Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1082-1090.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.06.001
• Meta-Analyses • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chinese patent medicine for atherosclerosis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
XU Jian1,2, LIU Yuntao1,2, LUO Zhihao3, ZHAO Zhen4, WANG Dawei5,6( ), LIU Qing4(
), LIU Qing4( )
)
- 1 Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome, the Second Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China
2 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Research on Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China
3 Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine-Hainan Hospital, Haikou 570100, China
4 Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine-Zhuhai Hospital, State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China
5 Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China
6 State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome, The First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China
-
Received:2022-12-22Accepted:2023-03-12Online:2024-12-15Published:2024-11-12 -
Contact:WANG Dawei, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China; State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome, The First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China. davidwang33@139.com
LIU Qing, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine-Zhuhai Hospital, State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China. 851757626@qq.com -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Regulation of nanomedicine on the immune microenvironment in the macrophage-rich area of arterial plaques based on IL-17 immunity(82274279, to Q.L.)
Cite this article
XU Jian, LIU Yuntao, LUO Zhihao, ZHAO Zhen, WANG Dawei, LIU Qing. Chinese patent medicine for atherosclerosis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1082-1090.
share this article
| Study ID | Sample (overall/dropout); sex: M/F | Age (years) | Participant | Intervention group | Control group | Treatment (months) | Follow-up (months) | Outcome measure | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moriarty et al 2014 | 116/19; T1: 36 (6/30), T2: 42 (13/29), C:38(9/27) | T1: 57.8±9, T2: 56.3±10.8, C: 56.0±12.5 | Dyslipidemia | Xuezhikang 1200 mg, or Xuezhikang 2400 mg daily | Placebo | 12 | 0 | LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
| Van Poppel et al 2015 | 23/3; T: 12, C: 11 (14/6) | 58.0±7.7 | Hyperlipidemia and hypertension | Danshen capsule | Placebo | 2 | 0 | LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
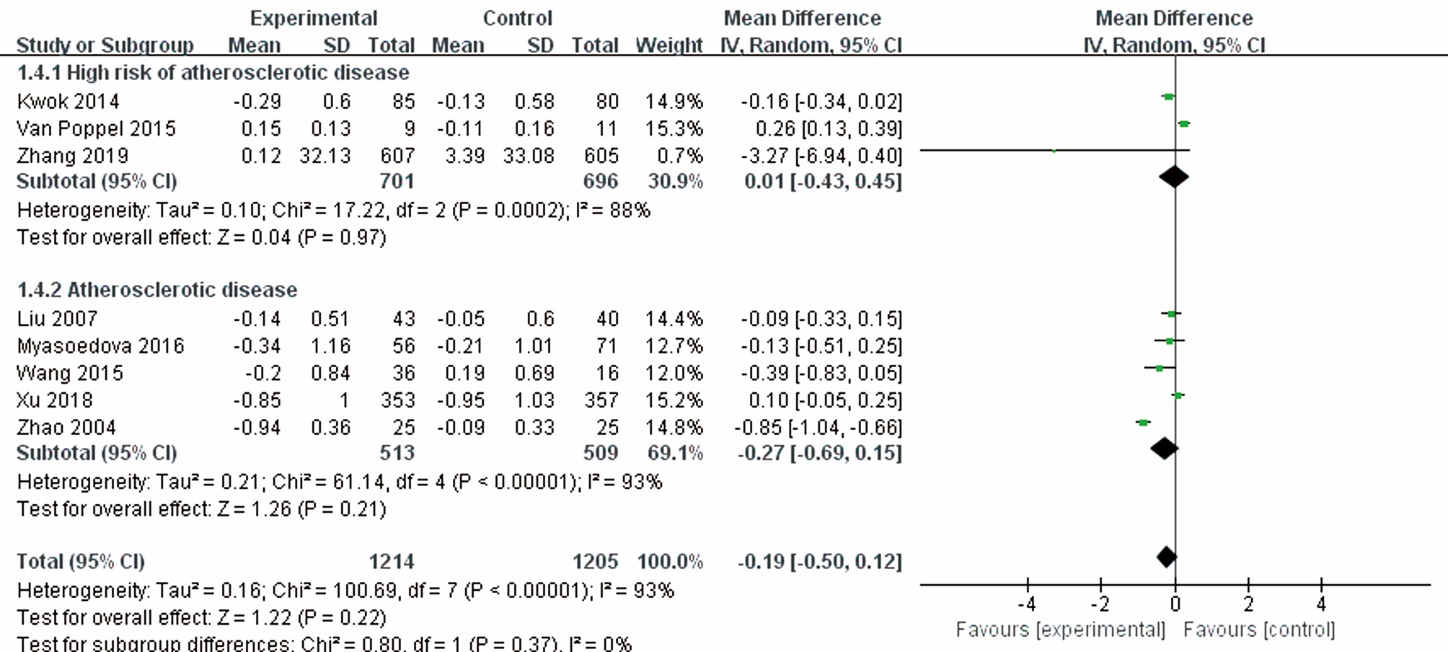
| Kwok et al 2014 | 165/22; T: 85 (0/85), C: 80 (0/80) | T: 56.5±4.1, C: 56.0±3.8 | Postmenopausal women with borderline hypercholesterolemia | Danshen and Gegen capsule | Placebo | 12 | 1 | IMT, LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
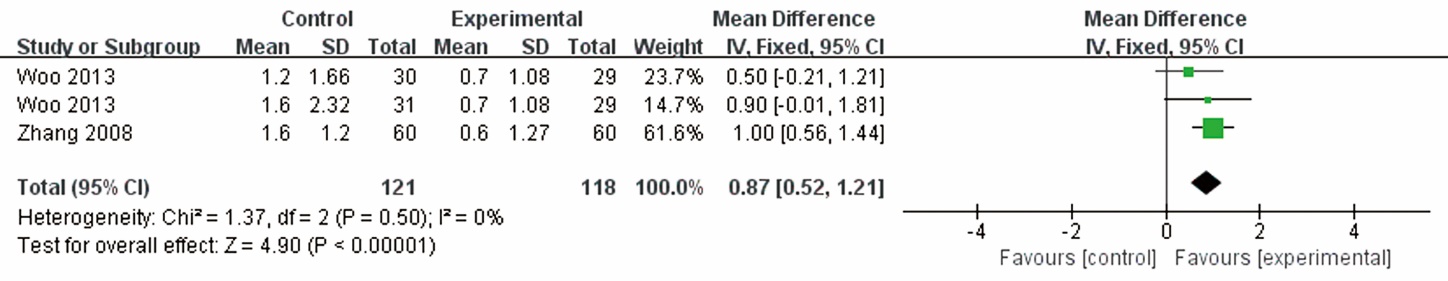
| Woo et al 2013 | 90/0; T1: 31 (27/4), T2: 30 (20/10), C: 29 (20/9) | T1: 51.7±7.7, T2: 56.9±7.4, C: 55.6±8.2 | Essential hypertension | Danshen and Gegen capsule | Placebo | 12 | 0 | FMD, IMT | ||||||||
| Li et al 2019 | 150/19; T: 75 (28/47), C: 75 (30/45) | T: 43.71±11.56, C: 45.54±10.16 | T2DM plus hyperlipemia | Simvastatin+ Maixuekang capsule | Simvastatin | 24 | 0 | IMT | ||||||||
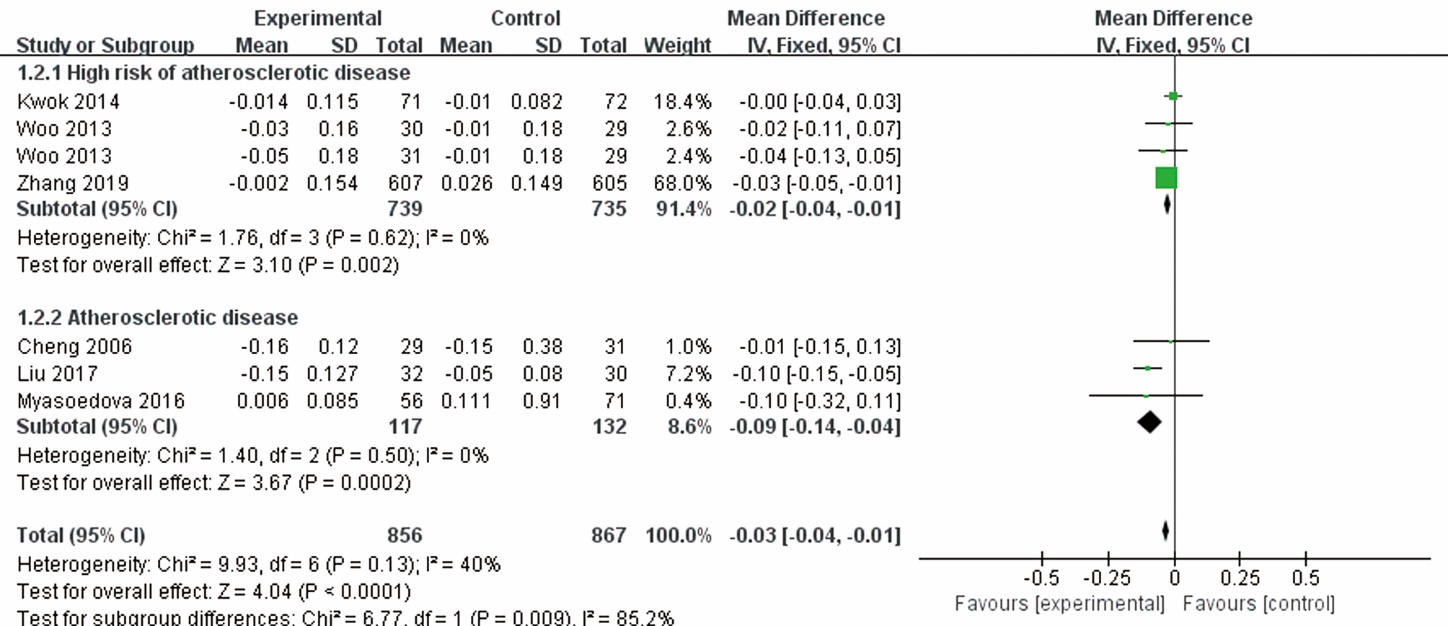
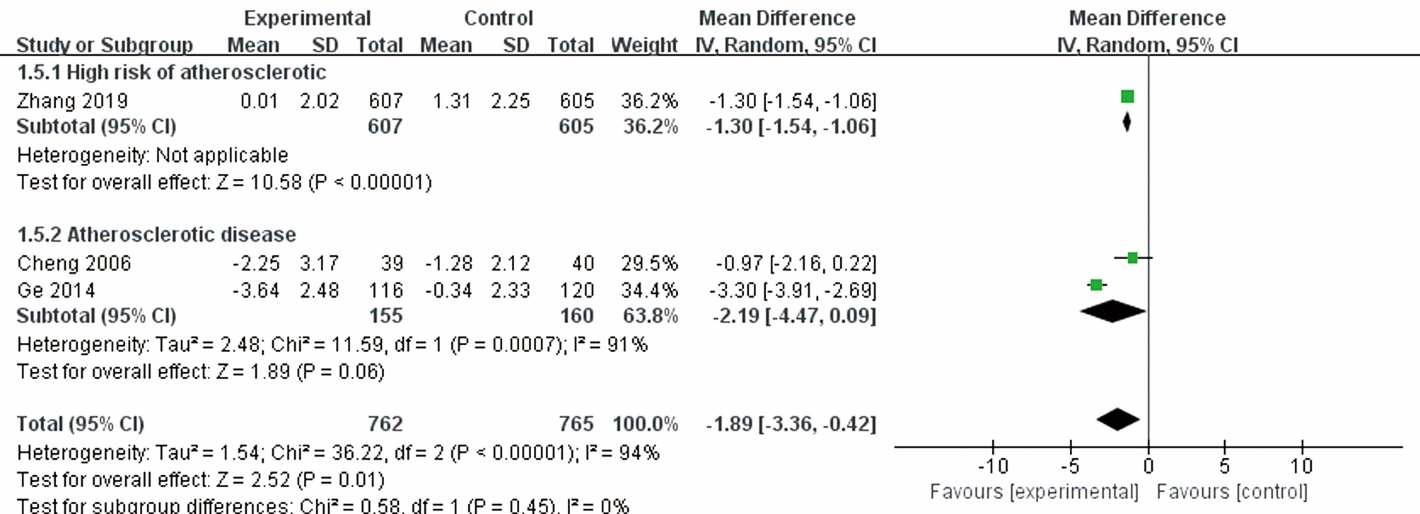
| Zhang et al 2019 | 1212/204; T: 607 (367/240), C: 605 (355/350) | T: 61.4±8.4, C: 61.4±8.2 | Patients with a focal IMT of ≥1.2 mm of the carotid arteries | Tongxinluo capsule | Placebo | 24 | 0 | clinical endpoint, IMT, LDL-C, hs-CRP, adverse events | ||||||||
| Liu et al 2007 | 103/20; T: 43 (37/6), C: 40 (33/7) | T: 59.83±7.83, C: 58.47±8.60 | Atherosclerosis in carotid arteries | Rhubarb capsules+CT | Placebo+CT | 6 | 9 | LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
| Wang et al 2015 | 57/5; T: 36 (17/19), C: 16 (11/5) | T: 68.72±10.92, C: 66.56±10.26 | Atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis | Huanshuai Recipe Oral Liquid+CT | Placebo+CT | 6 | 0 | LDL-C, clinical endpoint | ||||||||
| Myasoedova et al 2016 | 157/26; T: 77 (0/77), C: 80 (0/80) | T: 65±7, C: 65±6 | Subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in healthy postmenopausal women | Isoflavonoid-rich herbal preparation | Placebo | 12 | 12 | IMT, LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
