Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1144-1151.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.05.019
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of Yang-deficiency constitution on cognitive impairment in cerebral small vessel disease and its neuroimaging mechanism
LIU Xin1, YANG Shuning1( ), XU Yun2(
), XU Yun2( )
)
- 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
2 Department of Neurology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Clinical College of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210008, China
-
Received:2024-07-12Accepted:2024-12-30Online:2025-10-15Published:2025-09-15 -
Contact:VP. YANG Shuning, Department of Internal Medicine, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China. 373545058@qq.com.;
Prof. XU Yun, Department of Neurology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Clinical College of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210008, China. xuyun20042001@aliyun.com, Telephone: +86-25-18305153371 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Role and Mechanism of Microglial Environmental Sensing Element P2RY13 in Ischemic Brain Injury(81920108017);Key Research and Development Program of Jiangsu Province of China: Research on the Early Diagnosis, Treatment and Evaluation System and Early Warning Model of Ischemic Cerebrovascular Disease(BE2020620)
Cite this article
LIU Xin, YANG Shuning, XU Yun. Effect of Yang-deficiency constitution on cognitive impairment in cerebral small vessel disease and its neuroimaging mechanism[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1144-1151.
share this article
| Characteristic | CSVD-NC group (n = 73) | CSVD-CI group (n = 168) | Test value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General clinical information | ||||
| Sex [n (%)] | 5.479a | 0.019 | ||
| Male | 45 (61.64) | 76 (45.24) | ||
| Female | 28 (38.36) | 92 (54.76) | ||
| Age (years, | 65.11±10.19 | 68.36±7.87 | 2.688b | 0.008 |
| BMI (kg/m2, | 24.67±3.23 | 24.21±3.29 | -1.004b | 0.316 |
| Years of education [years, M (Q1, Q3)] | 12 (12, 16) | 9 (6, 12) | -6.460c | <0.001 |
| Smoking [n (%)] | 19 (26.03) | 40 (23.81) | 0.135a | 0.713 |
| Alcohol consumption [n (%)] | 18 (24.66) | 33 (19.64) | 0.767a | 0.381 |
| Family history [n (%)] | 23 (31.51) | 48 (28.57) | 0.211a | 0.646 |
| Assessment of CSVD | ||||
| Course of CSVD [years, M (Q1, Q3)] | 2 (1, 5) | 3 (1, 5) | -1.612c | 0.107 |
| Presence of dementia [n (%)] | 0 (0) | 4 (2.38) | 1.767d | 0.318 |
