Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 89-99.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240423.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Network pharmacology and animal experiments revealed the protective effects of Guilong prescription (归龙方) on chronic prostatitis and its possible mechanisms
ZHU Peixuan1, SU Zeqi2, FAN Qiongyin3, ZHANG Cai2( ), WANG Ting2(
), WANG Ting2( )
)
- 1 School of Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
2 Beijing Research Institute of Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Key Laboratory of Neuropsycho-pharmacology, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing 100850, China
-
Received:2023-12-12Accepted:2024-03-14Online:2025-02-15Published:2024-04-23 -
Contact:Prof. WANG Ting, Beijing Research Institute of Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China.wangting1973@sina.com ; Dr. ZHANG Cai, Beijing Research Institute of Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China.202202003@bucm.edu.cn Telephone: +86-18380447057 -
Supported by:National Major Scientific and the Technological Special Project: Establishment of a Clinically Oriented Preclinical Research and Development Technology Platform for New Chinese Medicines based on Famous Doctors' Prescriptions(2017ZX09301011);"Decoding Traditional Chinese Medicine" Project of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine: New Drugs Research and Development of Chinese Medicine based on Famous Doctors and Famous Prescriptions(90010961020020);the Horizontal Project: Preclinical Pharmacology and Pharmacodynamic Research of a New Chinese Medicine — Guilong Granules(2016110031007799)
Cite this article
ZHU Peixuan, SU Zeqi, FAN Qiongyin, ZHANG Cai, WANG Ting. Network pharmacology and animal experiments revealed the protective effects of Guilong prescription (归龙方) on chronic prostatitis and its possible mechanisms[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 89-99.
share this article
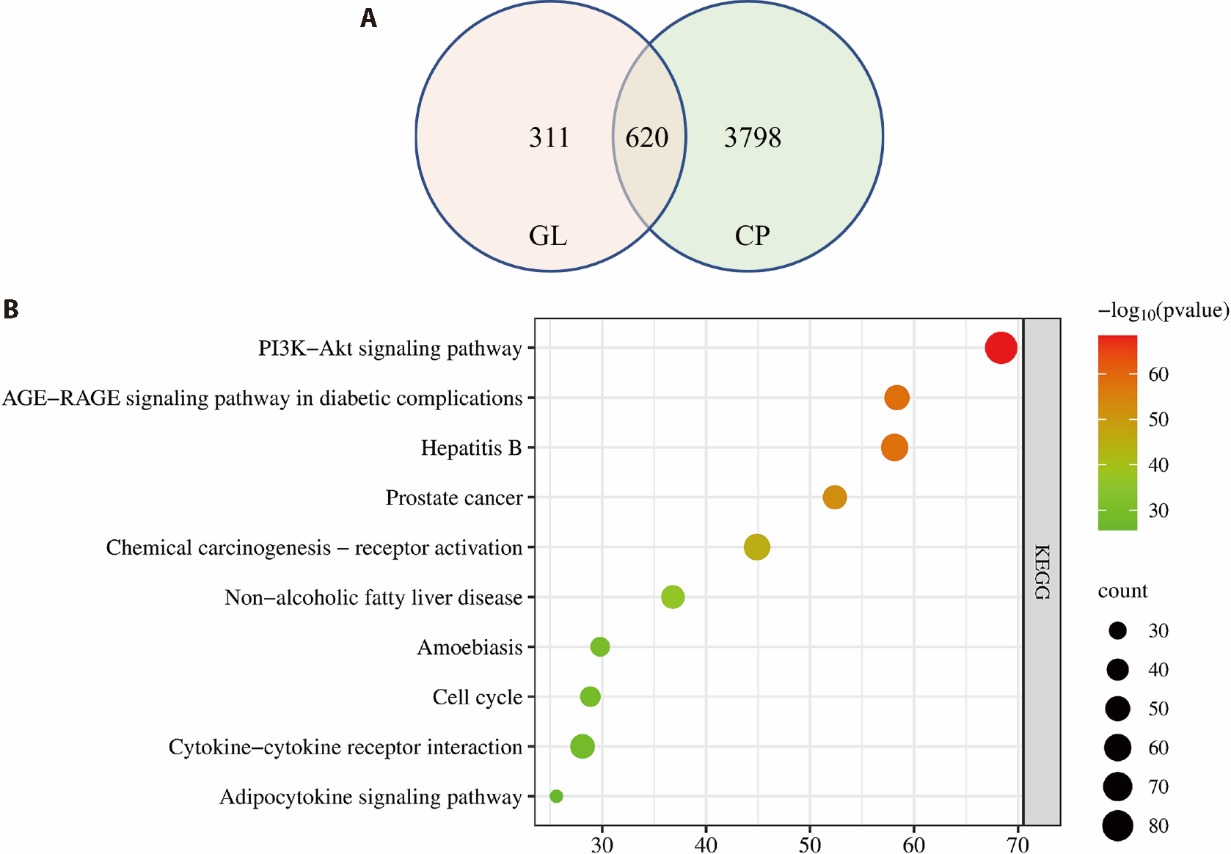
Figure 1 Possible mechanisms of GL in the treatment of CP based on network pharmacology A: common targets of compositions and disease; B: KEGG analysis of GL in the treatment of CP. GL: Guilong prescription; CP: chronic prostatitis; KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.

