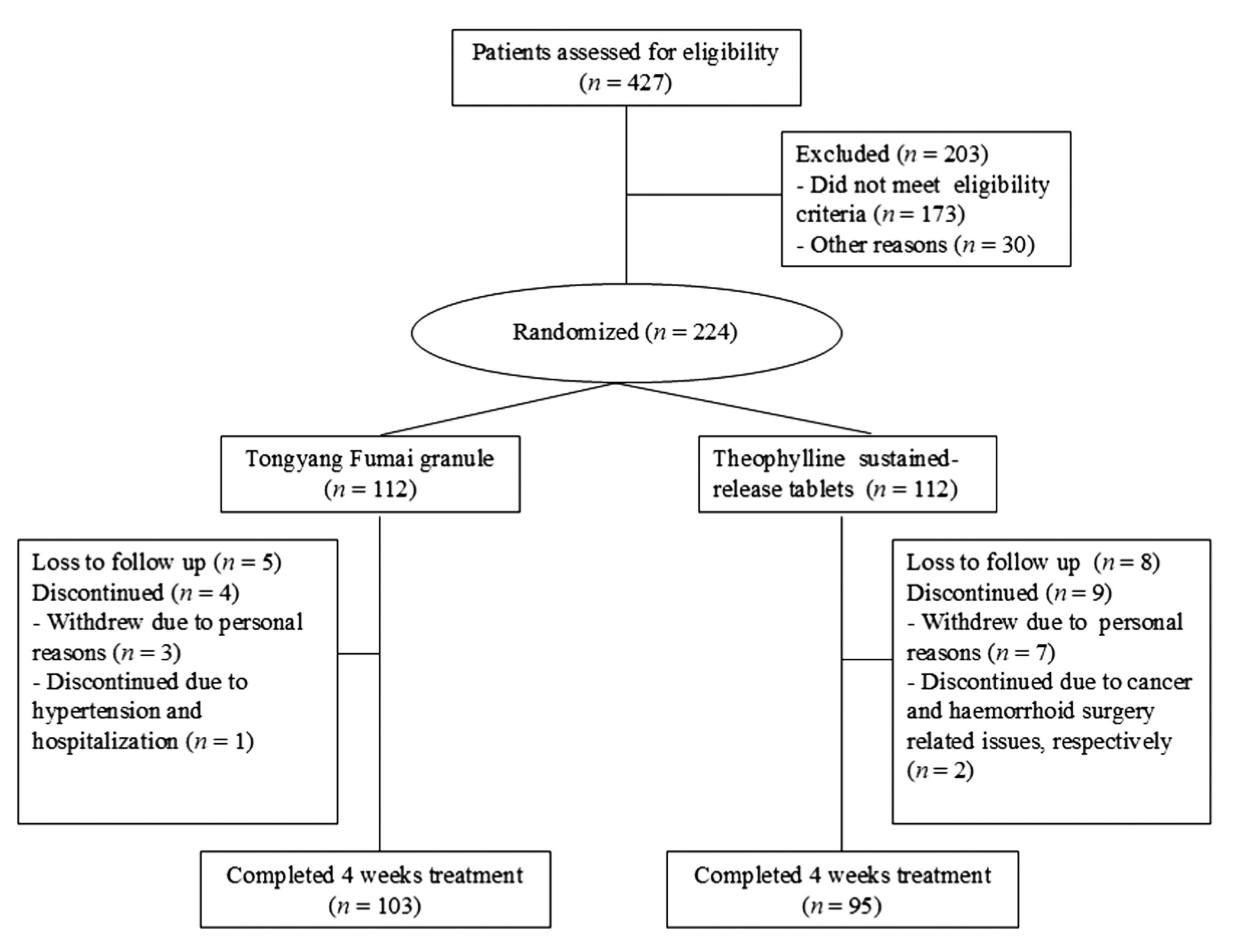
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1247-1253.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.06.010
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Compound Tongyang Fumai decoction (通阳复脉方) improves quality of life in sick sinus syndrome: a randomized controlled study
WU Qiaomin, GUAN Xuanke, LIU Jinfeng, WANG Yanli, CHANG Xing, LIU Zhiming( ), LIU Ruxiu(
), LIU Ruxiu( )
)
- Cardiovascular Department, Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China
-
Received:2023-01-11Accepted:2023-04-10Online:2024-12-15Published:2024-11-12 -
Contact:Prof. LIU Zhiming, Cardiovascular Department, Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China; tgzyeric@163.com
Prof. LIU Ruxiu, Cardiovascular Department, Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China; liuruxiu1@163.com -
Supported by:Beijing Clinical Application Research Project: Evaluation of the Therapeutic Efficacy of Tongyang Huoxue Decoction based on the Heart-Kidney Simultaneous Treatment for Sick Sinus Syndrome(Z181100001718184);Academic Inheritance and Communication Project of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences: Academic Experience Inheritance of Liu Zhiming(CI2022E012XB);High Level Chinese Medical Hospital Promotion Project: In-Hospital Pharmaceutical Preparation based on the Experience of Renowned Traditional Chinese Medicine Physicians(HLCMHPP2023053);Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Public Welfare Research Institutes: Mechanism of 'Kidney Tonifying, Yang Activating, and Blood Circulating' Chinese Medicine in Improving Sinoatrial Node Injury Under Hypoxic Stress(ZZ17-XRZ-028)
Cite this article
WU Qiaomin, GUAN Xuanke, LIU Jinfeng, WANG Yanli, CHANG Xing, LIU Zhiming, LIU Ruxiu. Compound Tongyang Fumai decoction (通阳复脉方) improves quality of life in sick sinus syndrome: a randomized controlled study[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1247-1253.
share this article