| WMH [n (%)] | 46 (63.01) | 135 (80.36) | 8.186a | 0.004 |
| LI [n (%)] | 41 (56.16) | 118 (70.24) | 4.490a | 0.034 |
| CMBs [n (%)] | 28 (38.36) | 93 (55.36) | 5.883a | 0.015 |
| Brain atrophy [n (%)] | 20 (27.40) | 58 (34.52) | 1.181a | 0.277 |
| Blood indexes | ||||
| TC (mmol/L) | 3.92±1.09 | 4.15±1.08 | -1.100b | 0.273 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.36±0.56 | 1.57±0.78 | 1.609b | 0.110 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.40±0.90 | 2.35±0.86 | 0.295b | 0.768 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.12±0.34 | 1.21±0.38 | -1.176b | 0.242 |
| Apo A1 (g/L) | 1.06±0.25 | 1.11±0.25 | -1.013b | 0.313 |
| Apo B (g/L) | 0.76±0.25 | 0.75±0.23 | 0.281b | 0.779 |
| Hcy (μmol/L) | 14.07±4.10 | 13.12±4.29 | 1.028b | 0.307 |
| Medical history | ||||
| Hypertension [n (%)] | 42 (57.53) | 124 (73.81) | 6.288a | 0.012 |
| Diabetes [n (%)] | 20 (27.40) | 47 (27.98) | 0.008a | 0.927 |
| Coronary heart disease [n (%)] | 7 (9.59) | 10 (5.95) | 1.026a | 0.311 |
| Hyperlipidemia [n (%)] | 22 (30.14) | 38 (22.62) | 1.538a | 0.215 |
| Obesity [n (%)] | 12 (16.44) | 23 (13.69) | 0.310a | 0.578 |
| Carotid artery plaque [n (%)] | 10 (13.70) | 19 (11.31) | 0.274a | 0.600 |
| Insomnia [n (%)] | 26 (35.62) | 54 (32.14) | 0.277a | 0.599 |
| Anxiety-depression [n (%)] | 22 (30.14) | 70 (41.67) | 2.866a | 0.090 |
| OSAS [n (%)] | 9 (12.33) | 15 (8.93) | 0.656a | 0.418 |
| Hearing loss [n (%)] | 10 (13.70) | 27 (16.07) | 0.220a | 0.639 |
| Abnormal smell [n (%)] | 7 (9.59) | 14 (8.33) | 0.101a | 0.751 |
| Long-term constipation [n (%)] | 16 (21.92) | 42 (25.00) | 0.265a | 0.607 |
| COPD [n (%)] | 4 (5.48) | 6 (3.57) | 0.466d | 0.496 |
| Hypothyroidism [n (%)] | 12 (16.44) | 14 (8.33) | 3.473a | 0.062 |
| Life history | ||||
| Lack of nutrition [n (%)] | 1 (1.37) | 6 (3.57) | 0.875d | 0.678 |
| High-fat diet [n (%)] | 23 (31.51) | 46 (27.38) | 0.424a | 0.515 |
| Presence of reading habits [n (%)] | 37 (50.64) | 38 (22.62) | 18.70a | <0.001 |
| Lack of exercise [n (%)] | 46 (63.01) | 117 (69.64) | 1.022a | 0.312 |
| Lack of social interaction [n (%)] | 6 (8.22) | 10 (5.95) | 0.422d | 0.516 |
| Do household chores [n (%)] | 29 (39.73) | 49 (29.17) | 2.592a | 0.107 |
| Daily life dependence [n (%)] | 6 (8.22) | 16 (9.52) | 0.104a | 0.747 |
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of the participants
| Characteristic | CSVD-NC group (n = 73) | CSVD-CI group (n = 168) | Test value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General clinical information | ||||