Figure 2 GL alleviated the pathological characteristics of prostate in CP rats induced by carrageenan A: histopathological changes in different groups, HE staining of prostate at × 40 magnification, scale bar = 100 μm. Red circle: interstitial edema, blue circle: interstitial hemorrhage, green circle: interstitial foam-like macrophages and infiltration of interstitial inflammatory cells (mainly lymphocyte). B: general observation of prostate, scale bar = 1 cm. C: Laser speckle pattern of blood perfusion in the prostate. A1, B1, C1: Control group, treated only with animal drinking water. A2, B2, C2: Sham group, the prostate was injected with sterile saline and treated with animal drinking water. A3, B3, C3: CP group, the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with animal drinking water. A4, B4, C4: GL low dose (GL-L) group, the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with low dose (3.5 g/kg) of GL. A5, B5, C5: GL medium dose (GL-M) group, the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with medium dose (7 g/kg) of GL. A6, B6, C6: GL high dose (GL-H) group, the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with high dose (14 g/kg) of GL. GL: Guilong prescription; CP: chronic prostatitis; HE: hematoxylin-eosin.
| Group | n | Prostate injury score | Prostate index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 10 | 37.00±10.85 | 1.60±0.23 |
| Sham | 10 | 36.50±13.75 | 1.61±0.23 |
| CP | 10 | 135.50±26.71a | 1.98±0.25a |
| GL-L | 10 | 61.50±24.39b | 1.63±0.23b |
| GL-M | 10 | 45.50±23.39b | 1.66±0.24c |
| GL-H | 10 | 44.50±14.42b | 1.58±0.16b |
Table 1 Statistical results of prostate injury score and prostate index in each group ( x - ?± s)
| Group | n | Prostate injury score | Prostate index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 10 | 37.00±10.85 | 1.60±0.23 |
| Sham | 10 | 36.50±13.75 | 1.61±0.23 |
| CP | 10 | 135.50±26.71a | 1.98±0.25a |
| GL-L | 10 | 61.50±24.39b | 1.63±0.23b |
| GL-M | 10 | 45.50±23.39b | 1.66±0.24c |
| GL-H | 10 | 44.50±14.42b | 1.58±0.16b |
| Group | n | IL-4 | IL-10 | TNF-α | IL-1β | IFN-γ | CXCL1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8 | 1.55±0.59 | 1.21±0.55 | 0.93±0.49 | 1.33±0.54 | 0.34±0.30 | 4.89±2.90 |
| Sham | 8 | 0.72±0.17 | 0.72±0.22 | 0.70±0.30 | 1.05±0.25 | 0.73±0.61 | 3.64±2.28 |
| CP | 8 | 0.30±0.14a | 0.52±0.12a | 3.71±1.48a | 2.29±0.61a | 2.26±0.83a | 13.45±10.84d |
| GL-L | 8 | 0.75±0.27b | 0.80±0.26c | 1.73±0.80b | 1.14±0.32b | 0.93±0.25b | 4.11±2.46b |
| GL-M | 8 | 0.65±0.34c | 0.82±0.23b | 1.23±0.84b | 0.71±0.38b | 0.85±0.79c | 2.85±2.04b |
| GL-H | 8 | 0.47±0.22 | 0.51±0.21 | 1.90±0.98c | 1.31±0.71c | 1.21±0.86c | 6.39±4.19 |
Table 2 Statistical results of inflammatory cytokine levels in each group (pg/mg, x - ?± s)
| Group | n | IL-4 | IL-10 | TNF-α | IL-1β | IFN-γ | CXCL1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8 | 1.55±0.59 | 1.21±0.55 | 0.93±0.49 | 1.33±0.54 | 0.34±0.30 | 4.89±2.90 |
| Sham | 8 | 0.72±0.17 | 0.72±0.22 | 0.70±0.30 | 1.05±0.25 | 0.73±0.61 | 3.64±2.28 |
| CP | 8 | 0.30±0.14a | 0.52±0.12a | 3.71±1.48a | 2.29±0.61a | 2.26±0.83a | 13.45±10.84d |
| GL-L | 8 | 0.75±0.27b | 0.80±0.26c | 1.73±0.80b | 1.14±0.32b | 0.93±0.25b | 4.11±2.46b |
