Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 520-529.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220519.001
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shenqihuatan formula (参七化痰方) reduces inflammation by inhibiting transforming growth factor-beta-stimulated signaling pathway in airway smooth muscle cells
CHEN Jingjing1, WANG Yuanyuan2, ZHANG Nianzhi3( ), XUE Xiaoming1
), XUE Xiaoming1
- 1 Shanxi Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Taiyuan 030012, China
2 Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230038, China
3 Department of Respiratory, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
-
Received:2021-04-29Accepted:2021-07-02Online:2022-08-15Published:2022-07-12 -
Contact:ZHANG Nianzhi -
About author:Prof. ZHANG Nianzhi, Department of Respiratory, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China. zhangnz@ahtcm.edu.cn, Telephone: +86-13505615645
-
Supported by:Study on the Mechanism of the Method of Yiqi Huoxue Huata regulating autophagy in airway epithelial cells of COPD based on SIRT1/mTOR signaling pathway(82174312);Study on the mechanism of the method of YIQI HUOXUE HUATA intervention in COPD airway remodeling based on RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway(81473675)
Cite this article
CHEN Jingjing, WANG Yuanyuan, ZHANG Nianzhi, XUE Xiaoming. Shenqihuatan formula (参七化痰方) reduces inflammation by inhibiting transforming growth factor-beta-stimulated signaling pathway in airway smooth muscle cells[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 520-529.
share this article

Figure 1 SQHT inhibits TGF-β-stimulated cell processes A: CCK-8 results of the viability of ASMCs; B1: representative micrographs show the migration of ASMCs via crystal violet staining (×100); B2: histogram of Transwell assay; C: representative micrographs of F-actin staining demonstrat the F-actin formation and cytoskeletal reorganization of ASMCs via immunofluorescence (×100). Scale bar, 20 μm. aP < 0.01, vs Control; bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01, vs TGF-β group. SQHT: Shenqihuatan formula; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-beta; CCK-8: cell counting kit (CCK)-8; ASMCs: airway smooth muscle cells.
