Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 915-921.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220922.001
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of Qingre Huashi decoction (清热化湿方) on infection of Helicobacter pylori: inhibiting adhesion, antioxidant, and anti-inflammation
HUANG Qiuyue, YE Hui, SHI Zongming, JIA Xiaofen, LIN Miaomiao, CHU Yingming, YU Jing, ZHANG Xuezhi( )
)
- Department of Endocrinology, People's Hospital Affiliated to Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350004, China
-
Received:2021-12-12Accepted:2022-02-22Online:2022-12-15Published:2022-09-22 -
Contact:YE Hui,SHI Zongming,CHU Yingming,YU Jing,ZHANG Xuezhi -
About author:Prof. ZHANG Xuezhi, Department of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China. zhang.xuezhi@263.net,Telephone: +86-10-83572634
-
Supported by:Research on Mechanisms of Jinghua Weikang Capsule Interving HP Infection and Related Inflammation through Adhersin-ROS/ MAPKR-NFκB Pathway(81973615);Effect and Mechanism of Jinghua Weikang Capsule Inhibiting the Adhesion Effect of Helicobacter pylori(7172220)
Cite this article
HUANG Qiuyue, YE Hui, SHI Zongming, JIA Xiaofen, LIN Miaomiao, CHU Yingming, YU Jing, ZHANG Xuezhi. Efficacy of Qingre Huashi decoction (清热化湿方) on infection of Helicobacter pylori: inhibiting adhesion, antioxidant, and anti-inflammation[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 915-921.
share this article
| Primer name | Sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|
| 16s rRNA fwd | GGGTGAGTAACGCATAGGTCA |
| 16s rRNA rev | TTTACGCCCAGTGATTCCGA |
| babA fwd | TTAGACGGTGTGCCTGATAGC |
| babA rev | GCATGTGGCTAAAAAGCCTGT |
| sabA fwd | AATCGCAAACACTAAGACGGCTA |
| sabA rev | TTTGGTTTTGAGCGAAAGCGTA |
| napA fwd | TTGGAATGTGAAAGGCACCGATTTT |
| napA rev | GCCTTCTTTTTCAGCGGTGTTAGA |
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| Primer name | Sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|
| 16s rRNA fwd | GGGTGAGTAACGCATAGGTCA |
| 16s rRNA rev | TTTACGCCCAGTGATTCCGA |
| babA fwd | TTAGACGGTGTGCCTGATAGC |
| babA rev | GCATGTGGCTAAAAAGCCTGT |
| sabA fwd | AATCGCAAACACTAAGACGGCTA |
| sabA rev | TTTGGTTTTGAGCGAAAGCGTA |
| napA fwd | TTGGAATGTGAAAGGCACCGATTTT |
| napA rev | GCCTTCTTTTTCAGCGGTGTTAGA |
| No | RT (min) | Observed (m/z) | Neutral mass (Da) | Adducts | Formula | Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.17 | 352.1557 | 351.14706 | M+H | C38H42N2O6 | Tetrandrine |
| 2 | 4.19 | 320.0931 | 319.08446 | M+H | C19H13NO4 | Decarine |
| 3 | 3.71 | 338.1397 | 337.13141 | M+H | - | 13,13a-dideoxy-9,10-dimethoxy-2,3-methylenedioxyberberine |
| 4 | 4.47 | 336.1242 | 335.11576 | M+H | C20H18NO4+ | Epiberberine |
| 5 | 2.22 | 342.1707 | 341.16271 | M+H | C20H23NO4 | Dthaliporphine |
| 6 | 3.04 | 322.1077 | 321.10011 | M+H | C19H16ClNO4 | Berberrubine |
| 7 | 1.98 | 314.1754 | 313.16779 | M+H | C19H23NO3 | Armepavine |
| 8 | 10.98 | 265.2527 | 264.24532 | M+H | C18H34O | CIS, CIS-9,12-OCTADECADIENOL |
| 9 | 0.6 | 455.1154 | 432.12678 | M+Na | C18H24O12 | Oxalic acid |