| Sex [n (%)] | 5.479a | 0.019 | ||
| Male | 45 (61.64) | 76 (45.24) | ||
| Female | 28 (38.36) | 92 (54.76) | ||
| Age (years, | 65.11±10.19 | 68.36±7.87 | 2.688b | 0.008 |
| BMI (kg/m2, | 24.67±3.23 | 24.21±3.29 | -1.004b | 0.316 |
| Years of education [years, M (Q1, Q3)] | 12 (12, 16) | 9 (6, 12) | -6.460c | <0.001 |
| Smoking [n (%)] | 19 (26.03) | 40 (23.81) | 0.135a | 0.713 |
| Alcohol consumption [n (%)] | 18 (24.66) | 33 (19.64) | 0.767a | 0.381 |
| Family history [n (%)] | 23 (31.51) | 48 (28.57) | 0.211a | 0.646 |
| Assessment of CSVD | ||||
| Course of CSVD [years, M (Q1, Q3)] | 2 (1, 5) | 3 (1, 5) | -1.612c | 0.107 |
| Presence of dementia [n (%)] | 0 (0) | 4 (2.38) | 1.767d | 0.318 |
| WMH [n (%)] | 46 (63.01) | 135 (80.36) | 8.186a | 0.004 |
| LI [n (%)] | 41 (56.16) | 118 (70.24) | 4.490a | 0.034 |
| CMBs [n (%)] | 28 (38.36) | 93 (55.36) | 5.883a | 0.015 |
| Brain atrophy [n (%)] | 20 (27.40) | 58 (34.52) | 1.181a | 0.277 |
| Blood indexes | ||||
| TC (mmol/L) | 3.92±1.09 | 4.15±1.08 | -1.100b | 0.273 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.36±0.56 | 1.57±0.78 | 1.609b | 0.110 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.40±0.90 | 2.35±0.86 | 0.295b | 0.768 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.12±0.34 | 1.21±0.38 | -1.176b | 0.242 |
| Apo A1 (g/L) | 1.06±0.25 | 1.11±0.25 | -1.013b | 0.313 |
| Apo B (g/L) | 0.76±0.25 | 0.75±0.23 | 0.281b | 0.779 |
| Hcy (μmol/L) | 14.07±4.10 | 13.12±4.29 | 1.028b | 0.307 |
| Medical history | ||||
| Hypertension [n (%)] | 42 (57.53) | 124 (73.81) | 6.288a | 0.012 |
| Diabetes [n (%)] | 20 (27.40) | 47 (27.98) | 0.008a | 0.927 |
| Coronary heart disease [n (%)] | 7 (9.59) | 10 (5.95) | 1.026a | 0.311 |
| Hyperlipidemia [n (%)] | 22 (30.14) | 38 (22.62) | 1.538a | 0.215 |
| Obesity [n (%)] | 12 (16.44) | 23 (13.69) | 0.310a | 0.578 |
| Carotid artery plaque [n (%)] | 10 (13.70) | 19 (11.31) | 0.274a | 0.600 |
| Insomnia [n (%)] | 26 (35.62) | 54 (32.14) | 0.277a | 0.599 |
| Anxiety-depression [n (%)] | 22 (30.14) | 70 (41.67) | 2.866a | 0.090 |
| OSAS [n (%)] | 9 (12.33) | 15 (8.93) | 0.656a | 0.418 |
| Hearing loss [n (%)] | 10 (13.70) | 27 (16.07) | 0.220a | 0.639 |
| Abnormal smell [n (%)] | 7 (9.59) | 14 (8.33) | 0.101a | 0.751 |
| Long-term constipation [n (%)] | 16 (21.92) | 42 (25.00) | 0.265a | 0.607 |
| COPD [n (%)] | 4 (5.48) | 6 (3.57) | 0.466d | 0.496 |
| Hypothyroidism [n (%)] | 12 (16.44) | 14 (8.33) | 3.473a | 0.062 |
| Life history | ||||