| Zhao et al 2018 | 130/9; T: 65 (36/29), C: 65 (38/27) | T: 68.88±5.75, C: 67.26±5.49 | ACS patients after PCI | Danhong injection+Naoxintong capsule+CT | Placebo+CT | 3 | 3 | Clinical endpoint, adverse events | ||||||||
| Chen et al 2006 | 335/21; T: 157 (124/33), C: 157 (123/34) | T: 58.52±10.30, C: 58.74±9.91 | CHD after PCI | XS0601+CT | Aspirin+ CT | 6 | 6 | Clinical endpoint, adverse events | ||||||||
| Ge et al 2014 | 236/0; T: 116 (68/48), C: 120 (72/48) | T: 65.23±12.19, C: 67.03±13.46 | ACS after PCI | Maixuekang Capsule+CT | CT | 6 | 6 | hs-CRP, LDL-C, clinical endpoint | ||||||||
| Zhao et al 2004 | 50/0; T: 25 (15/10), C: 25 (14/11) | T: 58.2±14.2, C: 59.1±6.3 | CHD | Xuezhikang+CT | Placebo+CT | 3/2 | 0 | LDL-C | ||||||||
| Zhang et al 2008 | 120; T: 60 (36/24), C: 60 (35/25) | T: 55.9±16.1, C: 54.2±14.3 | CHD complicated by diabetes mellitus | Shengmai injection+CT | CT | 3/4 | 0 | FMD, adverse events | ||||||||
| Xu et al 2018 | 710/24; T: 353 (157/196), C: 357 (147/210) | T: 58.31±9.82, C:57.20±9.84 | Patients with CHD or at high risk of CHD | Zhibitai compound capsule+CT | CT | 2 | 0 | LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
| Cheng et al 2006 | 79; T: 39 (33/6), C: 40 (31/9) | T: 52.73±7.89, C: 53.11±7.01 | Primary hypertension and coronary artery disease | Garlicin+CT | CT | 13 | 0 | Hs-CRP, IMT, adverse events | ||||||||
| Liu et al 2017 | 62; T: 32 (22/10), C: 30 (20/10) | T: 61.1±12.0, C: 60.4±13.4 | CHD and hyperhomocysteinemia | Allicin+CT | CT | 3 | 0 | IMT | ||||||||
| Study ID | Sample (overall/dropout); sex: M/F | Age (years) | Participant | Intervention group | Control group | Treatment (months) | Follow-up (months) | Outcome measure | ||||||||
| Chu et al 2010 | 90/4; T1: 30 (18/12), T2: 30 (15/15), C: 30 (20/10) | T1: 61.7±9.6, T2: 61.6±9.2, C: 58.8±8.9 | Patients with unstable angina and blood-stasis syndrome after PCI | T1: Xuefu Zhuyu capsule + placebo of Shenmai capsule + CT T2: Shengmai capsule + placebo of Xuefu Zhuyu capsule + CT | Placebo of Xuefu Zhuyu capsule and Shengmai capsule +CT | 1 | 0 | Adverse events | ||||||||
Table 1 Main characteristics of the studies