| Characteristic | Control group (n = 112) | TYFM group (n = 112) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 63.05±12.01 | 61.95±11.09 | 0.477a |
| Male [n (%)] | 35 (31.25) | 49 (43.75) | 0.053b |
| Course of SSS (years) | 6.64±8.09 | 6.86±8.69 | 0.950a |
| Body temperature (℃) | 36.26±0.22 | 36.22±0.20 | 0.194a |
| Respiratory rate (breaths/min) | 17.86±1.51 | 18.71±6.53 | 0.177 a |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 54.60±9.48 | 53.04±6.94 | 0.161a |
| Longest RR interval (s) | 1.95±0.53 | 2.02±0.54 | 0.327a |
| Number of long RR during 24 h | 190.55±687.97 | 136.98±431.68 | 0.486a |
| Hypertension [n (%)] | 55 (49.1) | 51 (45.5) | 0.688b |
| Ischemic heart disease [n (%)] | 22 (19.6) | 25 (22.3) | 0.743b |
| Dyslipidemia [n (%)] | 45 (40.2) | 37 (33.0) | 0.332b |
| Diabetes [n (%)] | 19 (17.0) | 9 (8.0) | 0.069b |
Table 1 Baseline information of the participant (ITT)
| Characteristic | Control group (n = 112) | TYFM group (n = 112) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 63.05±12.01 | 61.95±11.09 | 0.477a |
| Male [n (%)] | 35 (31.25) | 49 (43.75) | 0.053b |
| Course of SSS (years) | 6.64±8.09 | 6.86±8.69 | 0.950a |
| Body temperature (℃) | 36.26±0.22 | 36.22±0.20 | 0.194a |
| Respiratory rate (breaths/min) | 17.86±1.51 | 18.71±6.53 | 0.177 a |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 54.60±9.48 | 53.04±6.94 | 0.161a |
| Longest RR interval (s) | 1.95±0.53 | 2.02±0.54 | 0.327a |
| Number of long RR during 24 h | 190.55±687.97 | 136.98±431.68 | 0.486a |
| Hypertension [n (%)] | 55 (49.1) | 51 (45.5) | 0.688b |
| Ischemic heart disease [n (%)] | 22 (19.6) | 25 (22.3) | 0.743b |
| Dyslipidemia [n (%)] | 45 (40.2) | 37 (33.0) | 0.332b |
| Diabetes [n (%)] | 19 (17.0) | 9 (8.0) | 0.069b |
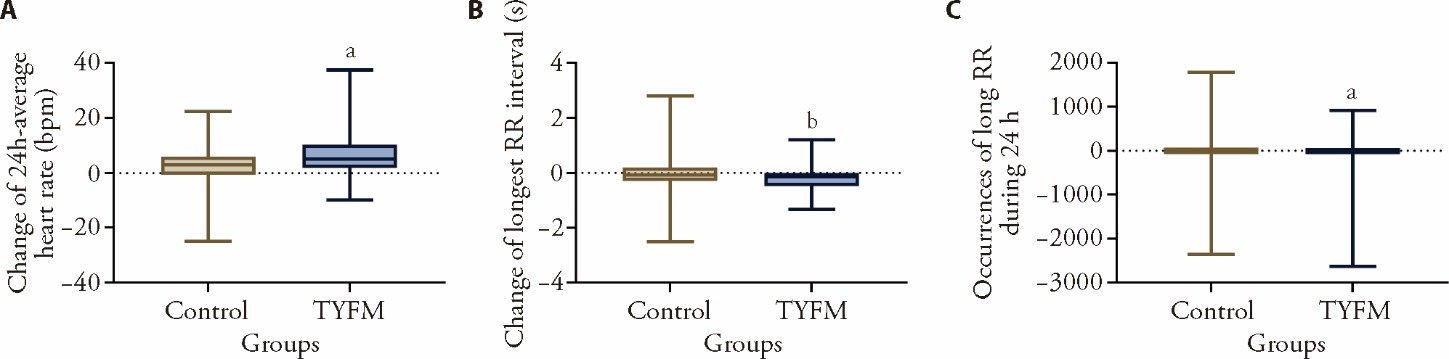
Figure 2 Change in average heart rate, longest RR interval, and occurrences of long RR intervals during 24 h A: change of 24 h-average heart rate; B: change of longest RR interval; C: occurrences of long RR during 24 h. Control group: received oral theophylline sustained-release tablets; TYFM group: received Tongyang Fumai granules. Bpm: beats/min; RR: R to R. The difference represents the values after treatment minus the values before treatment. The data adopts nonparametric test. Compared with control group, aP < 0.01; bP < 0.05.
