Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 868-875.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220907.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Spinosin protects Neuro-2a/APP695 cells from oxidative stress damage by inactivating p38
ZHANG Xiaoying1, WANG Ruixuan1, WANG Yiqing2, XU Fanxing3, YAN Tingxu4, WU Bo4, ZHANG Ming5( ), JIA Ying4(
), JIA Ying4( )
)
- 1 School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016, China
2 School of Pharmacy, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016, China
3 Wuya College of Innovation, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016, China
4 Faculty of Functional Food and Wine, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016, China
5 Gynecology Department, Shenyang Women's and Children's Hospital, Shenyang 110011, China
-
Received:2022-07-11Accepted:2022-09-02Online:2023-10-15Published:2023-08-29 -
Contact:JIA Ying, Faculty of Functional Food and Wine, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016, China.jiayingsyphu@126.com ;ZHANG Ming, Shenyang Women's and Children's Hospital, Shenyang 110011, China.fysyl2016@163.com . Telephone: +86-24-43520305 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on the Basis and Mechanism of Antidepressant Substances in Which Schisandra Chinensis Regulates the Endocannabinoid System in the Body and Participates in "Gut-Brain Dialogue"(82173961);National Natural Science Foundation of China: to Investigate the Pharmacological Substance Basis and Mechanism of Suanzaoren Decoction in Improving Depression by Crosstalk Regulating "Gut Microbiota-Gut-Brain" Axis Based on TLR4-NF-κB/NLRP3 and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways(82003926);Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Liaoning Province: Study on the Mechanism of Antidepressant Action of Schisandra Chinensis Mediated by Intestinal