Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 65-72.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20210624.001
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shugan Huoxue Huayu Fang (疏肝活血化瘀方) attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats by inhibiting transforming growth factor-β1/Smad signaling
Lei LIU1, Hanbin GUO1, Cuiping SHAO1, Lin WANG1, Youqing XU1( ), Yiming ZHOU2(
), Yiming ZHOU2( )
)
- 1 Department of Gastroenterology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100070, China
2 Department of Hepatology, the seventh medical center of the People's Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2021-03-09Accepted:2021-05-07Online:2022-02-15Published:2021-06-24 -
Contact:Youqing XU,Yiming ZHOU -
About author:ZHOU Yiming, Department of Hepatology, the seventh medical center of the People's Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing 100700, China. zhzhym2006 @163.com
XU Youqing, Department of Gastroenterology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100070, China. youqingxuttyy@163.com;
-
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Study on the Anti-Liver Fibrosis Mechanism of Shugan Huoxue Huayu Fang Based on miRNA-146a Regulating TGF-β/Smads Signaling Pathway)(81373538);National Natural Science Foundation of China (Role of Intracellular Endocytosis of Tight Junction Protein in Intestinal Leakage in Alcoholic Liver Disease)(81570536)
Cite this article
Lei LIU, Hanbin GUO, Cuiping SHAO, Lin WANG, Youqing XU, Yiming ZHOU. Shugan Huoxue Huayu Fang (疏肝活血化瘀方) attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats by inhibiting transforming growth factor-β1/Smad signaling[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 65-72.
share this article
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| α-SMA | 5′-CCGAGATCCL4ACCGACTACC-3' | 5′-TCCAGAGCGACATAGCACAG-3' |
| TGF-β1 | 5'-CA CCAT CCATGACATGAACC-3' | 5'-TCATG TTGGACAACTGCCL4C-3' |
| Smad2 | 5′-TCACAGCCATCATGAGCCL4AAGG-3′ | 5′-TGTGACGCATGGAAGGTCCL4TC-3′ |
| Smad3 | 5′-AGCACACAATAACTTGGACC-3′ | 5′-TAAGACACACTGGAACAGCGGATG-3′ |
| Smad7 | 5′-GGCATACTGGGAGGAGAAGA-3' | 5′-CTGTTGAAGATGACCCL4CAGC-3' |
| GAPDH | 5′- CCCCCAATGTATCCGTTGTG -3′ | 5′-TAGCCCAGGATGCCCTTTAGT-3′ |
Table 1 Primer sequences for PCR
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| α-SMA | 5′-CCGAGATCCL4ACCGACTACC-3' | 5′-TCCAGAGCGACATAGCACAG-3' |
| TGF-β1 | 5'-CA CCAT CCATGACATGAACC-3' | 5'-TCATG TTGGACAACTGCCL4C-3' |
| Smad2 | 5′-TCACAGCCATCATGAGCCL4AAGG-3′ | 5′-TGTGACGCATGGAAGGTCCL4TC-3′ |
| Smad3 | 5′-AGCACACAATAACTTGGACC-3′ | 5′-TAAGACACACTGGAACAGCGGATG-3′ |
| Smad7 | 5′-GGCATACTGGGAGGAGAAGA-3' | 5′-CTGTTGAAGATGACCCL4CAGC-3' |
| GAPDH | 5′- CCCCCAATGTATCCGTTGTG -3′ | 5′-TAGCCCAGGATGCCCTTTAGT-3′ |
| No. | Compound | Formula | Instensity |
| 1 | Naringin | C27H32O14 | 5704608 |
| 2 | Nobiletin | C27H32O14 | 5704608 |
| 3 | Hesperidin | C28H34O15 | 5185715 |
| 4 | Neohesperidin | C28H34O15 | 5185715 |
| 5 | Ligustilide | C12H14O2 | 5173107 |
| 6 | Rhizoma ligustici wallichii phthalein | C12H14O2 | 5173107 |
| 7 | Butylphthalide | C12H14O2 | 5173107 |
| 8 | Safflomin A | C27H32O16 | 3662158 |
| 9 | Hydroxysafflor yellow A | C27H32O16 | 3662158 |
| 10 | Cyperenone | C15H22O | 3162062 |
| 11 | Nootkatone | C15H22O | 3162062 |
| 12 | Senkyunolide A | C12H16O2 | 2005805 |
| 13 | Eriodictyonine | C27H32O15 | 1865273 |
