Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 152-159.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.01.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of add-on therapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine on the survival of patients with anemic lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes in the real-world setting: a retrospective study
QU Weiying1, TAN Xyucheng1, ZHAO Yihan1, YU Yanan2( ), ZHAO Lin3(
), ZHAO Lin3( )
)
- 1 Department of Hematology, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200120, China
2 Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
3 Department of Hematology and CHEN Jianjie National Famous Old Chinese Medicine Expert Inheritance Studio, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200120, China
-
Received:2023-06-16Accepted:2023-12-23Online:2025-02-15Published:2025-01-10 -
Contact:ZHAO Lin, Department of Hematology, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200120, China; CHEN Jianjie National Famous Old Chinese Medicine Expert Inheritance Studio, Shanghai 200120, China.sg1520@shutcm.edu.cn ; YU Yanan, Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China.yyn433@sina.com Telephone: +86-21-53827352 -
Supported by:China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences Innovation Fund: Precise Positioning Decision-making Platform for Clinical Trials of Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on Predicition Model(CI2021A04707);The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Public Welfare Research Institutes: Research on Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Differentiation-based a Bayesian Decision Model of Basket Trial(ZZ13-YQ-076);The Fifth Batch of National TCM Clinical Outstanding Talent Training Program. The Fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Science Foundation Project): Effect of Compound Shenlu Granule on Apoptosis of CD34+ Cells in Lower-risk Myelodysplastic Syndromes Bone Marrow based on p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Pathway(81403233)
Cite this article
QU Weiying, TAN Xyucheng, ZHAO Yihan, YU Yanan, ZHAO Lin. Effect of add-on therapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine on the survival of patients with anemic lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes in the real-world setting: a retrospective study[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 152-159.
share this article

Figure 1 Flowchart of patient recruitment for the current study LR-MDS: lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes; IPSS-R: International Prognostic Scoring System and its revised version; Hb: hemoglobin; TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine.
| Characteristic | TCM group (n = 78) | Non-TCM group (n = 84) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years, median) | 51 (18, 80) | 55 (20, 80) | 0.204 | |
| Sex [n (%)] | Male | 38 (48.72) | 37 (44.05) | 0.989 |
| Female | 40 (51.28) | 47 (55.95) | ||
| WHO Classification at diagnosis [n (%)] | RA | 7 (8.97) | 10 (11.90) | 0.843 |
| RARS | 4 (5.13) | 6 (7.14) | ||
| RCMD | 57 (73.08) | 62 (73.81) | ||