| Item | Control group (n = 95) | TYFM group (n = 103) | P value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 4 | Difference (95% CI) | Baseline | Week 4 | Difference (95% CI) | |||
| PF | 45±10 | 46±9 | 1.5 (-0.2, 3.1) | 46±9 | 50±7a | 5 (3, 6) | 0.001 | |
| RP | 33±21 | 44±20a | 12 (7, 16) | 34±23 | 55±12a | 20 (16, 25) | <0.001 | |
| BP | 46±7 | 49±7a | 3 (1, 4) | 47±7 | 54±7a | 8 (6, 9) | <0.001 | |
| GH | 36±12 | 36±11 | -0.7 (-3, 1.7) | 37±11 | 45±10a | 8(6, 10) | <0.001 | |
| VT | 52±9 | 54±9b | 2.1 (0.4, 3.8) | 51±9 | 58±7a | 7 (5, 9) | <0.001 | |
| SF | 53±11 | 56±11a | 3 (1, 5) | 54±9 | 62±7a | 8 (6, 10) | <0.001 | |
| RE | 42±24 | 49±20a | 7 (2, 12) | 45±22 | 56±10a | 12 (7, 16) | 0.002 | |
| MH | 51±9 | 52±10 | 1.3 (-0.3, 3.0) | 49±11 | 55±9a | 6 (6, 7) | 0.024 | |
| PCS | 39±10 | 44±10a | 4 (2, 6) | 41±10 | 51±6a | 10 (8, 12) | <0.001 | |
| MCS | 52±13 | 54±12 | 2.3 (-0.3, 4.8) | 52±14 | 58±8a | 6 (4, 8) | 0.014 | |
Table 2 Comparison of SF-36 scores (per-protocol set)
| Item | Control group (n = 95) | TYFM group (n = 103) | P value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 4 | Difference (95% CI) | Baseline | Week 4 | Difference (95% CI) | |||
| PF | 45±10 | 46±9 | 1.5 (-0.2, 3.1) | 46±9 | 50±7a | 5 (3, 6) | 0.001 | |
| RP | 33±21 | 44±20a | 12 (7, 16) | 34±23 | 55±12a | 20 (16, 25) | <0.001 | |
| BP | 46±7 | 49±7a | 3 (1, 4) | 47±7 | 54±7a | 8 (6, 9) | <0.001 | |
| GH | 36±12 | 36±11 | -0.7 (-3, 1.7) | 37±11 | 45±10a | 8(6, 10) | <0.001 | |
| VT | 52±9 | 54±9b | 2.1 (0.4, 3.8) | 51±9 | 58±7a | 7 (5, 9) | <0.001 | |
| SF | 53±11 | 56±11a | 3 (1, 5) | 54±9 | 62±7a | 8 (6, 10) | <0.001 | |
| RE | 42±24 | 49±20a | 7 (2, 12) | 45±22 | 56±10a | 12 (7, 16) | 0.002 | |
| MH | 51±9 | 52±10 | 1.3 (-0.3, 3.0) | 49±11 | 55±9a | 6 (6, 7) | 0.024 | |