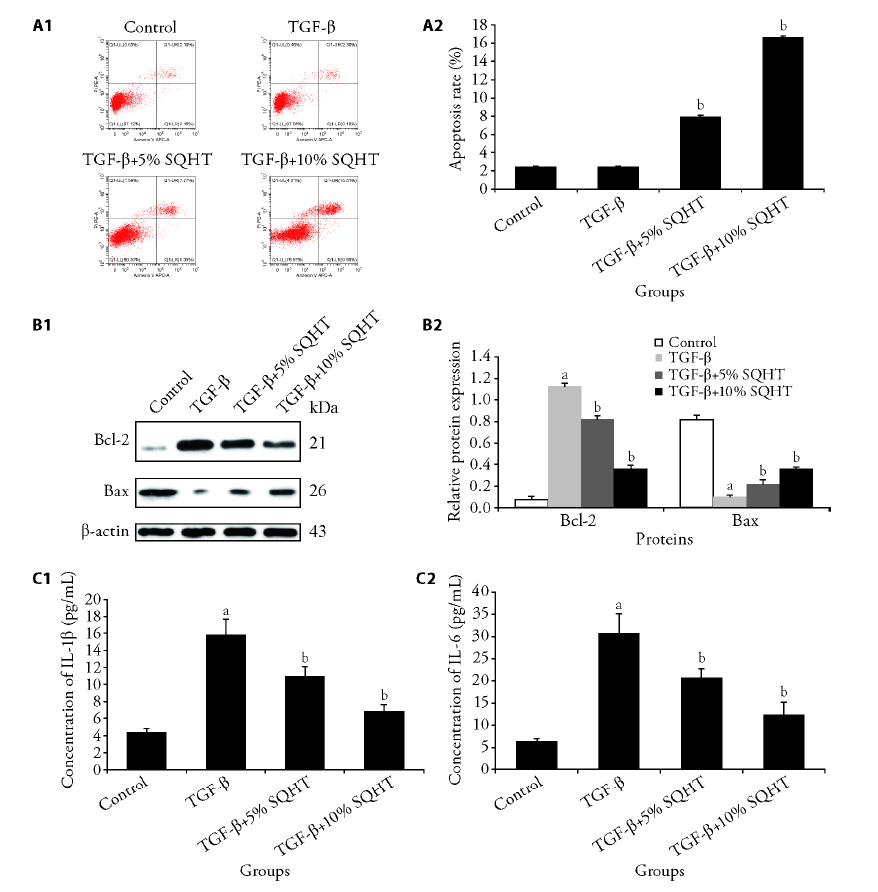
Figure 2 SQHT drives apoptosis in stimulated ASMCs A1: representative micrographs of flow cytometry show apoptosis; A2: histogram of flow cytometry shows apoptosis; B1: representative immunoblotting bands of Western blotting results show the relative protein expression levels of Bcl-2 and Bax; B2: histogram of Western blotting results; C1: ELISA results of the concentration of IL-1β; C2: ELISA results of the concentration of IL-6. aP < 0.01, vs Control; bP < 0.01, vs TGF-β group. SQHT: Shenqihuatan formula; ASMCs: airway smooth muscle cells; Bcl-2: B cell lymphoma 2; Bax: Bcl-2-Associated X; ELISA: enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-beta.

Figure 3 SQHT exhibits comparable inhibition to Fasudil on the cell processes A: CCK-8 results of the cell proliferation; B1: representative micrographs of Transwell results show the migration of ASMCs via crystal violet staining (×100); B2: histogram of Transwell results; C: representative micrographs of F-actin staining reveal the F-actin formation and cytoskeletal reorganization of ASMCs via immunofluorescence (×100). Scale bar, 20 μm; D1: representative images of flow cytometry show apoptosis in the groups; D2: histogram of flow cytometry shows apoptosis in the groups; E1: representative immunoblotting band of Western blotting results of the relative protein expression levels of Bcl-2 and Bax. E2: histogram of Western blotting results. aP < 0.01, vs Control; bP < 0.01, vs TGF-β group. SQHT: Shenqihuatan formula; CCK-8: Cell counting kit (CCK)-8; ASMCs: airway smooth muscle cells; Bcl-2: B cell lymphoma 2; Bax: Bcl-2-Associated X; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-beta.
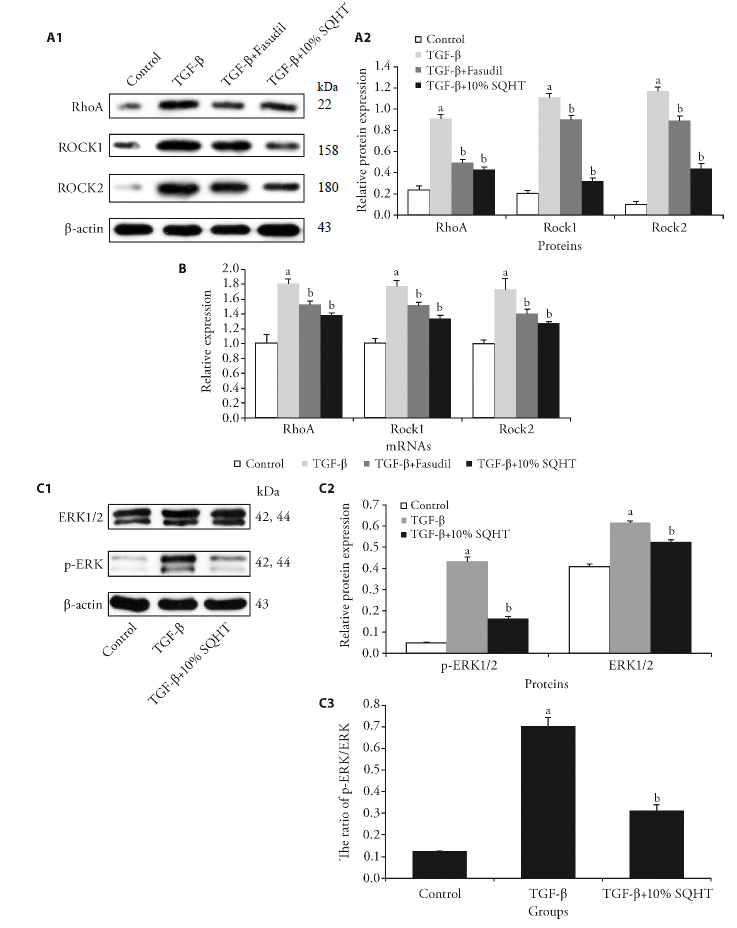
