Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 660-669.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240626.003
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Adenosine triphosphate mediates the pain tolerance effect of manual acupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) in mice
LI Zhongzheng1,2, ZHAO Yadan3, Ma Weigang1,2, Zhang Yonglong1,2, XU Zhifang1,2, XI Qiang5, LI Yanqi5, QIN Siru1,2, ZHANG Zichen1,2, WANG Songtao1,2, ZHAO Xue4, LIU Yangyang4, GUO Yi1,2( ), GUO Yongming4(
), GUO Yongming4( )
)
- 1 Research Center of Experimental Acupuncture Science, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China
2 National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Tianjin 301617, China
3 Department of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Qingdao Hiser Hospital Affiliated of Qingdao University (Qingdao Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital), Qingdao 266033, China
4 School of Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Tuina, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China
5 School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China
-
Received:2023-01-11Accepted:2023-07-24Online:2024-08-15Published:2024-06-26 -
Contact:GUO Yi, Research Center of Experimental Acupuncture Science, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China; National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Tianjin 301617, China.guoyi_168@163.com Telephone: +86-13920921016; GUO Yongming, School of Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Tuina, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China,guoymxr@163.com Telephone: +86-13920619116 -
Supported by:National Key R&D Program of China: Biological Mechanisms of Acupoint Function-Effect Associations(2019YFC1709003);National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) Top-level Project: Study on the Neuroimmunological Mechanism of Macrophage Phenotypic Polarisation for Anti-inflammation Regulated by Acupuncture(81873369);National Natural Science Foundation of China Young Science Fund Project: Study on the Neuromodulation Mechanism of Electroacupuncture to Improve Neutropenia after Chemotherapy for Lung Cancer(81704146);National Natural Science Foundation of China Key Project: Research on the Initial Kinetic Regulation Mechanism of Acupuncture Effect Based on the Physicochemical Coupling Network of Acupuncture Point Microenvironment(82030125)
Cite this article
LI Zhongzheng, ZHAO Yadan, Ma Weigang, Zhang Yonglong, XU Zhifang, XI Qiang, LI Yanqi, QIN Siru, ZHANG Zichen, WANG Songtao, ZHAO Xue, LIU Yangyang, GUO Yi, GUO Yongming. Adenosine triphosphate mediates the pain tolerance effect of manual acupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) in mice[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 660-669.
share this article
| Group | n | PTT before MA | PTT after MA |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 9 | 7.4±1.7 | 9.8±2.3a |
| B | 9 | 6.5±1.3 | 8.2±2.2a |
| C | 9 | 6.4±0.7 | 7.9±2.2a |
| D | 9 | 7.0±1.2 | 10.1±2.0a |
| E | 9 | 7.0±1.1 | 8.4±1.3a |
Table 1 Comparison of pain tolerance threshold before and after acupuncture in mice of every group (s, $\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | PTT before MA | PTT after MA |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 9 | 7.4±1.7 | 9.8±2.3a |