Flora(2019-BS-233);High-Level Innovation and Entrepreneurship Team of Liaoning Province: "Healthy Liaoning" Functional Food Quality and Safety Innovation Team, "Xingliao Talent Plan" High-Level Innovation and Entrepreneurship Team(XLYC2008029);Guizhou Provincial Natural Science Foundation: Probing the Chemical Components and the Detailed Working Mechanisms of Danggui Buxue Tang for Mitigating the Menopausal Syndrome(QKH-J[2020]1Y377)
Cite this article
ZHANG Xiaoying, WANG Ruixuan, WANG Yiqing, XU Fanxing, YAN Tingxu, WU Bo, ZHANG Ming, JIA Ying. Spinosin protects Neuro-2a/APP695 cells from oxidative stress damage by inactivating p38[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 868-875.
share this article
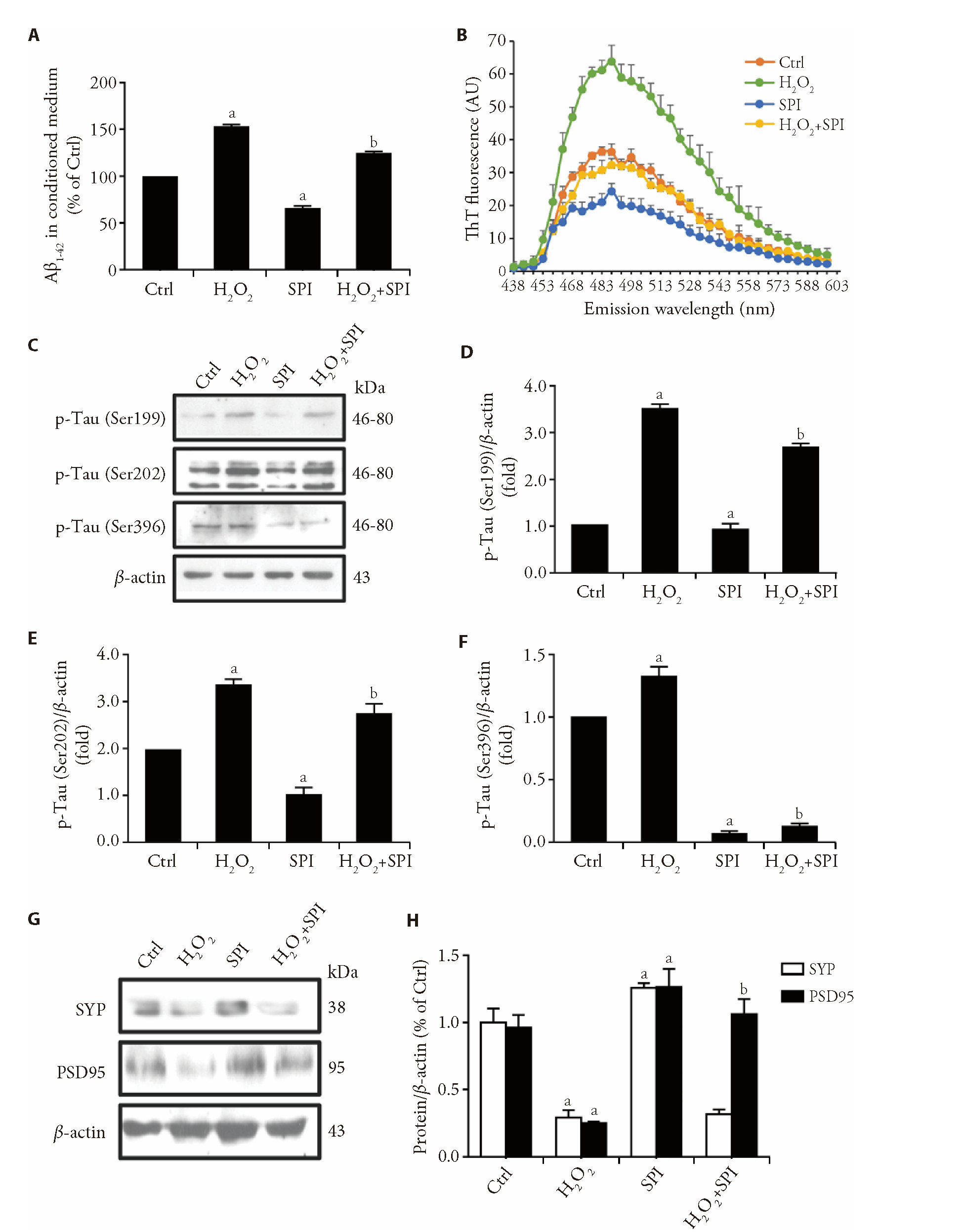
Figure 1 Spinosin protected N2a/APP695 cells from H2O2-induced damage. Cells were treated with spinosin (25 μM) for 22 h alone or after H2O2 model construction (6.25 μM for 2 h). A: Aβ1-42 in conditioned medium was measured by ELISA kits; B: the deposition of Aβ1-42 is detected by ThT staining experiment; C: representative Western blot of p-Tau (Ser199), p-Tau (Ser202) and p-Tau (Ser396); D: quantitative analysis of p-Tau (Ser199) expression normalized to β-actin expression; E: quantitative analysis of p-Tau (Ser202) expression normalized to β-actin expression; F: quantitative analysis of p-Tau (Ser396) expression normalized to β-actin expression; G: representative Western blot of SYP and PSD95; H: quantitative analysis of SYP and PSD95 expression normalized to β-actin expression. N2a: Neuro-2a; ELISA: enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; SPI: spinosin; SYP: synaptophysin; PSD95: postsynaptic density protein 95. The statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Values are expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 3). aP < 0.05 vs Ctrl group; bP < 0.05 vs H2O2 group.