| EB-1 | 4 (5.13) | 3 (3.57) | ||
| U | 2 (2.56) | 3 (3.57) | ||
| Chromosomal abnormalities [n (%)] | 17 (21.79) | 13 (15.48) | 0.319 | |
| IPSS at diagnosis [n (%)] | Low | 10 (12.82) | 14 (16.67) | 0.108 |
| Intermediate-1 | 68(87.18) | 70 (83.33) | ||
| IPSS-R at diagnosis [n (%)] | Very low/low | 38 (48.71) | 40 (47.62) | 1.000 |
| Intermediate | 40 (51.28) | 44 (52.38) | ||
| Peripheral blood at onset of treatment | Hb (g/L, median) | 69 (31,99) | 69 (40,99) | 0.262 |
| ANC (×109/L, median) | 1.56 (0.42, 4.5) | 1.62 (0.1, 9.18) | 0.167 | |
| Platelets (×109/L, median) | 30 (3, 358) | 49 (3, 410) | 0.630 | |
| Transfusion dependence at onset of treatment [n (%)] | 37 (47.44) | 48 (57.14) | 0.271 | |
| Western medical treatment [n (%)] | Androgens | 33 (42.31) | 28 (33.33) | 0.259 |
| Androgens+epoetin alfa | 12 (15.38) | 20 (23.81) | 0.236 | |
| Androgens+CsA | 30 (38.46) | 32 (38.10) | 0.100 | |
| Androgens+others | 3 (3.85) | 4 (4.76) | 0.100 | |
| Time of TCM administration (month, median) | 12 (3, 120) | NA | NA | |
Table 1 Comparisons of characteristics
| Characteristic | TCM group (n = 78) | Non-TCM group (n = 84) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years, median) | 51 (18, 80) | 55 (20, 80) | 0.204 | |
| Sex [n (%)] | Male | 38 (48.72) | 37 (44.05) | 0.989 |
| Female | 40 (51.28) | 47 (55.95) | ||
| WHO Classification at diagnosis [n (%)] | RA | 7 (8.97) | 10 (11.90) | 0.843 |
| RARS | 4 (5.13) | 6 (7.14) | ||
| RCMD | 57 (73.08) | 62 (73.81) | ||
| EB-1 | 4 (5.13) | 3 (3.57) | ||
| U | 2 (2.56) | 3 (3.57) | ||
| Chromosomal abnormalities [n (%)] | 17 (21.79) | 13 (15.48) | 0.319 | |
| IPSS at diagnosis [n (%)] | Low | 10 (12.82) | 14 (16.67) | 0.108 |
| Intermediate-1 | 68(87.18) | 70 (83.33) | ||
| IPSS-R at diagnosis [n (%)] | Very low/low | 38 (48.71) | 40 (47.62) | 1.000 |
| Intermediate | 40 (51.28) | 44 (52.38) | ||
| Peripheral blood at onset of treatment | Hb (g/L, median) | 69 (31,99) | 69 (40,99) | 0.262 |
| ANC (×109/L, median) | 1.56 (0.42, 4.5) | 1.62 (0.1, 9.18) | 0.167 | |
| Platelets (×109/L, median) | 30 (3, 358) | 49 (3, 410) | 0.630 | |
| Transfusion dependence at onset of treatment [n (%)] | 37 (47.44) | 48 (57.14) | 0.271 | |
| Western medical treatment [n (%)] | Androgens | 33 (42.31) | 28 (33.33) | 0.259 |
| Androgens+epoetin alfa | 12 (15.38) | 20 (23.81) | 0.236 | |
| Androgens+CsA | 30 (38.46) | 32 (38.10) | 0.100 | |
| Androgens+others | 3 (3.85) | 4 (4.76) | 0.100 | |
| Time of TCM administration (month, median) | 12 (3, 120) | NA | NA | |
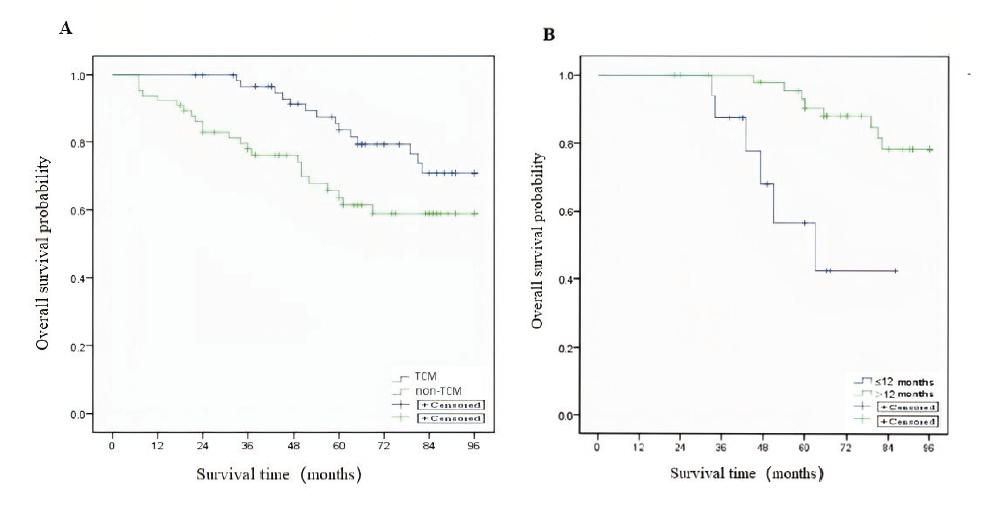
Figure 2 OS from the TCM group and non-TCM group A: Kaplan-Meier estimates of OS from the TCM and non-TCM group [HR = 0.484, 95% CI (0.249, 0.942), P = 0.029]; B: Kaplan-Meier estimates of OS from 2 group of patients: group: treaated with TCM ≤ 12 months and treated with TCM > 12 months [(log-rank P < 0.001, HR = 0.166, 95% CI (0.055, 0.508)]. TCM group: treated with combination of TCM (≥ 3 months) and Western Medicine, Non-TCM group: treated with Western Medicine alone. OS: overall survival; TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval.