| PCS | 39±10 | 44±10a | 4 (2, 6) | 41±10 | 51±6a | 10 (8, 12) | <0.001 | |
| MCS | 52±13 | 54±12 | 2.3 (-0.3, 4.8) | 52±14 | 58±8a | 6 (4, 8) | 0.014 | |
| Item | Control group (n = 95) | TYFM group (n = 103) | P value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 4 | Difference (95% CI) | Baseline | Week 4 | Difference (95% CI) | |||
| SAS | 42±9 | 38±9a | 5 (3-6) | 43±9 | 32±8a | 11 (10-13) | < 0.001 | |
| SDS | 41±11 | 39±10 | 2 (0-3) | 43±11 | 34±9a | 9 (8-11) | < 0.001 | |
Table 3 Comparison of SAS and SDS score (per-protocol set)
| Item | Control group (n = 95) | TYFM group (n = 103) | P value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 4 | Difference (95% CI) | Baseline | Week 4 | Difference (95% CI) | |||
| SAS | 42±9 | 38±9a | 5 (3-6) | 43±9 | 32±8a | 11 (10-13) | < 0.001 | |
| SDS | 41±11 | 39±10 | 2 (0-3) | 43±11 | 34±9a | 9 (8-11) | < 0.001 | |
| 1. |
Khanna S, Sreedharan R, Trombetta C, Ruetzler K. Sick sinus syndrome: sinus node dysfunction in the elderly. Anesthesiology 2020; 132: 377-8.
DOI PMID |
| 2. | Su SF, Wu MS. Arrhythmia perception and quality of life in bradyarrhythmia patients following permanent pacemaker implantation. Clin Nurs Res 2021; 30: 183-92. |
| 3. |
Jensen PN, Gronroos NN, Chen LY, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for sick sinus syndrome in the general population. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014; 64: 531-8.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Sidhu S, Marine JE. Evaluating and managing bradycardia. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2020; 30: 265-72. |
| 5. | Greenspon AJ, Patel JD, Lau E, et al. 16-year trends in the infection burden for pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in the United States 1993 to 2008. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011; 58: 1001-6. |
| 6. |
Alboni P, Menozzi C, Brignole M, et al. Effects of permanent pacemaker and oral theophylline in sick sinus syndrome the THEOPACE study: a randomized controlled trial. Circulation 1997; 96: 260-6.