| 14 | Arginine | C6H14N4O2 | 1516358 |
| 15 | Levistilide A | C24H28O4 | 1472974 |
| 16 | Sinensetin | C20H20O7 | 1050908 |
| 17 | Limonoid | C26H30O8 | 955304 |
| 18 | Linoleic acid | C18H32O2 | 765256 |
| 19 | Kaempferol-3-O-β-rutinoside | C27H30O15 | 652537 |
| 20 | 6-hydroxyapigenin-3,6-di-O-β-D-glucoside | C27H30O15 | 652537 |
Table 2 Main chemical constituents of Shugan Huoxue Huayu Fang
| No. | Compound | Formula | Instensity |
| 1 | Naringin | C27H32O14 | 5704608 |
| 2 | Nobiletin | C27H32O14 | 5704608 |
| 3 | Hesperidin | C28H34O15 | 5185715 |
| 4 | Neohesperidin | C28H34O15 | 5185715 |
| 5 | Ligustilide | C12H14O2 | 5173107 |
| 6 | Rhizoma ligustici wallichii phthalein | C12H14O2 | 5173107 |
| 7 | Butylphthalide | C12H14O2 | 5173107 |
| 8 | Safflomin A | C27H32O16 | 3662158 |
| 9 | Hydroxysafflor yellow A | C27H32O16 | 3662158 |
| 10 | Cyperenone | C15H22O | 3162062 |
| 11 | Nootkatone | C15H22O | 3162062 |
| 12 | Senkyunolide A | C12H16O2 | 2005805 |
| 13 | Eriodictyonine | C27H32O15 | 1865273 |
| 14 | Arginine | C6H14N4O2 | 1516358 |
| 15 | Levistilide A | C24H28O4 | 1472974 |
| 16 | Sinensetin | C20H20O7 | 1050908 |
| 17 | Limonoid | C26H30O8 | 955304 |
| 18 | Linoleic acid | C18H32O2 | 765256 |
| 19 | Kaempferol-3-O-β-rutinoside | C27H30O15 | 652537 |
| 20 | 6-hydroxyapigenin-3,6-di-O-β-D-glucoside | C27H30O15 | 652537 |
| Group | n | ALT (U/L) | AST (U/L) | ALP (U/L) | ALB (g/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 8 | 60±7 | 127±28 | 240±43 | 37±6 | |
| Model | 8 | 552±34a | 616±32a | 483±37a | 23±3a | |
| Low-dose group | 8 | 500±27b | 511±39b | 467±55 | 23±2 | |
| Medium-dose group | 8 | 461±23b | 451±24b | 391±54c | 26±2 | |
| High-dose group | 8 | 377±20b | 431±29b | 369±46b | 29±1c | |
| Colchicine | 8 | 388±19b | 442±15b | 396±40c | 29±2c |
Table 3 Effect of SGHXHYF on serum ALT, AST, ALP, and ALB levels ($\bar{x}$± s)
| Group | n | ALT (U/L) | AST (U/L) | ALP (U/L) | ALB (g/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 8 | 60±7 | 127±28 | 240±43 | 37±6 | |
| Model | 8 | 552±34a | 616±32a | 483±37a | 23±3a | |
| Low-dose group | 8 | 500±27b | 511±39b | 467±55 | 23±2 | |
| Medium-dose group | 8 | 461±23b | 451±24b | 391±54c | 26±2 | |
| High-dose group | 8 | 377±20b | 431±29b | 369±46b | 29±1c | |
| Colchicine | 8 | 388±19b | 442±15b | 396±40c | 29±2c |

Figure 2 SGHXHYF inhibits CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats A, B: representative liver sections stained with HE (A) and Masson’s stain (B) from normal control rats and CCl4-exposed rats treated with vehicle, SGHXHYF, or colchicine [magnification ×100 (A) and ×60 (B)]; C, D: serum collagen I (C) and collagen III (D) levels; E: liver fibrosis score. Normal control group (peanut oil solution); model group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution); low-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 0.3 mg/kg SGHXHYF); medium-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 0.6 mg/kg SGHXHYF); high-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 1.2 mg/kg SGHXHYF); colchicine group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 1 mg/kg colchicine). SGHXHYF: Shugan Huoxue Huayu Fang; CCl4: carbon tetrachloride; HE: hematoxylin and eosin. aP < 0.01 vs normal group, cP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs model group.

