Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1019-1027.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.05.008
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Characterization of acupuncture on central amino acid metabolism based on targeted neurotransmitter analysis in mice with inflammatory pain
WANG Yue1,2, LIU Xingxing1,2, GUO Yi1,2, GUO Yongming1,2, YUAN Gongming1,2, ZHANG Yu1,2, ZHENG Zhiyu1,2, XU Yuan1,2( ), LI Yuan3(
), LI Yuan3( )
)
- 1 School of Acupuncture & Moxibustion and Tuina, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China
2 National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Tianjin 300380, China
3 College of Acupuncture and Massage Health and Rehabilitation College, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China
-
Received:2024-06-11Accepted:2024-11-19Online:2025-10-15Published:2025-09-15 -
Contact:Assoc. Prof. XU Yuan, School of Acupuncture & Moxibustion and Tuina, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China; National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Tianjin 300380, China. 183412710@qq.com;
Lec. LI Yuan, College of Acupuncture and Massage Health and Rehabilitation College, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China, liyuan@njucm.edu.cn,Telephone: +86-13803090159, +86-13072057285 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on Acupuncture Alleviate Rheumatoid Arthritis Effect and Mechanism via miR-155 Reduce Monocyte Chemokine and Chemokine Receptor Expression(82004473);Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province: Study on the Role and Mechanism of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-mediated Acupuncture in Regulating Immune Homeostasis of the Gut-joint Axis in Rheumatoid Arthritis(BK20230453)
Cite this article
WANG Yue, LIU Xingxing, GUO Yi, GUO Yongming, YUAN Gongming, ZHANG Yu, ZHENG Zhiyu, XU Yuan, LI Yuan. Characterization of acupuncture on central amino acid metabolism based on targeted neurotransmitter analysis in mice with inflammatory pain[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1019-1027.
share this article
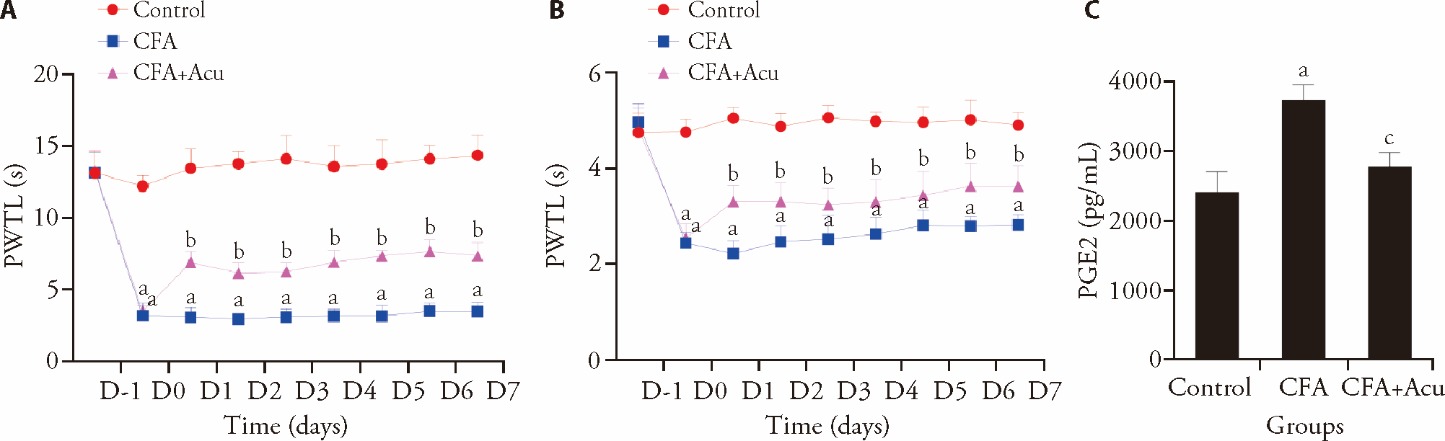
Figure 1 Analgesic effect of acupuncture on CFA-induced inflammatory pain A: PWTL of mice at different time points in each group; B: PWMT of mice at different time points in each group; C: Expression of PGE2 in the spinal cord. Control: control group (injected by 50 μL saline); CFA: CFA group (injected by 50 μL Complete Freund’s Adjuvant); CFA + Acu (injected by 50 μL CFA + acupuncture). PWTL: paw withdrawal thermal latency; PWMT: paw withdrawal mechanical threshold; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; ANOVA: analysis of variance. Behavioral tests were analyzed by repeated measures of variance; statistical significance between different groups was assessed using one-way ANOVA. PWTL and PWMT are presented as the mean ± standard deviation, PGE2 data is represented as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 10 per group in behavioral assessment, and n = 5 per group in PGE2 levels). aP < 0.01 versus control. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.05 versus CFA.