Figure 4 SQHT or Fasudil inhibit the RhoA and ERK1/2 pathway in TGF-β-stimulated ASMCs A1: representative immunoblotting band of western blotting results of the relative protein expression levels of RhoA, ROCK1 and 2; A2: histogram of western blotting results; B: qRT-PCR results of the relative mRNA expression levels of RhoA, ROCK1 and 2; C1: representative immunoblotting band of western blotting results of the relative protein expression levels of p-ERK1/2 and ERK1/2; C2: histogram of western blotting results of the relative protein expression levels of p-ERK1/2 and ERK1/2; C3: histogram of Western blotting results of the ratio of p-ERK/ERK. aP < 0.01, vs Control; bP < 0.01, vs TGF-β group. SQHT: Shenqihuatan formula; RhoA: Ras homolog gene family, member A; ERK1/2: extracellular regulated protein kinases 1/2; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-beta; ASMCs: airway smooth muscle cells; ROCK: recombinant rho associated coiled coil containing protein kinase; qRT-PCR: quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
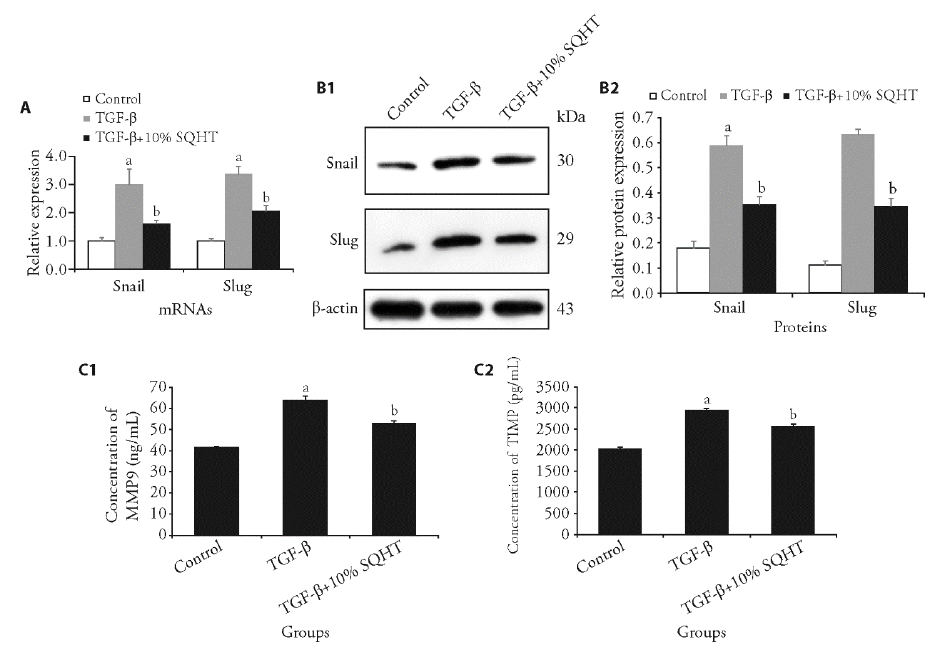
Figure 5 SQHT inhibits the Snail/Slug signaling pathway A: histogram of qRT-PCR results of the relative mRNA expression levels of Snail and Slug, respectively; B1: representative immunoblotting band of Western blotting results of the relative protein expression levels of Snail and Slug, respectively; B2: histogram of Western blotting results; C1: ELISA results of the concentration of MMP-9; C2: ELISA results of the concentration of TIMP-1. aP < 0.01, vs Control; bP < 0.01, vs TGF-β group. SQHT: Shenqihuatan formula; qRT-PCR: quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; ELISA: enzyme-linked immune sorbent assay; MMP-9: matrix metalloproteinase-9; TIMP-1: tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase.
| 1 |
Wang Y, Xu J, Meng Y, Adcock IM, Yao X. Role of inflammatory cells in airway remodeling in COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2018; 13: 3341-8.
