Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 873-880.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.04.017
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Traditional Chinese herbal medicine Qingre Xiaozheng formula (清热消癥方) improves renal outcomes in patients with diabetic kidney disease: a retrospective study
SUN Weiwei1,2, ZHANG Jiale1,2, YANG Hanwen1,2, YAN Runze1,2, WEI Shuwu1,2, WU Qiaoru1,2, CUI Zhaoli1,2, ZHENG Huijuan3( ), WANG Yaoxian1,2(
), WANG Yaoxian1,2( )
)
- 1 Department of Nephrology and Endocrinology, Dongzhimen Hospital, Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
2 Renal Research Institution of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
3 Key Laboratory of Chinese Internal Medicine of Ministry of Education and Beijing, Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2024-04-22Accepted:2024-11-25Online:2025-08-15Published:2025-07-25 -
Contact:ZHENG Huijuan,WANG Yaoxian -
About author:ZHENG Huijuan, Key Laboratory of Chinese Internal Medicine of Ministry of Education and Beijing, Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China. tcmzhenghuijuan@163.com,Telephone: +86-10-84013190
Prof. WANG Yaoxian, Department of Nephrology and Endocrinology, Dongzhimen Hospital, Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China; Renal Research Institution of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China. wyx3203@sina.com;
-
Supported by:Capital Health Research and Development of Special(2016-1-4192);Beijing University of Chinese Medicine's 2022 Basic Research Business Fee Disclosure Leading Project(2022-JYB-JBZR-038)
Cite this article
SUN Weiwei, ZHANG Jiale, YANG Hanwen, YAN Runze, WEI Shuwu, WU Qiaoru, CUI Zhaoli, ZHENG Huijuan, WANG Yaoxian. Traditional Chinese herbal medicine Qingre Xiaozheng formula (清热消癥方) improves renal outcomes in patients with diabetic kidney disease: a retrospective study[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 873-880.
share this article
| Item | All Patients (n = 144) | Treatment group (n = 72) | Control group (n = 72) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex [n (%)] | Men | 100 (69.4) | 50 (50.0) | 50 (50.0) | 1.000 |
| Women | 44 (30.6) | 22 (50.0) | 22 (50.0) | ||
| Age (years) | 58.7±9.6 | 56.7±9.7 | 55.7±6.7 | 0.790 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.0±3.6 | 25.6±3.7 | 27.5±4.5 | 0.277 | |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 140.0±17.8 | 142.0±18.1 | 147.0±12.9 | 0.012 | |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 79.0±10.1 | 81.0±13.1 | 80.0±9.5 | 0.166 | |
| Course of diabetes (years) | 16.1±6.6 | 17.7±6.3 | 14.2±6.8 | 0.266 | |
| Course of proteinuria (months) | 44.1±56.2 | 42.7±50.2 | 55.0±65.9 | 0.710 | |
| Smoking [n (%)] | 70 (48.6) | 32 (45.7) | 38 (54.3) | 0.198 | |