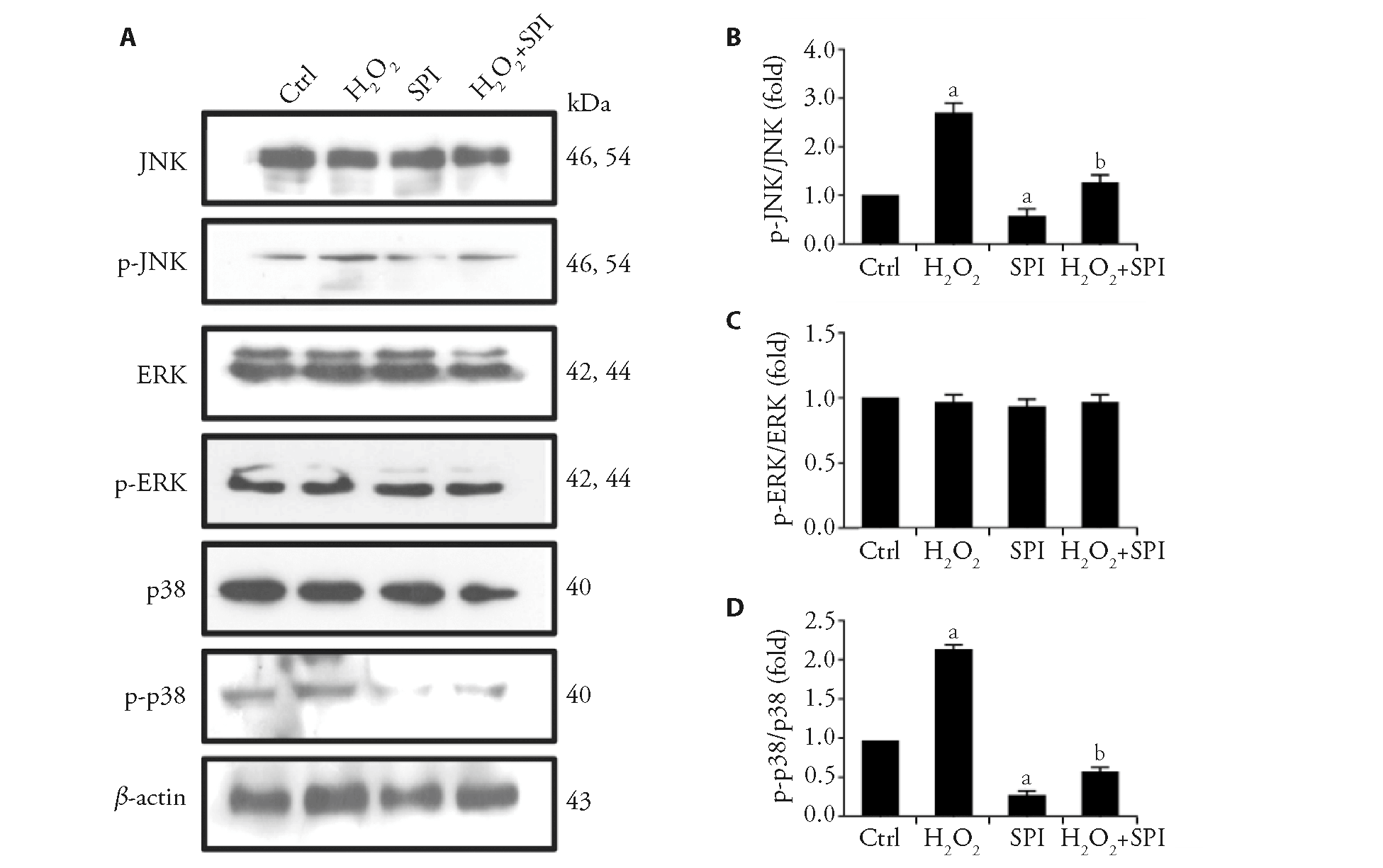
Figure 2 Effect of spinosin on the expression changes of MAPK family proteins caused by H2O2 Cells were treated with spinosin (25 μM) for 22 h alone or after H2O2 model construction (6.25 μM for 2 h). A: representative Western blot of JNK, p-JNK, ERK, p-ERK, p38 and p-p38; B: quantitative analysis of p-JNK expression normalized to JNK expression; C: quantitative analysis of p-ERK expression normalized to ERK expression; D: quantitative analysis of p-p38 expression normalized to p38 expression. MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; SPI: spinosin; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; ERK: extracellular regulated protein kinases. The statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Data are mean ± standard error of mean of three independent experiments (n = 3). aP < 0.05 vs Ctrl group; bP < 0.05 vs H2O2 group.