| Lack of nutrition [n (%)] | 1 (1.37) | 6 (3.57) | 0.875d | 0.678 |
| High-fat diet [n (%)] | 23 (31.51) | 46 (27.38) | 0.424a | 0.515 |
| Presence of reading habits [n (%)] | 37 (50.64) | 38 (22.62) | 18.70a | <0.001 |
| Lack of exercise [n (%)] | 46 (63.01) | 117 (69.64) | 1.022a | 0.312 |
| Lack of social interaction [n (%)] | 6 (8.22) | 10 (5.95) | 0.422d | 0.516 |
| Do household chores [n (%)] | 29 (39.73) | 49 (29.17) | 2.592a | 0.107 |
| Daily life dependence [n (%)] | 6 (8.22) | 16 (9.52) | 0.104a | 0.747 |
| TCM constitutional types | Cases (n = 241) | CSVD-NC group (n = 73) | CSVD-CI group (n = 168) | Test value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 24 (9.96) | 16 (21.92) | 8 (4.76) | 16.703 | < 0.001 |
| YADC | 49 (20.33) | 6 (8.22) | 43 (25.60) | 9.485 | 0.002 |
| YIDC | 22 (9.13) | 10 (13.70) | 12 (7.14) | 2.637 | 0.104 |
| QDC | 28 (11.62) | 10 (13.70) | 18 (10.71) | 0.441 | 0.506 |
| PDC | 26 (10.79) | 5 (6.85) | 21 (12.50) | 1.688 | 0.194 |
| DHC | 13 (5.39) | 5 (6.85) | 8 (4.76) | 0.434 | 0.510 |
| BSC | 37 (15.35) | 8 (10.96) | 29 (17.26) | 1.556 | 0.212 |
| ISC | 17 (7.05) | 6 (8.22) | 11 (6.55) | 0.217 | 0.641 |
| QSC | 25 (10.37) | 7 (9.59) | 18 (10.71) | 0.069 | 0.792 |
Table 2 Distribution characteristics of TCM constitution [n (%)]
| TCM constitutional types | Cases (n = 241) | CSVD-NC group (n = 73) | CSVD-CI group (n = 168) | Test value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 24 (9.96) | 16 (21.92) | 8 (4.76) | 16.703 | < 0.001 |
| YADC | 49 (20.33) | 6 (8.22) | 43 (25.60) | 9.485 | 0.002 |
| YIDC | 22 (9.13) | 10 (13.70) | 12 (7.14) | 2.637 | 0.104 |
| QDC | 28 (11.62) | 10 (13.70) | 18 (10.71) | 0.441 | 0.506 |
| PDC | 26 (10.79) | 5 (6.85) | 21 (12.50) | 1.688 | 0.194 |
| DHC | 13 (5.39) | 5 (6.85) | 8 (4.76) | 0.434 | 0.510 |
| BSC | 37 (15.35) | 8 (10.96) | 29 (17.26) | 1.556 | 0.212 |
| ISC | 17 (7.05) | 6 (8.22) | 11 (6.55) | 0.217 | 0.641 |
| QSC | 25 (10.37) | 7 (9.59) | 18 (10.71) | 0.069 | 0.792 |
| Variable | β value | SE | Wald value | P value | OR value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.05 | 0.019 | 6.944 | 0.008 | 1.051 | 1.013, 1.091 |
| Hypertension | 0.906 | 0.357 | 6.428 | 0.011 | 2.475 | 1.228, 4.988 |
| YADC | 1.211 | 0.522 | 5.381 | 0.020 | 3.356 | 1.207, 9.337 |
| BC | -1.708 | 0.573 | 8.896 | 0.003 | 0.181 | 0.059, 0.557 |
| Education | -0.294 | 0.054 | 29.984 | <0.001 | 0.746 | 0.671, 0.828 |
Table 3 Results of multiple logistic regression analysis of factors influencing CSVD-CI