| Drinking [n (%)] | 46 (31.9) | 20 (43.5) | 26 (56.5) | 0.284 | |
| Education [n (%)] | ≤6 years | 15 (10.4) | 7 (46.7) | 8 (53.3) | 0.632 |
| 6-12 years | 92 (63.9) | 44 (47.8) | 48 (52.2) | ||
| ≥12 years | 37 (25.7) | 21 (56.8) | 16 (43.2) | ||
| Coexisting diseases [n (%)] | Hypertension | 126 (88.7) | 62 (49.2) | 64 (50.8) | 0.596 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 107 (75.4) | 51 (47.7) | 56 (52.3) | 0.330 | |
| Hyperuricemia | 29 (20.4) | 16 (55.2) | 13 (44.8) | 0.532 | |
| Fatty liver | 44 (31.0) | 22 (50.0) | 22 (50.0) | 1.000 | |
| Coronary heart disease [n (%)] | 38 (29.0) | 15 (39.5) | 23 (60.5) | 0.110 | |
| Cerebrovascular disease [n (%)] | 27 (19.0) | 12 (44.4) | 15 (55.6) | 0.521 | |
| Albumin (g/L) | 36.6±5.5 | 32.6±5.8 | 32.8±4.7 | 0.443 | |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 22.3±15.6 | 19.6±14.6 | 21.5±10.7 | 0.947 | |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | 20.4±9.1 | 19.5±7.2 | 18.4±5.2 | 0.516 | |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 8.0±2.2 | 7.7±2.2 | 8.3±2.2 | 0.102 | |
| Glycated hemoglobin (%) | 7.0±1.0 | 6.9±1.0 | 7.1±1.0 | 0.138 | |
| eGFR (mL/min per 1.73 m2) | 71.8±26.3 | 60.0±19.0 | 58.1±23.7 | 0.129 | |
| Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 101.3±35.8 | 114.8±32.9 | 123.5±41.3 | 0.089 | |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mmol/L) | 8.5±3.5 | 9.0±2.9 | 9.7±3.7 | 0.144 | |
| Serum uric acid (μmol/L) | 376.0±103.1 | 365.2±106.9 | 386.9±98.8 | 0.207 | |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.1±1.5 | 5.0±1.4 | 5.3±1.6 | 0.273 | |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 2.9±3.1 | 2.7±1.1 | 3.3±3.5 | 0.703 | |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.9±1.0 | 3.4±1.2 | 3.5±1.3 | 0.375 | |
| 24 h total urine protein (g/24 h) | 3.3±3.1 | 6.5±2.6 | 7.1±3.3 | 0.704 | |
Table 1 Baseline characteristics between the treatment group and the control group among patients with diabetic kidney disease
| Item | All Patients (n = 144) | Treatment group (n = 72) | Control group (n = 72) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex [n (%)] | Men | 100 (69.4) | 50 (50.0) | 50 (50.0) | 1.000 |
| Women | 44 (30.6) | 22 (50.0) | 22 (50.0) | ||
| Age (years) | 58.7±9.6 | 56.7±9.7 | 55.7±6.7 | 0.790 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.0±3.6 | 25.6±3.7 | 27.5±4.5 | 0.277 | |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 140.0±17.8 | 142.0±18.1 | 147.0±12.9 | 0.012 | |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 79.0±10.1 | 81.0±13.1 | 80.0±9.5 | 0.166 | |
| Course of diabetes (years) | 16.1±6.6 | 17.7±6.3 | 14.2±6.8 | 0.266 | |
| Course of proteinuria (months) | 44.1±56.2 | 42.7±50.2 | 55.0±65.9 | 0.710 | |