Figure 3 Effect of BIRB796 on oxidative stress, Aβ1-42 secretion, Tau phosphorylation and synaptic plasticity in N2a/APP695 cells Cells were treated with spinosin (25 μM) for 22 h alone or after H2O2 model construction (6.25 μM for 2 h). For the p38 inhibitor group, cells were treated with H2O2 and BIRB796 (2 μM) for 2 h, which were then replaced with fresh medium for the following 22 h. A: intracellular MDA and LDH levels were measured by ELISA kits; B: Aβ1-42 in conditioned medium was measured by ELISA kits; C: representative Western blot of p-Tau (Ser396); D: quantitative analysis of p-Tau (Ser396) expression normalized to β-actin expression; E: cytoskeleton was stained with FITC-phalloidin, and then photographed with a confocal fluorescence microscope, ×200. E1: Ctrl group cells were labeled by FITC-phalloidin; E2: Ctrl group cells were labeled by DAPI; E3: FITC-phalloidin and DAPI stain labeled overlapping image of Ctrl cells; E4: H2O2 group cells were labeled by FITC-phalloidin; E5: H2O2 group cells were labeled by DAPI. E6: FITC-phalloidin and DAPI stain labeled overlapping image of H2O2 cells; E7: H2O2 + SPI group cells were labeled by FITC-phalloidin; E8: H2O2 + SPI group cells were labeled by DAPI. E9: FITC-phalloidin and DAPI stain labeled overlapping image of H2O2 + SPI cells; E10: H2O2 + BIRB796 group cells were labeled by FITC-phalloidin; E11: H2O2 + BIRB796 group cells were labeled by DAPI. E12: FITC-phalloidin and DAPI stain labeled overlapping image of H2O2 + BIRB796 cells. The statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. N2a: Neuro-2a; ELISA: enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; SPI: spinosin; MDA: malondialdehyde; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Data are mean ± standard error of mean of three independent experiments (n = 3). aP < 0.05 vs Ctrl group; bP < 0.05 vs H2O2 group.
| 1. |
Xu FX, Zhang XY, Wang JY, et al. Spinosin protects N2a cells from H2O2-induced neurotoxicity through inactivation of p38MAPK. J Pharm Pharmacol 2020; 72: 1607-14.
DOI URL |
| 2. |
Ennerfelt HE, Lukens JR. The role of innate immunity in Alzheimer's disease. Immunol Rev 2020; 297: 225-46.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Qi Y, Guo L, Jiang YB, Shi YJ, Sui HJ, Zhao L. Brain delivery of quercetin-loaded exosomes improved cognitive function in AD mice by inhibiting phosphorylated tau-mediated neurofibrillary tangles. Drug Deliv 2020; 27: 745-55.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Pooler AM, Noble W, Hanger DP. A role for tau at the synapse in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. Neuropharmacology 2014; 76 Pt A: 1-8.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Tu S, Okamoto S, Lipton SA, Xu H. Oligomeric Aβ-induced synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurodegener 2014; 9: 48.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Teixeira JP, de Castro AA, Soares FV, da Cunha EFF, Ramalho TC. Future therapeutic perspectives into the Alzheimer's disease targeting the oxidative stress hypothesis. Molecules 2019; 24: 4410.
DOI URL |
| 7. |
Tabassum R, Jeong NY. Potential for therapeutic use of hydrogen sulfide in oxidative stress-induced neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Med Sci 2019; 16: 1386-96.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Zuroff L, Daley D, Black KL, Koronyo HM. Clearance of cerebral Aβ in Alzheimer's disease: reassessing the role of microglia and monocytes. Cell Mol Life Sci 2017; 74: 2167-201.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Choi EY, Kang SS, Lee SK, Han BH. Polyphenolic biflavonoids inhibit amyloid-beta fibrillation and disaggregate preformed amyloid-beta fibrils. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2020; 28: 145-51.
DOI URL |
| 10. |
Duan Q, Si E. MicroRNA-25 aggravates Aβ1-42-induced hippocampal neuron injury in Alzheimer's disease by downregulating KLF2 via the Nrf2 signaling pathway in a mouse model. J Cell Biochem 2019; 120: 15891-905.
DOI URL |
| 11. | Michalska P, Mayo P, MC Fernández, et al. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective profiles of novel 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020; 9: 650. |
| 12. |
Song Y, Li N, Gu J, et al. β-Hydroxybutyrate induces bovine hepatocyte apoptosis via an ROS-p38 signaling pathway. J Dairy Sci 2016; 99: 9184-98.