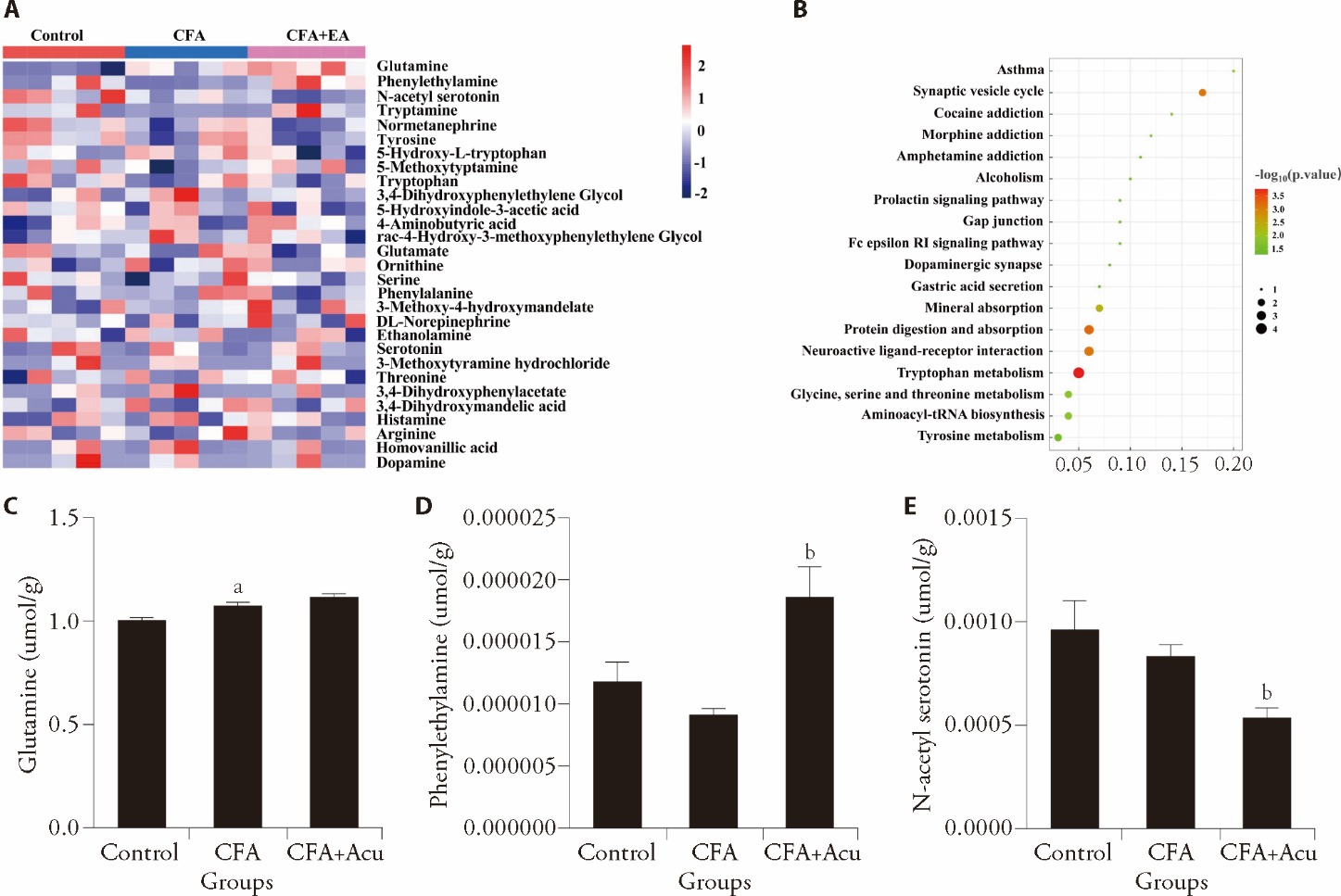
Figure 2 Effect of acupuncture on amino acid metabolites in the brain tissue of CFA mice A: heatmap of metabolites in each group; B: KEGG metabolic pathway in each group; C: levels of glutamine in each group; D: levels of phenylethylamine in each group; E: levels of N-acetyl serotonin in each group. Control: control group (injected by 50 μL saline); CFA: CFA group (injected by 50 μL Complete Freund’s Adjuvant); CFA + Acu (injected by 50 μL CFA + acupuncture). CFA: Complete Freund's Adjuvant; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; ANOVA: analysis of variance. Statistical significance between different groups was assessed using one-way ANOVA. All data are represented as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 5 per group). aP < 0.05 versus control. bP < 0.05 versus CFA.