| Smoking [n (%)] | 70 (48.6) | 32 (45.7) | 38 (54.3) | 0.198 | |
| Drinking [n (%)] | 46 (31.9) | 20 (43.5) | 26 (56.5) | 0.284 | |
| Education [n (%)] | ≤6 years | 15 (10.4) | 7 (46.7) | 8 (53.3) | 0.632 |
| 6-12 years | 92 (63.9) | 44 (47.8) | 48 (52.2) | ||
| ≥12 years | 37 (25.7) | 21 (56.8) | 16 (43.2) | ||
| Coexisting diseases [n (%)] | Hypertension | 126 (88.7) | 62 (49.2) | 64 (50.8) | 0.596 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 107 (75.4) | 51 (47.7) | 56 (52.3) | 0.330 | |
| Hyperuricemia | 29 (20.4) | 16 (55.2) | 13 (44.8) | 0.532 | |
| Fatty liver | 44 (31.0) | 22 (50.0) | 22 (50.0) | 1.000 | |
| Coronary heart disease [n (%)] | 38 (29.0) | 15 (39.5) | 23 (60.5) | 0.110 | |
| Cerebrovascular disease [n (%)] | 27 (19.0) | 12 (44.4) | 15 (55.6) | 0.521 | |
| Albumin (g/L) | 36.6±5.5 | 32.6±5.8 | 32.8±4.7 | 0.443 | |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 22.3±15.6 | 19.6±14.6 | 21.5±10.7 | 0.947 | |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | 20.4±9.1 | 19.5±7.2 | 18.4±5.2 | 0.516 | |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 8.0±2.2 | 7.7±2.2 | 8.3±2.2 | 0.102 | |
| Glycated hemoglobin (%) | 7.0±1.0 | 6.9±1.0 | 7.1±1.0 | 0.138 | |
| eGFR (mL/min per 1.73 m2) | 71.8±26.3 | 60.0±19.0 | 58.1±23.7 | 0.129 | |
| Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 101.3±35.8 | 114.8±32.9 | 123.5±41.3 | 0.089 | |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mmol/L) | 8.5±3.5 | 9.0±2.9 | 9.7±3.7 | 0.144 | |
| Serum uric acid (μmol/L) | 376.0±103.1 | 365.2±106.9 | 386.9±98.8 | 0.207 | |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.1±1.5 | 5.0±1.4 | 5.3±1.6 | 0.273 | |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 2.9±3.1 | 2.7±1.1 | 3.3±3.5 | 0.703 | |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.9±1.0 | 3.4±1.2 | 3.5±1.3 | 0.375 | |
| 24 h total urine protein (g/24 h) | 3.3±3.1 | 6.5±2.6 | 7.1±3.3 | 0.704 | |
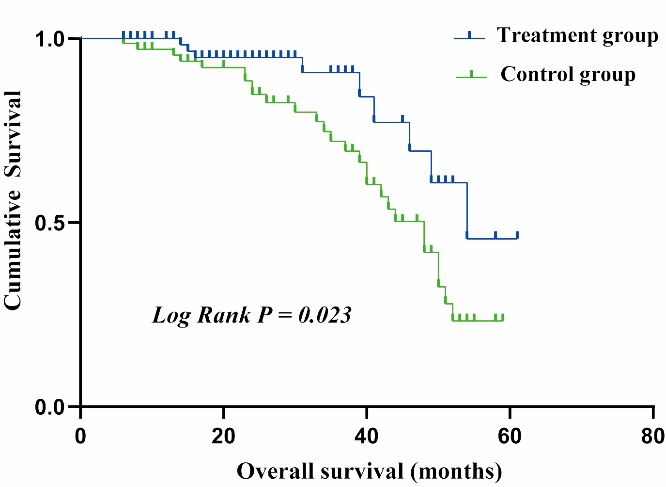
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival during follow-up in diabetic kidney disease between the treatment group and the control group (Log Rank P = 0.023) Treatment group: received conventional Western Medicine plus QRXZF (oral administration, 1 dose/day divided into 2 portions for morning and evening intake, 24-week course); Control group: received conventional Western Medicine only. QRXZF: Qingre Xiaozheng formula.
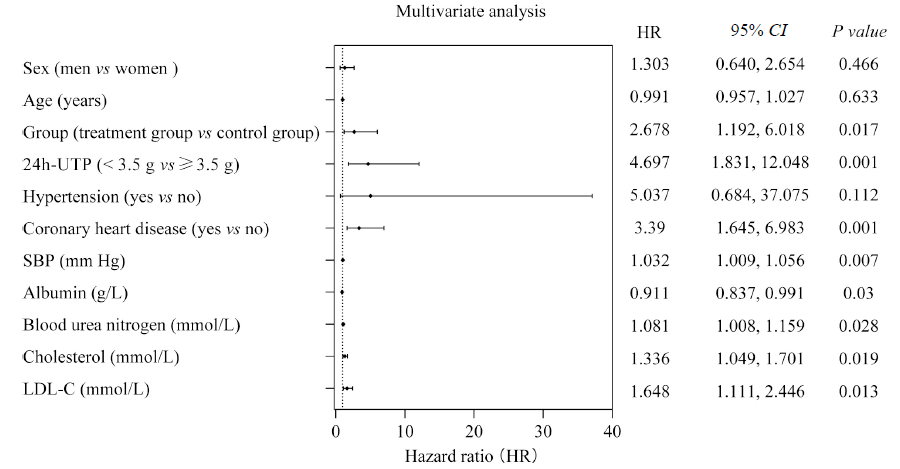
Figure 2 Forest plots of multivariate analysis of renal endpoint events Sex, age, group, 24h-UTP, coronary heart disease, SBP, albumin, blood urea nitrogen, cholesterol and LDL-C were all adjusted except the variable itself. 24h-UTP: 24 h urinary total protein; SBP: systolic blood pressure; LDL-C: low density lipoprotein cholesterol.