| GL-M | 8 | 0.65±0.34c | 0.82±0.23b | 1.23±0.84b | 0.71±0.38b | 0.85±0.79c | 2.85±2.04b |
| GL-H | 8 | 0.47±0.22 | 0.51±0.21 | 1.90±0.98c | 1.31±0.71c | 1.21±0.86c | 6.39±4.19 |

Figure 3 GL down regulated the expression of proteins associated with inflammation in CP rats induced by carrageenan A: immunohistochemical staining of ICAM-1 in the prostate at × 40 magnification, scale bar = 50 μm; B: immunohistochemical staining of iNOS in the prostate at × 40 magnification, scale bar = 50 μm. A1, B1: Control group, treated only with animal drinking water. A2, B2: Sham group, the prostate was injected with sterile saline and treated with animal drinking water. A3, B3: CP group, the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with animal drinking water. A4, B4: GL low dose (GL-L) group, the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with low dose (3.5 g/kg) of GL. A5, B5: GL medium dose (GL-M) group, the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with medium dose (7 g/kg) of GL. A6, B6: GL high dose (GL-H) group, the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with high dose (14 g/kg) of GL. GL: Guilong prescription; CP: chronic prostatitis; ICAM-1: intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1; iNOS: induce nitric oxide synthase.
| Group | n | IOD/Area of ICAM-1 | IOD/Area of iNOS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5 | 0.20±0.02 | 0.18±0.02 |
| Sham | 5 | 0.21±0.02 | 0.21±0.04 |
| CP | 5 | 0.37±0.04a | 0.28±0.03c |
| GL-L | 5 | 0.21±0.03b | 0.21±0.04d |
| GL-M | 5 | 0.27±0.03b | 0.22±0.03d |
| GL-H | 5 | 0.22±0.03b | 0.20±0.03b |
Table 3 Statistical results of ICAM-1 and iNOS expression in each group (pg/mg, x - ?± s)
| Group | n | IOD/Area of ICAM-1 | IOD/Area of iNOS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5 | 0.20±0.02 | 0.18±0.02 |
| Sham | 5 | 0.21±0.02 | 0.21±0.04 |
| CP | 5 | 0.37±0.04a | 0.28±0.03c |
| GL-L | 5 | 0.21±0.03b | 0.21±0.04d |
| GL-M | 5 | 0.27±0.03b | 0.22±0.03d |
| GL-H | 5 | 0.22±0.03b | 0.20±0.03b |

Figure 4 GL inhibited PI3K-Akt and NF-κB pathway related proteins in the prostate of CP rats induced by carrageenan A: the protein expression levels of PI3K, p-PI3K, Akt, p-Akt, GSK-3β, p-GSK-3β, and β-actin were tested by Western blot. B: The protein expression levels of P38, p-P38, p65, p-p65, IκBα, p-IκBα, and β-actin were tested by Western blot. Control: treated only with animal drinking water. Sham: the prostate was injected with sterile saline and treated with animal drinking water. CP: the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with animal drinking water. GL-L: the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with low dose (3.5 g/kg) of GL. GL-M: the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with medium dose (7 g/kg) of GL. GL-H: the prostate was injected with carrageenan and treated with high dose (14 g/kg) of GL. GL: Guilong prescription; CP: chronic prostatitis; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt: ribosome-associated complex-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase; GSK-3β: glycogen synthase kinase-3β; P38: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; p65: nuclear factor-κ-gene binding p65; IκBα: inhibitor of NF-κB-α.