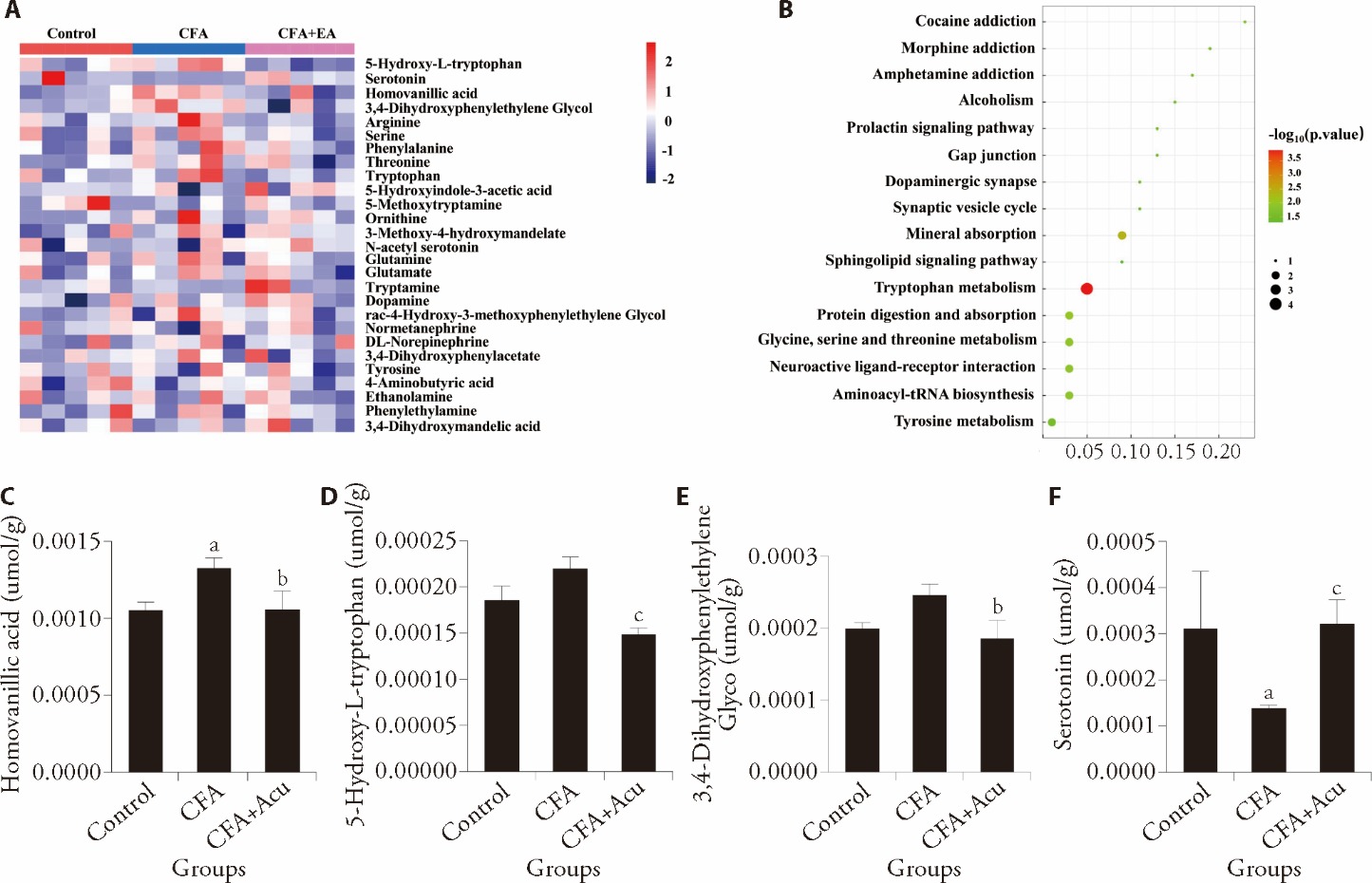
Figure 3 Effect of acupuncture on amino acid metabolites in the spinal cord of CFA mice A: heatmap of metabolites in each group; B: KEGG metabolic pathway in each group; C: levels of homovanillic acid in each group; D: levels of 5-hydroxy-L-tryptophan in each group; E: levels of 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylethylene Glyco in each group; F: levels of serotonin in each group. Control: control group (injected by 50 μL saline); CFA: CFA group (injected by 50 μL CFA); CFA + Acu (injected by 50 μL CFA + acupuncture). Statistical significance between different groups was assessed using one-way ANOVA. CFA: Complete Freund’s Adjuvant; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; ANOVA: analysis of variance. All data are represented as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 5 per group). aP < 0.05 versus control. bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01 versus CFA.