Figure 3 Effect of SGHXHYF on α-SMA expression in the liver. A: immunohistochemical analysis of α-SMA expression in liver sections from normal control rats and CCl4-exposed rats treated with vehicle, SGHXHYF, or colchicine (magnification ×100); B, C: Western blot analysis (B) and densitometric quantification (C) of α-SMA protein levels in liver sections; D: qRT-PCR of α-SMA mRNA expression in liver sections. Normal group (peanut oil solution); model group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution); low-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 0.3 mg/kg SGHXHYF); medium-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 0.6 mg/kg SGHXHYF); high-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 1.2 mg/kg SGHXHYF); colchicine group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 1 mg/kg colchicine). SGHXHYF: Shugan Huoxue Huayu Fang; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin. aP < 0.01 vs normal group, bP < 0.05 and cP < 0.01 vs model group.

Figure 4 SGHXHYF inhibits activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway in the liver A: Western blot analysis of TGF-β1, t-Smad2, t-Smad3, p-Smad2, p-Smad3, and Smad7 protein expression in livers from normal control rats and CCl4-exposed rats treated with vehicle, SGHXHYF, or colchicine; B-E: densitometric analysis of TGF-β1 (B), ratio of p/t-Smad2 (C), ratio of p/t-Smad3 (D), and Smad7 (E) protein expression. Normal group (peanut oil solution); model group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution); low-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 0.3 mg/kg SGHXHYF); medium-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 0.6 mg/kg SGHXHYF); high-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 1.2 mg/kg SGHXHYF); colchicine group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 1 mg/kg colchicine). aP < 0.01 vs normal group, cP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs model group. SGHXHYF: Shugan Huoxue Huayu Fang; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor-β1; CCl4: carbon tetrachloride; p-Smad: phosphorylated Smad; t-Smad: total Smad.
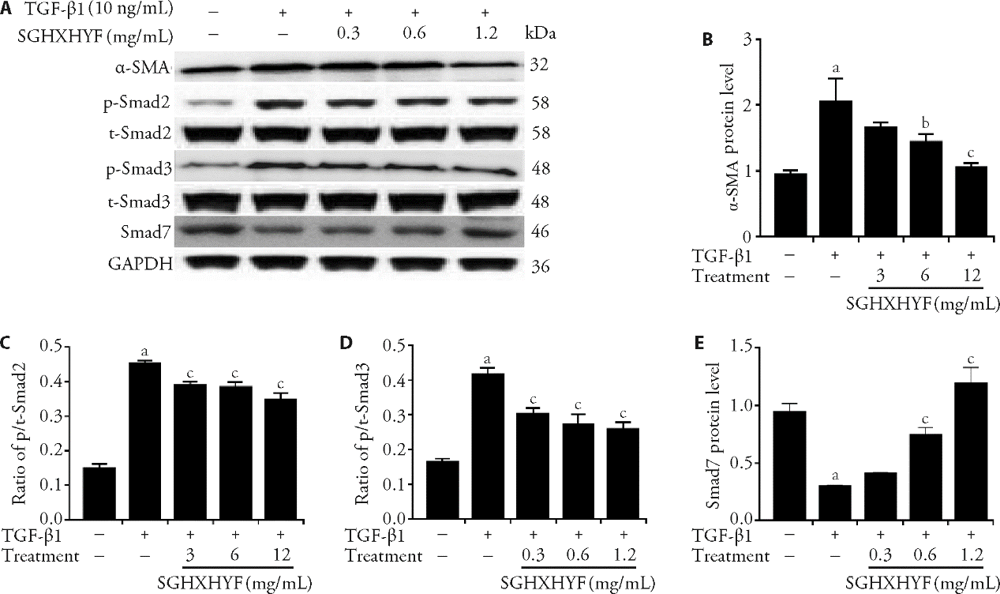
Figure 5 SGHXHYF inhibits activation of the TGF-β1-Smad signaling pathway in HSCs in vitro A: western blot analysis of α-SMA, Smad2, Smad3, p-Smad2, p-Smad3, and Smad7 expression in HSCs treated for 24 h with the indicated combinations of vehicle, TGF-β1, and SGHXHYF; B-E: densitometric analysis of α-SMA (B), ratio of p/t-Smad2 (C), ratio of p/t-Smad3 (D), and Smad7 (E) protein expression. Normal group (peanut oil solution); model group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution); low-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 0.3 mg/kg SGHXHYF); medium-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 0.6 mg/kg SGHXHYF); high-dose group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 1.2 mg/kg SGHXHYF); colchicine group (40%, 3 mL/kg CCl4 peanut oil solution + 1 mg/kg colchicine). SGHXHYF: Shugan Huoxue Huayu Fang; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor-β1; HSCs: hepatic stellate cells; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin; p-Smad: phosphorylated Smad; t-Smad: total Smad. aP < 0.01 vs normal group, bP < 0.05 and cP < 0.01 vs TGF-β1-treated group.