DOI URL |
| 2 |
Higham A, Quinn AM, Cancado JED, Singh D. The pathology of small airways disease in COPD: historical aspects and future directions. Respir Res 2019; 20: 49.
DOI URL |
| 3 |
Burney PG, Patel J, Newson R, Minelli C, Naghavi M. Global and regional trends in COPD mortality, 1990-2010. Eur Respir J 2015; 45: 1239-47.
DOI PMID |
| 4 |
Laniado-Laborin R. Smoking and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Parallel epidemics of the 21 century. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2009; 6: 209-24.
DOI URL |
| 5 |
Chung KF. The role of airway smooth muscle in the pathogenesis of airway wall remodeling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2005; 2: 347-54; discussion 371-2.
DOI URL |
| 6 |
Goldsmith AM, Bentley JK, Zhou L, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta induces airway smooth muscle hypertrophy. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2006; 34: 247-54.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
Gawaziuk JP, Sheikh F, Cheng ZQ, Cattini PA, Stephens NL. Transforming growth factor-beta as a differentiating factor for cultured smooth muscle cells. Eur Respir J 2007; 30: 643-52.
DOI PMID |
| 8 |
Salter B, Pray C, Radford K, Martin JG, Nair P. Regulation of human airway smooth muscle cell migration and relevance to asthma. Respir Res 2017; 18: 156.
DOI URL |
| 9 | Zhang Y, Alexander PB, Wang XF. TGF-beta family signaling in the control of cell proliferation and survival. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2017; 9: a022145. |
| 10 | Ojiaku CA, Yoo EJ, Panettieri RA, Jr. Transforming growth factor beta1 function in airway remodeling and hyperresponsiveness. The missing link? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2017; 56: 432-42. |
| 11 |
Pan Y, Liu L, Li S, et al. Activation of AMPK inhibits TGF-beta1-induced airway smooth muscle cells proliferation and its potential mechanisms. Sci Rep 2018; 8: 3624.
DOI URL |
| 12 |
Chaudhury A, Howe PH. The tale of transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) signaling: a soigne enigma. IUBMB Life 2009; 61: 929-39.
DOI PMID |
| 13 | Kumper S, Mardakheh FK, McCarthy A, et al. Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) function is essential for cell cycle progression, senescence and tumorigenesis. Elife 2016; 5: e12994. |
| 14 |
Priya R, Liang X, Teo JL, Duszyc K, Yap AS, Gomez GA. ROCK1 but not ROCK2 contributes to RhoA signaling and NMIIA-mediated contractility at the epithelial zonula adherens. Mol Biol Cell 2017; 28: 12-20.
DOI URL |
| 15 |
Shaifta Y, MacKay CE, Irechukwu N, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta enhances Rho-kinase activity and contraction in airway smooth muscle via the nucleotide exchange factor ARHGEF1. J Physiol 2018; 596: 47-66.
DOI URL |
| 16 |
Takeda N, Kondo M, Ito S, Ito Y, Shimokata K, Kume H. Role of RhoA inactivation in reduced cell proliferation of human airway smooth muscle by simvastatin. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2006; 35: 722-9.
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Chiba Y, Matsusue K, Misawa M. RhoA, a possible target for treatment of airway hyperresponsiveness in bronchial asthma. J Pharmacol Sci 2010; 114: 239-47.
