Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 345-352.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240203.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of acupuncture in attenuating cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury based on nuclear receptor coactivator 4 mediated ferritinophagy
ZHANG Xinchang1,2, HUANG Zheng1,2( ), HUANG Peiyan1,2, YANG Mengning1,2, ZHANG Zhihui1,2, NI Guangxia1,2(
), HUANG Peiyan1,2, YANG Mengning1,2, ZHANG Zhihui1,2, NI Guangxia1,2( )
)
- 1 College of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China
2 Key Laboratory of Acupuncture and Medicine Research of Ministry of Education, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China
-
Received:2022-12-25Accepted:2023-05-09Online:2024-04-15Published:2024-02-03 -
Contact:HUANG Zheng, College of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China.huangzheng0814@163.com ; NI Guangxia, College of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China.xgn66@njucm.edu.cn Telephone: +86-25-85811180 -
Supported by:The National Natural Science Foundation of China: Mechanism of Acupuncture in Extending Thrombolytic Time Window of Cerebral Infarction Based on Nuclear Receptor Coactivator 4 Mediated Ferritinophagy(82205238);National Natural Science Foundation of China: Exploring the Mechanism of Acupuncture Improving Thrombolytic Safety in Cerebral Infarction through the ERK1/2-mTOR Pathway Based on Autophagy Apoptosis Interaction(82074525);Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province: Experimental Study on Acupuncture Regulation of Ferroptosis-NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway to Reduce Hemorrhagic Transformation after Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction(BK20210689);Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Development Plan Project of Jiangsu Province: Clinical and Experimental Study on Acupuncture Improving the Safety of rt-PA Intravenous Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction(YB2020005)
Cite this article
ZHANG Xinchang, HUANG Zheng, HUANG Peiyan, YANG Mengning, ZHANG Zhihui, NI Guangxia. Mechanism of acupuncture in attenuating cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury based on nuclear receptor coactivator 4 mediated ferritinophagy[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 345-352.
share this article
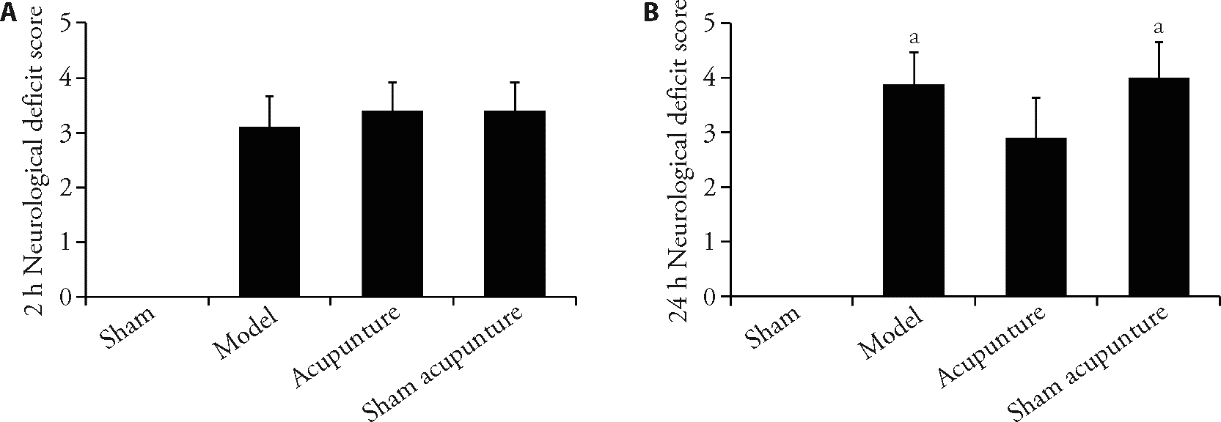
Figure 1 Acupuncture improved neurological function in rats with CIRI A: the neurological deficit score of rats 2 h after cerebral ischaemia in each group (n = 10); B: the neurological deficit score of rats 24 h after reperfusion in each group (n = 10). We took the tissue of the ischemic area of the right cerebral cortex from each group of rats at the 24-h ischemic time point and detected it using relevant reagent kits. At the time point of 2-h of ischemia, we performed acupuncture and sham acupuncture operations. We evaluated the neurobehavioral scores (Bederson 0-5 scores) of each group of rats at the time points of ischemia for 2-h and 24-h, respectively. CIRI: cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury. h: hour. Data were statistically analysed by least significant difference test. Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.05, compared with the acupuncture group.