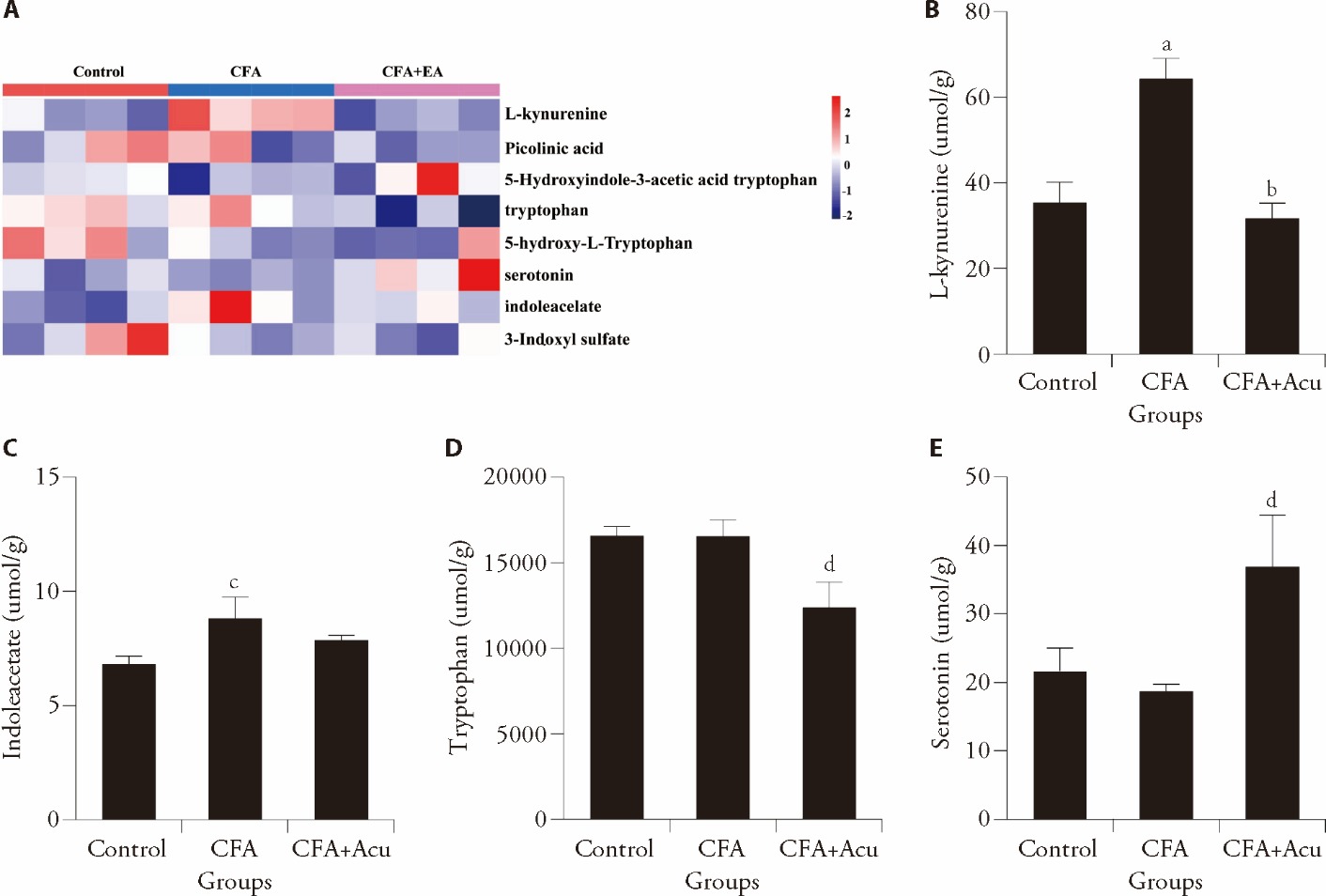
Figure 4 Effect of acupuncture on tryptophan metabolism and its metabolites in the spinal cord of CFA mice A: heatmap of tryptophan metabolites in each group; B: levels of L-kynurenine in each group, C: levels of indoleacetate in each group; D: levels of tryptophan in each group; E: levels of serotonin in each group. Control: control group (injected by 50 μL saline); CFA: CFA group (injected by 50 μL CFA); CFA + Acu (injected by 50 μL CFA + acupuncture). CFA: Complete Freund ’s adjuvant; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; ANOVA: analysis of variance. Statistical significance between different groups was assessed using one-way ANOVA. All data are represented as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 5 per group). aP < 0.01, cP < 0.05 versus control; bP < 0.01, dP < 0.05 versus CFA.