| Group | n | PI3K | p-PI3K | Akt | p-Akt | GSK-3β | p-GSK-3β | P38 | p-P38 | p65 | p-p65 | IκBα | p-IκBα |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6 | 0.54±0.22 | 0.28±0.04 | 0.51±0.08 | 0.24±0.07 | 1.02±0.23 | 0.31±0.04 | 0.59±0.21 | 1.36±0.09 | 0.97±0.18 | 0.22±0.04 | 0.56±0.11 | 0.16±0.04 |
| Sham | 6 | 0.55±0.09 | 0.29±0.07 | 0.55±0.10 | 0.30±0.06 | 1.18±0.22 | 0.35±0.09 | 0.64±0.21 | 1.61±0.09 | 1.08±0.23 | 0.26±0.07 | 0.58±0.21 | 0.25±0.08 |
| CP | 6 | 0.93±0.36a | 0.41±0.05b | 0.57±0.10 | 0.39±0.09b | 1.43±0.31a | 0.40±0.04b | 0.92±0.20a | 1.78±0.12b | 1.39±0.28a | 0.41±0.10b | 0.98±0.38a | 0.55±0.06b |
| GL-L | 6 | 0.64±0.33 | 0.28±0.05c | 0.54±0.11 | 0.37±0.10 | 1.02±0.13d | 0.27±0.07c | 0.62±0.22d | 1.45±0.05c | 0.97±0.23d | 0.20±0.08c | 0.74±0.32 | 0.29±0.05c |
| GL-M | 6 | 0.67±0.28 | 0.35±0.05 | 0.50±0.10 | 0.21±0.07c | 1.03±0.22d | 0.28±0.05c | 0.69±0.13d | 1.43±0.10c | 0.91±0.17c | 0.28±0.09d | 0.59±0.29 | 0.35±0.08c |
| GL-H | 6 | 0.58±0.41 | 0.33±0.06d | 0.47±0.09 | 0.24±0.07c | 1.00±0.16d | 0.38±0.15 | 0.71±0.38 | 1.63±0.08d | 0.99±0.15d | 0.40±0.22 | 0.62±0.24 | 0.46±0.08 |
Table 4 Statistical results of the relative expression levels of PI3K, p-PI3K, Akt, p-Akt, GSK-3β, p-GSK-3β, P38, p-P38, p65, p-p65, IκBα, p-IκBα ( x - ?± s)
| Group | n | PI3K | p-PI3K | Akt | p-Akt | GSK-3β | p-GSK-3β | P38 | p-P38 | p65 | p-p65 | IκBα | p-IκBα |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6 | 0.54±0.22 | 0.28±0.04 | 0.51±0.08 | 0.24±0.07 | 1.02±0.23 | 0.31±0.04 | 0.59±0.21 | 1.36±0.09 | 0.97±0.18 | 0.22±0.04 | 0.56±0.11 | 0.16±0.04 |
| Sham | 6 | 0.55±0.09 | 0.29±0.07 | 0.55±0.10 | 0.30±0.06 | 1.18±0.22 | 0.35±0.09 | 0.64±0.21 | 1.61±0.09 | 1.08±0.23 | 0.26±0.07 | 0.58±0.21 | 0.25±0.08 |
| CP | 6 | 0.93±0.36a | 0.41±0.05b | 0.57±0.10 | 0.39±0.09b | 1.43±0.31a | 0.40±0.04b | 0.92±0.20a | 1.78±0.12b | 1.39±0.28a | 0.41±0.10b | 0.98±0.38a | 0.55±0.06b |
| GL-L | 6 | 0.64±0.33 | 0.28±0.05c | 0.54±0.11 | 0.37±0.10 | 1.02±0.13d | 0.27±0.07c | 0.62±0.22d | 1.45±0.05c | 0.97±0.23d | 0.20±0.08c | 0.74±0.32 | 0.29±0.05c |
| GL-M | 6 | 0.67±0.28 | 0.35±0.05 | 0.50±0.10 | 0.21±0.07c | 1.03±0.22d | 0.28±0.05c | 0.69±0.13d | 1.43±0.10c | 0.91±0.17c | 0.28±0.09d | 0.59±0.29 | 0.35±0.08c |
| GL-H | 6 | 0.58±0.41 | 0.33±0.06d | 0.47±0.09 | 0.24±0.07c | 1.00±0.16d | 0.38±0.15 | 0.71±0.38 | 1.63±0.08d | 0.99±0.15d | 0.40±0.22 | 0.62±0.24 | 0.46±0.08 |
| 1. | Krieger JN, Nyberg L Jr, Nickel JC. NIH consensus definition and classification of prostatitis. JAMA 1999; 282: 236-7. |
| 2. | Magistro G, Wagenlehner FME, Pilatz A. Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Urologie 2023; 62: 590-6. |
| 3. |
Suskind AM, Berry SH, Ewing BA, et al. The prevalence and overlap of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men: results of the RAND Interstitial Cystitis Epidemiology male study. J Urol 2013; 189: 141-5.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Pena VN, Engel N, Gabrielson AT, et al. Diagnostic and management strategies for patients with chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Drugs Aging 2021; 38: 845-86. |
| 5. | Zhang J, Liang C, Shang X, Li H. Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a disease or symptom? current perspectives on diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Am J Mens Health 2020; 14: 1557988320903200. |
| 6. | Qin Z, Zhang C, Guo J, et al. Oral pharmacological treatments for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a systematic review and network Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. EClinicalMedicine 2022; 48: 101457. |
| 7. |
Nickel JC. Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: it is time to change our management and research strategy. BJU Int 2020; 125: 479-80.
