mitochondria-dependent caspase activation signaling pathways. PLoS One 2017; 8: e69403.
DOI URL |
| 14. |
Coleman MC, Ramakrishnan PS, Brouillette MJ, Martin JA. Injurious loading of articular cartilage compromises chondrocyte respiratory function. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016; 68: 662-71.
DOI URL |
| 15. |
He YC, Yocum L, Alexander PG, Jurczak MJ, Lin H. Urolithin a protects chondrocytes from mechanical overloading-induced injuries. Front Pharmacol 2021; 12: 703847.
DOI URL |
| 16. | Guo CQ, Si T, Wen JM, et al. A randomized controlled clinical study on the improvement of pain symptoms of knee osteoarthritis with acupotomy. Tianjin Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2012; 29: 35-8. |
| 17. | An XY, Wang T, Zhang W et al. Chondroprotective effects of combination therapy of acupotomy and human adipose mesenchymal stem cells in knee osteoarthritis rabbits via the GSK3β-Cyclin D1-CDK4/CDK 6 signaling pathway. Aging Dis 2020; 11: 1116-32. |
| 18. | Ma SN, Xie ZG, Guo Y, et al. Effect of acupotomy on FAK-PI3K aignaling pathways in KOA rabbit articular cartilages. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017; 2017: 4535326. |
| 19. |
He YC, Yocum L, Alexander PG, Jurczak MJ, Lin H. Urolithin a protects chondrocytes from mechanical overloading-induced injuries. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12: 703847.
DOI URL |
| 20. |
Zhang JM, Hao XX, Chi RM, Qi J, Xu T. Moderate mechanical stress suppresses the IL-1beta-induced chondrocyte apoptosis by regulating mitochondrial dynamics. J Cell Physiol 2021, 236: 7504-15.
DOI URL |
| 21. |
Videman T. Experimental osteoarthritis in the rabbit: comparison of different periods of repeated immobilization. Acta orthopaedica Scandinavica 1982; 53: 339-47.
PMID |
| 22. | Guo C. Acupotomology. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017: 199-204. |
| 23. | Lequesne MG, Mery C, Samson M, Gerard P. Indexes of severity for osteoarthritis of the hip and knee. Validation--value in comparison with other assessment tests. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl 1987; 65: 85-9. |
| 24. |
Shi XW, Yu WJ, Wang T, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates cartilage degradation: improvement in cartilage biomechanics via pain relief and potentiation of muscle function in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother 2020; 123: 109724.
DOI URL |
| 25. |
An XY, Wang T, Zhang W, et al. Chondroprotective effects of combination therapy of acupotomy and human adipose mesenchymal stem cells in knee osteoarthritis rabbits via the GSK3beta-Cyclin D1-CDK4/CDK6 signaling pathway. Aging Dis 2020; 11: 1116-32.
DOI URL |
| 26. | Jin X, Yang Y, Zhao J, Cao Y, Li J, Hao C. Rational analysis of using braking method to build rabbit KOA stage model. Zhong Guo Bi Jiao Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021; 31: 78-82. |
| 27. |
Adarmes H, Donders L, Dörner C, et al. Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) determination in healthy and damaged equine articular cartilage. Austral J Vet Sci 2017; 49: 129-133.
DOI URL |
| 28. |
Xu WC, Zhao X, Sun PP, Zhang C, Fu ZJ, Zhou DS. The effect of medical ozone treatment on cartilage chondrocyte autophagy in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res 2020; 12: 5967-76.
PMID |
| 29. |
Yusuf E, Nelissen RG, Ioan-Facsinay A, et al. Association between weight or body mass index and hand osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69: 761-5.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Otte P. Basic cell metabolism of articular cartilage. Manometric studies. Z Rheumatol 1991; 50: 304-12.
PMID |
| 31. |
Chen Y, Wu YY, Si HB, Lu YR, Shen B. Mechanistic insights into AMPK-SIRT3 positive feedback loop-mediated chondrocyte mitochondrial quality control in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Pharmacol Res 2021; 166: 105497.
DOI URL |
| 32. |
Eitner A, Sparing S, Kohler FC, et al. Osteoarthritis-induced metabolic alterations of human hip chondrocytes. Biomedicines 2022; 10: 1349.