| Variable | TCM group (n = 78) | Non-TCM group (n = 84) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Events [n (%)] | Death | 18 (23.08) | 31 (36.90) |
| Censor | 60 (76.92) | 53 (63.10) | |
| Survival rate [% (95% CI)] | 3 years | 96.7 (92.2, 100) | 77.9 (67.7, 88.1) |
| 5 years | 83.5 (73.7, 93.3) | 63.7 (51.0, 76.4) | |
| 7 years | 70.8 (57.5, 84.1) | 58.9 (45.6, 72.2) | |
Table 2 Comparisons of survival analysis
| Variable | TCM group (n = 78) | Non-TCM group (n = 84) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Events [n (%)] | Death | 18 (23.08) | 31 (36.90) |
| Censor | 60 (76.92) | 53 (63.10) | |
| Survival rate [% (95% CI)] | 3 years | 96.7 (92.2, 100) | 77.9 (67.7, 88.1) |
| 5 years | 83.5 (73.7, 93.3) | 63.7 (51.0, 76.4) | |
| 7 years | 70.8 (57.5, 84.1) | 58.9 (45.6, 72.2) | |
| Variable | Univariate analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | |
| Gender (female vs male) | 1.091 (0.573, 2.08) | 0.790 |
| Age (≤50 vs >50) | 1.386 (0.719, 2.672) | 0.329 |
| Interval from diagnosis to onset of therapy | 1.000 (0.997, 1.004) | 0.821 |
| IPSS-R (≤3 vs >3) | 1.285 (0.661, 2.498) | 0.459 |
| Hb (g/dL) (≤60 vs >60) | 0.938 (0.483, 1.823) | 0.851 |
| Transfusion dependence at onset of treatment (Yes vs No) | 1.616 (0.832, 3.142) | 0.157 |
| Androgens+TCM [n (%)] | 0.772 (0.393, 1.518) | 0.454 |
| Androgens+epoetin alfa [n (%)] | 0.413 (0.153, 1.408) | 0.219 |
| Androgens+CsA [n (%)] | 0.771 (0.399, 1.49) | 0.440 |
| TCM group vs non-TCM group | 0.484 (0.249, 0.942) | 0.033 |
Table 3 Cox proportional hazards model analysis predictors for overall survival
| Variable | Univariate analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | |
| Gender (female vs male) | 1.091 (0.573, 2.08) | 0.790 |
| Age (≤50 vs >50) | 1.386 (0.719, 2.672) | 0.329 |
| Interval from diagnosis to onset of therapy | 1.000 (0.997, 1.004) | 0.821 |
| IPSS-R (≤3 vs >3) | 1.285 (0.661, 2.498) | 0.459 |
| Hb (g/dL) (≤60 vs >60) | 0.938 (0.483, 1.823) | 0.851 |
| Transfusion dependence at onset of treatment (Yes vs No) | 1.616 (0.832, 3.142) | 0.157 |
| Androgens+TCM [n (%)] | 0.772 (0.393, 1.518) | 0.454 |
| Androgens+epoetin alfa [n (%)] | 0.413 (0.153, 1.408) | 0.219 |
| Androgens+CsA [n (%)] | 0.771 (0.399, 1.49) | 0.440 |
| TCM group vs non-TCM group | 0.484 (0.249, 0.942) | 0.033 |
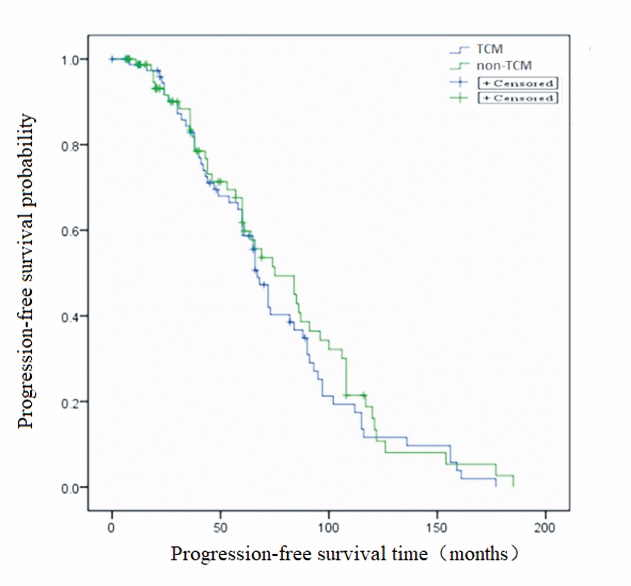
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier estimates of PFS from the TCM and non-TCM group (log-rank P = 0.426) PFS: progression-free survival; TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine.
| Variable | TCM group (n = 78) | Non-TCM group (n = 84) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| HI-E [n (%)] | 54/78 (69.23) | 44/84 (52.38) | 0.028 |
| HI-N [n (%)] | 10/78 (12.82) | 8/84 (9.52) | 0.505 |
| HI-P [n (%)] | 27/78 (34.62) | 22/84 (26.19) | 0.243 |
| HI-E maintenance (months) | 36 (2, 173) | 36 (2, 152) | 0.439 |
| Progress after HI-E [n (%)] | 25/54 (46.30) | 22/44 (50.00) | 0.521 |
| RBC-TI [n (%)] | 18/37 (48.65) | 22/48 (45.83) | 0.877 |
Table 4 Comparisons of HI