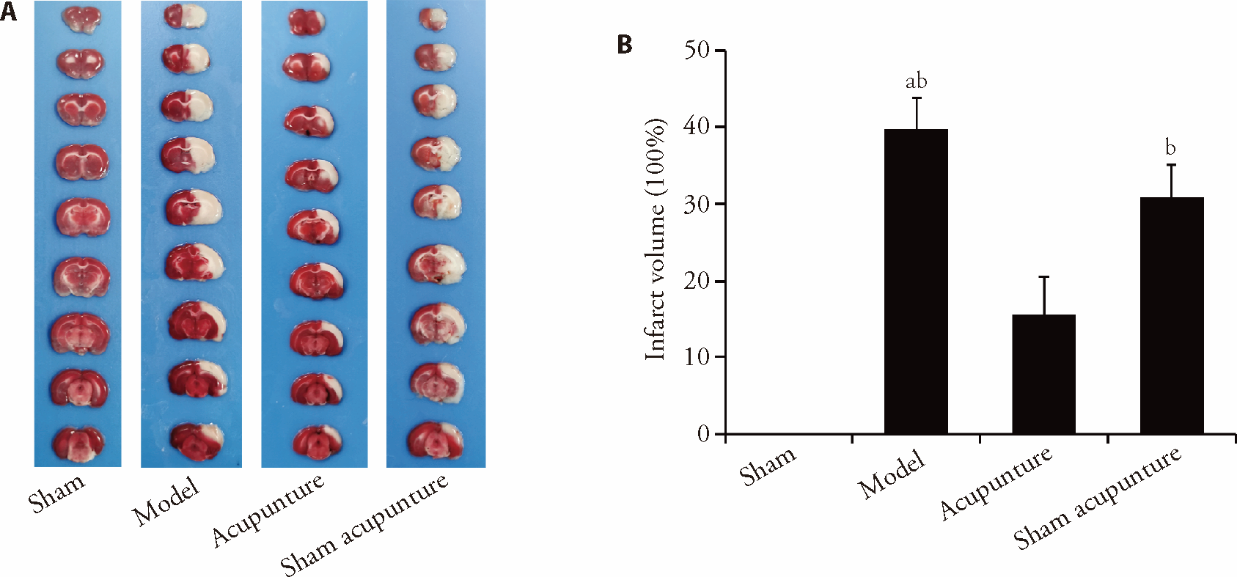
Figure 2 Acupuncture decreased infarct volume in rats with CIRI A: representative images of brain slices stained with TTC; B: comparison of the percentages of cerebral infarction volumes in rats from each group. We took the tissue of the ischemic area of the right cerebral cortex from each group of rats at the 24-h ischemic time point and detected it using relevant reagent kits. At the time point of 2-hour of ischemia, we performed acupuncture and sham acupuncture operations. TTC staining (8 g TTC, 40 mL PBS). CIRI: cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury; TTC: triphenyltetrazolium chloride. Data were statistically analysed by least significant difference test. Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). aP < 0.01, compared with the sham group; bP < 0.01, compared with the acupuncture group.
| Item | Sham group | Model group | Acupuncture group | Sham acupuncture group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe2+ | 4.0±0.9a | 10.3±1.0b | 6.4±1.3 | 9.9±2.0b |
| MDA | 2.6±0.9a | 8.6±0.8b | 6.4±0.5 | 8.2±0.9b |
Table 1 Acupuncture reduced the levels of Fe2+ and MDA in rats with CIRI (x? ± s, n = 6)
| Item | Sham group | Model group | Acupuncture group | Sham acupuncture group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe2+ | 4.0±0.9a | 10.3±1.0b | 6.4±1.3 | 9.9±2.0b |
| MDA | 2.6±0.9a | 8.6±0.8b | 6.4±0.5 | 8.2±0.9b |
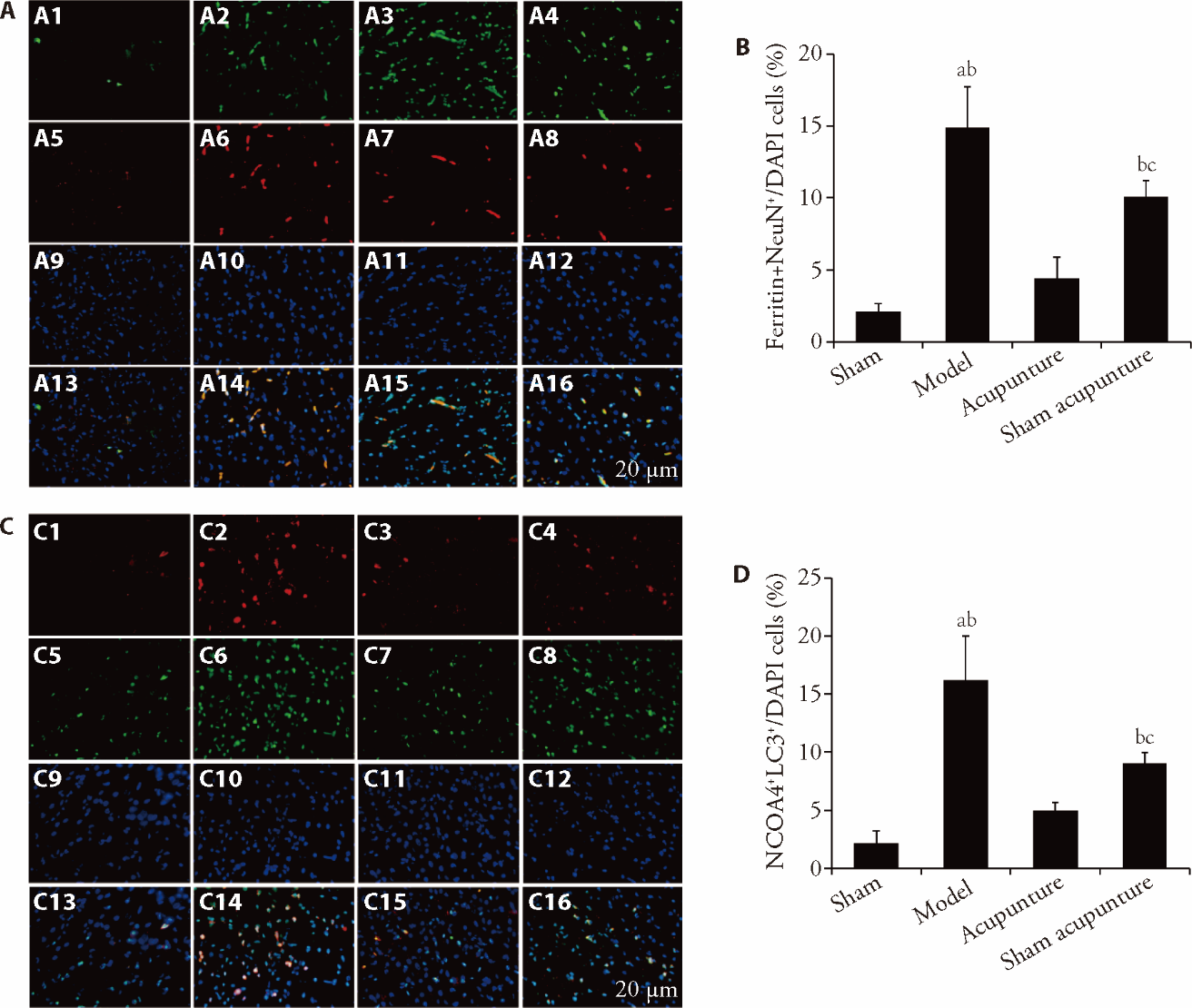
Figure 3 Acupuncture inhibited the level of ferritinophagy in rats with CIRI A: representative immunofluorescence images of ferritin increase in neurons (NeuN) (scale bar = 20 μm, n = 6, use of immunofluorescence staining); B: bar graphs showed quantitative evaluation of A; C: representative images show the colocalization of NCOA4 (red) with LC3 (green) (scale bar = 20 μm, n = 6, use