DOI URL |
| 13. |
Kales HC, Gitlin LN, Lyketsos CG. Assessment and management of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia. BMJ 2015; 350: h369.
DOI URL |
| 14. |
Fang X, Hao J, Zhou H, Zhu LX, Wang JH, Song FQ. Pharmacological studies on the sedative-hypnotic effect of Semen Ziziphi spinosae (Suanzaoren) and Radix et Rhizoma Salviae miltiorrhizae (Danshen) extracts and the synergistic effect of their combinations. Phytomedicine 2010; 17: 75-80.
DOI PMID |
| 15. |
Xu FX, He BS, Xiao F, et al. Neuroprotective effects of spinosin on recovery of learning and memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2019; 27: 71-7.
DOI URL |
| 16. |
Zhang XY, Wang JY, Gong GW, et al. Spinosin inhibits Aβ1-42production and aggregation via activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2020; 28: 259-66.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Karthick C, Nithiyanandan S, Essa MM, Guillemin GJ, Jayachandran SK, Anusuyadevi M. Time-dependent effect of oligomeric amyloid-β1-42-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration in rat model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurol Res 2019; 41: 139-50.
DOI URL |
| 18. |
Arias E, SS Gallego, Villarroya M, García AG, López MG. Unequal neuroprotection afforded by the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors galantamine, donepezil, and rivastigmine in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: role of nicotinic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005; 315: 1346-53.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Tang Y, Min Z, Xiang XJ, et al. Estrogen-related receptor alpha is involved in Alzheimer's disease-like pathology. Exp Neurol 2018; 305: 89-96.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Prasad K. AGE-RAGE stress: a changing landscape in pathology and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Cell Biochem 2019; 459: 95-112.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Xiao L, Liao F, Ide R, et al. Enzyme-digested Colla Corii Asini (E'jiao) prevents hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death and accelerates amyloid beta clearance in neuronal-like PC12 cells. Neural Regen Res 2020; 15: 2270-2.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Hu Y, Zhou KY, Wang ZJ, Lu Y, Yin M. N-stearoyl-l-Tyrosine inhibits the cell senescence and apoptosis induced by H2O2 in HEK293/Tau cells via the CB2 receptor. Chem Biol Interact 2017; 272: 135-44.
DOI URL |
| 23. |
Su B, Wang X, Lee HG, et al. Chronic oxidative stress causes increased tau phosphorylation in M17 neuroblastoma cells. Neurosci Lett 2010; 468: 267-71.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Tamagno E, Robino G, Obbili A, et al. H2O2 and 4-hydroxynonenal mediate amyloid beta-induced neuronal apoptosis by activating JNKs and p38MAPK. Exp Neurol 2003; 180: 144-55.
PMID |
| 25. |
Schnöder L, Hao W, Qin Y, et al.Deficiency of neuronal p38α MAPK attenuates amyloid pathology in Alzheimer disease mouse and cell models through facilitating lysosomal degradation of BACE1. J Biol Chem 2016; 291: 2067-79.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Hanger DP, Anderton BH, Noble W. Tau phosphorylation: the therapeutic challenge for neurodegenerative disease. Trends Mol Med 2009; 15: 112-9.
DOI PMID |
| 27. |
Su JH, Cummings BJ, Cotman CW. Early phosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer's disease occurs at Ser-202 and is preferentially located within neurites. Neuroreport 1994; 5: 2358-62.