| B | 9 | 6.5±1.3 | 8.2±2.2a |
| C | 9 | 6.4±0.7 | 7.9±2.2a |
| D | 9 | 7.0±1.2 | 10.1±2.0a |
| E | 9 | 7.0±1.1 | 8.4±1.3a |
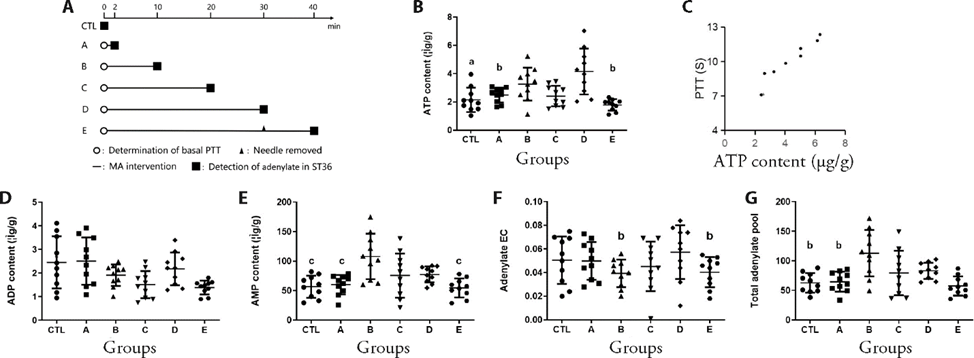
Figure 1 Adenylate content at Zusanli (ST36) was increased after MA in a dose-dependent manner A: flow chart of experimental intervention. Intervention stages are represented by different symbols: ○: determination of basal PTT; ■: detection of adenylate at Zusanli (ST36); ?: MA intervention; ▲: needle removal. After measurements of basal PTT, different MA interventions were performed in mice. B: ATP content at Zusanli (ST36) in each group; C: Scatter plot depicting the correlation between PTT and ATP concentration at Zusanli (ST36); D: ADP content at Zusanli (ST36) in each group; E: AMP content at Zusanli (ST36) in each group. F: Adenylate EC content at Zusanli (ST36) in each group. G: Total adenylate pool content at Zusanli (ST36) in each group. Control (CTL) group: direct detection of adenylate content at Zusanli (ST36). Group A: needle twisted immediately for 2 min. Group B: needle twisted immediately for 2 min and retained for 8 min. Group C: needle twisted immediately for 2 min and retained for 18 min. Group D: needle twisted immediately for 2 min and retained for 28 min. Group E: needle twisted immediately for 2 min and retained for 28 min before removal followed by a 10-minute rest. Adenylate content at Zusanli (ST36) was measured after MA intervention. MA: manual acupuncture; PTT: pain tolerance threshold; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; ADP: adenosine diphosphate; AMP: adenosine monophosphate; EC: energy charge. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 10 per group). The single factor analysis of variance of completely randomized design was used for parameter comparison between groups. Compared with group D, aP < 0.01 and bP < 0.05; Compared with group B, cP < 0.05.
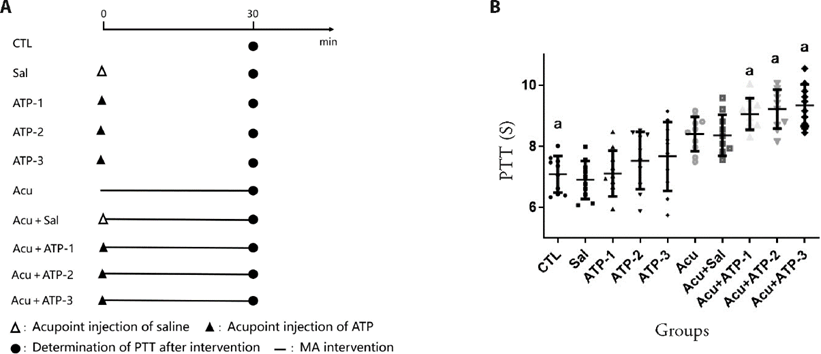
Figure 2 Effects of acupuncture on PTT were mediated by ATP and the P2X3 receptor at Zusanli (ST36) A: flow chart of experimental intervention. Intervention stages are represented by different symbols; ?: Acupoint injection of saline; ▲: Acupoint injection of ATP; ●: Determination of PTT after intervention; ?: MA intervention; B: comparison of PTT in each group. PTT of mice in the Control (CTL) group was measured to indicate the basal level. PTT of mice in the Sal, ATP-1, ATP-2, and ATP-3 groups was measured after acupoint injection of saline, ATP-1 (26 μg/2.6 μL), ATP-2 (52 μg/2.6 μL), and ATP-3 (104 μg/2.6 μL), respectively. PTT of mice in the Acu group was measured after MA intervention (needle was twisted for 2 min and retained for 28 min). Mice in the Acu + Sal, Acu + ATP-1, Acu + ATP-2, and Acu + ATP-3 groups were administered MA (intervention method was the same as that in the Acu group) after acupoint injection of saline, ATP-1 (26 μg/2.6 μL), ATP-2 (52 μg/2.6 μL), and ATP-3 (104 μg/2.6 μL), respectively, followed by measurement of PTT. ATP: adenosine triphosphate; PTT: pain tolerance threshold; P2X3: peripheral purinergic P2X receptor 3; MA: manual acupuncture. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 10 per group). The single factor analysis of variance of completely randomized design was used for parameter comparison between groups. Compared with group Acu, aP < 0.05.