DOI URL |
| 33. |
Liu H, Li ZY, Cao YP, et al. Effect of chondrocyte mitochondrial dysfunction on cartilage degeneration: a possible pathway for osteoarthritis pathology at the subcellular level. Mol Med Rep 2019; 20: 3308-16.
DOI PMID |
| 34. |
Croucher LJ, Crawford A, Hatton PV, Russell RG, Buttle DJ. Extracellular ATP and UTP stimulate cartilage proteoglycan and collagen accumulation in bovine articular chondrocyte pellet cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta 2000; 1502: 297-306.
PMID |
| 35. |
Liu D, Cai Z, Yang Y, et al. Mitochondrial quality control in cartilage damage and osteoarthritis: new insights and potential therapeutic targets. Osteoarthr Cartilage 2021; 30: 395-405.
DOI PMID |
| 36. |
Insil K, Sara R, John JL. Selective degradation of mitochondria by mitophagy. Arch Biochem Biophys 2007; 462: 245-53.
DOI PMID |
| 37. | Staines KA, Wood L, Mainenti M, et al. Mitophagy dysfunction localises to regions of natural osteoarthritis in str/ort mice. Osteoarthr Cartilage 2014; 22: 340-1. |
| 38. | Kuwahara M, Akasaki Y, Kurakazu I, et al. C10orf10/DEPP activates mitochondrial autophagy and maintains chondrocyte viability in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. FASEB J 2022; 36: e22145. |
| 39. |
Tang Q, Zheng G, Feng Z, et al. Trehalose ameliorates oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress via selective autophagy stimulation and autophagic flux restoration in osteoarthritis development. Cell Death Dis 2017; 8: e3081.
DOI URL |
| 40. |
Sun K, Jing X, Guo J, Yao X, Guo F. Mitophagy in degenerative joint diseases. Autophagy 2020; 17: 2082-92.
DOI URL |
| 41. |
Christian S, Alexander S, Peter R. Unlocking the presequence import pathway. Trends Cell Biol 2015; 25: 265-75.
DOI PMID |
| 42. |
Gong G, Song M, Gyorgy C, Daniel PK, Scot JM, Gerald WD. Parkin-mediated mitophagy directs perinatal cardiac metabolic maturation in mice. Science 2015; 350: aad2459.
DOI URL |
| 43. |
Kathryn M, Michael AH, Ryan L, Reed F. A systematic review and Meta-analysis of lower limb neuromuscular alterations associated with knee osteoarthritis during level walking. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2013; 28: 713-24.
DOI URL |
| 44. | Jin Z, Xu S, Yang Y, Yue Y, Bai L. Research progress of PINK1/ Parkin-mediated mitochondrial autophagy in osteoarthritis. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Yan Jiu 2021; 34: 258-61. |
| 45. |
Steele HE, Guo Y, Li B, Na S. Mechanotransduction of mitochondrial AMPK and its distinct role in flow-induced breast cancer cell migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2019; 514: 524-29.
DOI URL |
| 46. |
Zhang J, Hao X, Chi R, Qi J, Xu T. Moderate mechanical stress suppresses the IL-1beta-induced chondrocyte apoptosis by regulating mitochondrial dynamics. J Cell Physiol 2021; 236: 7504-15.
DOI URL |
| 47. | Wang Y, Wang Q, Wang M. The role of mitophagy in cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan 2022: 1-11. |
| 48. |
Nomura M, Sakitani N, Iwasawa H, et al. Thinning of articular cartilage after joint unloading or immobilization. An experimental investigation of the pathogenesis in mice. Osteoarthr Cartilage 2016; 25: 727-36.
