Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 408-421.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.015
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hypolipidemic effect and mechanism of Hedan tablet (荷丹片) based on network pharmacology
HU Huiming1, WENG Jiajun2, TANG Fangrui3, WANG Yaqi3, FAN Shengxian3, WANG Xuecheng3, CUI Can4, SHAO Feng3( ), ZHU Yanchen5(
), ZHU Yanchen5( )
)
- 1 College of pharmacy, Nanchang Medical College & Key Laboratory of Pharmacodynamics and Safety Evaluation, Health Commission of Jiangxi Province & Key Laboratory of Pharmacodynamics and Quality Evaluation on anti-Inflammatory Chinese Herbs, Jiangxi Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330052, China
2 Peking University Traditional Chinese Medicine Clinical Medical School (Xiyuan), Beijing 100191, China
3 Key Laboratory of Modern Preparation of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, China
4 College of pharmacy, Nanchang Medical College, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330052, China
5 College of Computer Science, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, China
-
Received:2023-12-22Accepted:2024-05-24Online:2025-04-15Published:2025-03-10 -
Contact:SHAO Feng, Key Laboratory of Modern Preparation of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, China. shaofeng0729@163.com; ZHU Yanchen, College of Computer Science, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, China. 20030761@jxutcm.edu.cn, Telephone: +86-791-87118658 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Effects of Hawthorn Leaves Flavonoids on Atherosclerosis Unstable Plaques based on the Mechanism of Liver-gut axis Liver X Receptor (LXR-a)-mediated Iron and Lipid Metabolism Disorders(82260794);Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province: based on Secreted Phospholipase A2 Type ⅡA (sPLA2-ⅡA) Regulating Lipid Mediated Foam Cell Formation to Explore the Effect and Molecular Mechanism of Hawthorn Leaf Flavonoids on Anti-atherosclerosis(20212BAB206013);Key R&D Program of Jiangxi Province: Research on the Quality Enhancement and Industrialization Technology Improvement of the Lipid-Lowering Traditional Chinese Medicine "Hedan Tablet"(20201BBG71005);Science and Technology Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education: based on the "Phlegm-Stasis" Theory to Explore the Effects and Molecular Mechanisms of Hawthorn Leaves Flavonoids on Improving Iron and Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Atherosclerosis(GJJ2203502)
Cite this article
HU Huiming, WENG Jiajun, TANG Fangrui, WANG Yaqi, FAN Shengxian, WANG Xuecheng, CUI Can, SHAO Feng, ZHU Yanchen. Hypolipidemic effect and mechanism of Hedan tablet (荷丹片) based on network pharmacology[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 408-421.
share this article
| No. | Compound | Formula | Retein time | Theoretical value | Experimental value m/z | Error ppm | MS | Reference | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adenine | C5H5N5 | 1.79 | 136.06177 | 136.06143 | -2.5 | 119.0350, 94.0376 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 2 | Guanine | C5H5N5O | 1.83 | 152.05669 | 152.05673 | 0.3 | 135.0286, 110.0327 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 3 | Isopsoralen | C11H6O3 | 12.18 | 187.03897 | 187.03886 | -0.6 | 159.0439, 143.0491 | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | |
| 4 | Psoralenoside | C17H18O9 | 12.25 | 367.10236 | 367.10221 | -0.4 | 187.0389 | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | |
| 5 | Coclaurine | C17H19NO3 | 12.87 | 286.14377 | 286.14287 | -3.1 | 286.1425, 269.1165, 237.0901, 209.0952, 178.0849, 175.0749 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 6 | Rutin | C27H30O16 | 13.55 | 611.16066 | 611.15805 | -4.3 | 465.1006, 303.0494, 137.0238 | Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae) | |
| 7 | Quercetin | C15H10O7 | 13.89 | 303.04993 | 303.04961 | -1.1 | 165.0197, 153.0195, 137.0224 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 8 | kaempferol | C15H10O6 | 14.73 | 287.05501 | 287.05371 | -4.6 | 153.0199, 135.0243 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 9 | N-Nornuciferine | C18H19NO2 | 15.01 | 282.14886 | 282.14788 | -3.5 | 265.1200, 250.0971, 235.0728, 207.0791 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 10 | Nuciferine | C19H21NO2 | 15.18 | 296.16451 | 296.16436 | -0.5 | 296.1629, 250.0969, 234.1044, 219.0782, 207.0788, 191.0852, 179.0848 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 11 | Liriodenine | C17H9NO3 | 16.21 | 276.06552 | 276.06481 | -2.6 | 248.0691 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 12 | Eupafolin | C16H12O7 | 16.68 | 317.06558 | 317.06443 | -3.6 | 243.0658, 183.0431 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 13 | Tanshindiol B | C18H16O5 | 16.82 | 313.10705 | 313.10674 | -1 | 295.0967, 267.0995 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 14 | Jaceosidin | C17H14O7 | 17.83 | 331.08123 | 331.08007 | -3.5 | 316.0606, 167.0348 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 15 | Psoralen | C11H6O3 | 18.71 | 187.03897 | 187.03886 | -0.6 | 143.0491, 115.0541, 159.0439, 131.0491, 103.0541 | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | |
| 16 | Tanshinone IIB | C19H18O4 | 22.66 | 311.12779 | 311.1263 | -4.8 | 293.1187, 275.1073, 267.1385, 252.1135, 237.1281, 223.0756 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 17 | Neobavaisoflavone | C20H18O4 | 23.02 | 323.12779 | 323.12715 | -2 | 267.0651, 239.0695 | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | |
| 18 | Tanshinaldehyde | C19H16O4 | 23.52 | 309.11214 | 309.11193 | -0.7 | 281.1178, 263.1034, 235.0749 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 19 | Corylifolinin | C20H20O4 | 23.55 | 325.14344 | 325.14223 | -3.7 | 269.0810, 205.0861 | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | |
| 20 | 15, 16-Dihydrotanshinone I | C18H14O3 | 25.15 | 279.10157 | 279.10083 | -2.6 | 279.0994, 261.0890, 251.1046, 233.0951, 205.0995 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 21 | Asiatic acid | C30H48O5 | 25.57 | 489.35745 | 489.3555 | -4 | 401.3341, 107.0843 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 22 | Danshenxinkun B | C18H16O3 | 25.7 | 281.11722 | 281.11662 | -2.1 | 263.1064, 235.1116, 207.1163 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 23 | Methyl tanshinonate | C20H18O5 | 26.26 | 339.1227 | 339.12102 | -5 | 279.1003, 261.0907, 233.0962, 205.1013, 190.0786 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 24 | Cryptotanshinone | C19H20O3 | 27.29 | 297.14852 | 297.14846 | -0.2 | 297.1480, 251.1417 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 25 | TanshinoneⅠ | C18H12O3 | 27.71 | 277.08592 | 277.08492 | -3.6 | 277.0839, 262.0605, 249.0892, 234.0659, 203.0843, 193.1002, 178.0768 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 26 | Aristolone | C15H22O | 28.34 | 219.17434 | 219.17424 | -0.5 | 203.1438, 177.1451, 121.0674, | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 27 | 1,2-Dihydrotanshinone I | C18H14O3 | 28.47 | 279.10157 | 279.10083 | -4.4 | 279.0994, 261.0890, 233.0951, 218.0712, 205.0994, 190.0763 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 28 | Tanshinone II A | C19H18O3 | 29.463 | 295.13287 | 295.13156 | -4.4 | 277.1221, 262.0988, 249.1271, 234.1032, 220.0855, 206.1080, 191.0855, 179.0861, 165.0698 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 29 | Miltirone | C19H22O2 | 29.85 | 283.16926 | 283.16871 | -1.9 | 265.1580, 241.1216, 237.1628, 223.1110 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 30 | Ursolic acid | C30H48O3 | 31.22 | 457.36762 | 457.36722 | -0.9 | 248.5500, 204.5100, 191.1815 | Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae) |