| [1] | Williams R. Global challenges in liver disease. Hepatology 2006;44:521-6. |
| [2] | Tsochatzis EA, Bosch J, Burroughs AK. Liver cirrhosis. The Lancet 2014;383:1749-61. |
| [3] | Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 2005;115:209-18. |
| [4] | Friedman SL, Bansal MB. Reversal of hepatic fibrosis-fact or fantasy? Hepatology 2006;43:S82-8. |
| [5] | Pinzani M, Rombouts K. Liver fibrosis: from the bench to clinical targets. Dig Liver Dis 2004;36:231-42. |
| [6] | Zhu YP, Woerdenbag HJ. Traditional Chinese herbal medicine. Pharm World Sci 1995;17:103-12. |
| [7] | Gao HY, Li GY, Lou MM, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of Matrine salvianolic acid B salt on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis. J Inflam 2012;9:1-9. |
| [8] | Balta C, Herman H, Boldura OM, et al. Chrysin attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact 2015;240:94-101. |
| [9] | Weiss A, Attisano L. The TGF-beta superfamily signaling pathway. Wires Dev Biol 2013;2:47-63. |
| [10] | Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 2008;134:1655-69. |
| [11] | Fabregat I, Moreno-Caceres J, Sanchez A, et al. TGF-beta signalling and liver disease. FEBS J 2016;283:2219-32. |
| [12] | Schuppan D, Kim YO. Evolving therapies for liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 2013;123:1887-901. |
| [13] | Xie H, Su D, Zhang J, et al. Raw and vinegar processed Curcuma wenyujin regulates hepatic fibrosis via bloking TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways and up-regulation of MMP-2/TIMP-1 ratio. J Ethnopharmacol 2020;246:111768. |
| [14] | Zhou Y, Tong X, Ren S, et al. Synergistic anti-liver fibrosis actions of total astragalus saponins and glycyrrhizic acid via TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway modulation. J Ethnopharmacol 2016;190:83-90. |
| [15] | Wang Y, Shen RW, Han B, et al. Notch signaling mediated by TGF-β/Smad pathway in concanavalin A-induced liver fibrosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2017;23:2330-36. |
| [16] | Park SA, Kim MJ, Park SY, et al. EW-7197 inhibits hepatic, renal, and pulmonary fibrosis by blocking TGF-β/Smad and ROS signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci 2015;72:2023-39. |
| [17] | Lee JH, Jang EJ, Seo HL, et al. Sauchinone attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact 2014;224:58-67. |
| [18] | Du CY, Choi RC, Zheng KY, et al. Yu Ping Feng San, an ancient Chinese herbal decoction containing Astragali Radix, Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma and Saposhnikoviae Radix, regulates the release of cytokines in murine macrophages. PLoS One 2013;8:e78622. |
| [19] | Liu H, Zhang Z, Hu H, et al. Protective effects of Liuweiwuling tablets on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 2018;18:212. |
| [20] | Li XM, Peng JH, Sun ZL, et al. Chinese medicine CGA formula ameliorates DMN-induced liver fibrosis in rats via inhibiting MMP2/9, TIMP1/2 and the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2016;37:783-93. |
| [21] | Jiang Y, Wang C, Li YY, et al. Mistletoe alkaloid fractions alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis through inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation via TGF-β/Smad interference. J Ethnopharmacol 2014;158:230-8. |
| [22] | Chen Q, Zhang H, Cao Y, et al. Schisandrin B attenuates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats by regulation of Nrf2-ARE and TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathways. Drug Des Devel Ther 2017;11:2179-91. |
| [23] | Wang ZF, Wang MY, Yu DH, et al. Therapeutic effect of chitosan on CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Mol Med Rep 2018;18:3211-8. |
| [24] | Paz Z, Shoenfeld Y. Antifibrosis: to reverse the irreversible. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2010;38:276-86. |
| [25] | Dooley S, Delvoux B, Streckert M, et al. Transforming growth factor β signal transduction in hepatic stellate cells via Smad2/3 phosphorylation, a pathway that is abrogated during in vitro progression to myofibroblasts, TGF-β signal transduction during transdifferentiation of hepatic stellate cells. FEBS Lett 2001;502:4-10. |
| [26] | Zou Y, Li S, Li Z, et al. MiR-146a attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting transforming growth factor-beta1 mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocytes. Cell Signal 2019;58:1-8. |
| [27] | Ying HZ, Chen Q, Zhang WY, et al. PDGF signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis pathogenesis and therapeutics (review). Mol Med Rep 2017;16:7879-89. |