| Variable | β value | SE | Wald value | P value | OR value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.05 | 0.019 | 6.944 | 0.008 | 1.051 | 1.013, 1.091 |
| Hypertension | 0.906 | 0.357 | 6.428 | 0.011 | 2.475 | 1.228, 4.988 |
| YADC | 1.211 | 0.522 | 5.381 | 0.020 | 3.356 | 1.207, 9.337 |
| BC | -1.708 | 0.573 | 8.896 | 0.003 | 0.181 | 0.059, 0.557 |
| Education | -0.294 | 0.054 | 29.984 | <0.001 | 0.746 | 0.671, 0.828 |
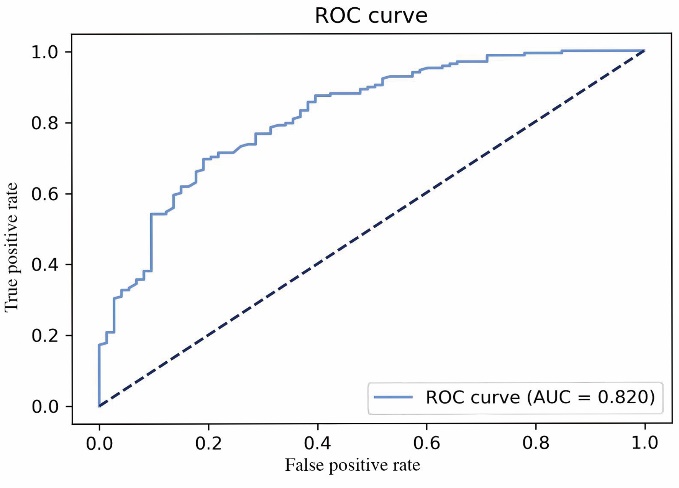
Figure 1 AUC for prediction models of CSVD-CI CSVD-CI: cerebral small vessel disease with cognitive impairment; ROC curve: receiver operator characteristic curve; AUC: area under the curve. The AUC was calculated to evaluate the efficiency of the risk model. The AUC ranges from 0.5 to 1.0, whereby 0.9-1.0 indicates an excellent effect, 0.7-0.9 a good effect, and 0.5-0.7 a mediocre effect. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
| Item | Non-YADC group (n = 192) | YADC group (n = 49) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left whole hippocampus | 3099±327 | 2935±389 | 0.003 |
| Left hippocampal tail | 508±70 | 490±80 | 0.088 |
| Left subiculum | 399±49 | 370±62 | 0.001 |
| Left CA1 | 567±71 | 541±66 | 0.018 |
| Left hippocampal fissure | 173±29 | 166±27 | 0.158 |
| Left presubiculum | 296±42 | 275±43 | 0.002 |
| Left parasubiculum | 60±13 | 55±13 | 0.025 |
| Left molecular layer | 501±56 | 473±63 | 0.003 |
| Left GC-ML-DG | 252±30 | 240±35 | 0.015 |
| Left CA3 | 168±25 | 165±30 | 0.474 |
| Left CA4 | 217±25 | 207±28 | 0.014 |
| Left fimbria | 76±22 | 68±22 | 0.022 |
| Left HATA | 53±9 | 51±9 | 0.294 |
| Right whole hippocampus | 3214±346 | 3036±391 | 0.002 |
| Right hippocampal tail | 542±75 | 511±81 | 0.013 |
| Right subiculum | 404±49 | 378±57 | 0.001 |
| Right CA1 | 610±80 | 577±80 | 0.009 |
| Right hippocampal fissure | 186±30 | 184±29 | 0.731 |
| Right presubiculum | 282±38 | 263±35 | 0.001 |
| Right parasubiculum | 56±12 | 52±10 | 0.055 |
| Right molecular layer | 524±60 | 495±67 | 0.003 |
| Right GC-ML-DG | 263±30 | 251±38 | 0.046 |
| Right CA3 | 181±26 | 180±30 | 0.784 |
| Right CA4 | 224±26 | 215±32 | 0.061 |
| Right fimbria | 71±19 | 61±18 | 0.001 |
| Right HATA | 55±9 | 54±9 | 0.489 |
Table 4 Comparison of hippocampal volume between YADC and non-YADC patients (volume/mm3)
| Item | Non-YADC group (n = 192) | YADC group (n = 49) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left whole hippocampus | 3099±327 | 2935±389 | 0.003 |