Table 1 Identification of chemical constituents of Hedan tablet by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS
| No. | Compound | Formula | Retein time | Theoretical value | Experimental value m/z | Error ppm | MS | Reference | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adenine | C5H5N5 | 1.79 | 136.06177 | 136.06143 | -2.5 | 119.0350, 94.0376 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 2 | Guanine | C5H5N5O | 1.83 | 152.05669 | 152.05673 | 0.3 | 135.0286, 110.0327 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 3 | Isopsoralen | C11H6O3 | 12.18 | 187.03897 | 187.03886 | -0.6 | 159.0439, 143.0491 | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | |
| 4 | Psoralenoside | C17H18O9 | 12.25 | 367.10236 | 367.10221 | -0.4 | 187.0389 | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | |
| 5 | Coclaurine | C17H19NO3 | 12.87 | 286.14377 | 286.14287 | -3.1 | 286.1425, 269.1165, 237.0901, 209.0952, 178.0849, 175.0749 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 6 | Rutin | C27H30O16 | 13.55 | 611.16066 | 611.15805 | -4.3 | 465.1006, 303.0494, 137.0238 | Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae) | |
| 7 | Quercetin | C15H10O7 | 13.89 | 303.04993 | 303.04961 | -1.1 | 165.0197, 153.0195, 137.0224 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 8 | kaempferol | C15H10O6 | 14.73 | 287.05501 | 287.05371 | -4.6 | 153.0199, 135.0243 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 9 | N-Nornuciferine | C18H19NO2 | 15.01 | 282.14886 | 282.14788 | -3.5 | 265.1200, 250.0971, 235.0728, 207.0791 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 10 | Nuciferine | C19H21NO2 | 15.18 | 296.16451 | 296.16436 | -0.5 | 296.1629, 250.0969, 234.1044, 219.0782, 207.0788, 191.0852, 179.0848 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 11 | Liriodenine | C17H9NO3 | 16.21 | 276.06552 | 276.06481 | -2.6 | 248.0691 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 12 | Eupafolin | C16H12O7 | 16.68 | 317.06558 | 317.06443 | -3.6 | 243.0658, 183.0431 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 13 | Tanshindiol B | C18H16O5 | 16.82 | 313.10705 | 313.10674 | -1 | 295.0967, 267.0995 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 14 | Jaceosidin | C17H14O7 | 17.83 | 331.08123 | 331.08007 | -3.5 | 316.0606, 167.0348 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 15 | Psoralen | C11H6O3 | 18.71 | 187.03897 | 187.03886 | -0.6 | 143.0491, 115.0541, 159.0439, 131.0491, 103.0541 | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | |
| 16 | Tanshinone IIB | C19H18O4 | 22.66 | 311.12779 | 311.1263 | -4.8 | 293.1187, 275.1073, 267.1385, 252.1135, 237.1281, 223.0756 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 17 | Neobavaisoflavone | C20H18O4 | 23.02 | 323.12779 | 323.12715 | -2 | 267.0651, 239.0695 | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | |
| 18 | Tanshinaldehyde | C19H16O4 | 23.52 | 309.11214 | 309.11193 | -0.7 | 281.1178, 263.1034, 235.0749 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 19 | Corylifolinin | C20H20O4 | 23.55 | 325.14344 | 325.14223 | -3.7 | 269.0810, 205.0861 | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | |
| 20 | 15, 16-Dihydrotanshinone I | C18H14O3 | 25.15 | 279.10157 | 279.10083 | -2.6 | 279.0994, 261.0890, 251.1046, 233.0951, 205.0995 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 21 | Asiatic acid | C30H48O5 | 25.57 | 489.35745 | 489.3555 | -4 | 401.3341, 107.0843 | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 22 | Danshenxinkun B | C18H16O3 | 25.7 | 281.11722 | 281.11662 | -2.1 | 263.1064, 235.1116, 207.1163 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 23 | Methyl tanshinonate | C20H18O5 | 26.26 | 339.1227 | 339.12102 | -5 | 279.1003, 261.0907, 233.0962, 205.1013, 190.0786 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 24 | Cryptotanshinone | C19H20O3 | 27.29 | 297.14852 | 297.14846 | -0.2 | 297.1480, 251.1417 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 25 | TanshinoneⅠ | C18H12O3 | 27.71 | 277.08592 | 277.08492 | -3.6 | 277.0839, 262.0605, 249.0892, 234.0659, 203.0843, 193.1002, 178.0768 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 26 | Aristolone | C15H22O | 28.34 | 219.17434 | 219.17424 | -0.5 | 203.1438, 177.1451, 121.0674, | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) | |
| 27 | 1,2-Dihydrotanshinone I | C18H14O3 | 28.47 | 279.10157 | 279.10083 | -4.4 | 279.0994, 261.0890, 233.0951, 218.0712, 205.0994, 190.0763 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 28 | Tanshinone II A | C19H18O3 | 29.463 | 295.13287 | 295.13156 | -4.4 | 277.1221, 262.0988, 249.1271, 234.1032, 220.0855, 206.1080, 191.0855, 179.0861, 165.0698 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 29 | Miltirone | C19H22O2 | 29.85 | 283.16926 | 283.16871 | -1.9 | 265.1580, 241.1216, 237.1628, 223.1110 | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | |
| 30 | Ursolic acid | C30H48O3 | 31.22 | 457.36762 | 457.36722 | -0.9 | 248.5500, 204.5100, 191.1815 | Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae) |
| No. | ID | Ingredients | Herbs | No. | ID | Ingredients | Herbs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | Kaempferol | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis), Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae), Fanxieye (Folium Sennae) | 10 | DS2 | Cryptotanshinone | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) |
| 2 | B | Quercetin | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis), Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae) | 11 | DS3 | Tanshinone I | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) |
| 3 | C | Rutin | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis), Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae), Fanxieye (Folium Sennae), Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | 12 | DS4 | Tanshinone IIA | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) |