| Study ID | Sample (overall/dropout); sex: M/F | Age (years) | Participant | Intervention group | Control group | Treatment (months) | Follow-up (months) | Outcome measure | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moriarty et al 2014 | 116/19; T1: 36 (6/30), T2: 42 (13/29), C:38(9/27) | T1: 57.8±9, T2: 56.3±10.8, C: 56.0±12.5 | Dyslipidemia | Xuezhikang 1200 mg, or Xuezhikang 2400 mg daily | Placebo | 12 | 0 | LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
| Van Poppel et al 2015 | 23/3; T: 12, C: 11 (14/6) | 58.0±7.7 | Hyperlipidemia and hypertension | Danshen capsule | Placebo | 2 | 0 | LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
| Kwok et al 2014 | 165/22; T: 85 (0/85), C: 80 (0/80) | T: 56.5±4.1, C: 56.0±3.8 | Postmenopausal women with borderline hypercholesterolemia | Danshen and Gegen capsule | Placebo | 12 | 1 | IMT, LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
| Woo et al 2013 | 90/0; T1: 31 (27/4), T2: 30 (20/10), C: 29 (20/9) | T1: 51.7±7.7, T2: 56.9±7.4, C: 55.6±8.2 | Essential hypertension | Danshen and Gegen capsule | Placebo | 12 | 0 | FMD, IMT | ||||||||
| Li et al 2019 | 150/19; T: 75 (28/47), C: 75 (30/45) | T: 43.71±11.56, C: 45.54±10.16 | T2DM plus hyperlipemia | Simvastatin+ Maixuekang capsule | Simvastatin | 24 | 0 | IMT | ||||||||
| Zhang et al 2019 | 1212/204; T: 607 (367/240), C: 605 (355/350) | T: 61.4±8.4, C: 61.4±8.2 | Patients with a focal IMT of ≥1.2 mm of the carotid arteries | Tongxinluo capsule | Placebo | 24 | 0 | clinical endpoint, IMT, LDL-C, hs-CRP, adverse events | ||||||||
| Liu et al 2007 | 103/20; T: 43 (37/6), C: 40 (33/7) | T: 59.83±7.83, C: 58.47±8.60 | Atherosclerosis in carotid arteries | Rhubarb capsules+CT | Placebo+CT | 6 | 9 | LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
| Wang et al 2015 | 57/5; T: 36 (17/19), C: 16 (11/5) | T: 68.72±10.92, C: 66.56±10.26 | Atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis | Huanshuai Recipe Oral Liquid+CT | Placebo+CT | 6 | 0 | LDL-C, clinical endpoint | ||||||||
| Myasoedova et al 2016 | 157/26; T: 77 (0/77), C: 80 (0/80) | T: 65±7, C: 65±6 | Subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in healthy postmenopausal women | Isoflavonoid-rich herbal preparation | Placebo | 12 | 12 | IMT, LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