| Left hippocampal tail | 508±70 | 490±80 | 0.088 |
| Left subiculum | 399±49 | 370±62 | 0.001 |
| Left CA1 | 567±71 | 541±66 | 0.018 |
| Left hippocampal fissure | 173±29 | 166±27 | 0.158 |
| Left presubiculum | 296±42 | 275±43 | 0.002 |
| Left parasubiculum | 60±13 | 55±13 | 0.025 |
| Left molecular layer | 501±56 | 473±63 | 0.003 |
| Left GC-ML-DG | 252±30 | 240±35 | 0.015 |
| Left CA3 | 168±25 | 165±30 | 0.474 |
| Left CA4 | 217±25 | 207±28 | 0.014 |
| Left fimbria | 76±22 | 68±22 | 0.022 |
| Left HATA | 53±9 | 51±9 | 0.294 |
| Right whole hippocampus | 3214±346 | 3036±391 | 0.002 |
| Right hippocampal tail | 542±75 | 511±81 | 0.013 |
| Right subiculum | 404±49 | 378±57 | 0.001 |
| Right CA1 | 610±80 | 577±80 | 0.009 |
| Right hippocampal fissure | 186±30 | 184±29 | 0.731 |
| Right presubiculum | 282±38 | 263±35 | 0.001 |
| Right parasubiculum | 56±12 | 52±10 | 0.055 |
| Right molecular layer | 524±60 | 495±67 | 0.003 |
| Right GC-ML-DG | 263±30 | 251±38 | 0.046 |
| Right CA3 | 181±26 | 180±30 | 0.784 |
| Right CA4 | 224±26 | 215±32 | 0.061 |
| Right fimbria | 71±19 | 61±18 | 0.001 |
| Right HATA | 55±9 | 54±9 | 0.489 |
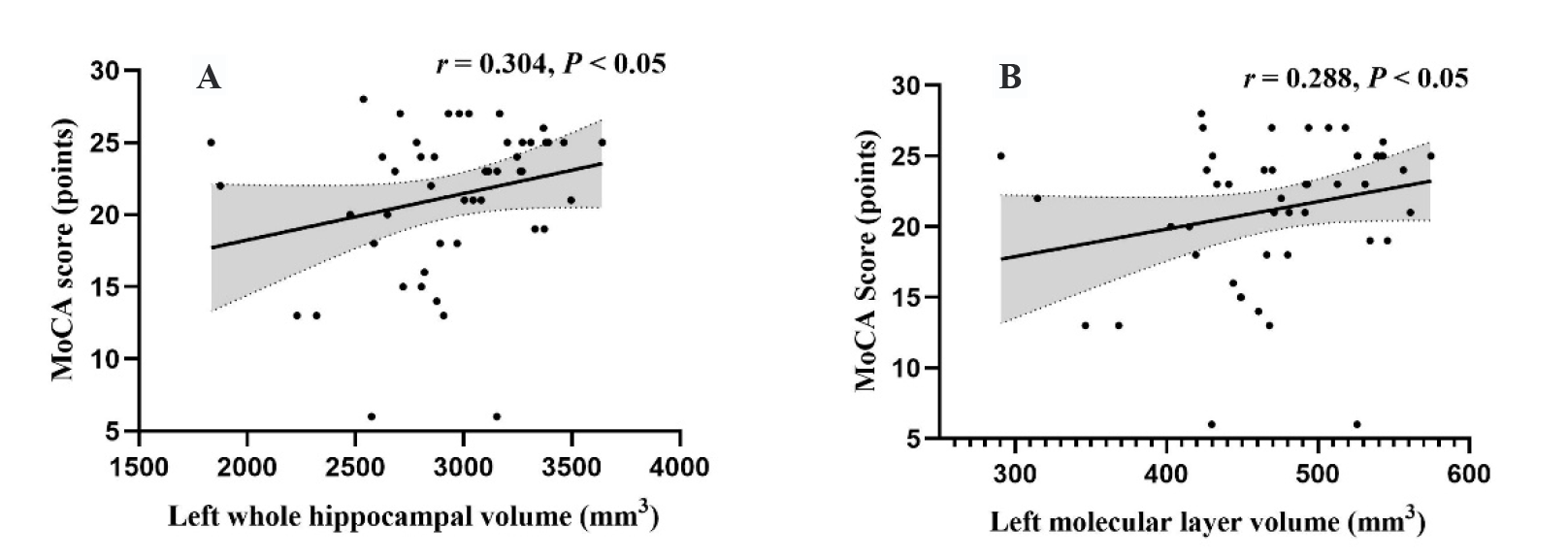
Figure 2 Correlation between hippocampal subregion volume and cognitive function in the YADC group A: correlation between the left whole hippocampal volume and MoCA score in the YADC group; B: correlation between tthe left molecular layer volume and MoCA score in the YADC group. YADC group: Yang-deficiency constitution group. MoCA: the Montreal Cognitive Assessment. Spearman correlation analysis was used for correlation analysis. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
| 1. |
Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 2013; 12: 822-38.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Kester MI, Goos JD, Teunissen CE, et al. Associations between cerebral small-vessel disease and Alzheimer disease pathology as measured by cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. JAMA Neurol 2014; 71: 855-62.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Gorelick PB, Scuteri A, Black SE, et al. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: a statement for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2011; 42: 2672-713.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Liang X, Wang Q, Jiang Z, et al. Clinical research linking Traditional Chinese Medicine constitution types with diseases: a literature review of 1639 observational studies. J Tradit Chin Med 2020; 40: 690-702.