| 4 | D | Ursolic acid | Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae), Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | 13 | DS5 | Tanshinone IIB | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) |
| 5 | BGZ1 | Corylifolinin | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | 14 | HY1 | Adenine | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) |
| 6 | BGZ2 | Isopsoralen | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | 15 | HY2 | Asiatic acid | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) |
| 7 | BGZ3 | Neobavaisoflavone | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | 16 | HY3 | Coclaurine | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) |
| 8 | BGZ4 | Psoralen | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | 17 | HY4 | Eupafolin | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) |
| 9 | DS1 | 15,16-Dihydrotanshinone I | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | 18 | HY5 | Guanine | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) |
Table 2 Information of 18 active compounds in Hedan tablet
| No. | ID | Ingredients | Herbs | No. | ID | Ingredients | Herbs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | Kaempferol | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis), Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae), Fanxieye (Folium Sennae) | 10 | DS2 | Cryptotanshinone | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) |
| 2 | B | Quercetin | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis), Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae) | 11 | DS3 | Tanshinone I | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) |
| 3 | C | Rutin | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis), Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae), Fanxieye (Folium Sennae), Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | 12 | DS4 | Tanshinone IIA | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) |
| 4 | D | Ursolic acid | Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae), Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | 13 | DS5 | Tanshinone IIB | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) |
| 5 | BGZ1 | Corylifolinin | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | 14 | HY1 | Adenine | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) |
| 6 | BGZ2 | Isopsoralen | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | 15 | HY2 | Asiatic acid | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) |
| 7 | BGZ3 | Neobavaisoflavone | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | 16 | HY3 | Coclaurine | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) |
| 8 | BGZ4 | Psoralen | Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae) | 17 | HY4 | Eupafolin | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) |
| 9 | DS1 | 15,16-Dihydrotanshinone I | Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | 18 | HY5 | Guanine | Heye (Folium Nelumbinis) |

Figure 1 “TCMs - active ingredient- target" network diagram Blue diamonds represent herbs, yellow circles represent active ingredients of drugs, and red hexagons represent "herbs-disease" co-targets. The larger the pattern and the darker the color represents the greater the degree, meaning the more critical the node; DS: Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae); SZ: Shanzha (Fructus Crataegus Pinnatifidae); BGZ: Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae); FXY: Fanxieye (Folium Sennae); HY: Heye (Folium Nelumbinis); A: Kaempferol; B: Quercetin; C: Rutin; D: Ursolic acid; BGZ1: Corylifolinin; BGZ2: Isopsoralen; BGZ3: Neobavaisoflavone; BGZ4: Psoralen; DS1: 15,16-Dihydrotanshinone I; DS2: Cryptotanshinone; DS3: Tanshinone I; DS4: Tanshinone ⅡA; DS5: Tanshinone ⅡB; HY1: Adenine; HY2: Asiatic acid; HY3: Coclaurine; HY4: Eupafolin; HY5: Guanine; SELP: p-selectin; TXNIP: thioredoxin-interacting protein; NPC1L1: Niemann-Pick C1-like 1; PIK3C2A: phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase C2 domain containing subunit alpha; NR1H3: nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group H member 3 (LXRα); PDX1: pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1; APOA1: apolipoprotein A-I; SHBG: sex hormone-binding globulin; SREBF2: sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 2; PON2: paraoxonase 2; PHKA2: phosphorylase kinase regulatory subunit alpha 2; APOB: apolipoprotein B; LCAT: lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase; CAV1: caveolin-1; CYBA: cytochrome b-245 light chain; AKT2: RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase; INS: insulin; ABCG5: ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 5; ITGB3: integrin beta-3; INSR: insulin receptor; LDLR: low-density lipoprotein receptor; ADIPOQ: adiponectin; FASN: fatty acid synthase; UCP1: uncoupling protein 1; SERPINE1: serpin family E member 1 (plasminogen activator inhibitor-1); CPT1A: carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A; PYGL: glycogen phosphorylase, liver form; SREBF1: sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1; SELE: e-selectin; CRP: C-reactive protein; MTTP: microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; APOE: apolipoprotein E; ACE: angiotensin-converting enzyme; LEPR: leptin receptor; PON1: paraoxonase 1; ESR1: estrogen receptor 1; CDKN2A: cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; ABCA1: ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 1; EGF: epidermal growth factor; LRP1: low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; F3: coagulation factor Ⅲ (tissue factor); ALB: albumin; VCAM1: vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; SLC2A4: solute carrier family 2 member 4 (glucose transporter 4); PLAT: plasminogen activator, tissue type; IL-18: interleukin-18; PPARA: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; IRS1: insulin receptor substrate 1; IGF1: insulin-like growth factor 1; CCL5: C-C motif chemokine ligand 5; OLR1: oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1; MPO: myeloperoxidase; F2: coagulation factor Ⅱ (thrombin); LEPR: leptin receptor; ICAM1: intercellular adhesion molecule 1; CD36: CD36 molecule; NR3C1: nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 1 (glucocorticoid receptor); CCL2: C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; HMGCR: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; SOD1: superoxide dismutase 1; AGT: angiotensinogen; CAT: catalase; EDN1: endothelin 1; GPT: glutamate pyruvate transaminase; CXCL8: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8 (interleukin-8); PPARG: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; VEGFA: vascular endothelial growth factor A; NOS3: nitric oxide synthase 3; MMP9: matrix metallopeptidase 9; FOS: fos proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit; CYP3A4: cytochrome P450 3A4; IL1B: interleukin-1 beta; IL6: interleukin-6; TNF: tumor necrosis factor.