| 10 | 2.76 | 392.2427 | 391.23587 | M+H | - | HokbusiMe B |
| 11 | 3.56 | 779.2367 | 756.24768 | M+Na | C34H44O19 | Forsythoside B |
| 12 | 10.98 | 247.242 | 246.23475 | M+H | - | (3,3-dimethyldecane) -benzene |
| 13 | 13.61 | 693.5075 | 670.51724 | M+Na | - | 3-O-Decanoyl-16-O-acetylisoiridogermanal |
| 14 | 3.1 | 324.122 | 323.11576 | M+H | C19H17NO4 | (-)-STYLOPINE |
| 15 | 3.9 | 336.1234 | 335.11576 | M+H | C17H17N | Berbine |
| 16 | 8.09 | 279.232 | 278.22458 | M+H | C18H30O2 | Gamma linolenic Acid |
| 17 | 3.14 | 390.228 | 389.22022 | M+H | C22H13O5N | OxytubersteMonine |
| 18 | 3.21 | 352.1187 | 351.11067 | M+H | C20H17NO5 | Oxyberberine |
| 19 | 2.1 | 477.1413 | 476.13186 | M+H | - | 5-hydroxy-6,4'-dimethoxyflavone-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| 20 | 1.93 | 506.2031 | 505.1948 | M+H | C23H25O10N2 | Cimicifugamide |
Table 2 Mass condition of the 20 compounds
| No | RT (min) | Observed (m/z) | Neutral mass (Da) | Adducts | Formula | Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.17 | 352.1557 | 351.14706 | M+H | C38H42N2O6 | Tetrandrine |
| 2 | 4.19 | 320.0931 | 319.08446 | M+H | C19H13NO4 | Decarine |
| 3 | 3.71 | 338.1397 | 337.13141 | M+H | - | 13,13a-dideoxy-9,10-dimethoxy-2,3-methylenedioxyberberine |
| 4 | 4.47 | 336.1242 | 335.11576 | M+H | C20H18NO4+ | Epiberberine |
| 5 | 2.22 | 342.1707 | 341.16271 | M+H | C20H23NO4 | Dthaliporphine |
| 6 | 3.04 | 322.1077 | 321.10011 | M+H | C19H16ClNO4 | Berberrubine |
| 7 | 1.98 | 314.1754 | 313.16779 | M+H | C19H23NO3 | Armepavine |
| 8 | 10.98 | 265.2527 | 264.24532 | M+H | C18H34O | CIS, CIS-9,12-OCTADECADIENOL |
| 9 | 0.6 | 455.1154 | 432.12678 | M+Na | C18H24O12 | Oxalic acid |
| 10 | 2.76 | 392.2427 | 391.23587 | M+H | - | HokbusiMe B |
| 11 | 3.56 | 779.2367 | 756.24768 | M+Na | C34H44O19 | Forsythoside B |
| 12 | 10.98 | 247.242 | 246.23475 | M+H | - | (3,3-dimethyldecane) -benzene |
| 13 | 13.61 | 693.5075 | 670.51724 | M+Na | - | 3-O-Decanoyl-16-O-acetylisoiridogermanal |
| 14 | 3.1 | 324.122 | 323.11576 | M+H | C19H17NO4 | (-)-STYLOPINE |
| 15 | 3.9 | 336.1234 | 335.11576 | M+H | C17H17N | Berbine |
| 16 | 8.09 | 279.232 | 278.22458 | M+H | C18H30O2 | Gamma linolenic Acid |
| 17 | 3.14 | 390.228 | 389.22022 | M+H | C22H13O5N | OxytubersteMonine |
| 18 | 3.21 | 352.1187 | 351.11067 | M+H | C20H17NO5 | Oxyberberine |
| 19 | 2.1 | 477.1413 | 476.13186 | M+H | - | 5-hydroxy-6,4'-dimethoxyflavone-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| 20 | 1.93 | 506.2031 | 505.1948 | M+H | C23H25O10N2 | Cimicifugamide |
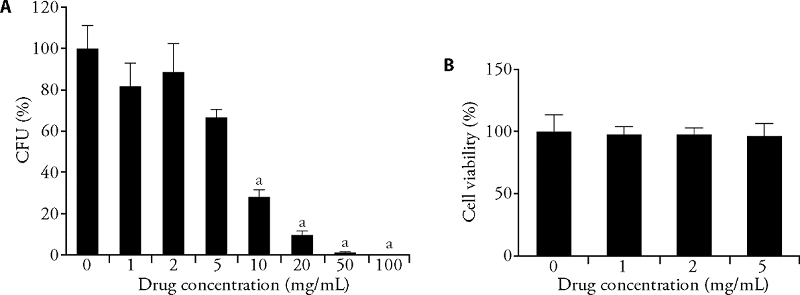
Figure 1 Drug concentration was determined as 1, 2, and 5 mg/mL A: toxicology test. H.pylori was treated by QHD with different concentrations in Brucella broth containing 10% FBS (n = 3). QHD: Qingre Huashi decoction; FBS: foetal bovine serum; CFU: colony-forming units; CCK-8: cell counting kit-8. aP < 0.05, compared with 0 mg/mL QHD. B: CCK-8 assay. GES-1 cells were treated by QHD with different concentrations in culture medium (n = 5).