| Item | Treatment group (n = 23) | Control group (n = 25) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | Men | 15 (46.9) | 17 (53.1) | 0.838 |
| Women | 8 (50.0) | 8 (50.0) | ||
| Age (years) | 56.7±9.7 | 55.7±6.7 | 0.661 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.6±3.7 | 27.5±4.5 | 0.077 | |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 142.0±18.1 | 147.0±12.9 | 0.058 | |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 81.0±13.1 | 80.0±9.5 | 0.860 | |
| Course of diabetes (years) | 17.8±6.3 | 14.2±6.8 | 0.069 | |
| Course of proteinuria (months) | 42.7±50.2 | 55.0±65.9 | 0.671 | |
| Smoking [n (%)] | 11 (47.8) | 12 (52.2) | 0.308 | |
| Drinking [n (%)] | 6 (37.5) | 10 (62.5) | 0.307 | |
| Education [n (%)] | ≤6 years | 4 (57.1) | 3 (42.9) | 0.686 |
| 6-12 years | 14 (50.0) | 14 (50.0) | ||
| ≥12 years | 5 (38.5) | 8 (61.5) | ||
| Coexisting diseases [n (%)] | Hypertension | 20 (45.5) | 24 (54.5) | 0.476 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 17 (45.9) | 20 (54.1) | 0.820 | |
| Hyperuricemia | 4 (40.0) | 6 (60.0) | 0.627 | |
| Fatty liver | 3 (27.3) | 8 (72.7) | 0.138 | |
| Coronary heart disease | 7 (41.2) | 10 (58.8) | 0.565 | |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | 0.479 | |
| Albumin (g/L) | 32.6±5.8 | 32.8±4.7 | 0.891 | |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 19.6±14.6 | 21.5±10.7 | 0.292 | |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | 19.5±7.2 | 18.4±5.2 | 0.650 | |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 7.2±2.2 | 8.0±2.1 | 0.261 | |
| Glycated hemoglobin (%) | 6.6 ±1.0 | 7.0±0.9 | 0.165 | |
| eGFR (mL/min per 1.73 m2) | 60.0±19.0 | 58.1±23.7 | 0.556 | |
| Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 114.8±32.9 | 123.5±41.3 | 0.427 | |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mmol/L) | 9.0±2.9 | 9.7±3.7 | 0.520 | |
| Serum uric acid (μmol/L) | 350.3±117.5 | 371.7±129.1 | 0.529 | |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 6.0±1.3 | 5.8±1.9 | 0.536 | |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 2.7±1.1 | 3.3±3.5 | 0.726 | |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 3.4 ±1.2 | 3.5±1.3 | 0.852 | |
Table 2 Baseline characteristics of diabetic kidney disease according to albuminuria
| Item | Treatment group (n = 23) | Control group (n = 25) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | Men | 15 (46.9) | 17 (53.1) | 0.838 |
| Women | 8 (50.0) | 8 (50.0) | ||
| Age (years) | 56.7±9.7 | 55.7±6.7 | 0.661 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.6±3.7 | 27.5±4.5 | 0.077 | |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 142.0±18.1 | 147.0±12.9 | 0.058 | |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 81.0±13.1 | 80.0±9.5 | 0.860 | |