| Variable | TCM group (n = 78) | Non-TCM group (n = 84) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| HI-E [n (%)] | 54/78 (69.23) | 44/84 (52.38) | 0.028 |
| HI-N [n (%)] | 10/78 (12.82) | 8/84 (9.52) | 0.505 |
| HI-P [n (%)] | 27/78 (34.62) | 22/84 (26.19) | 0.243 |
| HI-E maintenance (months) | 36 (2, 173) | 36 (2, 152) | 0.439 |
| Progress after HI-E [n (%)] | 25/54 (46.30) | 22/44 (50.00) | 0.521 |
| RBC-TI [n (%)] | 18/37 (48.65) | 22/48 (45.83) | 0.877 |
| Latin name | Chinese name | Number of patients [n (%)] | Common dosage for patients (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radix Codonopsis | Dangshen | 74 (94.87) | 10-15 |
| Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae | Baizhu | 71 (91.03) | 10-15 |
| Poria | Fuling | 70 (89.74) | 10-15 |
| Radix Astragali Mongolici | Huangqi | 63 (80.77) | 15-30 |
| Radix Angelicae Sinensis | Danggui | 52 (66.67) | 10-15 |
| Cornu Cervi Elaphi | Lujiao | 46 (58.97) | 10-15 |
| Carapax et Plastrum Testudinis | Guijia | 46 (58.97) | 10-15 |
| Semen Cuscutae | Tusizi | 44 (56.41) | 15-20 |
| Radix Rehmanniae Praeparata | Shudihuang | 42 (53.85) | 10-15 |
| Fructus Psoraleae | Buguzhi | 39 (50.00) | 10-15 |
Table 5 Ten most common herbs prescribed for patients with LR-MDS
| Latin name | Chinese name | Number of patients [n (%)] | Common dosage for patients (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radix Codonopsis | Dangshen | 74 (94.87) | 10-15 |
| Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae | Baizhu | 71 (91.03) | 10-15 |
| Poria | Fuling | 70 (89.74) | 10-15 |
| Radix Astragali Mongolici | Huangqi | 63 (80.77) | 15-30 |
| Radix Angelicae Sinensis | Danggui | 52 (66.67) | 10-15 |
| Cornu Cervi Elaphi | Lujiao | 46 (58.97) | 10-15 |
| Carapax et Plastrum Testudinis | Guijia | 46 (58.97) | 10-15 |
| Semen Cuscutae | Tusizi | 44 (56.41) | 15-20 |
| Radix Rehmanniae Praeparata | Shudihuang | 42 (53.85) | 10-15 |
| Fructus Psoraleae | Buguzhi | 39 (50.00) | 10-15 |
| 1. |
Zeidan AM, Linhares Y, Gore SD. Current therapy of myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood Rev 2013; 27: 243-59.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Bejar R, Steensma DP. Recent developments in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2014; 124: 2793-803.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Fenaux P, Adès L. How we treat lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2013; 121: 4280-286.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Hiwase DK, Kutyna MM, Chhetri R. Transfusion dependency is associated with inferior survival even in very low and low risk IPSS-R patients. Blood 2013; 122: 1518. |
| 5. | Merz A, Germing U, Kobbe G, et al. EASIX for prediction of survival in lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood Cancer 2019; 9: 85. |
| 6. |
Carraway HE, Saygin C. Therapy for lower-risk MDS. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2020; 2020: 426-33.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Santini V, Almeida A, Giagounidis A, et al. A randomized phase Ⅲ study of lenalidomide versus placebo in RBC transfusion-dependent patients with lower-risk non-del(5q) myelodysplastic syndromes and ineligible for or refractory to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents. J Clin Oncol 2016; 34: 2988-96. |