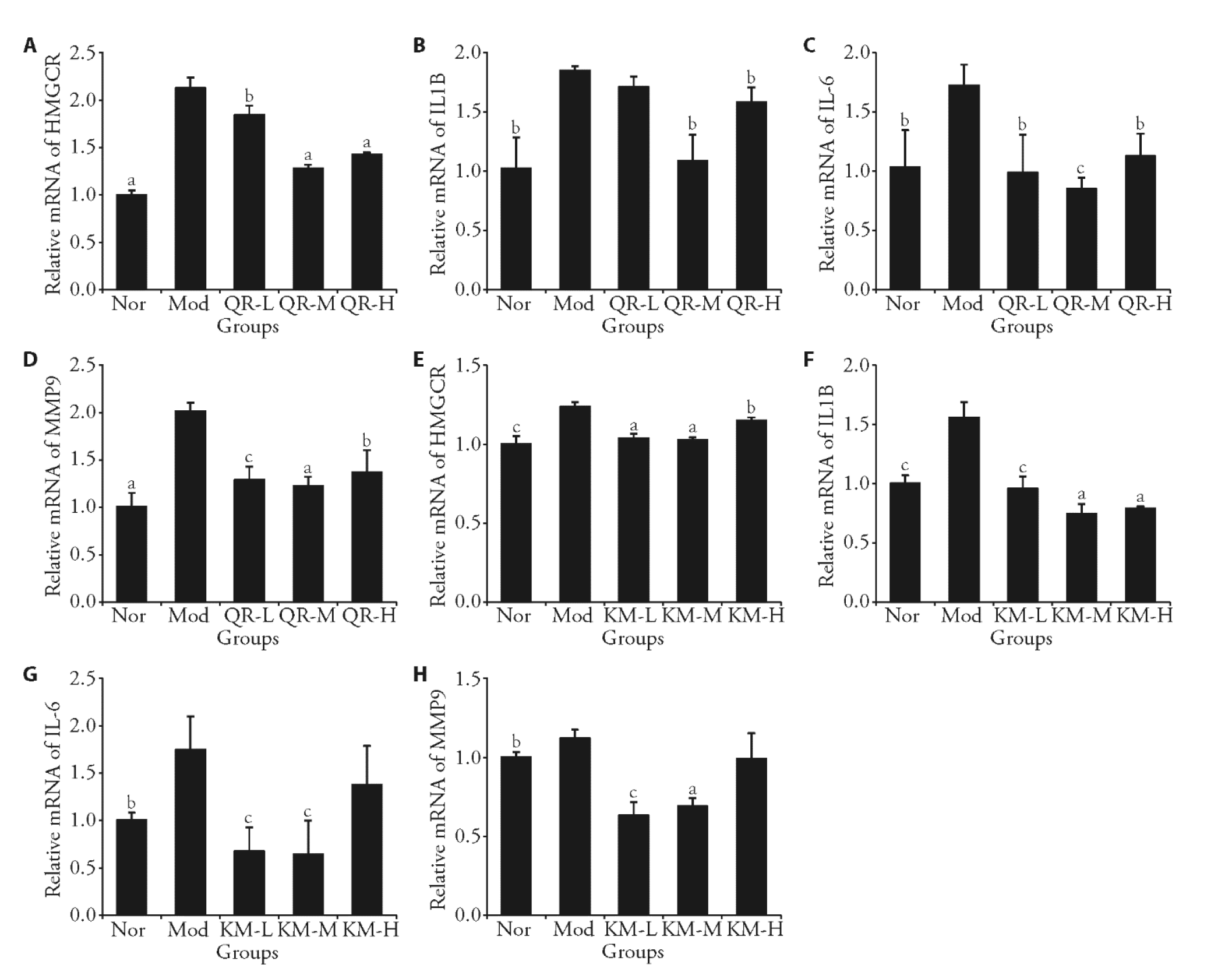
Figure 2 Effect of QR and KM on the mRNA expression of key factors in HepG2 cells A: the expression of HMGCR mRNA in each group of cells by QR; B: the expression of IL1B mRNA in each group of cells by QR; C: the expression of IL-6 mRNA in each group of cells by QR; D: the expression of MMP9 mRNA in each group of cells by QR; E: the expression of HMGCR mRNA in each group of cells by KM; F: the expression of IL-1β mRNA in each group of cells by KM; G: the expression of IL-6 mRNA in each group of cells by KM; H: the expression of MMP9 mRNA in each group of cells by KM. Nor: Normal control group, Mod: Model control group, QR-L: 5μmol/L of quercetin, QR-M: 10 μmol/L of quercetin, QR-H: 20 μmol/L of quercetin, KM-L: 5 μmol/L of kaempferol, KM-M: 10 μmol/L of kaempferol, KM-H: 20 μmol/L of kaempferol. HMGCR: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; QR: quercetin; IL-1β: interleukin 1 beta; IL-6: interleukin-6; MMP9: matrix metalloproteinase 9; KM: kaempferol; QR-L: quercetin low dose group; QR-M: quercetin medium dose group; QR-H: quercetin high dose group; KM-L: kaempferol low dose group; KM-M: kaempferol medium dose group; KM-H: kaempferol high dose group. These data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3); t-test, compared with Mod, aP < 0.001, bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01.