of immunofluorescence staining); D: bar graphs showed quantitative evaluation of B. A1: ferritin of sham group. A2: ferritin of model group. A3: ferritin of acupuncture group. A4: ferritin of sham acupuncture group. A5: NeuN of sham group. A6: NeuN of model group. A7: NeuN of acupuncture group. A8: NeuN of sham acupuncture group. A9: DAPI of sham group. A10: DAPI of model group. A11: DAPI of acupuncture group. A12: DAPI of sham acupuncture group. A13: merge of sham group. A14: merge of model group. A15: merge of acupuncture group. A16: merge of sham acupuncture group. C1: NCOA4 of sham group. C2: NCOA4 of model group. C3: NCOA4 of acupuncture group. C4: NCOA4 of sham acupuncture group. C5: LC3 of sham group. C6: LC3 of model group. C7: LC3 of acupuncture group. C8: LC3 of sham acupuncture group. C9: DAPI of sham group. C10: DAPI of model group. C11: DAPI of acupuncture group. C12: DAPI of sham acupuncture group. C13: merge of sham group. C14: merge of model group. C15: merge of acupuncture group. C16: merge of sham acupuncture group. We took the tissue of the ischemic area of the right cerebral cortex from each group of rats at the 24-h ischemic time point and detected it using relevant reagent kits. At the time point of 2-h of ischemia, we performed acupuncture and sham acupuncture operations. NCOA4: nuclear receptor coactivator 4; LC3: microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3; NeuN: neuron; merge: NCOA4 with LC3; CIRI: cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Statistical significance between multiple groups was determined in this study primarily using one-way or two-way analysis of variance. All data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). aP < 0.01, compared with the sham group; bP < 0.01, compared with the acupuncture group; cP < 0.01, compared with the model group.