| Course of diabetes (years) | 17.8±6.3 | 14.2±6.8 | 0.069 | |
| Course of proteinuria (months) | 42.7±50.2 | 55.0±65.9 | 0.671 | |
| Smoking [n (%)] | 11 (47.8) | 12 (52.2) | 0.308 | |
| Drinking [n (%)] | 6 (37.5) | 10 (62.5) | 0.307 | |
| Education [n (%)] | ≤6 years | 4 (57.1) | 3 (42.9) | 0.686 |
| 6-12 years | 14 (50.0) | 14 (50.0) | ||
| ≥12 years | 5 (38.5) | 8 (61.5) | ||
| Coexisting diseases [n (%)] | Hypertension | 20 (45.5) | 24 (54.5) | 0.476 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 17 (45.9) | 20 (54.1) | 0.820 | |
| Hyperuricemia | 4 (40.0) | 6 (60.0) | 0.627 | |
| Fatty liver | 3 (27.3) | 8 (72.7) | 0.138 | |
| Coronary heart disease | 7 (41.2) | 10 (58.8) | 0.565 | |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | 0.479 | |
| Albumin (g/L) | 32.6±5.8 | 32.8±4.7 | 0.891 | |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 19.6±14.6 | 21.5±10.7 | 0.292 | |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | 19.5±7.2 | 18.4±5.2 | 0.650 | |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 7.2±2.2 | 8.0±2.1 | 0.261 | |
| Glycated hemoglobin (%) | 6.6 ±1.0 | 7.0±0.9 | 0.165 | |
| eGFR (mL/min per 1.73 m2) | 60.0±19.0 | 58.1±23.7 | 0.556 | |
| Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 114.8±32.9 | 123.5±41.3 | 0.427 | |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mmol/L) | 9.0±2.9 | 9.7±3.7 | 0.520 | |
| Serum uric acid (μmol/L) | 350.3±117.5 | 371.7±129.1 | 0.529 | |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 6.0±1.3 | 5.8±1.9 | 0.536 | |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 2.7±1.1 | 3.3±3.5 | 0.726 | |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 3.4 ±1.2 | 3.5±1.3 | 0.852 | |
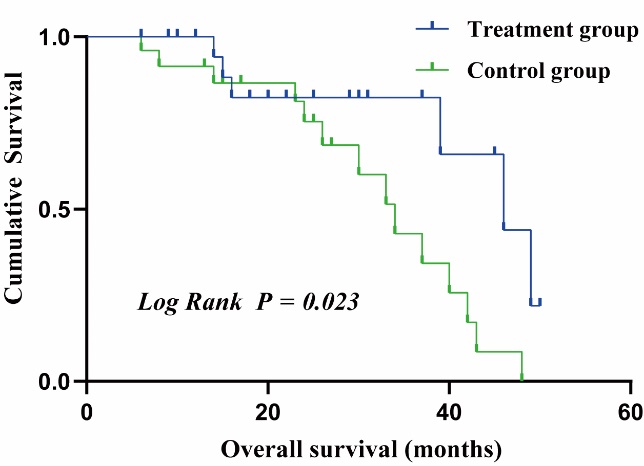
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier survival estimates during follow-up in patients with diabetic kidney disease and 24 h-urinary total protein ≥ 3.5 g, between the treatment group and the control group (Log Rank P = 0.023) Treatment group: received conventional Western Medicine plus QRXZF (oral administration, 1 dose/day divided into 2 portions for morning and evening intake, 24-week course); control group: received conventional Western Medicine only. QRXZF: Qingre Xiaozheng formula.
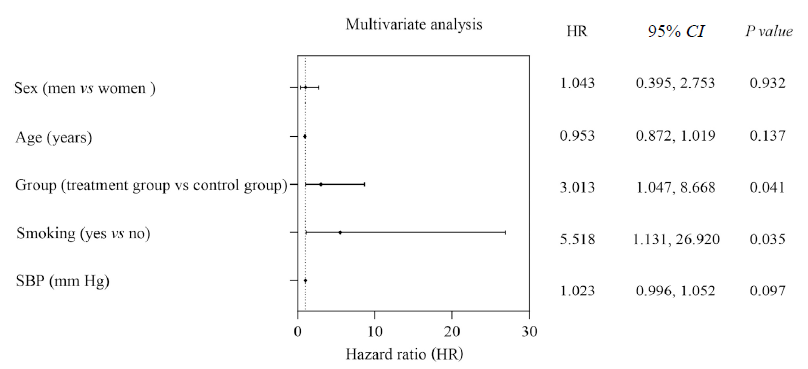
Figure 4 Forest plots of multivariate analysis of renal endpoint events for patients with diabetic kidney disease and 24 h-urinary total protein ≥3.5 g Sex, age, group, smoking, and systolic blood pressure were all adjusted except the variable itself. SBP: systolic blood pressure.