PMID |
| 28. | Yao E, Tang Y, Liu X, Wang MH. TPPU protects tau from H2O2-induced hyperphosphorylation in HEK293/tau cells by regulating PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Hua Zhong Ke Ji Da Xue Xue Bao 2016; 36: 785-90. |
| 29. |
Borovac J, Bosch M, Okamoto K. Regulation of actin dynamics during structural plasticity of dendritic spines: signaling messengers and actin-binding proteins. Mol Cell Neurosci 2018; 91: 122-30.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | HUANG Hongmei, YANG Maojun, LI Ting, WANG Dandan, LI Ying, TANG Xiaochi, YUAN Lu, GU Shi, XU Yong. Neferine inhibits the progression of diabetic nephropathy by modulating the miR-17-5p/nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 axis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 44-53. |
| [2] | ZHAO Ming, LUO Yimiao, WANG Huichan, CAO Yu, MA Lina, PEI Hui, LI Hao. Guilingji capsule (龟龄集胶囊) for Alzheimer's disease: secondary analysis of a randomized non-inferiority controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 1019-1025. |
| [3] | LIU Bingbing, LI Jieru, SI Jianchao, CHEN Qi, YANG Shengchang, JI Ensheng. Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy in db/db mice by regulating the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/Nrf2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 906-914. |
| [4] | ZHOU Hua, LI Hui, WANG Haihua. Potential protective effects of the water-soluble Chinese propolis on experimental ulcerative colitis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 925-933. |
| [5] | TIAN Meijing, HE Yannan, ZHENG Mingcui, QIN Gaofeng, GONG Zhuoyan, HUANG Shuaiyang, WANG Pengwen. Chinese herbal compound Jinsiwei (金思维) improves synaptic plasticity in mice with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease induced by streptozotocin [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 78-86. |
| [6] | ZHENG Wei, WANG Mingxing, LIU Shanxue, LUAN Chao, ZHANG Yanqiu, XU Duoduo, WANG Jian. Buyang Huanwu Tang (补阳还五汤) protects H2O2-induced RGC-5 cell against oxidative stress and apoptosis via reactive oxygen species-mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 885-891. |
| [7] | HENG Xianpei, LI Liang, YANG Liuqin, WANG Zhita. Efficacy of Dangua Fang (丹瓜方) on endothelial cells damaged by oxidative stress [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 900-907. |
| [8] | HUANG Qiuyue, YE Hui, SHI Zongming, JIA Xiaofen, LIN Miaomiao, CHU Yingming, YU Jing, ZHANG Xuezhi. Efficacy of Qingre Huashi decoction (清热化湿方) on infection of Helicobacter pylori: inhibiting adhesion, antioxidant, and anti-inflammation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 915-921. |
| [9] | HU Xijiao, LI Shuoxi, YANG Dongxia, GU Na, LIU Jinzhe, WANG Yawen, LIU Li, SUN Yiming. Modified Gexiazhuyu decoction (膈下逐瘀汤加减方) alleviates chronic salpingitis via p38 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 213-220. |
| [10] | Xing DU, Tianlong LIU, Wendi TAO, Maoxing LI, Xiaolin LI, Lan YAN. Effect of aqueous extract of Astragalus membranaceus on behavioral cognition of rats living at high altitude [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 58-64. |
| [11] | WANG Shengchun, JIANG Yiming, QIU Lirong, SU Meng. Efficacy of needling acupoints of Guanyuan(CV4), Sanyinjiao(SP6), Zusanli(ST36), Pishu(BL20), Shenshu(BL23), Zigong(EX-CA1) on expression of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in ovarian tissue in rats with premature ovarian failure induced by cyclophosp [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 953-958. |
| [12] | WU Mingyun, YU Jianer, BAI Li, XUE Zheng, JIANG Shenhua, LI Liqing, PIAO Xiang, XU Wanchao, WANG Jiani, SHEN Qian. Pingchuan formula(平喘方) improves allergic asthma in mice through inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 883-890. |
| [13] | CAI Liang, ZONG Daokuan, TONG Guoqing, LI Li. Apoptotic mechanism of premature ovarian failure and rescue effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine: a review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 491-498. |
| [14] | LIU Chunhua, LU Dingyan, YOU Jingrui, LU Yuan, SUN Jia, PAN Jie, WANG Yonglin, WANG Aimin, LAN Yanyu, LI Yongjun, LIU Ting. Efficacy of water fraction from Dioscorea cirrhosa on oxidative stress and apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes induced by H_2O_2 [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(1): 51-58. |
| [15] | LIU Huahua, ZHAO Jingjing, PAN Sunlei, ZHU Yeke, FU Guosheng, TANG Weiliang, PENG Fang. Shexiang Tongxin dropping pill(麝香通心滴丸) protects against sodium laurate-induced coronary microcirculatory dysfunction in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(1): 89-97. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 378
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 289
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