| 1. |
Cohen SP, Vase L, Hooten WM. Chronic pain: an update on burden, best practices, and new advances. Lancet 2021; 397: 2082-97.
DOI PMID |
| 2. | Qiao L, Guo M, Qian J, et al. Research advances on acupuncture analgesia. Am J Chin Med 2020; 48: 245-58. |
| 3. |
Gunn J, Hill MM, Cotten BM, et al. An analysis of biomarkers in patients with chronic pain. Pain Physician 2020; 23: E41-9.
PMID |
| 4. | Zhang Q, Zhou M, Huo M, et al. Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on inflammatory pain. Mol Pain 2023; 19: 1-22. |
| 5. | Gong Y, Li N, Lyu Z, et al. The neuro-immune microenvironment of acupoints-initiation of acupuncture effectiveness. J Leukoc Biol 2020; 108: 189-98. |
| 6. |
Cseh EK, Veres G, Körtési T et al. Neurotransmitter and tryptophan metabolite concentration changes in the complete Freund's adjuvant model of orofacial pain. J Headache Pain 2020; 21: 35.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Ciapała K, Mika J, Rojewska E. The kynurenine pathway as a potential target for neuropathic pain therapy design: from basic research toclinical perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 11055. |
| 8. | Jovanovic F, Candido KD, Knezevic NN. The role of the kynurenine signaling pathway in different chronic pain conditions and potential use of therapeutic agents. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 6045. |
| 9. | Lyu Z, Guo Y, Gong Y, et al. The role of neuroglial crosstalk and synaptic plasticity-mediated central sensitization in acupuncture analgesia. Neural Plast 2021; 2021: 8881557. |
| 10. | American Veterinary Medical Association. AVMA guidelines for the euthanasia of animals:2020 edition. American Veterinary Medical Association online, 2020-02-24, cited 2021-01-01; 60-4. Avilable from URL: https://www.avma.org/resources-tools/avma-policies/avma-guidelines-euthanasia-animals . |
| 11. | Xu Y, Hong S, Zhao X, et al. Acupuncture alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by immune-network modulation. Am J Chin Med 2018; 46: 997-1019. |
| 12. | Kanda H, Kobayashi K, Yamanaka H, et al. Localization of prostaglandin E 2 synthases and E-prostanoid receptors in the spinal cord in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Brain Res 2021; 1750: 147153. |
| 13. | Tanaka M, Török N, Tóth F, et al. Co-players in chronic pain: neuroinflammation and the tryptophan-kynurenine metabolic pathway. Biomedicines 2021; 9: 897. |
| 14. | Körtési T, Spekker E, Vécsei L. Exploring the tryptophan metabolic pathways in migraine-related mechanisms. Cells 2022; 11: 3795. |
| 15. |
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Verri WA Jr, Chiu IM. Nociceptor sensory neuron-immune interactions in pain and inflammation. Trends Immunol 2017; 38: 5-19.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Zhang R, Lao L, Ren K, Berman BM. Mechanisms of acupuncture- electroacupuncture on persistent pain. Anesthesiology 2014; 120: 482-503. |
| 17. | Badawy AA. Kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism: regulatory and functional aspects. Int J Tryptophan Res 2017; 10: 1178646917691938. |
| 18. | Savitz J. The kynurenine pathway: a finger in every pie. Mol Psychiatry 2020; 25: 131-47. |
| 19. | Pires AS, Sundaram G, Heng B, et al. Recent advances in clinical trials targeting the kynurenine pathway. Pharmacol Ther 2022; 236: 108055. |
| 20. |
Kim H, Chen L, Lim G, et al. Brain indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase contributes to the comorbidity of pain and depression. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 2940-54.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Lukács M, Warfvinge K, Kruse LS, et al. KYNA analogue SZR72 modifies CFA-induced dural inflammation-regarding expression of pERK1/2 and IL-1β in the rat trigeminal ganglion J Headache Pain 2016; 17: 64.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Lukács M, Warfvinge K, Tajti J, et al. Topical dura mater application of CFA induces enhanced expression of c-fos and glutamate in rat trigeminal nucleus caudalis: attenuated by KYNA derivate (SZR72). J Headache Pain 2017; 18: 39.