| 8. |
Toma A, Kosmider O, Chevret S, et al. Lenalidomide with or without erythropoietin in transfusion-dependent erythropoiesis-stimulating agent-refractory lower-risk MDS without 5q deletion. Leukemia 2016; 30: 897-905.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Shenoy N, Vallumsetla N, Rachmilewitz E, Verma A, Ginzburg Y. Impact of iron overload and potential benefit from iron chelation in low-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2014; 124: 873-81.
DOI PMID |
| 10. | Zhao MM, Zhang Y, Li LS, Zi KY, Bo L. Efficacy and safety of Danggui Buxue Decoction in combination with western medicine treatment of anemia for renal anemia: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Ann Transl Med 2017; 5: 136-44. |
| 11. |
Yang M, Chan GC, Deng R, et al. An herbal decoction of Radix Astragali and Radix Angelicae sinensis promotes hematopoiesis and thrombopoiesis. J Ethnopharmacol 2009; 124: 87-97.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Linn YC, Lu J, Lim LC, Sun H, Sun J, Zhou YM. Traditional Chinese herbal medicine in the supportive management of patients with chronic cytopaenic marrow diseases e A phase Ⅰ/Ⅱ clinical study. Complement Ther Clin Pract 2011; 17: 152-6. |
| 13. | Sun SZ, Ma R, Hu XM, et al. Karyotype and DNA-methylation responses in myelodysplastic syndromes following treatment with traditional Chinese formula containing arsenic. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012: 2012: 969476. |
| 14. | Vardiman J. The classification of MDS: from FAB to WHO and beyond. Leuk Res 2012; 36: 1453-8. |
| 15. |
Cheson BD, Greenberg PL, Bennett JM, et al. Clinical application and proposal for modification of the International Working Group (IWG) response criteria in myelodysplasia. Blood 2006; 108: 419-25.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Volpe VO, Komrokji RS. Treatment options for lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Where are we now? Ther Adv Hematol 2021: 12: 2040620720986641. |
| 17. | Expert Committee on Myelodysplastic Syndromes of Hematology Committee of China Association of Integrative Medicine. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of Myelodysplastic Syndrome with Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. Chin J Integrated Tradit Chin West Med 2018; 038: 914-20. |
| 18. | Liu X, Wang P, Xia YY, et al. Observation on the efficacy of low-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in the adjuvant treatment of kidney and spleen. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2015; 33: 3680-2. |
| 19. | Shen XH, Sun WL, Bao JZ, et al. Clinical observation on the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome in the detoxification of spleen and kidney tonifying. Shanghai Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2012; 26: 34-7. |
| 20. |
Fenaux P, Ades L. How we treat lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2013; 121: 4280-6.