| Zhao et al 2018 | 130/9; T: 65 (36/29), C: 65 (38/27) | T: 68.88±5.75, C: 67.26±5.49 | ACS patients after PCI | Danhong injection+Naoxintong capsule+CT | Placebo+CT | 3 | 3 | Clinical endpoint, adverse events | ||||||||
| Chen et al 2006 | 335/21; T: 157 (124/33), C: 157 (123/34) | T: 58.52±10.30, C: 58.74±9.91 | CHD after PCI | XS0601+CT | Aspirin+ CT | 6 | 6 | Clinical endpoint, adverse events | ||||||||
| Ge et al 2014 | 236/0; T: 116 (68/48), C: 120 (72/48) | T: 65.23±12.19, C: 67.03±13.46 | ACS after PCI | Maixuekang Capsule+CT | CT | 6 | 6 | hs-CRP, LDL-C, clinical endpoint | ||||||||
| Zhao et al 2004 | 50/0; T: 25 (15/10), C: 25 (14/11) | T: 58.2±14.2, C: 59.1±6.3 | CHD | Xuezhikang+CT | Placebo+CT | 3/2 | 0 | LDL-C | ||||||||
| Zhang et al 2008 | 120; T: 60 (36/24), C: 60 (35/25) | T: 55.9±16.1, C: 54.2±14.3 | CHD complicated by diabetes mellitus | Shengmai injection+CT | CT | 3/4 | 0 | FMD, adverse events | ||||||||
| Xu et al 2018 | 710/24; T: 353 (157/196), C: 357 (147/210) | T: 58.31±9.82, C:57.20±9.84 | Patients with CHD or at high risk of CHD | Zhibitai compound capsule+CT | CT | 2 | 0 | LDL-C, adverse events | ||||||||
| Cheng et al 2006 | 79; T: 39 (33/6), C: 40 (31/9) | T: 52.73±7.89, C: 53.11±7.01 | Primary hypertension and coronary artery disease | Garlicin+CT | CT | 13 | 0 | Hs-CRP, IMT, adverse events | ||||||||
| Liu et al 2017 | 62; T: 32 (22/10), C: 30 (20/10) | T: 61.1±12.0, C: 60.4±13.4 | CHD and hyperhomocysteinemia | Allicin+CT | CT | 3 | 0 | IMT | ||||||||
| Study ID | Sample (overall/dropout); sex: M/F | Age (years) | Participant | Intervention group | Control group | Treatment (months) | Follow-up (months) | Outcome measure | ||||||||
| Chu et al 2010 | 90/4; T1: 30 (18/12), T2: 30 (15/15), C: 30 (20/10) | T1: 61.7±9.6, T2: 61.6±9.2, C: 58.8±8.9 | Patients with unstable angina and blood-stasis syndrome after PCI | T1: Xuefu Zhuyu capsule + placebo of Shenmai capsule + CT T2: Shengmai capsule + placebo of Xuefu Zhuyu capsule + CT | Placebo of Xuefu Zhuyu capsule and Shengmai capsule +CT | 1 | 0 | Adverse events | ||||||||