DOI URL |
| 18 | Rojas A, Padidam M, Cress D, Grady WM. TGF-beta receptor levels regulate the specificity of signaling pathway activation and biological effects of TGF-beta. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1793: 1165-73. |
| 19 |
Wortzel I, Seger R. The ERK cascade: distinct functions within various subcellular organelles. Genes Cancer 2011; 2: 195-209.
DOI PMID |
| 20 |
Yap HM, Israf DA, Harith HH, Tham CL, Sulaiman MR. Crosstalk between signaling pathways involved in the regulation of airway smooth muscle cell hyperplasia. Front Pharmacol 2019; 10: 1148.
DOI URL |
| 21 | Zhang N, Chen W, Li G, et al. Clinical study on treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease at stable stage with Yiqi Huoxue Huatan formula. Zhong Yi Yao Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2014; 26: 151-2. |
| 22 | Wang Y. The Distribution of TCM syndromes in COPD patients of grade Ⅰ and Ⅱ and the effect of SQHTF on the expression of inflammatory makers in COPD rats. Hefei: Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, 2019: 33-7. |
| 23 |
An SS, Laudadio RE, Lai J, Rogers RA, Fredberg JJ. Stiffness changes in cultured airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2002; 283: C792-801.
DOI URL |
| 24 | Stamatiou R, Paraskeva E, Gourgoulianis K, Molyvdas PA, Hatziefthimiou A. Cytokines and growth factors promote airway smooth muscle cell proliferation. ISRN Inflamm 2012; 2012: 731472. |
| 25 |
Wang J, Wang HS, Su ZB. MicroRNA-142 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis in airway smooth muscle cells during airway remodeling in asthmatic rats via the inhibition of TGF-beta-dependent EGFR signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 2018; 47: 1682-95.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Hubchak SC, Runyan CE, Kreisberg JI, Schnaper HW. Cytoskeletal rearrangement and signal transduction in TGF-beta1-stimulated mesangial cell collagen accumulation. J Am Soc Nephrol 2003; 14: 1969-80.
PMID |
| 27 |
Aghasafari P, George U, Pidaparti R. A review of inflammatory mechanism in airway diseases. Inflamm Res 2019; 68: 59-74.
DOI PMID |
| 28 |
Wu YJ, Neoh CA, Tsao CY, Su JH, Li HH. Sinulariolide suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 through MAPKs and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci 2015; 16: 16469-82.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Qiu Q, Yang M, Tsang BK, Gruslin A. EGF-induced trophoblast secretion of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 involves activation of both PI3K and MAPK signalling pathways. Reproduction 2004; 128: 355-63.
DOI PMID |
| 30 | Li Y, Lu Y, Zhao Z, et al. Relationships of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 proteins with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease risk: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Res Med Sci 2016; 21: 12. |
| 31 |
Churg A, Zhou S, Wright JL. Series "matrix metalloproteinases in lung health and disease": Matrix metalloproteinases in COPD. Eur Respir J 2012; 39: 197-209.
DOI PMID |
| 32 | Eblen ST. Extracellular-regulated kinases: signaling from Ras to ERK substrates to control biological outcomes. Adv Cancer Res 2018; 138: 99-142. |
| 33 | Srinivasan R, Zabuawala T, Huang H, et al. Erk1 and Erk2 regulate endothelial cell proliferation and migration during mouse embryonic angiogenesis. PLoS One 2009; 2009; 4: e8283. |
| 34 |
Sun L, Diamond ME, Ottaviano AJ, Joseph MJ, Ananthanarayan V, Munshi HG. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 promotes matrix metalloproteinase-9-mediated oral cancer invasion through snail expression. Mol Cancer Res 2008; 6: 10-20.
DOI URL |
| 35 |
Welch-Reardon KM, Ehsan SM, Wang K, et al. Angiogenic sprouting is regulated by endothelial cell expression of Slug. J Cell Sci 2014; 127: 2017-28.
DOI PMID |
| 36 |
de Herreros AG, Peiro S, Nassour M, Savagner P. Snail family regulation and epithelial mesenchymal transitions in breast cancer progression. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2010; 15: 135-47.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 519
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 293
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