| [28] | Miao CG, Yang YY, He X, et al. Wnt signaling in liver fibrosis: progress, challenges and potential directions. Biochimie 2013;95:2326-35. |
| [1] | WANG Miao, ZHU Yan, ZHAO Hui, ZHAO Hongfang. Moxibustion enables protective effects on rheumatoid arthritis-induced myocardial injury via transforming growth factor beta1 signaling and metabolic reprogramming [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1190-1199. |
| [2] | SU Chengguo, ZHAO Xiaoyan, YE Jiangnan, ZHANG Xin, JIANG Yuqing, GUO Junjie, ZHANG Xiyuan, QI Wenchuan, ZHU Jun. Effect of Tuina along “bladder meridian” alleviating intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating the transforming growth factor-β1/Smad signaling pathway in a rabbit model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 991-1000. |
| [3] | WAN Feng, YANG Ruchun, TANG Yuewen. Uncovering pharmacological mechanisms of Phellinus linteus on focal segmental glomeruloscleosis rats through tandem mass tag-based quantitative proteomic analysis, network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 744-750. |
| [4] | ZHAO Ye, WANG Xian, GU Ling, LI Zihang, ZHU Jingtian, WANG Wenkai, ZHANG Liang, XUE Mei. Efficacy of Danggui Buxue decoction (当归补血汤) on diabetic nephropathy-induced renal fibrosis in rats and possible mechanism [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 507-513. |
| [5] | ZHANG Junli, HE Ying, ZHANG Xia, FU Hongfang, HU Xiaoyu. Fuzheng Huayu preparation (扶正化瘀胶囊/片) combined with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate on hepatitis B: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 221-230. |
| [6] | LI Yue, WEN Shuting, ZHAO Runyuan, FAN Dongmei, ZHAO Dike, LIU Fengbin, MI Hong. Efficacy of active ingredients in Qingdai (Indigo Naturalis) on ulcerative colitis: a network pharmacology-based evaluation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 124-133. |
| [7] | ZHAO Jie, WANG Li, CAO Ai-li, WANG Yun-man, CHI Yang-feng, WANG Yi, WANG Hao, PENG Wen. Huangqi decoction (黄芪汤) attenuates renal interstitial fibrosis via transforming growth factor-β1/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in 5/6 nephrectomy mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 723-731. |
| [8] | HU Xijiao, CHENG Yinglong, KANG Huanan, LI Shuoxi, WANG Yawen, LIU Jinzhe, SUN Yiming, LIU Li. Electroacupuncture attenuates chronic salpingitis via transforming growth factor-β1/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 781-787. |
| [9] | ZHOU Kaixuan, ZHANG Dong, BAO Huiwei, LI Lijing. Network pharmacology and molecular docking study on the effect of Kaempferol in treatment of metabolic associated fatty liver disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 788-794. |
| [10] | CHEN Jingjing, WANG Yuanyuan, ZHANG Nianzhi, XUE Xiaoming. Shenqihuatan formula (参七化痰方) reduces inflammation by inhibiting transforming growth factor-beta-stimulated signaling pathway in airway smooth muscle cells [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 520-529. |
| [11] | ZHANG Di, WEI Muyun, CHEN Luan, WU Hao, WANG Ting, ZHANG Zhiruo, ZHANG Ying, YU Juan, HUANG Jinming, ZHU Jinhang, QIN Shengying. Drug response biomarkers of Pien Tze Huang (片仔癀) treatment for hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 530-538. |
| [12] | Jiaru LIN, Li WANG, Bo CHEN, Santao OU, Jianhua QIN, Junming FAN. Shenweifang-containing serum inhibits transforming growth factor-β1-induced myofibroblast differentiation in normal rat kidney interstitial fibroblast cells [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 39-48. |
| [13] | PIAO Xiang, WANG Wei, CHEN Hanjiang, YAN Rong, LI Mengquan. Effect of Rongchang capsule (茸菖胶囊) on seizure behavior,cognitive impairment,and hippocampal DNA damage and inflammatory factors in epileptic rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 438-446. |
| [14] | YU Juan;XIA Fei;LI Xiang;PENG Qinghua;. Effects of Qingguang'an(青光安)containing serum on the expression levels of autophagy-related genes in human Tenon's fibroblasts induced by transforming growth factor beta 1 [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(2): 236-245. |
| [15] | Xia Xichao, Mao Dongxue, Dai Hongmei, Wu Xi, Zhang Zuyuan, Wang Huaying, Zhou Wenwen, Dong Yanmei, Wang Mengqi, Li Yuan, Shao Xiangyang, Ouyang Jingfeng. Effect of Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharides on streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(6): 956-964. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||