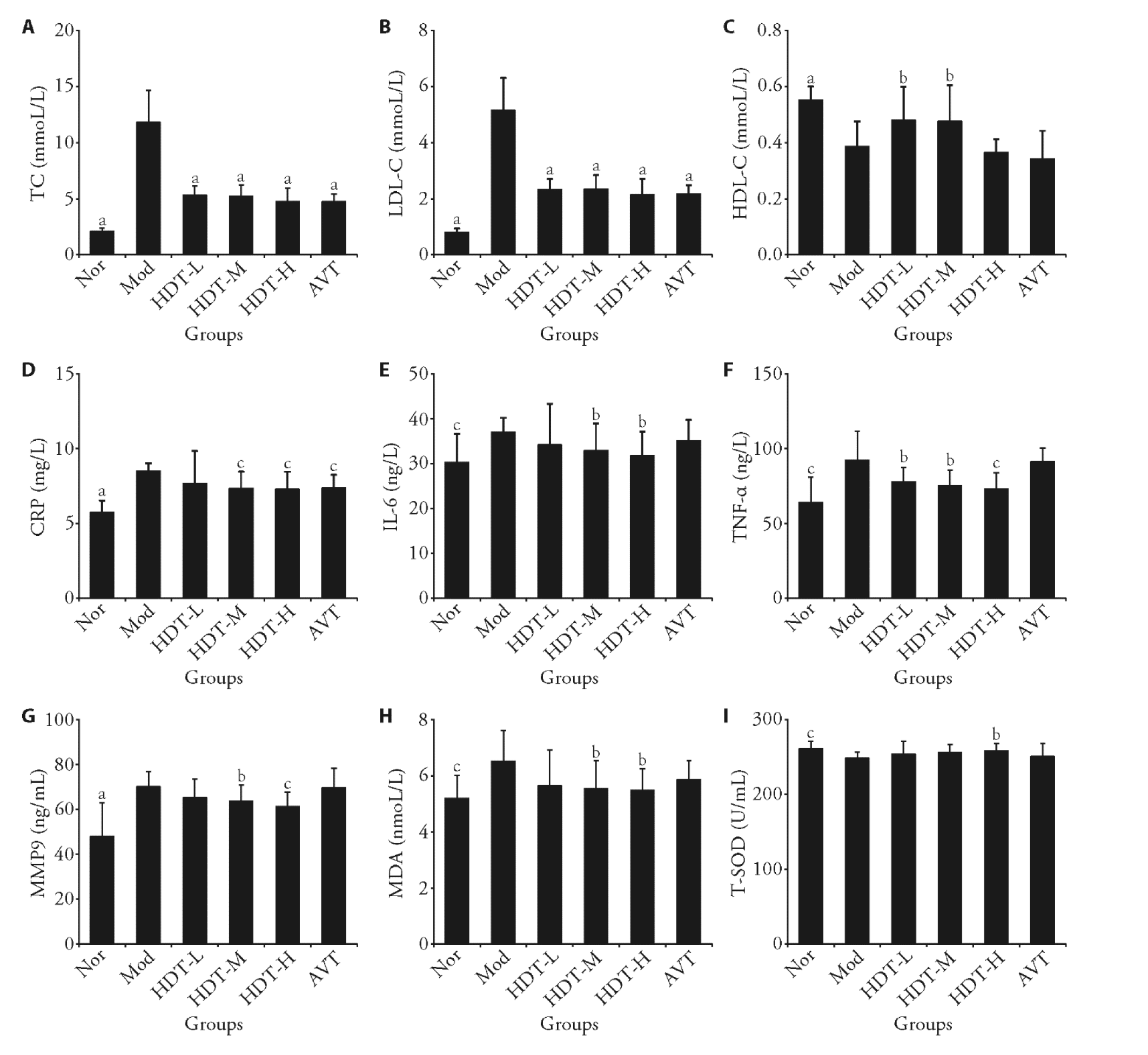
Figure 3 Results of in vivo experiments A: the levels of serum TC in rats; B: the levels of serum LDL-C in rats; C: the levels of serum HDL-C in rats; D: the levels of plasma CRP in rats; E: the levels of plasma IL-6 in rats; F: the levels of plasma TNF-α in rats; G: the levels of plasma MMP9 in rats; H: the levels of plasma MDA in rats; I: the levels of plasma T-SOD in rats. Nor: the normal control group, Mod: the high-fat diet model group, HDT-L: low-dose group of Hedan tablet (0.22 g/kg), HDT-M: medium-dose group of Hedan tablet (0.44 g/kg), HDT-H: high-dose group of Hedan tablet (0.88 g/kg), AVT: atorvastatin (7 mg/kg). TC: serum total cholesterol; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; CRP: C-reactive protein; IL-6: interleukin-6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; MMP9: matrix metalloproteinase 9; MDA: malondialdehyde; T-SOD: total superoxide dismutase. These data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 10); t-test, compared with Mod, aP < 0.001, bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01.