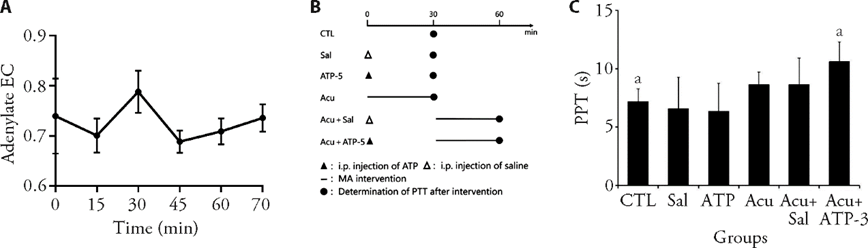
Figure 3 Systemici pre-treatment wth ATP ameliorated PTT in mice A: dynamic adenylate EC content of mice after intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of ATP within 70 min (n = 5 per group). B: flow chart of experimental intervention. Intervention stages are represented by different symbols: ▲: i.p. injection of ATP; ?: i.p. injection of saline; ?: MA intervention; ●: determination of PTT after intervention; C: comparison of PTT in each group (n = 15 per group). PTT of mice in the Control (CTL) group was measured after 30 min. PTT of mice in the Sal and ATP-5(4 μg/g) groups was measured 30 min after i.p. administration of saline and ATP-5, respectively. PTT of mice in the Acu group was measured 30 min after MA intervention (needle was twisted for 2 min and retained for 28 min). Mice in the Acu + Sal and Acu + ATP-5 groups received i.p. injections of saline and ATP, respectively. Mice were subjected to MA 30 min later (the intervention method was the same as that in the Acu group) followed by measurement of PTT. ATP: adenosine triphosphate; PTT: pain tolerance threshold; MA: Manual acupuncture; EC: energy charge. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. The single factor analysis of variance of completely randomized design was used for parameter comparison between groups. Compared with group Acu, aP < 0.05.
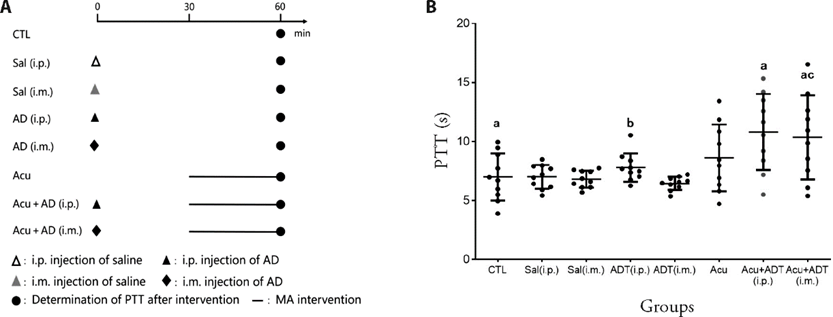
Figure 4 Pretreatment with adenosine disodium ameliorated the effects of acupuncture A: flow chart of experimental intervention. Intervention stages are represented by different symbols: ?: intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of saline; ▲: i.p. injection of adenosine disodium (represented by AD); ▲: i.m. injection of saline; ?: i.m. injection of AD; ●: determination of PTT after intervention; ?: MA intervention; B: comparison of PTT in each group. PTT of mice in the Control (CTL) group was measured to indicate the basal level. PTT of mice in the Sal (i.p.), Sal (i.m.), AD (i.p.), and AD (i.m.) groups was measured after i.p. or i.m. injections of saline or AD. PTT of mice in the Acu group was measured after MA intervention (needle was twisted for 2 min and retained for 28 min). Mice in the Acu + AD (i.p.) and Acu + AD (i.m.) groups were subjected to MA (the intervention method was the same as that in the Acu group) after i.p. or i.m. injections of AD, respectively, followed by measurement of PTT. MA: Manual acupuncture; PTT: pain tolerance threshold; AD: adenosine disodium. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 10 per group). The single factor analysis of variance of completely randomized design was used for parameter comparison between groups. Compared with group Acu, aP < 0.05; compared with group Acu +AD (i.p.), cP < 0.05; compared with group AD (i.m.), bP < 0.05.