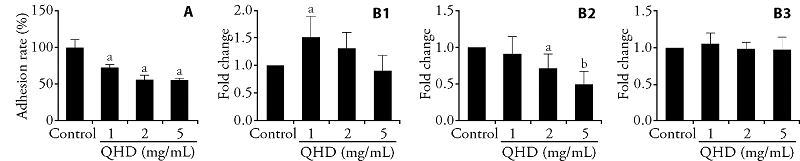
Figure 2 QHD prevents H. pylori adhesion to human gastric epithelial cells A: Urease assay. Control group: GES-1 cells were infected with H. pylori for 2 h without drug intervention. QHD: Qingre Huashi decoction. aP < 0.001, compared with control group (n = 6). B1-B3: qPCR detection of bacterial genes. B1: blood group antigen binding adhesin. B2: sialic acid binding adhesin. B3: neutrophil activating protein. Control group: fresh cultured H. pylori without drug intervention. qPCR: quantitative polymerase chain reaction. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001, compared with control group (n = 4).
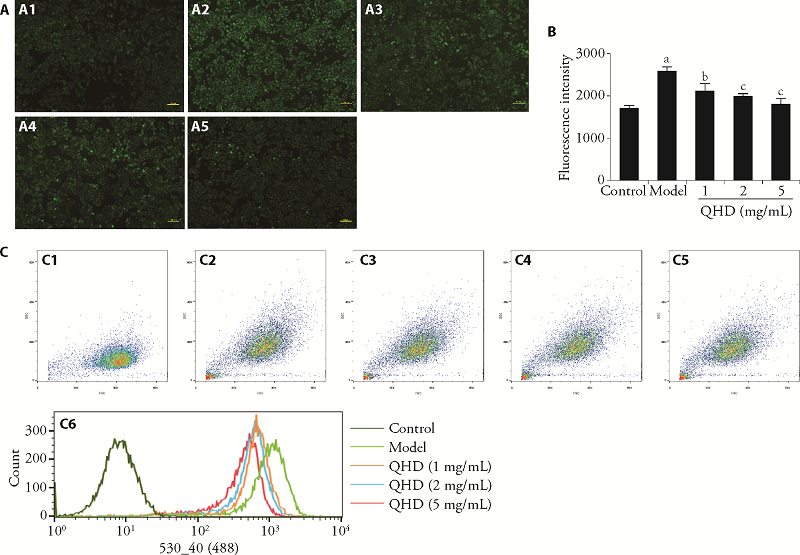
Figure 3 QHD exhibits antioxidant activity in H. pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells A: fluorescence micrographs of intracellular ROS (100 × magnification). scale bar: 100 μm. B: fluorescence intensity in uninfected and H. pylori-infected GES-1 cells. C: Fluorescence micrographs of GES-1 cells isolated by flow cytometry. A1, C1: Control group, GES-1 cells; A2, C2: model group, GES-1 cells infected with H. pylori; A3-A5, C3-C5: GES-1 cells infected with H. pylori were pretreated with 1, 2, and 5 mg/mL QHD; C6: merged picture of cell fluorescence intensity of each group. ROS: reactive oxygen species; QHD: Qingre Huashi decoction. aP < 0.001, compared with control group; bP < 0.01 cP < 0.001, compared with model group (n = 3).