DOI PMID |
| 21. | Steensma DP. Graphical representation of clinical outcomes for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Lymphoma 2016; 57: 17-20. |
| 22. | Anna WG, Krzysztof M, Rafał M, et al. Red blood cell transfusion dependency and hyperferritinemia are associated with impaired survival in patients diagnosed with myelodysplastic syndromes: results from the first polish MDS-PALG registry. Adv Clin Exp Med 2016; 25: 633-41. |
| 23. |
Mayra BL, Sarah RR, Thomas S, Kulasekararaj AG, Matos JE, Tang D. Association between red blood cell transfusion dependence and burden in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: a systematic literature review and Meta-analysis. Eur J Haematol 2021; 107: 3-23.
DOI PMID |
| 24. | Harnan S, Ren S, Gomersall T, et al. Association between transfusion status and overall aurvival in patients with myelodysplastic ayndromes: a systematic literature review and Meta-analysis. Acta Haematol 2016; 136: 23-42. |
| 25. |
Platzbecker U, Symeonidis A, Oliva EN, et al. A phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trial of darbepoetin alfa in patients with anemia and lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2017; 31: 1944-50.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Fenaux P, Santini V, Spiriti MAA, et al. A phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled study assessing the efficacy and safety of epoetin-alpha in anemic patients with low-risk MDS. Leukemia 2018; 32: 2648-58. |
| 27. | Wang DX, Xu YG, Du Y, et al. Arsenic concentration in peripheral blood is correlated with efficacy of a Traditional Chinese Medicine regimen containing realgar for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome. J Tradit Chin Med 2021; 41: 630-5. |
| 28. | Chen WD, Huang HS, Su YC, et al. The characteristics and prescription patterns of Chinese herbal medicine in clinical practice for the treatment of anemia. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2018; 57: 570-7. |
| 29. | Dang ZB, Liu XL, Wang XH, et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine supporting Qi and enriching blood for cancer related anemia in patients not receiving chemoradiotherapy: a Meta-analysis and systematic review. Drug Des Devel Ther 2019; 13: 221-30. |
| 30. | Yang FX, Wang Y, Xia PF, et al. Review of chemical constituents,pharmacological effects and clinical applications of Danggui Buxue decoction and prediction and analysis of its Q-markers. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2021; 46: 2677-85. |
| 31. | Hu X, Lu H, Deng YL, Wan Q, Yie SM. Effect of rat medicated serum containing Zuo Gui Wan and/or You Gui Wan on the differentiation of stem cells derived from human first trimester umbilical cord into oocyte-like cells in vitro. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015; Article ID 825805. |
| 32. | Huang JJ, Dai D, Shen XH. Study on the mechanism of Astragalus dangshen in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome based on network pharmacology. Zhong Yi Lin Chuang Yan Jiu 2021; 13: 6. |
| 33. |
Zheng KY, Choi RC, Xie HQ, et al. The expression of erythropoietin triggered by Danggui Buxue Tang, a Chinese herbal decoction prepared from Radix Astragali and Radix Angelicae Sinensis, is mediated by the hypoxia-inducible factor in cultured HEK293T cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2010; 132: 259-67.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Gao QT, Cheung JK, Choi RC, et al. A Chinese herbal decoction prepared from Radix Astragali and Radix Angelicae Sinensis induces the expression of erythropoietin in cultured Hep3B cells. Planta Med 2008; 74: 392-5. |
| 35. | Huang GC, Chen SY, Tsai PW, et al. Effects of Dang-GuiBu-Xue-Tang, an herbal decoction, on iron uptake in iron-deficient anemia. Drug Des Dev Ther 2016; 10: 949-57. |
| 36. |
Yang X, Huang CG, Du SY, et al. Effect of Danggui Buxue Tang on immune-mediated aplastic anemia bone marrow proliferation mice. Phytomedicine 2014; 21: 640-6.