DOI |
| 5. | Bai MH, Wong W, Hou SJ, et al. Development and evaluation of short form of constitution in Chinese medicine questionnaire: a national epidemiological survey data of 21 948 case. J Tradit Chin Med 2022; 42: 122-31. |
| 6. | Deng X, Teng J, Nong X, et al. Characteristics of TCM constitution and related biomarkers for mild cognitive impairment. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2021; 17: 1115-24. |
| 7. | Sun Z, Ping P, Li Y, et al. Relationships between Traditional Chinese Medicine constitution and age-related cognitive decline in Chinese centenarians. Front Aging Neurosci 2022; 14: 870442. |
| 8. |
Giuliano A, Donatelli G, Cosottini M, Tosetti M, Retico A, Fantacci ME. Hippocampal subfields at ultra high field MRI: an overview of segmentation and measurement methods. Hippocampus 2017; 27: 481-94.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Evans TE, Adams HHH, Licher S, et al. Subregional volumes of the hippocampus in relation to cognitive function and risk of dementia. Neuroimage 2018; 178: 129-35.
DOI PMID |
| 10. | Snytte J, Fenerci C, Rajagopal S, et al. Volume of the posterior hippocampus mediates age-related differences in spatial context memory and is correlated with increased activity in lateral frontal, parietal and occipital regions in healthy aging. Neuroimage 2022; 254: 119164. |
| 11. |
Vander-Flier WM, Van Buchem MA, Weverling-Rijnsburger AW, et al. Memory complaints in patients with normal cognition are associated with smaller hippocampal volumes. J Neurol 2004; 251: 671-75.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Professional Committee Consensus Writing Group, Chinese Research Hospital Association. Chinese consensus on diagnosis and therapy of cerebral small vessel disease 2021. Zhong Guo Cu Zhong Za Zhi 2021; 16: 716-26. |
| 13. |
Hobson J. The montreal cognitive assessment (MoCA). Occup Med (Lond) 2015; 65: 764-5.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | China Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Classification and determination of constitution in TCM (ZYYXH/T 157-2009). Shi Jie Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2009; 4: 303-4. |
| 15. |
Iglesias JE, Augustinack JC, Nguyen K, et al. A computational atlas of the hippocampal formation using ex vivo, ultra-high resolution MRI: Application to adaptive segmentation of in vivo MRI. Neuroimage 2015; 115: 117-37.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Shu ZY, Mao DW, Xu YY, Shao Y, Pang PP, Gong XY. Prediction of the progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease using a radiomics-integrated model. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 2021; 14: 17562864211029551. |
| 17. | Wong FCC, Yatawara C, Low A, et al. Cerebral small vessel disease influences hippocampal subfield atrophy in mild cognitive impairment. Transl Stroke Res 2021; 12: 284-92. |
| 18. |
Zanon Zotin MC, Sveikata L, Viswanathan A, Yilmaz P. Cerebral small vessel disease and vascular cognitive impairment: from diagnosis to management. Curr Opin Neurol 2021; 34: 246-57.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | Pei H, Ma L, Cao Y, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine for Alzheimer's disease and other cognitive impairment: a review. Am J Chin Med 2020; 48: 487-511. |
| 20. | Wang J, Li Y, Ni C, Zhang HM, Li L, Wang Q. Cognition research and constitutional classification in Chinese medicine. Am J Chin Med 2011; 39: 651-60. |
| 21. |
Bu X, Zhang Y, Bazzano LA, et al. Effects of early blood pressure reduction on cognitive function in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke 2016; 11: 1009-19.
PMID |
| 22. | Lövdén M, Fratiglioni L, Glymour MM, Lindenberger U. Education and cognitive functioning across the life span. Psychol Sci Public Interest 2020; 21: 6-41. |
| 23. |
Yamamoto Y, Hase Y, Ihara M, et al. Neuronal densities and vascular pathology in the hippocampal formation in CADASIL. Neurobiol Aging 2021; 97: 33-40.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Bartsch T, Wulff P. The hippocampus in aging and disease: from plasticity to vulnerability. Neuroscience 2015; 309: 1-16.