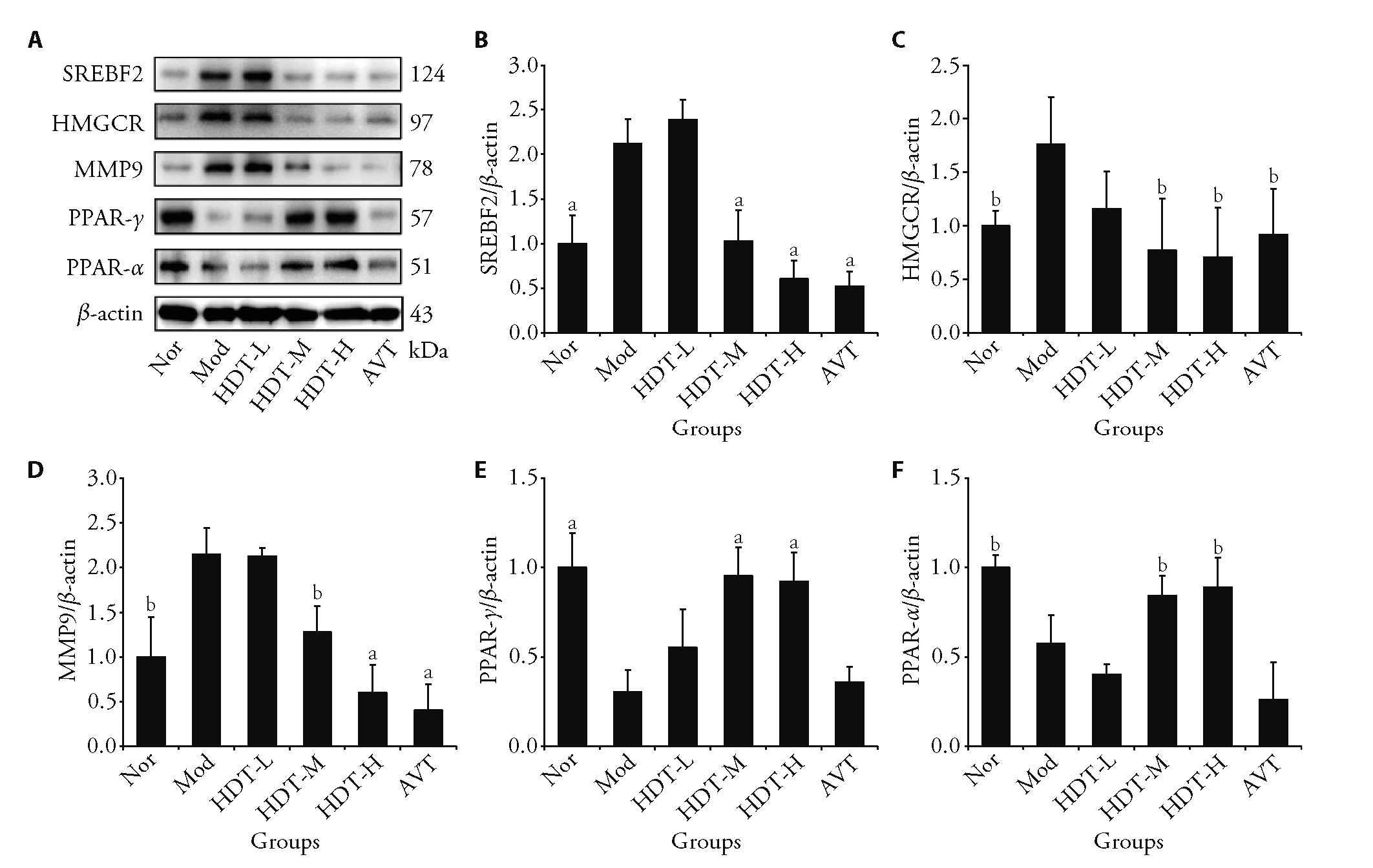
Figure 4 Effects of HDT on expression of proteins for the potential drug targets A: representative photographs of proteins by Western blotting; B: the expression levels of SREBF2; C: the expression levels of HMGCR; D: the expression levels of MMP9; E: the expression levels of PPAR-γ; F: the expression levels of PPAR-α. Nor: the normal control group, Mod: the high-fat diet model group, HDT-L: low-dose group of Hedan tablet (0.22 g/kg), HDT-M: medium-dose group of Hedan tablet (0.44 g/kg), HDT-H: high-dose group of Hedan tablet (0.88 g/kg), AVT: atorvastatin (7 mg/kg) SREBF2: sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 2; HMGCR: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; MMP9: matrix metalloproteinase 9; PPAR-γ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. These data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3); t-test, compared with Mod, aP < 0.01, bP < 0.05.
| 1. | Newton SL, Hoffmann AP, Yu Z, Haidermota S, Natarajan P, Honigberg MC. Management of severe and moderate hyper-cholesterolemia in young women and men. JAMA Cardiol 2022; 7: 227-30. |
| 2. | Hegele RA. Apolipoprotein C-Ⅲ inhibition to lower triglycerides: one ring to rule them all? Eur Heart J 2022; 43: 1413-5. |
| 3. | Ward NC, Chan DC, Watts GF. A tale of two new targets for hypertriglyceridaemia: which choice of therapy? Bio Drugs 2022; 36: 121-35. |
| 4. | Stone NJ. Treating severe hypercholesterolemia-If not now, when? JAMA Cardiol 2022; 7: 128-9. |
| 5. |
Mortensen MB, Falk E. Primary prevention with statins in the elderly. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018; 71: 85-94.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Thompson W, Jarbol DE, Nielsen JB, Haastrup P, Pottegard A. Statin use and discontinuation in Danes age 70 and older: a nationwide drug utilisation study. Age Ageing 2021; 50: 554-8.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Yourman LC, Cenzer IS, Boscardin WJ, et al. Evaluation of time to benefit of statins for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events in adults aged 50 to 75 years. JAMA Intern Med 2021; 181. |
| 8. | Zhang HY, Tian JX, Lian FM, et al. Therapeutic mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine to improve metabolic diseases via the gut microbiota. Biomed Pharmacother 2021; 133: 110857. |
| 9. |
Zhang Y, Kishi H, Kobayashi S. Add-on therapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine: an efficacious approach for lipid metabolism disorders. Pharmacol Res 2018; 134: 200-11.