Figure 4 Acupuncture inhibited NCOA4-medicated ferritinophagy in rats with CIRI A: Western blot showing NCOA4 expression in CIRI rats (n = 6). B: bar graphs showed quantitative evaluation of A. C: Western blot showing FTH1 expression in CIRI rats (n = 6). D: bar graphs showed quantitative evaluation of C. E: Representative images show the colocalization of NCOA4 (red) with ferritin (green) (scale bar = 20 μm, n = 6, use of immunofluorescence staining). F: bar graphs showed quantitative evaluation of E. E1: NCOA4 of sham group. E2: NCOA4 of model group. E3: NCOA4 of acupuncture group. E4: NCOA4 of sham acupuncture group. E5: ferritin of sham group. E6: ferritin of model group. E7: ferritin of acupuncture group. E8: ferritin of sham acupuncture group. E9: DAPI of sham group. E10: DAPI of model group. E11: DAPI of acupuncture group. E12: DAPI of sham acupuncture group. E13: merge of sham group. E14: merge of model group. E15: merge of acupuncture group. E16: merge of sham acupuncture group. We took the tissue of the ischemic area of the right cerebral cortex from each group of rats at the 24-h ischemic time point and detected it using relevant reagent kits. At the time point of 2-h of ischemia, we performed acupuncture and sham acupuncture operations. NCOA4: nuclear receptor coactivator 4; NeuN: neuron; merge: NCOA4 with ferritin; CIRI: cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Statistical significance between multiple groups was determined in this study primarily using one-way or two-way analysis of variance. All data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). aP < 0.01, compared with the sham group; bP < 0.01, compared with the acupuncture group; cP < 0.05, compared with the model group; dP < 0.01, compared with the model group.
| 1. |
GBD 2016 Neurology Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol 2019; 18: 459-80.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Barthels D, Das H. Current advances in ischemic stroke research and therapies. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2020; 1866: 165260.
DOI URL |
| 3. |
Wu S, Wu B, Liu M, et al. Stroke in China: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol 2019; 18: 394-405.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Dong Q, Dong Y, Liu L, et al. The Chinese stroke Association scientific statement: intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischaemic stroke. Stroke Vasc Neurol 2017; 2: 147-59.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Zhu W, Ye Y, Liu Y, et al. Mechanisms of acupuncture therapy for cerebral ischemia: an evidence-based review of clinical and animal studies on cerebral Ischemia. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2017; 12: 575-92.
DOI URL |
| 6. |
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012; 149: 1060-72.
DOI PMID |
| 7. |
Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth B, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol 2014; 16: 1180-91.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Alim I, Caulfield JT, Chen Y, et al. Selenium drives a transcriptional adaptive program to block ferroptosis and treat stroke. Cell 2019; 177: 1262-79.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Tuo Q, Zhang S, Lei P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med Res Rev 2022; 42: 259-305.
DOI URL |
| 10. |
Mancias JD, Wang X, Gygi SP, Harper JW, Kimmelman AC. Quantitative proteomics identifies NCOA4 as the cargo receptor mediating ferritinophagy. Nature 2014; 509: 105-9.
DOI |
| 11. |
Li W, Li W, Wang Y, Leng Y, Xia Z. Inhibition of DNMT-1 alleviates ferroptosis through NCOA4 mediated ferritinophagy during diabetes myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Discov 2021; 7: 267.
DOI PMID |
| 12. |
Gao M, Monian P, Pan Q, Zhang W, Xiang J, Jiang X. Ferroptosis is an autophagic cell death process. Cell Res 2016; 26: 1021-32.
DOI PMID |
| 13. |
Mancias JD, Pontano Vaites L, et al. Ferritinophagy via NCOA 4 is required for erythropoiesis and is regulated by iron dependent HERC2-mediated proteolysis. Elife 2015; 4: e10308.
DOI URL |
| 14. |
Li C, Sun G, Chen B, et al. Nuclear receptor coactivator 4-mediated ferritinophagy contributes to cerebral ischemia-induced ferroptosis in ischemic stroke. Pharmacol Res 2021; 174: 105933.