PMID |
| 7. | Huang YF, Lu L, Zhu DJ, et al. Effects of astragalus polysaccharides on dysfunction of mitochondrial dynamics induced by oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016; 2016: 9573291. |
| 8. | Liu RX, Tan S, Liu M, Peng J, Wang YL, Liu ZM. Effects of Chinese herbal medicine serum on the apoptosis of sinoatrial node cells induced by simulated ischemia-reperfusion. J Tradit Chin Med 2011; 31: 224-7. |
| 9. |
Liu R, Li J, Liu Y, Peng J, Guan X. The Effect of astragaloside on pacemaker current and the cytoskeleton in rabbit sinoatrial node cells under the ischemia and reperfusion condition. Front Pharmacol 2018; 9: 551.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Li J, Guan XK, Liu RX. Role of Chinese herbal medicines in regulation of energy metabolism in treating cardiovascular diseases. Chin J Integr Med 2019; 25: 307-15.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Epstein AE, DiMarco JP, Ellenbogen KA, et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA/HRS focused update incorporated into the ACCF/AHA/HRS 2008 guidelines for device-based therapy of cardiac rhythm abnormalities: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation 2013; 127: e283-352. |
| 12. | Zheng X. Clinical research guiding principle for the new Chinese herbal medicine. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2002: 1-390. |
| 13. | Wu Q, Chen Y, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Huang Y, Liu R. Reliability, validity, and sensitivity of short-form 36 health survey (SF-36) in patients with sick sinus syndrome. Medicine 2023; 102: e33979. |
| 14. | Wu WY. A self-rating anxiety scale. Behavioral medicine inventory manual. Beijing: the Chinese Medicine Electronic Audio and Video Publishing House, 2005: 213-4. |
| 15. | Wang CF, Cai ZH, Xu Q. Evaluation analysis of self-rating depression disorder scale in 1340 people. Chin J Nervous Mental Dis 2009; 12: 267-8. |
| 16. | Jin IT, Yoon N, Jeong HK, Lee KH, Park HW, Cho JG. Positive chronotropic effects of theophylline and cilostazol in patients with symptomatic sick sinus syndrome who have declined permanent pacing. Rev Cardiovasc Med 2020; 21: 473-80. |
| 17. | Tomsits P, Clauss S, Kääb S. Genetic insight into sick sinus syndrome. Is there a pill for it or how far are we on the translational road to personalized medicine? Eur Heart J 2021; 42: 1972-5. |
| 18. |
Holmberg MJ, Moskowitz A, Wiberg S, et al. Guideline removal of atropine and survival after adult in-hospital cardiac arrest with a non-shockable rhythm. Resuscitation 2019; 137: 69-77.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | Neumar RW, Otto CW, Link MS, et al. Part 8: adult advanced cardiovascular life support: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation 2010; 122: S729-67. |
| 20. |
Bertolet BD, Eagle DA, Conti JB, Mills RM, Belardinelli L. Bradycardia after heart transplantation: reversal with theophylline. J Am Coll Cardiol 1996; 28: 396-9.
PMID |
| 21. |
Cawley MJ, Al-Jazairi AS, Stone EA. Intravenous theophylline--an alternative to temporary pacing in the management of bradycardia secondary to AV nodal block. Ann Pharmacother 2001; 35: 303-7.
PMID |
| 22. |
Levine JH, Michael JR, Guarnieri T. Multifocal atrial tachycardia: a toxic effect of theophylline. Lancet 1985; 1: 12-4.
PMID |
| 23. |
Greenspon AJ, Patel JD, Lau E, et al. Trends in permanent pacemaker implantation in the United States from 1993 to 2009: increasing complexity of patients and procedures. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012; 60: 1540-5.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Cingolani E, Goldhaber JI, Marbán E. Next-generation pacemakers: from small devices to biological pacemakers. Nat Rev Cardiol 2018; 15: 139-50.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Liu S, Tian G, Chen J, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine for bradyarrhythmia: evidence and potential mechanisms. Front Pharmacol 2018; 9: 324.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Wan-Tong Z, Bao-Chen Z, Zhao L, et al. Compassionate use of yuanjiang decoction, a traditional Chinese medicinal prescription, for symptomatic bradyarrhythmia. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 764930. |
| 27. | Liu J, Liu R, Peng J, Wang Y. Effects of Yiqi Tongyang on HCN4 protein phosphorylation in damaged rabbit sinoatrial node cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016; 2016: 4379139. |
| 28. | Wu Q, Chang X, Wang Y, et al. The electrophysiological effects of Tongyang Huoxue granules on the ignition phase during hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in sinoatrial node cells. Front Physiol 2024; 15: 1402478. |