DOI PMID |
| 10. | Luo H, Chen H, Liu C, et al. The key issues and development strategy of Chinese classical formulas pharmaceutical preparations. Chin Med 2021; 16: 1-14. |
| 11. |
He J, Feng X, Wang K, Liu C, Qiu F. Discovery and identification of quality markers of Chinese medicine based on pharmacokinetic analysis. Phytomedicine 2018; 44: 182-6.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Liu LY, Zhou L, Liu XZ, Zou DJ. Effect of Hedan tablets on body weight and insulin resistance in patients with metabolic syndrome. Obes Facts 2022; 15: 180-5. |
| 13. | Xu RX, Wu NQ, Li S, et al. Effects of Hedan tablet on lipid profile, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 and high-density lipoprotein subfractions in patients with hyperlipidemia: a primary study. Chin J Integr Med 2016; 22: 660-5. |
| 14. | Jin H, Zhu Y, Wang XD, et al. BDNF corrects NLRP3 inflammasome-induced pyroptosis and glucose metabolism reprogramming through KLF2/HK1 pathway in vascular endothelial cells. Cell Signal 2021; 78: 109843. |
| 15. | Wang X, Wang ZY, Zheng JH, Li S. TCM network pharmacology: a new trend towards combining computational, experimental and clinical approaches. Chin J Nat Med 2021; 19: 1-11. |
| 16. | Nogales C, Mamdouh ZM, List M, Kiel C, Casas AI, Schmidt H. Network pharmacology: curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2022; 43: 136-50. |
| 17. |
Kim S, Chen J, Cheng T, et al. PubChem in 2021: new data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 2021; 49: D1388-95.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Davis AP, Grondin CJ, Johnson RJ, et al. Comparative toxicogenomics database (CTD):update 2021. Nucleic Acids Res 2021; 49: D1138-43. |
| 19. |
UniProt C. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res 2021; 49: D480-9.
DOI PMID |
| 20. | Fishilevich S, Zimmerman S, Kohn A, et al. Genic insights from integrated human proteomics in GeneCards. Database (Oxford) 2016; 2016: 1-17. |
| 21. |
Chen T, Zhang H, Liu Y, Liu YX, Huang L. EVenn: easy to create repeatable and editable Venn diagrams and Venn networks online. J Genet Genomics 2021; 48: 863-6.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Mousavian Z, Khodabandeh M, Sharifi-Zarchi A, Nadafian A, Mahmoudi A. StrongestPath: a Cytoscape application for protein-protein interaction analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 2021; 22: 352.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, et al. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun 2019; 10: 1523.
DOI PMID |
| 24. | Liang N, Li YM, He Z, et al. Rutin and Quercetin decrease cholesterol in HepG 2 Cells but not plasma cholesterol in hamsters by oral administration. Molecules 2021; 26: 3766. |
| 25. | Tie F, Ding J, Hu N, Dong Q, Chen Z, Wang H. Kaempferol and Kaempferide attenuate oleic acid-induced lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in HepG2 cells. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 1-17. |
| 26. | Yang D, Hu C, Deng X, et al. Therapeuticeffect of Chitooligosaccharide tablets on lipids in high-fat diets induced hyperlipidemic rats. Molecules 2019; 24: 1-16. |
| 27. | Tao SY, Zhao FJ, Yang MJ, et al. Therapeutic efects of Hedan tablet on rats with nonalcoholic steatohepatiti. Chin J Integr Trad West Med Liver Dis 2013; 23: 39-41. |
| 28. | Sui ZY, Hou PY. Rapid identification the components of Nelumbinis Folium based on UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap platform. Zhong Guo Yao Xue Za Zhi 2019; 54: 813-8. |
| 29. | Diao YP. Chemical composition of Compound Ziling capsule by UPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS-MS. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2011; 17: 64-8. |
| 30. | Liu C. Methodology study of quality control and chemical components in Chinese medicinal herb Hedan tables. Shanghai: The Second Military Medical University, 2010: 11-20. |
| 31. | Xiao GL, Jiang JY, Xu AL, Li YX, Bi XL. Analysis of chemical constituents in Bushao Tiaozhi capsules by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2020; 26: 190-9. |
| 32. | Huang HY, Kang JL, Yu YH, et al. Identification of chemical constituents of Bufei Yishen formula by UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS. Fen Xi Ce Shi Xue Bao 2019; 38: 1-13. |
| 33. | Dantas E, Monteiro J, de Medeiros L, et al. Dereplication of Aporphine Alkaloids by UHPLC-HR-ESI-MS/MS and NMR from Duguetia lanceolata St.-Hil (Annonaceae) and antiparasitic activity evaluation. J Braz Chem Soc 2020; 31: 1908-16. |
| 34. | Chen JH, Zhang YX, Liu MH, et al. Chemical profiling of Danshen water extract by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS /MS. Guangdong Yao Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2020; 36: 1-9. |
| 35. | Ren XL, Huo JH, Sun GD, Wei WF, Wang WM. Analysis of chemical components as Coumarin in Saposhnikovia divaricata by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Zhong Guo Yao Fang 2019; 30: 349-54. |
| 36. | Liu LW, Zhou L, Sun Z, et al. Main chemical constituents research of Qishen Yiqi dropping pills based on UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS. Zhong Cao Yao 2018; 49: 5761-71. |
| 37. | Guan XY, Li HF, Yang WZ, et al. HPLC-DAD-MS(n) analysis and HPLC quantitation of chemical constituents in Xian-ling-gu-bao capsules. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2011; 55: 923-33. |
| 38. | Liu AH, Lin YH, Yang M, et al. Development of the fingerprints for the quality of the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza and its related preparations by HPLC-DAD and LC-MS(n). J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2007; 846: 32-41. |
| 39. |
Zheng L, Fang L, Cong H, et al. Identification of chemical constituents and rat metabolites of Kangxianling granule by HPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Biomed Chromatogr 2015; 29: 1750-8.