DOI URL |
| 15. |
Chavez LM, Huang S, MacDonald I, Lin J, Lee Y, Chen Y. Mechanisms of acupuncture therapy in ischemic stroke rehabilitation: a literature review of basic studies. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18: 2270.
DOI URL |
| 16. |
Li G, Li X, Dong J, Han Y. Electroacupuncture ameliorates cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Front Neurol 2021; 12: 619043.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Takakura N, Takayama M, Yajima H. The difference of Park and Streitberger single-blind needles from Takakura double-blind needle. J Integr Med 2015; 13: 212-4.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Huang W, Kutner N, Bliwise D. Complexity of sham acupuncture. Jama Intern Med 2013; 173: 713.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Streitberger K, Witte S, Mansmann U, et al. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture for chronic pain caused by gonarthrosis: a study protocol of an ongoing multi-centre randomised controlled clinical trial [ISRCTN27450856]. BMC Complement Altern Med 2004; 4: 6.
DOI URL |
| 20. | CAAM. Names and locations of common acupoints in laboratory animals part 2: rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2021; 46: 351-2. |
| 21. |
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 1986; 17: 472-6.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Bieber M, Gronewold J, Scharf A, et al. Validity and reliability of neurological scores in mice exposed to middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 2019; 50: 2875-82.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
Qian ZM, Shen X. Brain iron transport and neurodegeneration. Trends Mol Med 2001; 7: 103-8.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Xu Y, Li K, Zhao Y, Zhou L, Liu Y, Zhao J. Role of ferroptosis in stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2023; 43: 205-22.
DOI |
| 25. |
Bogdan AR, Miyazawa M, Hashimoto K, Tsuji Y. Regulators of iron homeostasis: new players in metabolism, cell death, and disease. Trends Biochem Sci 2016; 41: 274-86.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Weiland A, Wang Y, Wu W, et al. Ferroptosis and its role in diverse brain diseases. Mol Neurobiol 2019; 56: 4880-93.
DOI PMID |
| 27. |
Latunde-Dada GO. Ferroptosis: role of lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 2017; 1861: 1893-900.
DOI URL |
| 28. |
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell 2017; 171: 273-85.
DOI PMID |
| 29. |
Lei P, Bai T, Sun Y. Mechanisms of ferroptosis and relations with regulated cell death: a review. Front Physiol 2019; 10: 139.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Hou W, Xie Y, Song X, et al. Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy 2016; 12: 1425-8.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Wang P, Shao B, Deng Z, Chen S, Yue Z, Miao C. Autophagy in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 2018; 163-4: 98-117. |
| 32. |
Zhang Y, Lu X, Tai B, Li W, Li T. Ferroptosis and its multifaceted roles in cerebral stroke. Front Cell Neurosci 2021; 15: 615372.
DOI URL |
| 33. |
Liu J, Guo Z, Yan X, et al. Crosstalk between autophagy and ferroptosis and its putative role in ischemic stroke. Front Cell Neurosci 2020; 14: 577403.
DOI URL |
| 34. |
Hanke N, Rami A. Cerebral ischemia induces iron deposit, ferritin accumulation, nuclear receptor coactivator 4-depletion, and ferroptosis. Curr Neurovasc Res 2022; 19: 47-60.
DOI URL |
| 35. |
Hsiu H, Huang S, Chen C, Hsu C, Hsu W. Acupuncture stimulation causes bilaterally different microcirculatory effects in stroke patients. Microvasc Res 2011; 81: 289-94.
DOI PMID |
| 36. |
Ratmansky M, Levy A, Messinger A, Birg A, Front L, Treger I. The effects of acupuncture on cerebral blood flow in post-stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Altern Complement Med 2016; 22: 33-7.
DOI URL |
| 37. |
Zhang C, Wen Y, Fan X, et al. Therapeutic effects of different durations of acupuncture on rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neural Regen Res 2015; 10: 159.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Zhou J, Zhao L, Meng L, et al. Acupuncture treatment for carotid atherosclerotic plaques: study protocol for a pilot randomized, single blinded, controlled clinical trial. Trials 2020; 21: 768.
DOI PMID |
| 39. | Feng S, Li B, Zhang H, et al. Placebo control and its methodological issues on clinical trials of acupuncture therapy. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2022; 42: 437-41. |
| 40. | Hui Juan Y, Xin Z, Qi Wen T. Literature analysis of false acupuncture. Henan Zhong Yi 2014; 34: 128-9. |
| 41. | Zhang X, Gu Y, Xu W, et al. Early electroacupuncture extends the rtPA time window to 6 h in a male rat model of embolic stroke via the ERK1/2-MMP9 pathway. Neural Plast 2020; 2020: 1-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