DOI PMID |
| 8. | Xue Y, Duan Y, Gong X, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine on treating chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019; 98: e16136. |
| 9. | Franco JV, Turk T, Jung JH, et al. Pharmacological interventions for treating chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2019; 10: CD012552. |
| 10. | Zhang ZJ (Eastern Han dynasty). Jin Gui Yao Lüe. Beijing: XueYuan Publishing House, 2007: 116. |
| 11. |
Li H, Hung A, Yang AWH. Herbal formula (Danggui Beimu Kushen Wan) for prostate disorders: a systematic review of classical literature. Integr Med Res 2019; 8: 240-6.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Li H, Hung A, Yang AWH. A classic herbal formula Danggui Beimu Kushen Wan for chronic prostatitis: from traditional knowledge to scientific exploration. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018; 2018: 1612948. |
| 13. |
Yang X, Yuan L, Chen J, et al. Multitargeted protective effect of Abacopteris penangiana against carrageenan-induced chronic prostatitis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2014; 151: 343-51.
DOI PMID |
| 14. |
Hajighorbani M, Ahmadi-Hamedani M, Shahab E, et al. Evaluation of the protective effect of pentoxifylline on carrageenan-induced chronic non-bacterial prostatitis in rats. Inflammopharmacology 2017; 25: 343-50.
DOI PMID |
| 15. | Nair AB, Jacob S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharm 2016; 7: 27-31. |
| 16. | Zhang C, Wang X, Wang C, et al. Qingwenzhike prescription alleviates acute lung injury induced by LPS via inhibiting TLR4/NF-kB pathway and NLRP 3 inflammasome activation. Front Pharmacol 2021; 12: 790072. |
| 17. | Wu Y, Zhang F, Yang K, et al. SymMap: an integrative database of Traditional Chinese Medicine enhanced by symptom mapping. Nucleic Acids Res 2019; 47: D1110-7. |
| 18. | Stelzer G, Rosen N, Plaschkes I, et al. The Gene Cards Suite: from gene data mining to disease genome sequence analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 2016; 54: 1.30. 1-33. |
| 19. |
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, et al. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun 2019; 10: 1523.
DOI PMID |
| 20. | He H, Luo H, Xu H, et al. Preclinical models and evaluation criteria of prostatitis. Front Immunol 2023; 14: 1183895. |
| 21. | Epstein JI, Netto GJ. Biopsy interpretation of the prostate. Fifth edition ed.Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2015: 9. |
| 22. |
Cho IR, Keener TS, Nghiem HV, et al. Prostate blood flow characteristics in the chronic prostatitis/pelvic pain syndrome. J Urol 2000; 163: 1130-3.
PMID |
| 23. | Meng LQ, Yang FY, Wang MS, et al. Quercetin protects against chronic prostatitis in rat model through NF-kappa B and MAPK signaling pathways. Prostate 2018; 78: 790-800. |
| 24. |
de Lima NM, Ferreira EO, Fernandes MY, et al. Neuroinflammatory response to experimental stroke is inhibited by boldine. Behav Pharmacol 2017; 28: 223-37.