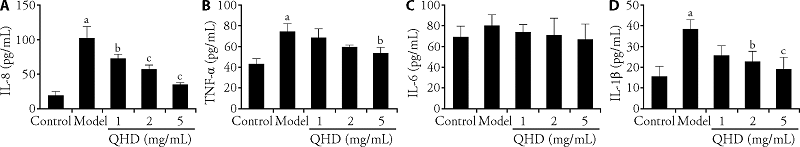
Figure 4 QHD exhibits anti-inflammatory activity in H. pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells A: the level of IL-8; B: the level of TNF-α; C: the level of IL-6; D: the level of IL-1β. Control group: GES-1 cells; model group: GES-1 cells infected with H. pylori. IL: interleukin; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; QHD: Qingre Huashi decoction. aP < 0.01, compared with control group; bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01 compared with model group (n = 3).
| [1] |
Cover TL, Blaser MJ. Helicobacter pylori in health and disease. Gastroenterology 2009; 136: 1863-73.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Sugano K, Tack J, Kuipers EJ. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gut 2015; 64: 1353-67. |
| [3] |
Choi IJ, Kook MC, Kim YI. Helicobacter pylori therapy for the prevention of metachronous gastric cancer. N Engl J Med 2018; 378: 1085-95.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Hu Y, Zhu Y, Lu NH. Primary antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori in China. Dig Dis Sci 2017; 62: 1146-54.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Savoldi A, Carrara E, Graham DY, Conti M, Tacconelli E. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: a systematic review and Meta-analysis in World Health Organization regions. Gastroenterology 2018; 155: 1372-82.e17.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Takeuchi H, Trang VT, Morimoto N, Nishida Y, Matsumura Y, Sugiura T. Natural products and food components with anti-Helicobacter pylori activities. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20: 8971-8. |
| [7] |
Goderska K, Agudo Pena S, Alarcon T. Helicobacter pylori treatment: antibiotics or probiotics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2018; 102: 1-7.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Hu FL, Zhang SS. National consensus on integrated treatment of Helicobacter pylori related "disease-syndrome". Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xiao Hua Za Zhi 2018; 26: 715-23. |
| [9] |
Abadi ATB. Strategies used by helicobacter pylori to establish persistent infection. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23: 2870-82.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Keilberg D, Ottemann KM. How Helicobacter pylori senses, targets and interacts with the gastric epithelium. Environ Microbiol 2016; 18: 791-806.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Oleastro M, Ménard A. The role of Helicobacter pylori outer membrane proteins in adherence and pathogenesis. Biology (Basel) 2013; 2: 1110-34. |
| [12] |
Ofek I, Hasty DL, Sharon N. Anti-adhesion therapy of bacterial diseases: prospects and problems. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2003; 38: 181-91.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Ohno T, Vallström A, Rugge M, et al. Effects of blood group antigen-binding adhesin expression during Helicobacter pylori infection of Mongolian gerbils. J Infect Dis 2011; 203: 726-35.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Ishijima N, Suzuki M, Ashida H, et al. BabA-mediated adherence is a potentiator of the Helicobacter pylori type Ⅳ secretion system activity. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 25256-64.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Unemo M, Aspholm-Hurtig M, Ilver D, et al. The sialic acid binding SabA adhesin of Helicobacter pylori is essential for nonopsonic activation of human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 15390-7.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Butcher LD, den Hartog G, Ernst PB, Crowe SE. Oxidative stress resulting from Helicobacter pylori infection contributes to gastric carcinogenesis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017; 3: 316-22.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Sun YM, Huang J, Chen Q, et al. Exploring the inflammatory microenvironment of Hp-related CAG from the theory of dampness-heat of spleen and stomach. Xian Dai Zhong Yi Lin Chuang 2021; 13: 64-6. |
| [18] | Huang QY, Ye H, Shi ZM, Yang SS, Jia XF, Zhang XZ. Understanding the inflammatory process of Helicobacter pylori adhesion based on damp-heat theory. Shi Jie Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2021; 16: 185-8. |
| [19] | Yang SS, Ye H, Huang QY, Deng X, Xiao HX, Zhang XZ. A randomized controlled clinical study of Qingre Huashi decoction combined with triple therapy in treating Helicobacter pylori infection of damp-heat type of spleen and stomach. Shi Jie Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2020; 15: 1734-8. |
| [20] | Yu J, Ye H, Li N, Li J, Chen Y, Zhang XZ. Anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory effects of Qingre Huashi formula on Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Zhong Cheng Yao 2017; 39: 7-14. |
| [21] |
Vale FF, Oleastro M. Overview of the phytomedicine approaches against Helicobacter pylori. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20: 5594-609.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Salehi B, Sharopov F, Martorell M, et al. Phytochemicals in Helicobacter pylori infections: what are we doing now? Int J Mol Sci 2018; 19: 2361.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Chen Y, Liu QY, Ye H, et al. Multi-center study of Chinese medicine syndrome types and syndrome factors evolvement law of Helicobacter pylori related gastropathy. Xian Dai Zhong Yi Lin Chuang 2015; 22: 12-6. |
| [24] |
Ye H, Shi ZM, Chen Y, Yu J, Zhang XZ. Innovative perspectives of integrated chinese medicine on H. pylori. Chin J Integr Med 2018; 24: 873-80.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Alarcón T, Domingo D, Prieto N, López-Brea M. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activity of ranitidine bismuth citrate in Helico-bacter pylori clinical isolates. Rev Esp Quimioter. 1999; 12: 64-8. |
| [26] |
Ilver D, Arnqvist A, Ogren J, et al. Helicobacter pylori adhesin binding fucosylated histo-blood group antigens revealed by retagging. Science 1998; 279: 373-7.