| 1. | Zhang L, Long J, Jiang W, et al. Trends in chronic kidney disease in China. N Engl J Med 2016; 375: 905-6. |
| 2. |
American Diabetes Association 11. Microvascular complications and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes care 2021; 44: S151-67.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Młynarska E, Buławska D, Czarnik W, et al. Novel insights into diabetic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci 2024; 25: 10222. |
| 4. | Miyamoto S, Heerspink HJL, de Zeeuw D, et al. A randomized, open-label, clinical trial examined the effects of canagliflozin on albuminuria and eGFR decline using an individual pre-intervention eGFR slope. Kidney Int 2024; 106: 972-84. |
| 5. |
Fadini GP, Longato E, Morieri ML, et al. Comparative renal outcomes of matched cohorts of patients with type 2 diabetes receiving SGLT2 inhibitors or GLP-1 receptor agonists under routine care. Diabetologia 2024; 67: 2585-97.
DOI PMID |
| 6. | McEwan P, Gabb PD, Davis JA, et al. The long-term effects of dapagliflozin in chronic kidney disease: a time-to-event analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2024; 39: 2040-7.. |
| 7. | Green JB, Mottl AK, Bakris G, et al. Design of the combination effect of finerenone and empagliflozin in participants with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes using a UACR Endpoint study (CONFIDENCE). Nephrol Dial Transplant 2023; 38: 894-903. |
| 8. | Zhang L, Miao R, Yu T, et al. Comparative effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and sodium glucose cotransporter inhibitors in patients with diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and network Meta-analysis. Pharmacol Res 2022; 177: 106111. |
| 9. | Wang B (Tang dynasty). Huang Di Nei Jing Su Wen. Beijing: People's Health Publishing House, 1963: 145. |
| 10. |
Wang M, Wang Z, Zhou J, et al. Effects of traditional Chinese herbal medicine in patients with diabetic kidney disease: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2018; 19: 389.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Wang YX. Thirteen forms of treatment based on pathogenesis differentiation. Beijing: Chinese Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024: 219-29. |
| 12. | Gao YB, Guo J, Miao RP, et al. Wang Yaoxian's experience in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy by clearing heat and eliminating mass. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao 2020; 39: 152-4. |
| 13. | Wang XN, Wang YX, Yan RZ, Yang HW, Sun WW, Zhou JW. Clinical observation on the treatment of middle stage diabetic kidney disease with clearing heat and dispersing mass therapy. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao 2020; 35: 5873-6. |
| 14. | Wang MD, Liu MC, Zhao WJ, Zhou JW, Wang YX. Improvement of proteinuria and effects on serum sTNFR1 and sTNFR2 in patients with diabetic kidney disease by Qingre Xiaozheng formula. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao 2022; 37: 6183-8. |
| 15. | Wang YJ, Wang J, Zhou JW. Effect of Qingre Xiaozheng formula on improving renal injury in a rat model of diabetic kidney disease. Zhong Guo Quan Ke Yi Xue 2022; 25: 3678-85. |
| 16. | Wu Q, Yan R, Yang H, et al. Qing-Re-Xiao-Zheng-Yi-Qi formula relieves kidney damage and activates mitophagy in diabetic kidney disease. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 992597. |
| 17. | Chinese Diabetes Society. The consensus for prevention and treatment of diabetic kidney disease 2014. Zhong Hua Tang Niao Bing 2014; 6: 792-801. |
| 18. | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease Kidney Int Suppl 2013; 31: 1-150. |
| 19. |
Mogensen CE. Early renal involvement and nephropathy. Can treatment modalities be predicted from identification of risk factors in diabetics? Toxicol Lett 1989; 46: 213-26.