DOI PMID |
| 37. | Choi EJ, Lee JH, Park HS, et al. Androgen therapy for patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndrome and significant cytopenia: a retrospective study. Br J Haematol 2019; 187: e4-7. |
| 38. | Copley GB, Schnatter AR, Armstrong TW, et al. Hospital-Based case-control study of MDS subtypes and benzene exposure in Shanghai. J Occup Environ Med 2017; 59: 349-55. |
| 39. | Lee YJ, Park SW, Lee IH, et al. Report on outcomes of hypomethylating therapy for analyzing prognostic value of Revised International Prognostic Scoring System for patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Ann Hematol 2016; 95: 1795-804. |
| [1] | SU Rui, SU Youzhu, WANG Shuo, FAN Jie, LIU Qingquan, LIU Mifeng. A real-world study of the differences in Traditional Chinese Medicine diagnosis and treatment rules for coronavirus disease 2019 between Northern and Southern China [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 822-829. |
| [2] | XU Guihua, CHEN Feifei, ZHANG Wei, WU Yingen, CHEN Xiaorong, SHI Kehua, WANG Zhenwei, SHI Miaoyan, ZHANG Xing, LU Yunfei, YUAN Weian, LYU Hua, CHEN Xuan. Effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine on coronavirus disease 2019 in 92 patients: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 582-587. |
| [3] | Wang Lei, Li Xiu, Zhou Rongyao, Shan Yawei. Effect of Bushen Jianpi formula on survival of patients with moderate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(4): 683-689. |
| [4] | Sun Yuying, Tan Yong, Chen Shuping. Effectiveness of nourishing Yin and tonifying Yang sequential therapy in combination with Climen on diminished ovarian reserve: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(1): 150-156. |
| [5] | Sun Yan, Chen Hai, Wu Chengyan. Effect of the medication injection site on treatment efficacy in pediatric cerebral palsy: conventional sites vs acupoints [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(05): 716-721. |
| [6] | Pang Bing, Guo Jing, Zhao Linhua, Zhao Xiyan, Zhou Qiang, Tong Xiaolin. Retrospective study of Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(03): 307-313. |
| [7] | Yantao Jin, Zhibin Liu, Xiumin Chen, Xin Wang, Dan Wang, Ziqiang Jiang, Ying Liu, Jian Wang, Wen Zou, Huijun Guo, Liran Xu. Survival of people living with HIV after treatment with Traditional Chinese Medicine in Henan province of China: a retrospective cohortstudy [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014, 34(04): 430-436. |
| [8] | Quanfang Chen, Wei Wang, Qibin Li, Yulong Bai, Xiaoying Zou, Yanbin Wu. Effect of externally applied Jidesheng anti-venom on skin and soft-tissue necrosis after Chinese cobra bite: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014, 34(02): 150-154. |
| [9] | Zhibin Liu, Jiping Yang, Huijuan Liu, Yantao Jin. Factors associated with fatigue in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with antiretroviral drug adverse reactions: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(03): 316-321. |
| [10] | Kelei Su, Fangshi Zhu, Lizhong Guo, Yao Zhu, Wenlin Li, Xingjiang Xiong. Retrospective study on Professor Zhongying Zhou's experience in Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment on diabetic nephropathy [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(02): 262-267. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