| 1. | Moudgil KD, Berman BM. Traditional Chinese Medicine: potential for clinical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2014; 10: 819-22. |
| 2. | Goh YL, Ho CE, Zhao B. Acupuncture and depth: future direction for acupuncture research. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 2014: 871217. |
| 3. | Li NC, Li MY, Chen B, Guo Y. A new perspective of acupuncture: the interaction among three networks leads to neutralization. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019; 2019: 2326867. |
| 4. | Madsen MV, Gøtzsche PC, Hróbjartsson A. Acupuncture treatment for pain: systematic review of randomised clinical trials with acupuncture, placebo acupuncture, and no acupuncture groups. BMJ 2009; 338: a3115. |
| 5. | Lee IS, Cheon S, Park JY. Central and peripheral mechanism of acupuncture analgesia on visceral pain: a systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019; 2019: 1304152. |
| 6. | Zhao ZQ. Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog Neurobiol 2008; 85: 355-75. |
| 7. | Kagitani F, Uchida S, Hotta H. Afferent nerve fibers and acupuncture. Auton Neurosci 2010; 157: 2-8. |
| 8. | Chang KH, Bai SJ, Lee H, Lee BH. Effects of acupuncture stimulation at different acupoints on formalin-induced pain in rats. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 2014; 18: 121-7. |
| 9. | Vixner L, Schytt E, Stener-Victorin E, Waldenström U, Pettersson H, Mårtensson LB. Acupuncture with manual and electrical stimulation for labour pain: a longitudinal randomised controlled trial. BMC Complement Altern Med 2014; 14: 187. |
| 10. | Kong J, Gollub R, Huang T, et al. Acupuncture De Qi, from qualitative history to quantitative measurement. J Altern Complement Med 2007; 13: 1059-70. |
| 11. | Leong PK, Wong HS, Chen J, Ko KM. Yang/Qi invigoration: an herbal therapy for chronic fatigue syndrome with Yang deficiency. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015; 945901. |
| 12. | Ko KM, Chiu PY. Biochemical basis of the "Qi-invigorating" action of Schisandra berry (wu-wei-zi) in Chinese medicine. Am J Chin Med 2006; 34: 171-6. |
| 13. |
Wallace DC. Mitochondria as chi. Genetics 2008; 179: 727-35.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Huang Y, Kwan K, Leung KW, et al. The extracts and major compounds derived from Astragali Radix alter mitochondrial bioenergetics in cultured cardiomyocytes: comparison of various polar solvents and compounds. Int J Mol Sci 2018; 19: 1574. |
| 15. | Yegutkin GG. Enzymes involved in metabolism of extracellular nucleotides and nucleosides: functional implications and measurement of activities. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 2014; 49: 473-97. |
| 16. |
Tang Y, Yin HY, Liu J, Rubini P, Illes P. P2X receptors and acupuncture analgesia. Brain Res Bull 2019; 151: 144-52.
DOI PMID |
| 17. |
Surprenant A, North RA. Signaling at purinergic P2X receptors. Annu Rev Physiol 2009; 71: 333-59.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Kasuya G, Fujiwara Y, Tsukamoto H, et al. Structural insights into the nucleotide base specificity of P2X receptors. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 45208.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | Shi L, Zhang HH, Hu J, Jiang XH, Xu GY. Purinergic P2X receptors and diabetic neuropathic pain. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2012; 64: 531-42. |
| 20. |
Xiao Z, Ou S, He WJ, Zhao YD, Liu XH, Ruan HZ. Role of midbrain periaqueductal gray P2X3 receptors in electroacupuncture-mediated endogenous pain modulatory systems. Brain Res 2010; 1330: 31-44.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Goldman N, Chen M, Fujita T, et al. Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nat Neurosci 2010; 13: 883-88.