PMID |
| 20. |
Mogensen CE, Schmitz A, Christensen CK. Comparative renal pathophysiology relevant to IDDM and NIDDM patients. Diabetes Metab Rev 1988; 4: 453-83.
PMID |
| 21. | The Diabetic Kidney Disease Group of Endocrine Committee of Chinese Association of Integrative Medicine and Chinese Medicine and Microcirculation Committee of the Chinese Society of Microcirculation. Expert consensus on the prevention and treatment of diabetic kidney disease with the integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine (2023 edition). Zhong Hua Tang Niao Bing 2023; 15: 690-702. |
| 22. | Chen DQ, Wu J, Li P. Therapeutic mechanism and clinical application of Chinese herbal medicine against diabetic kidney disease. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 1055296. |
| 23. | Chen HY, Pan HC, Chen YC, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine use is associated with lower end-stage renal disease and mortality rates among patients with diabetic nephropathy: a population-based cohort study. BMC Complement Altern Med 2019; 19: 81. |
| 24. | Guo JC, Pan HC, Yeh BY, et al. Associations between using Chinese herbal medicine and long-term outcome among pre-dialysis diabetic nephropathy patients: a retrospective population-based cohort study. Front Pharmacol 2021; 12: 616522. |
| 25. | Liu J, Zhang X, Xu G. Clinical efficacy, safety, and cost of nine Chinese patent medicines combined with ACEI/ARB in the treatment of early diabetic kidney disease: a network meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 939488. |
| 26. | Zhang W, Zhou J, Wang C, et al. Efficacy and safety of Keluoxin capsule in combination with Western Medicine for diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol 2023; 13: 1052852. |
| 27. | Li W, Xia P, Sun W, et al. Effects of the Huangkui capsule on chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2023; 43: 6-13. |
| 28. | Wu C, Tang H, Cui X, et al. A single-cell profile reveals the transcriptional regulation responded for Abelmoschus manihot (L.) treatment in diabetic kidney disease. Phytomedicine 2024; 130: 155642. |
| 29. | Chan KW, Kwong ASK, Tsui PN, et al. Add-on astragalus in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a multi-center, assessor-blind, randomized controlled trial. Phytomedicine 2024; 130: 155457. |
| 30. | Gao Y, Su X, Xue T, Zhang N. The beneficial effects of astragaloside IV on ameliorating diabetic kidney disease. Biomed Pharmacother 2023; 163: 114598. |
| 31. |
Zhong Y, Lee K, Deng Y, et al. Arctigenin attenuates diabetic kidney disease through the activation of PP2A in podocytes. Nat Commun 2019; 10: 4523.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Zhang J, Li Y, Zhang F, et al. Hirudin delays the progression of diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting glomerular endothelial cell migration and abnormal angiogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother 2024; 179: 117300. |
| 33. | Long C, Zhang C, Xie Y. Study on the mechanism of hirudin multi target delaying renal function decline in chronic kidney disease based on the "gut-kidney axis" theory. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2024; 397: 7951-62. |
| [1] | XU Bojun, TAO Tian, ZHAO Liangbin, ZHENG Hui, ZHAN huakui, GUO Julan. Bushen Tongluo recipe (补肾通络方) improves oxidative stress homeostasis, inhibits transforming growth factor/Notch signaling pathway, and regulates the lncRNA maternally expressed gene 3/miR-145 axis to delay diabetic kidney disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 561-570. |
| [2] | YUAN Jiayao, WU Suhui, MENG Yufan, LI Hanbing, LI Genlin, XU Jiangyan. Yishen Tongluo formula (益肾通络方) ameliorates kidney injury via modulating inflammation and apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic kidney disease mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 254-265. |