| 1. | Fredman G, Spite M. Recent advances in the role of immunity in atherosclerosis. Circ Res 2013; 113: e111-4. |
| 2. | Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 2011; 473: 317-25. |
| 3. |
Smith SC, Collins A, Ferrari R, et al. Our time: a call to save preventable death from cardiovascular disease (heart disease and stroke). J Am Coll Cardiol 2012; 60: 2343-8.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Sever PS, Dahlof B, Poulter NR, et al. Investigators. Prevention of coronary and stroke events with atorvastatin in hypertensive patients who have average or lower-than-average cholesterol concentrations, in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial-Lipid Lowering Arm (ASCOT-LLA): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London, England) 2003; 361: 1149-58. |
| 5. | Collins R, Armitage J, Parish S, Sleight P, Peto R, Collaborati HPS. MRC/BHF heart protection study of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin in 5963 people with diabetes: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (London, England) 2003; 361: 2005-16. |
| 6. |
Stroes ES, Thompson PD, Corsini A, et al. Society. Statin-associated muscle symptoms: impact on statin therapy-European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel Statement on Assessment, Aetiology and Management. Eur Heart J 2015; 36: 1012-22b.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Hao PP, Jiang F, Cheng J, Ma LY, Zhang Y, Zhao YX. Traditional Chinese Medicine for cardiovascular disease evidence and potential mechanisms. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017; 69: 2952-66. |
| 8. |
Sedighi M, Bahmani M, Asgary S, Beyranvand F, Rafieian-Kopaei M. A review of plant-based compounds and medicinal plants effective on atherosclerosis. J Res Med Sci 2017; 22: 30.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Hao PP, Jiang F, Chen YG, et al. Evidence for traditional Chinese medication to treat cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 2015; 12: 374. |
| 10. |
Liu CQ, Huang Y. Chinese herbal medicine on cardiovascular diseases and the mechanisms of action. Front Pharmacol 2016; 7: 469.