DOI PMID |
| 40. | Ma Z, Zhang M, Song Z. Characterization of tanshinones with quinone reductase induction activity from Radix Salvia miltiorrhiza by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2009; 23: 2857-66. |
| 41. | Tundis R, Deguin B, Menichini F, François T. Iridoids from Putoria calabrica. Biochem Syst Ecol 2002; 30: 689-91. |
| 42. | Matsumura T, Sankai T, Yamagishi K, et al. Impact of major cardiovascular risk factors on the incidence of cardiovascular disease among overweight and non-overweight individuals: the circulatory risk in communities study (CIRCS). J Atheroscler Thromb 2022; 29: 422-37. |
| 43. | Gaspar JC, Okine BN, Llorente-Berzal A, Roche M, Finn DP. Pharmacological blockade of PPAR isoforms increases conditioned fear responding in the presence of nociceptive tone. Molecules 2020; 25: 1007-21. |
| 44. | Hernandez-Anzaldo S, Brglez V, Hemmeryckx B, et al. Novel role for matrix metalloproteinase 9 in modulation of cholesterol metabolism. J Am Heart Assoc 2016; 5: 1-16. |
| 45. | Feingold KR, Grunfeld C. Role of cytokines in inducing hyperlipidemia. Diabetes 1992; 41: 97-101. |
| 46. | Masenga SK, Kabwe LS, Chakulya M, Kirabo A. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in metabolic syndrome. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24: 7898. |
| 47. |
Bassiouni W, Ali MAM, Schulz R. Multifunctional intracellular matrix metalloproteinases: implications in disease. FEBS J 2021; 288: 7162-82.
DOI PMID |
| 48. | Wells JM, Gaggar A, Blalock JE. MMP generated matrikines. Matrix Biol 2015; 44: 122-9. |
| 49. | Kim IS, Yang WS, Kim CH. Physiological properties, functions, and trends in the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in inflammation-mediated human diseases. Curr Med Chem 2023; 30: 2075-112. |
| 50. | Botta M, Audano M, Sahebkar A, Sirtori CR, Mitro N, Ruscica M. PPAR agonists and metabolic syndrome: an established role? Int J Mol Sci 2018; 19: 1-21. |
| 51. |
Montaigne D, Butruille L, Staels B. PPAR control of metabolism and cardiovascular functions. Nat Rev Cardiol 2021; 18: 809-23.
DOI PMID |
| 52. | Ruscica M, Busnelli M, Runfola E, Corsini A, Sirtori CR. Impact of PPAR-Alpha polymorphisms-the case of metabolic disorders and atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 1-14. |
| 53. |
Glodowski M, Christen S, Saxon DR, Hegele RA, Eckel RH. Novel PPARG mutation in multiple family members with chylomicronemia. J Clin Lipidol 2021; 15: 431-4.
DOI PMID |
| 54. | Liu J, Wang Q, Wei Y, Zhang S, Chai E, Tang F. Calpain inhibitor prevents atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice by regulating mRNA expression of genes related to cholesterol uptake and efflux. Microvasc Res 2022; 140: 104276. |
| 55. | Song Y, Li S, He C. PPAR gamma gene polymorphisms, metabolic disorders, and coronary artery disease. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022; 9: 808929. |
| 56. | Qiu Y, Wang J, Li H, et al. Emerging views of OPTN (optineurin) function in the autophagic process associated with disease. Autophagy 2022; 18: 73-85. |
| 57. |
Gawrieh S, Noureddin M, Loo N, et al. Saroglitazar, a PPAR-alpha/gamma agonist, for treatment of NAFLD: a randomized controlled double-blind phase 2 trial. Hepatology 2021; 74: 1809-24.
DOI PMID |
| 58. | Jain N, Bhansali S, Kurpad AV, et al. Effect of a dual PPAR alpha/gamma agonist on insulin sensitivity in patients of type 2 diabetes with hypertriglyceridemia- randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Sci Rep 2019; 9: 19017. |
| 59. |
Rastogi A, Dunbar RL, Thacker HP, Bhatt J, Parmar K, Parmar DV. Abrogation of postprandial triglyceridemia with dual PPAR alpha/gamma agonist in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Acta Diabetol 2020; 57: 809-18.
DOI PMID |
| 60. |
van den Boomen DJH, Volkmar N, Lehner PJ. Ubiquitin-mediated regulation of sterol homeostasis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2020; 65: 103-11.
DOI PMID |
| 61. | Williams MJ, Alsehli AM, Gartner SN, et al. The statin target hmgcr yegulates energy metabolism and food intake through central mechanisms. Cells 2022; 22: 427-37. |
| 62. |
Hosseini A, Razavi BM, Banach M, Hosseinzadeh H. Quercetin and metabolic syndrome: a review. Phytother Res 2021; 35: 5352-64.
DOI PMID |
| 63. | Yi H, Peng H, Wu X, et al. The therapeutic effects and mechanisms of Quercetin on metabolic diseases: pharmacological data and clinical evidence. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021; 2021: 1-16. |
| 64. | Chun JH, Henckel MM, Knaub LA, et al. (-)-Epicatechin improves vasoreactivity and mitochondrial respiration in thermoneutral-housed wistar rat vasculature. Nutrients 2022; 14: 1-16. |
| 65. | Hid EJ, Mosele JI, Prince PD, Fraga CG, Galleano M. (-)-Epicatechin and cardiometabolic risk factors: a focus on potential mechanisms of action. Pflugers Arch 2022; 474: 99-115. |
| 66. | Ponnian SMP. Preventive effects of (-) epicatechin on tachycardia, cardiac hypertrophy, and nuclear factor- kappa B inflammatory signaling pathway in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarcted rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2022; 924: 174909. |
| 67. | Alam W, Khan H, Shah MA, Cauli O, Saso L. Kaempferol as a dietary anti-inflammatory agent: current therapeutic standing. Molecules 2020; 25: 1-12. |
| 68. | Dabeek WM, Marra MV. Dietary Quercetin and Kaempferol: bioavailability and potential cardiovascular-related bioactivity in humans. Nutrients 2019; 11: 1-19. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