| [3] | QU Weiying, TAN Xyucheng, ZHAO Yihan, YU Yanan, ZHAO Lin. Effect of add-on therapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine on the survival of patients with anemic lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes in the real-world setting: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 152-159. |
| [4] | SU Rui, SU Youzhu, WANG Shuo, FAN Jie, LIU Qingquan, LIU Mifeng. A real-world study of the differences in Traditional Chinese Medicine diagnosis and treatment rules for coronavirus disease 2019 between Northern and Southern China [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 822-829. |
| [5] | LI Shuang, DUAN Shuwei, DONG Zheyi, QU Yilun, LUO Yayong, KE Jianghua, WANG Conghui, PENG Yangzhi, ZHOU Xuefeng, CHEN Xiangmei. Distribution of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes in diabetic kidney disease chronic kidney disease 1-5: a correlation study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 572-580. |
| [6] | WANG Yuhuang, ZHANG Le, ZHANG Zhengshan, YAO Zhi, LI Xiyao, SUN Luying, LIAO Xing. Characteristics and quality of clinical practice guidelines for diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 609-619. |
| [7] | HUANG Hongmei, YANG Maojun, LI Ting, WANG Dandan, LI Ying, TANG Xiaochi, YUAN Lu, GU Shi, XU Yong. Neferine inhibits the progression of diabetic nephropathy by modulating the miR-17-5p/nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 axis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 44-53. |
| [8] | XU Guihua, CHEN Feifei, ZHANG Wei, WU Yingen, CHEN Xiaorong, SHI Kehua, WANG Zhenwei, SHI Miaoyan, ZHANG Xing, LU Yunfei, YUAN Weian, LYU Hua, CHEN Xuan. Effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine on coronavirus disease 2019 in 92 patients: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 582-587. |
| [9] | QU Yilun, CHENG Haimei, WANG Qian, LI Shuang, DUAN Shuwei, FENG Zhe, LI Weizhen, JIANG Shuangshuang, YANG Hongtao, MAO Yonghui, GENG Yanqiu, LI Jijun, LIU Yuning, TIAN Jinzhou, LIU Hongfang, DONG Zheyi, CHEN Xiangmei. Noninvasive identificational diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy and non-diabetic renal disease based on clinical characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine symptom pattern and conventional medicine [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 588-593. |
| [10] | XIE Jing, BI Zheng, WANG Sihai, SHEN Guoming, FANG Zhaohui. Danzhi Jiangtang capsule (丹蛭降糖胶囊) reduces renal injury in rats with diabetes induced by high fat diet and streptozotocin via downregulating toll-like receptor 4-nuclear factor-κB pathway and apoptosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 312-321. |
| [11] | GUO Yangzhi, DU Juan, JIANG Min, GUO Wei. Full composition granules of Huanglian (Rhizoma Coptidis) decrease the serum monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and connective tissue growth factor levels and inhibit kidney nuclear factor-κB expression in rats with high-fat diet-induced diabetes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 424-431. |
| [12] | HAN Jiarui, ZHANG Yage, SHI Xiujie, PENG Zining, XING Yufeng, PANG Xinxin. Tongluo Digui decoction(通络地龟汤) treats renal injury in diabetic rats by promoting autophagy of podocytes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(1): 125-132. |
| [13] | Xia Xichao, Mao Dongxue, Dai Hongmei, Wu Xi, Zhang Zuyuan, Wang Huaying, Zhou Wenwen, Dong Yanmei, Wang Mengqi, Li Yuan, Shao Xiangyang, Ouyang Jingfeng. Effect of Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharides on streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(6): 956-964. |
| [14] | Wang Lei, Li Xiu, Zhou Rongyao, Shan Yawei. Effect of Bushen Jianpi formula on survival of patients with moderate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(4): 683-689. |
| [15] | Sun Yuying, Tan Yong, Chen Shuping. Effectiveness of nourishing Yin and tonifying Yang sequential therapy in combination with Climen on diminished ovarian reserve: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(1): 150-156. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