DOI PMID |
| 25. | Li L, Yao H, Wang J, et al. The Role of Chinese medicine in health maintenance and disease prevention: application of constitution theory. Am J Chin Med 2019, 47: 495-506. |
| 26. | Li YS, Li Y. Progress in the study of Yang-deficiency constitution in terms of Traditional Chinese Medicine: a narrative review. J Tradit Chin Med 2023; 43: 409-16. |
| [1] | LONG Xi, WU Zixuan, YU Yunfeng, LIN Jie, PENG Qinghua. Identification of characteristic genes of Yin and Yang deficiency constitutions: an integrated analysis based on bioinformatics and machine learning [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 909-921. |
| [2] | LI Tianxing, ZHU Linghui, WANG Xueke, TANG Jun, YANG Lingling, PANG Guoming, LI Huang, WANG Liying, DONG Yang, ZHAO Shipeng, LI Yingshuai, LI Lingru. Gut microbial characteristics of the damp-heat constitution: a population-based multicenter cross-sectional study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 140-151. |
| [3] | LI Zhenxuan, WANG Xuerui, Luis Ulloa, Ayman Youssef, BAI Yunjing, XU Xiaolong, LIU Qingquan. Complementary and alternative medicine on cognitive defects and neuroinflammation after sepsis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 408-416. |
| [4] | LI Xingjie, LIU Qiqi, XIA Rui, LIU Jun, WANG Dan, SHI Jiao, KUANG Yuxing, DAI Yalan, HUANG Haoyu, TANG Wei, CHEN Shangjie. Moxibustion modulates working memory in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 801-808. |
| [5] | MIN Youjiang, YAO Haihua, WANG Zhiqin, LUO Kaitao, SUN Jie, YUAN Zheng, WU Huiqi, CHENG Lihong. Efficacy of suspended moxibustion stimulating Shenshu (BL23) and Guanyuan (CV4) on the amygdala-HPA axis in rats with kidney-Yang deficiency symptom pattern induced by hydrocortisone [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 113-123. |
| [6] | LI Han, HUANG Xiaomin, CAI Haiyang, HEROK George, HE Jing, SU Yixun, LI Weihong, YI Chenju, OLIVER Brian G, CHEN Hui. Mitochondrial dysfunction in a rat model and the related risk of metabolic disorders [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 95-104. |
| [7] | FANG Jing, PAN Wen, WANG Xiangyun, LI Fengxing, ZHAO Ling, HUANG Zouqin, SHEN Xueyong. Efficacy of stimulating Mingmen (GV4) and Guanyuan (CV4) on kidney Yang deficiency in rat model: laser irradiation vs traditional moxibustion [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 972-979. |
| [8] | Jingjing WEI, Rongjuan GUO, Guojing FU, Xiao LIANG, Zhenmin XU, Min JIA, Zixiu ZENG, Wanqing DU, Weiwei JIAO, Linjuan SUN, Hongmei LIU, Chunli GUO, Chenguang TONG, Yunling ZHANG, Xing LIAO. Registration of intervention trials of Traditional Chinese Medicine for four neurological diseases on Chinese Clinical Trial Registry and ClinicalTrials.gov: a narrative review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 148-153. |
| [9] | Huixiang ZHANG, Limei WANG, Jipeng GUO, Jiai WANG, Qianqian ZHANG, Yutao WANG, Xun LIU, Lihuan ZHANG, Lanlan SHI, Hongxiang WU, Xue CAO. Gut microbiota and differential genes-maintained homeostasis is key to maintaining health of individuals with Yang-deficiency constitution [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 96-101. |
| [10] | PIAO Xiang, WANG Wei, CHEN Hanjiang, YAN Rong, LI Mengquan. Effect of Rongchang capsule (茸菖胶囊) on seizure behavior,cognitive impairment,and hippocampal DNA damage and inflammatory factors in epileptic rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 438-446. |
| [11] | ZHAO Xuesong;YANG Tao;CHENG Fang;YANG Song;ZHU Wanlin;LI Shaowu;FAN Yongping;. Abnormalcortical thickness in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis,correlations with cognition impairment,and effect of modified Bushenyisui decoction(补肾益髓汤)on cognitive function of multiple sclerosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(2): 316-325. |
| [12] | Ma Jie, Wang Yu, Zhang Yunyun, Guo Qihao, Zhen Xiaomin, Shi Moyi. Neuropsychological features in post-stroke cognitive impairment with no dementia patients with different Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(01): 97-102. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