PMID |
| 11. |
Al-Shehabi TS, Iratni R, Eid AH. Anti-atherosclerotic plants which modulate the phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells. Phytomedicine 2016; 23: 1068-81.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Wang D, Yu W, Liu Y, et al. Roles of autophagy in ischemic heart diseases and the modulatory effects of Chinese herbal medicine. Am J Chin Med 2017; 45: 1401-19. |
| 13. | Liu Q, Li J, Hartstone-Rose A, et al. Chinese herbal compounds for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis: experimental evidence and mechanisms. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015: 2015: 752610. |
| 14. |
Jian X, Liu Y, Zhao Z, Zhao L, Wang D, Liu Q. The role of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis through the regulation of macrophage activity. Biomed Pharmacother 2019, 118: 109375.
DOI |
| 15. | Liu Q, Li J, Liang Q, et al. Sparstolonin B suppresses rat vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration, inflammatory response and lipid accumulation. Vascul Pharmacol 2015; 67-69: 59-66. |
| 16. | Wang D, Liu Y, Zhong G, Wang Y, Zhang T, Zhao Z. Compatibility of Tanshinone ⅡA and Astragaloside Ⅳ in attenuating hypoxia-induced cardiomyocytes injury. J Ethnopharmacology 2017; 204: 67-76. |
| 17. | Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and Meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med 2009; 6: e1000100. |
| 18. | Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from http://www.cochrane-handbook.org/. |
| 19. | Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011; 343: d5928. |
| 20. |
Moriarty PM, Roth EM, Karns A, et al. Effects of Xuezhikang in patients with dyslipidemia: a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Lipidol 2014; 8: 568-75.
DOI PMID |
| 21. | Van Poppel PCM, Breedveld P, Abbink EJ, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza root water-extract (Danshen) has no beneficial effect on cardiovascular risk factors. A randomized double-blind cross-over trial. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0128695. |
| 22. |
Kwok T, Leung PC, Lam C, et al. A randomized placebo controlled trial of an innovative herbal formula in the prevention of atherosclerosis in postmenopausal women with borderline hypercholesterolemia. Complement Ther Med 2014; 22: 473-80.