PMID |
| [27] |
Magalhães A, Marcos-Pinto R, Nairn AV, et al. Helicobacter pylori chronic infection and mucosal inflammation switches the human gastric glycosylation pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015; 1852: 1928-39.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Fu HW. Helicobacter pylori neutrophil-activating protein: from molecular pathogenesis to clinical applications. World journal of gastroenterology 2014; 20: 5294-301.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Messing J, Niehues M, Shevtsova A, Borén T, Hensel A. Antiadhesive properties of arabinogalactan protein from ribes nigrum seeds against bacterial adhesion of Helicobacter pylori. Molecules 2014; 19: 3696-717.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
de Klerk N, Maudsdotter L, Gebreegziabher H, et al. Lactobacilli reduce Helicobacter pylori attachment to host gastric epithelial cells by inhibiting adhesion gene expression. Infection and immunity 2016; 84: 1526-35.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Bagheri V, Memar B, Momtazi AA, Sahebkar A, Gholamin M, Abbaszadegan MR. Cytokine networks and their association with Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric carcinoma. J Cell Physiol 2018; 233: 2791-803.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Handa O, Naito Y, Yoshikawa T. Helicobacter pylori: a ROS-inducing bacterial species in the stomach. Inflamm Res 2010; 59: 997-1003.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Kuete V, Efferth T. Cameroonian medicinal plants: pharmacology and derived natural products. Front Pharmacol 2010; 1: 123.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Lee JH, Shim JS, Lee JS, Kim MK, Chung MS, Kim KH. Pectin-like acidic polysaccharide from Panax ginseng with selective antiadhesive activity against pathogenic bacteria. Carbohydr Res 2006; 341: 1154-63.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Thöle C, Brandt S, Ahmed N, Hensel A. Acetylated rhamnogalacturonans from immature fruits of abelmoschus esculentus inhibit the adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to human gastric cells by interaction with outer membrane proteins. Molecules 2015; 20: 16770-87.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Wittschier N, Faller G, Hensel A. Aqueous extracts and polysaccharides from liquorice roots (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.) inhibit adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to human gastric mucosa. J Ethnopharmacol 2009; 125: 218-23.
DOI PMID |
| [37] | Li Y, Li X, Tan Z. An overview of Traditional Chinese Medicine therapy for Helicobacter pylori-related gastritis. Helicobacter 2021: e12799. |
| [38] |
Chang CH, Wu JB, Yang JS, et al. The suppressive effects of geniposide and genipin on Helicobacter pylori infections in vitro and in vivo. J Food Sci 2017; 82: 3021-8.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Luo H, Wu H, Yu X, et al. A review of the phytochemistry and pharmacological activities of Magnoliae officinalis cortex. J Ethnopharmacol 2019; 236: 412-42.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Tan L, Li C, Chen H, et al. Epiberberine, a natural protoberberine alkaloid, inhibits urease of Helicobacter pylori and jack bean: susceptibility and mechanism. Eur J Pharm Sci 2017; 110: 77-86.
DOI PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