DOI PMID |
| 23. | Maganin AG, Souza GR, Fonseca MD, et al. Meningeal dendritic cells drive neuropathic pain through elevation of the kynurenine metabolic pathway in mice. J Clin Invest 2022; 132: e153805. |
| 24. |
Rojewska E, Ciapała K, Piotrowska A, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2 and kynurenine 3-monooxygenase, enzymes of the kynurenine pathway, significantly diminishes neuropathic pain in a rat model. Front Pharmacol 2018; 9: 724.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Rojewska E, Piotrowska A, Makuch W, et al. Pharmacological kynurenine 3-monooxygenase enzyme inhibition significantly reduces neuropathic pain in a rat model. Neuropharmacology 2016; 102: 80-91.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Yaksh TL, Schwarcz R, Snodgrass HR. Characterization of the effects of L-4-Chlorokynurenine on nociception in rodents. J Pain 2017; 18: 1184-96.
DOI PMID |
| 27. |
Pineda-Farias JB, Pérez-Severiano F, González-Esquivel DF, et al. The L-kynurenine-probenecid combination reduces neuropathic pain in rats. Eur J Pain 2013; 17: 1365-73.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Zhang Q, Li Q, Liu S, et al. Decreased amino acids in the brain might contribute to the progression of diabetic neuropathic pain. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2021; 176: 108790. |
| 29. | Russo MA, Georgius P, Pires AS, et al. Novel immune biomarkers in complex regional pain syndrome. J Neuroimmunol 2020; 347: 577330. |
| 30. |
Barjandi G, Louca Jounger S, Löfgren M, et al. Plasma tryptophan and kynurenine in females with temporomandibular disorders and fibromyalgia-An exploratory pilot study. J Oral Rehabil 2020; 47: 150-7.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Staats Pires A, Tan VX, Heng B, et al. Kynurenine and tetrahydrobiopterin pathways crosstalk in pain hypersensitivity. Front Neurosci 2020; 14: 620. |
| 32. | Jiang SW, Lin YW, Hsieh CL. Electroacupuncture at Hua Tuo Jia Ji acupoints reduced neuropathic pain and increased GABAA receptors in rat spinal cord. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018; 2018: 8041820. |
| 33. | Huang CP, Lin YW, Lee DY, Hsieh CL. Electroacupuncture relieves CCI-induced neuropathic pain involving excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019; 2019: 6784735. |
| 34. |
Zhang Y, Li A, Xin J, et al. Involvement of spinal serotonin receptors in electroacupuncture anti-hyperalgesia in an inflammatory pain rat model. Neurochem Res 2011; 36: 1785-92.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Cong W, Peng Y, Meng B, Jia X, Jin Z. The effect of electroacupuncture on regulating pain and depression-like behaviors induced by chronic neuropathic pain. Ann Palliat Med 2021; 10: 104-13.