DOI PMID |
| 23. | Woo KS, Yip TWC, Chook P, et al. Cardiovascular protective effects of adjunctive alternative medicine (Salvia miltiorrhiza and Pueraria lobata) in high-risk hypertension. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013: 2013: 132912. |
| 24. | Li DQ, Lyu FF, Li ZC, Dai ZY, Wang HX, Han Y. Anti-atherosclerotic effects between a combined treatment with simvastatin plus hirudin and single simvastatin therapy in patients with early type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Transl Med 2019; 7: 302. |
| 25. |
Zhang M, Liu Y, Xu M, et al. Carotid artery plaque intervention with Tongxinluo capsule (CAPITAL): a multicenter randomized double-blind parallel-group placebo-controlled study. Sci Rep 2019; 9: 4545.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Liu YF, Yu HM, Zhang C, et al. Treatment with rhubarb improves brachial artery endothelial function in patients with atherosclerosis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Am J Chin Med 2007; 35: 583-95. |
| 27. | Wang XJ, Rao XR, Li S, et al. Effect of Huanshuai recipe oral liquid ([characters: see text]) on renal dysfunction progression in patients with atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Chin J Integr Med 2015; 21: 811-6. |
| 28. | Myasoedova VA, Kirichenko TV, Melnichenko AA, et al. Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects of a Phytoestrogen-Rich Herbal Preparation in Postmenopausal Women. Int J Mol Sci 2016; 17: 1318. |
| 29. | Zhao S, Tang Y, Cai H, et al. Treatment of Danhong injection combined with Naoxintong capsule in acute coronary syndrome patients undergoing PCI operation: study for a randomized controlled and double-blind trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018: 2018: 8485472. |
| 30. | Chen KJ, Shi DZ, Xu H, et al. XS0601 reduces the incidence of restenosis: a prospective study of 335 patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention in China. Chin Med J (Engl) 2006; 119: 6-13. |
| 31. | Ge CJ, Yuan F, Feng LX, et al. Clinical effect of Maixuekang Capsule on long-term prognosis in patients with acute coronary syndrome after percutaneous coronary intervention. Chin J Integr Med 2014; 20: 88-93. |
| 32. |
Zhao SP, Liu L, Cheng YC, et al. Xuezhikang, an extract of cholestin, protects endothelial function through antiinflammatory and lipid-lowering mechanisms in patients with coronary heart disease. Circulation 2004; 110: 915-20.
PMID |
| 33. | Zhang YC, Lu BJ, Zhao MH, Rong YZ, Chen RM. Effect of Shengmai injection on vascular endothelial and heart functions in patients with coronary heart disease complicated with diabetes mellitus. Chin J Integr Med 2008; 14: 281-5. |
| 34. |
Xu D, Hu J, Wu Q, et al. Efficacy and safety of Zhibitai in combination with atorvastatin for lipid lowering in patients with coronary heart disease. Oncotarget 2018; 9: 9489-97.
DOI PMID |
| 35. | Cheng WL, Ke YN, Shi ZX, et al. Clinical study on effect of garlicin in stabilizing the carotid artery atherosclerotic plaque in patients with primary hypertension and coronary artery disease. Chin J Integr Med 2006; 12: 166-70. |
| 36. | Liu DS, Wang SL, Li JM, Liang ES, Yan MZ, Gao W. Allicin improves carotid artery intima-media thickness in coronary artery disease patients with hyperhomocysteinemia. Exp Ther Med 2017; 14: 1722-6. |
| 37. | Chu FY, Wang J, Yao KW, Li ZZ. Effect of Xuefu Zhuyu capsule on the symptoms and signs and health-related quality of life in the unstable angina patients with blood-stasis syndrome after percutaneous coronary intervention: a randomized controlled trial. Chin J Integr Med 2010; 16: 399-405. |
| 38. | Xu S, Little PJ, Lan T, et al. Tanshinone Ⅱ-A attenuates and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein-E knockout mice fed a high cholesterol diet. Arch Biochem Biophys 2011; 515: 72-9. |
| 39. |
Duan J, Xiang D, Luo H, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine suppresses lipid accumulation in macrophages via upregulation of the ATP-binding cassette transporters and downregulation of scavenger receptors. Oncol Rep 2017; 38: 2267-76.
DOI PMID |
| 40. | Wang Y, Zhao X, Wang YS, Song SL, Liang H, Ji AG. An extract from medical leech improve the function of endothelial cells in vitro and attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE null mice by reducing macrophages in the lesions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014; 455: 119-25. |
| 41. | Zhang X, Liu MH, Qiao L, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 enhances atherosclerotic plaque stability by skewing macrophages to the M2 phenotype. J Cell Mol Med 2017; 22: 409-16. |
| 42. |
Qiao L, Zhang X, Liu M, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 enhances atherosclerotic plaque stability by improving autophagy and lipid metabolism in macrophage foam cells. Front Pharmacol 2017; 8: 727.
DOI PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||