DOI PMID |
| 22. | De la Fuente IM, Cortés JM, Valero E, et al. On the dynamics of the adenylate energy system: homeorhesis vs homeostasis. PLoS One 2014; 9: e108676. |
| 23. | Choi JW, Kang SY, Choi JG, et al. Analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain via spinal opioidergic and adrenergic mechanisms in mice. Am J Chin Med 2015; 43: 57-70. |
| 24. | Lu KW, Hsu CK, Hsieh CL, Yang J, Lin YW. Probing the effects and mechanisms of electroacupuncture at ipsilateral or contralateral ST36-ST37 Acupoints on CFA-induced inflammatory pain. Sci Rep 2016; 6: 22123. |
| 25. |
You X, Wang Y, Wu J, et al. Zusanli (ST36) Acupoint injection with neostigmine for paralytic postoperative ileus following radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer: a randomized clinical trial. J Cancer 2018; 9: 2266-74.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Lorenzini L, Giuliani A, Giardino L, Calzà L. Laser acupuncture for acute inflammatory, visceral and neuropathic pain relief: an experimental study in the laboratory rat. Res Vet Sci 2010; 88: 159-65.
DOI PMID |
| 27. |
Park JH, Kim SK, Kim HN, et al. Spinal cholinergic mechanism of the relieving effects of electroacupuncture on cold and warm allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Physiol Sci 2009; 59: 291-8.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Yang X, Li X, Fu N, et al. Effect of acupuncture for pain threshold among the groups of different constitutions. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2016; 36: 491-5. |
| 29. |
Barlas P, Ting SL, Chesterton LS, Jones PW, Sim J. Effects of intensity of electroacupuncture upon experimental pain in healthy human volunteers: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Pain 2006; 122: 81-9.
PMID |
| 30. |
Bai L, Qin W, Tian J, et al. Time-varied characteristics of acupuncture effects in fMRI studies. Hum Brain Mapp 2009; 30: 3445-460.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Bodin P, Burnstock G. Purinergic signalling: ATP release. Neurochem Res 2001; 26: 959-69.
DOI PMID |
| 32. |
Katsuragi T, Migita K. The mechanism of ATP release as an autocrine/paracrine molecule. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi 2004; 123: 382-388.
PMID |
| 33. | Kuan YH, Shyu BC. Nociceptive transmission and modulation via P2X receptors in central pain syndrome. Mol Brain 2016; 9: 58. |
| 34. | Brederson JD, Jarvis MF. Homomeric and heteromeric P2X3 receptors in peripheral sensory neurons. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2008; 9: 716-25. |
| 35. | Zhang ZJ, Wang XM, McAlonan GM. Neural acupuncture unit: a new concept for interpreting effects and mechanisms of acupuncture. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012; 2012: 429412. |
| 36. |
Burnstock G. Purinergic signalling: from discovery to current developments. Exp Physiol 2014; 99: 16-34.
DOI PMID |
| 37. |
Lambertucci C, Dal Ben D, Buccioni M, Marucci G, Thomas A, Volpini R. Medicinal chemistry of P2X receptors: agonists and orthosteric antagonists. Curr Med Chem 2015; 22: 915-28.