DOI PMID |
| 25. | Wang HQ, Hu J, Yan HY, et al. Corydaline inhibits enterovirus 71 replication by regulating COX-2 expression. J Asian Nat Prod Res 2017; 19: 1124-33. |
| 26. | Li Y, Zhang L, Zhang P, Hao Z. Dehydrocorydaline protects against sepsis-induced myocardial injury through modulating the TRAF6/NF-κB pathway. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2021; 12: 709604. |
| 27. | Jiang D, Rasul A, Batool R, et al. Potential anticancer properties and mechanisms of action of formononetin. Biomed Res Int 2019; 2019: 5854315. |
| 28. | Chen MH, Gu YY, Zhang AL, et al. Biological effects and mechanisms of matrine and other constituents of Sophora flavescens in colorectal cancer. Pharmacol Res 2021; 171: 105778. |
| 29. |
Tarabasz D, Kukula-Koch W. Palmatine: a review of pharmacological properties and pharmacokinetics. Phytother Res 2020; 34: 33-50.
DOI PMID |
| 30. | Yang G, Zeng R, Song X, et al. Sophocarpine alleviates injury-induced intima hyperplasia of carotid arteries by suppressing inflammation in a rat model. J Clin Med 2021; 10: 5449. |
| 31. | Hao Q, Wu Y, Vadgama JV, Wang P. Phytochemicals in inhibition of prostate cancer: evidence from molecular mechanisms studies. Biomolecules 2022; 12: 1306. |
| 32. |
Peng X, Guo H, Chen J, et al. The effect of pirfenidone on rat chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome and its mechanisms. Prostate 2020; 80: 917-25.
DOI PMID |
| 33. |
Schwartz ES, La JH, Young EE, et al. Chronic prostatitis induces bladder hypersensitivity and sensitizes bladder afferents in the mouse. J Urol 2016; 196: 892-901.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Chen L, Zhang M, Liang C. Chronic prostatitis and pelvic pain syndrome: another autoimmune disease? Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2021; 69: 24. |
| 35. |
Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Regulation of NF-κB by TNF family cytokines. Semin Immunol 2014; 26: 253-66.
DOI PMID |
| 36. |
Shidid S, Bluth MH, Smith-Norowitz TA. The role of inflammasomes in mediating urological disease: a short literature review. J Inflamm Res 2022; 15: 4359-65.
DOI PMID |
| 37. |
Motrich RD, Breser ML, Molina RI, et al. Patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome show T helper type 1 (Th1) and Th17 self-reactive immune responses specific to prostate and seminal antigens and diminished semen quality. BJU Int 2020; 126: 379-87.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Hu Q, Lyon CJ, Fletcher JK, et al. Extracellular vesicle activities regulating macrophage- and tissue-mediated injury and repair responses. Acta Pharm Sin B 2021; 11: 1493-512.
DOI PMID |
| 39. | Soundararajan L, Dharmarajan A, Samji P. Regulation of pleiotropic physiological roles of nitric oxide signaling. Cell Signal 2023; 101: 110496. |
| 40. |
Ückert S, Kedia GT, Tsikas D, et al. Emerging drugs to target lower urinary tract symptomatology (LUTS)/benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): focus on the prostate. World J Urol 2020; 38: 1423-35.
DOI PMID |
| 41. | Korbecki J, Barczak K, Gutowska I, et al. CXCL1: gene, promoter, regulation of expression, mRNA stability, regulation of activity in the intercellular space. Int J Mol Sci 2022; 23: 792. |
| 42. | Bui TM, Wiesolek HL, Sumagin R. ICAM-1: a master regulator of cellular responses in inflammation, injury resolution, and tumorigenesis. J Leukoc Biol 2020; 108: 787-99. |
| 43. |
Heeb LEM, Egholm C, Boyman O. Evolution and function of interleukin-4 receptor signaling in adaptive immunity and neutrophils. Genes Immun 2020; 21: 143-9.
DOI PMID |
| 44. | Saraiva M, Vieira P, O'Garra A. Biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin-10. J Exp Med 2020; 217: e20190418. |
| 45. |
Kameritsch P, Renkawitz J. Principles of leukocyte migration strategies. Trends Cell Biol 2020; 30: 818-32.
DOI PMID |
| 46. | Song W, Sun Y, Liang XC, et al. Jinmaitong ameliorates diabetes-induced peripheral neuropathy in rats through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 2021; 266: 113461. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