DOI URL |
| 49. | Ma SN, Xie ZG, Guo Y, et al. Effect of acupotomy on FAK-PI3K signaling pathways in KOA rabbit articular cartilages. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017; 2017: 4535326. |
| [1] | YANG Yi, YE Huijun, ZHENG Huiling, JIN Lihua. Clinical observation on 90 cases of primary dysmenorrhea treated by buccal acupuncture therapy: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 172-181. |
| [2] | Chen Xilin, GUO Yan, LU Juan, QIN Luxue, HU Tingyao, ZENG Xin, WANG Xinyue, ZHANG Anran, ZHUANG Yuxin, ZHONG Honggang, GUO Changqing. Acupotomy ameliorates subchondral bone absorption and mechanical properties in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis by regulating bone morphogenetic protein 2-Smad1 pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 734-743. |
| [3] | CHEN Ying, SUN Jingqing, LYU Tianli, HONG Jiahui, LIU Yuhan, ZHU Liying, LI Bin, LIU Lu. Effect of acupuncture treatment on nonketotic hyperglycemic hemichorea-hemiballismus: a case report [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 829-833. |
| [4] | QIN Luxue, GUO Changqing, ZHAO Ruili, WANG Tong, WANG Junmei, GUO Yan, ZHANG Wei, HU Tingyao, CHEN Xilin, ZHANG Qian, ZHANG Dian, XU Yue. Acupotomy inhibits aberrant formation of subchondral bone through regulating osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand pathway in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis induced by modified Videman method [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 389-399. |
| [5] | ZHAO Lixia, SUN Wei, BAI Decheng. Protective effect of resveratrol on rat cardiomyocyte H9C2 cells injured by hypoxia/reoxygenation by regulating mitochondrial autophagy via PTEN-induced putative kinase protein 1/Parkinson disease protein 2 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 176-186. |
| [6] | YAO Nan, CHEN Guocai, LU Yanyan, XU Xuemeng, ZHAO Chuanxi, HUANG Xuejun, LIU Wengang, PENG Sha, WU Huai. Bushen Qiangjin capsule(补肾强筋胶囊) inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin pathway to ameliorate papain-induced knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 935-942. |
| [7] | LIU Di, WU Yongli, LI Chun, WANG Minglei, MA Xiaoxiu, LIU Junwei, ZHANG Yanling, YANG Lei. Warming moxibustion attenuates inflammation and cartilage degradation in experimental rabbit knee osteoarthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 959-967. |
| [8] | FAN Bingbing, LI Tianjiao, MENG Xiansheng, WANG Shuai, BAO Yongrui, WANG Fei. Mechanism of total glucosides from Chishao(Radix Paeoniae Rubra)on proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 677-683. |
| [9] | LIU Wenjun, XU Xinzhu, DUAN Zhiyuan, LIANG Xicai, MA Dan, LI Gege, XIE Xin, CHAI Jiyan, CHEN Jing, SHAN Dehong. Efficacy of Sijunzi decoction (四君子汤) on limb weakness in spleen Qi deficiency model rats through adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1 signaling [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 617-623. |
| [10] | Fang Ting, Li Qi, Zhou Fanyuan, Liu Fushui, Liu Zhongyong, Zhao Meimei, Chen Mei, You Jianyu, Jin Yuli, Xie Jinmei. Effect and safety of acupotomy in treatment of knee osteoarthritis:a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(3): 355-364. |
| [11] | Zhang Wei, Gao Yang, Guo Changqing, Ibrahim Zeyad Ali Khattab, Farid Mokhtari. Effect of acupotomy versus electroacupuncture on ethology and morphology in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(02): 229-236. |
| [12] | Cao Yong, Zhang Shuyong, Zhang Ge, Zhang Na, Zhang Lixia, Huang Yuanliang, Yuan Naijun, Tang Xiaojuan, Du Jiajin, Fang Jiuyun. Effect of compound Guizhu capsule on phosphate and tension homology deleted on chromsome ten and murine double mimute 2 gene expression in lung cancer of mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(04): 461-465. |
| [13] | Ding Yu, Yuan Xueling, Wang Yongcheng, Wang Aiyuan, Shi Xian, Wang Lu, Daniela Litscher, Ingrid Gaischek, Irmgard Th.Lippe, Gerhard Litscher. Acupotomy versus sodium hyaluronate for treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rabbits [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(03): 404-411. |
| [14] | Zheng Yu, Lu Luo, Yu Li, Qiaofeng Wu, Shufang Deng, Shouying Lian, Fanrong Liang. Different manual manipulations and electrical parameters exert different therapeutic effects of acupuncture [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014, 34(06): 754-758. |
| [15] | Tao Huang, Lijian Yang, Shuyong Jia, Xiang Mu, Mozheng Wu, Hang Ye, Weizhe Liu, Xinnong Cheng. Capillary blood flow in patients with dysmenorrhea treated with acupuncture [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(06): 757-760. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