DOI PMID |
| 38. | Chen B, Li MY, Guo Y, Zhao X, Liu YY. Mast cell-derived exosome participates in acupoint-stimulation initiated local network activities. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2015; 40: 82-5. |
| 39. | Song dynasty. Ling Shu Jing. Taiyuan: Shanxi Science and Technology Press, 1992: 4. |
| 40. | Yin CS, Chae Y, Kang OS, et al. De Qi is double-faced: the acupuncture practitioner's and the subject's perspective. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015; 2015: 635089. |
| 41. | Bo C, Ming-yue LI, Sha-sha D, et al. Research progress on regulations on nerve-endocrine-immune network by acupuncture. World J Acupunct Moxibustion 2014; 24: 49-53. |
| 42. |
Illes P, Ribeiro JA. Neuronal P2 receptors of the central nervous system. Curr Top Med Chem 2004; 4: 831-8.
PMID |
| 43. | Khakh BS, North RA. P2X receptors as cell-surface ATP sensors in health and disease. Nature 2006; 442: 527-32. |
| [1] | YAN Jing, FENG Huimin, QIU Fang, WANG Haijun, YIN Luyun, JIN Xiaofei, ZHAO Jiyu, WANG Hongyang, YAN Xiaoqin. Effect on serum metabolomics of rats with premature ovarian insufficiency by Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 722-733. |
| [2] | CHEN Yonglin, OUYANG Ling, MENG Lingling, WU Bufan, PENG Rou, LIU Sitong, HOU Dan, WANG Yaling, JING Xinyue, LU Shengfeng, FU Shuping. Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 734-744. |
| [3] | SUN Junjian, XIE Henghui, LI Huanhuan, TIAN Xiangming, FANG Yigong, ZHOU Wenhui. Acupuncture improves the live birth of patients with repeated implantation failure: a retrospective cohort study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 830-838. |
| [4] | ZHU Wenting, GUO Changqing, DU Mei, MA Yunxuan, CUI Yongqi, CHEN Xilin, GUO Changqing. Acupotomy alleviates knee osteoarthritis in rabbit by regulating chondrocyte mitophagy via Pink1-Parkin pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 468-477. |
| [5] | YU Wenxi, TANG Lina, LI Hongtao, WANG Yonggang, SHEN Zan. Neiguan (PC6) acupoint stimulation for preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: a cost-effective supplement in guideline-inconsistent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting prophylaxis subgroup [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 581-585. |
| [6] | WANG Dingyue, YU Yana, WANG Yiyuan, ZHANG Zhen. Musculoskeletal ultrasound to evaluate the efficacy of acupuncture: a review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 629-632. |
| [7] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xinchang, HUANG Zheng, HUANG Peiyan, YANG Mengning, ZHANG Zhihui, NI Guangxia. Mechanism of acupuncture in attenuating cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury based on nuclear receptor coactivator 4 mediated ferritinophagy [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 345-352. |
| [9] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [10] | SUN Qianhui, CHENG Kai, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, WU Xiaoling, XU Chang, QIU Xinghua, GAO Xiaofeng, LIU Daonan, YANG Qirui. Effect of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) at different time points on myocardial ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 113-121. |
| [11] | LIU Tingting, LIU Tongou, LIU Mingfu. Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture in treatment of pregnancy-related symptoms: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 16-26. |
| [12] | YANG Yi, YE Huijun, ZHENG Huiling, JIN Lihua. Clinical observation on 90 cases of primary dysmenorrhea treated by buccal acupuncture therapy: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 172-181. |
| [13] | LI Menghan, WANG Yu, RAN Dawei, YANG Xinming, DENG Shizhe, SHI Lei, MENG Zhihong. Effects of anterior sciatic nerve acupuncture on lower limb paralysis after cerebral infarction: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 205-211. |
| [14] | DU Zhongheng, CONG Wenjie, TANG Kejing, ZHENG Qiqi, SONG Zhiwei, CHEN Yong, YANG Su, ZHANG Chunwu, YE Tianshen. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) in mice with collagen-induced arthritis leads to adenosine A2A receptor-mediated alteration of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1103-1109. |
| [15] | QIN Xihui, PANG Jianli, XIONG Guan, FENG Jie. Bo′s abdominal acupuncture improves disordered metabolism in obese type 2 diabetic rats through regulating fibroblast growth factor 21 and its related adipokines [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1200-1208. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