| 29. | Zhang X, Zhou Y, Chang X, Wu Q, Liu Z, Liu R. Tongyang Huoxue decoction (TYHX) ameliorating hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced disequilibrium of calcium homeostasis via regulating β-tubulin in rabbit sinoatrial node cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2024; 318: 117006. |
| 30. |
Fumincelli L, Mazzo A, Martins JCA, Mendes IAC. Quality of life and ethics: a concept analysis. Nurs Ethics 2019; 26: 61-70.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | QIAN Jianan, XU Yan, HU Hongyi, ZHAO Aiguang. Clinical efficacy and safety evaluation of Buzhongyiqi pills (补中益气丸) on appetite improvement in patients with colorectal cancer receiving chemotherapy: a pilot randomized cross-over clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1254-1267. |
| [2] | DENG Yasheng, HAN Siyin, XI Lanhua, HUANG Hui, LIANG Tianwei, ZHENG Yiqing, FAN Yanping, LIN Jiang. Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of recurrent respiratory tract infections in children: an overview of systematic reviews and Meta-analyses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 871-884. |
| [3] | GU Xiangchen, QIU Meisi, XIE Lin, CHEN Min, DENG Yueyi, ZHANG Changming, JIAN Guihua, WANG Chen, WANG Yi. Individualized Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment vs antibiotics for recurrent urinary tract infections: a multicenter, randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 524-529. |
| [4] | TIAN Haolin, YANG Yuanbin, ZHANG Hu, ZHAO Wenjing, ZHOU Jing, TIAN Jingfeng, HE Long, LI Xuechao, SHEN Qinxuan, SHUAI Mei. Efficacy of Daoyin combined with lower limb robot as a comprehensive rehabilitation intervention for stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 530-536. |
| [5] | LI Xiyu, YANG Yanhong, SUN Jian, NIE Quanfang, LIU Lifen, LI Guifen, YU Junping, ZHANG Zhuangjin, XU Yi, ZOU Ting, SHI Yun. Effectiveness and safety of Jiawei Xiaoyao pill (加味逍遥丸) in the treatment of premenstrual syndrome (liver depression, spleen deficiency, and blood-heat syndrome): a multi-center, randomized, placebo-controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 373-380. |
| [6] | YU Zhengqiu, YU Liuda, CHEN Ye, LI Mingjing, CAI Wanru. Effectiveness and safety of Qidong Huoxue decoction (芪冬活血饮) in treatment of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized, controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 381-387. |
| [7] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [8] | ZHOU Mingwang, DONG Zhuanli, WEI Changhao, FENG Lufang, WANG Xiaoping, LIU Haiping, JI Xing, YANG Kehu, LI Shenghua. Efficacy and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy combined with sodium hyaluronate in treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 243-250. |
| [9] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [10] | DAI Xiaoling, ZHANG Anming, LIN Hui, SHI Bei, REN Yi, WEN Hongzhu, FEI Xiaoyan, LIN Jiang. Qingchang suppositry (清肠栓) induced remission in patients with mild-to-moderate ulcerative proctitis: a multicenter, prospective, randomized, parallel-controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 156-162. |
| [11] | WANG Yichen, WU Shiyi, WANG Zhengyan, CHANG Wenling, XIE Zhihao, TANG Xing, ZHAO Songmei, ZHOU Jing, CHEN Zehong, WANG Chao, YANG Chunxia. Efficacy of Zhumian Tang formula granules (助眠汤配方颗粒) combined with eszopiclone for the treatment of poor sleep quality: a multi-center, randomized controlled, superiority trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 163-171. |
| [12] | YANG Yi, YE Huijun, ZHENG Huiling, JIN Lihua. Clinical observation on 90 cases of primary dysmenorrhea treated by buccal acupuncture therapy: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 172-181. |
| [13] | DAI Zeqi, LIAO Xing, GUAN Yueyue, ZENG Zixiu, TANG Jun, HU Jing. Bloodletting puncture in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: protocol for a mixed-method study of a multi-center randomized controlled trial and focus group [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1259-1267. |
| [14] | XU Yani, ZHANG Yutong, HE Weile, DAI Linglin, TANG Ding, WANG Jialing, ZHANG Xufen, CHEN Qin, CHEN Lifang, WANG Zhanglian, ZHAN Mingjie. Efficiency and safety of acupuncture for women with premature ovarian insufficiency: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1268-1274. |
| [15] | XU Xiangru, ZHOU Yi, CHEN Gang, LEI Ming, ZHANG Wen, WU Xinxin, PU Yuting, CHEN Caiyu, SUN Yuting, ZHOU Shuang, FANG Bangjiang. Clinical efficacy of Buzhong Yiqi decoction (补中益气汤) in the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia with multi-drug resistant bacteria: a prospective, randomized, multicenter controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 1010-1018. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||