DOI PMID |
| 36. | Lee MJ, Ryu JS, Won SK, et al. Effects of acupuncture on chronic stress-induced depression-like behavior and its central neural mechanism. Front Psychol 2019; 10: 1353. |
| 37. | Han X, Wu H, Yin P, et al. Electroacupuncture restores hippocampal synaptic plasticity via modulation of 5-HT receptors in a rat model of depression. Brain Res Bull 2018; 139: 256-62. |
| 38. | Roth W, Zadeh K, Vekariya R, Ge Y, Mohamadzadeh M. Tryptophan metabolism and gut-brain homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 2973. |
| [1] | PAN Tingyu, YAO Jing, GE Yue, YANG Shuang, SUN Zikai, WEI Yu, WU Jieyu, XU Yong, ZHOU Xianmei, HE Hailang. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolomics study of the protective mechanism of Shenji Guben decoction (参吉固本方) on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1009-1018. |
| [2] | GUO Jixing, JI Changchun, XIE Chaoju, RAO Xiang, SUN Zhangyin, XING Yu, ZHANG Rongni, QU Qiangqiang, DONG Youpeng, YANG Jinsheng. Various acupuncture therapies for managing nonspecific low back pain: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 954-962. |
| [3] | WANG Raoqiong, HAO Linyao, LU Ye, WANG Lingxue, LI Jianrong, PENG Yan, TANG Hongmei, LI Shuangyang, BAI Xue. Mechanism analysis of Tongqiao Yizhi decoction (通窍益智颗粒) in treating vascular dementia rats by brain tissue untargeted metabonomics and fecal 16S rRNA gene sequencing [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 759-769. |
| [4] | ZHAO Ping, HE Xingbo, HAN Xudong, CHEN Xinyue, LI Zhanglong, SONG Jike, XING Wenjia, WU Jiangfeng, GUO Bin, BI Hongsheng. Mechanism of electroacupuncture involve in lens-induced myopia guinea pigs by inhibiting wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 796-805. |
| [5] | ZHENG Ruwen, DONG Xu, WANG Tianyi, FENG Liyuan, ZHANG Hongyan, HUO Hong, ZHANG Ying, ZHANG Qianshi, ZHU Xingyan, WANG Dongyan. Electroacupuncture versus conventional acupuncture of scalp motor area for post-stroke wrist dyskinesia and its effect on muscle function: a randomized, controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 852-859. |
| [6] | SONG Jianfei, QIN Zhengyuan, GU Xinlu, ZHANG Yan, LI Xingrui. Efficacy of acupuncture combined with upper limb rehabilitation robot-assisted training for neuroplasticity and functional recovery of patients with stroke: a prospective cohort study based on functional near-infrared spectroscopy technology [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 860-866. |
| [7] | Kanae Umemoto, SHAN Xiyao, Takuro Ishikawa, Tadashi Watsuji, Yasuharu Watanabe, Munekazu Naito. Novel insight into the site-specificity of Hegu (LI4): morphological, biomechanical, and histological analyses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 867-872. |
| [8] | JIANG Jinglei, YU Tao, QIAN Yulin, WANG Meng. Understanding the role of microglia in Alzheimer's disease: insights into mechanisms, acupuncture, and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 922-936. |
| [9] | SUN Jiao, WANG Yueming, LYU Jian, LIU Xin, YUE Bingnan, LI Yinyin, LIU Jipeng, SUN Yize, LIU Qingguo, YAN Liu. Effect of electroacupuncture on hypertensive and sympathetic excitability mechanism mediated by the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in spontaneous hypertensive rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 586-596. |
| [10] | MIN Yu, ZHENG Meifeng, SUN Ju, PENG Zetong, CAO Zhixian, HUANG Xiaohua. Systematic acupuncture explains acupuncture at Baihui (GV20) and Fengchi (GB20) targeting the inflammatory response to regulate migraine [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 610-617. |
| [11] | XIONG Yanyan, TANG Renjin, LI Xuelin, LIU Hong. Effect of Neibu Huangqi Youhua formula (内补黄芪汤优化方) on postoperative wound healing, inflammatory factors and pain mediators of anal fistula [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 628-632. |
| [12] | CHEN Shumin, LIU Zhenyu, JI Jia, CHANG Jin, LI Zhihua, WANG Yingying, YANG Jinsheng. Acupuncture with different frequencies for tobacco dependence: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 651-659. |
| [13] | WEN Zhigang, LU Shuai, CHENG Xiumei. Clinical observation on the effect of warming meridian medicinal wine, polarized light external application combined with acupuncture and moxibustion on pain after vertebroplasty [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 660-666. |
| [14] | WANG Yiying, DONG Shuai, LI Bo, HAN Mei, CAO Huijuan. Update evidence of effectiveness on pain relieving of cupping therapy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 234-253. |
| [15] | LI Yongfeng, CHEN Xinyi, REN Wei, QIAO Haifa. Electroacupuncture stimulation of auricular concha region improves loss of control over stress induced depression-like behavior by modulating 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 326-334. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

