Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 417-426.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240402.003
• Meta-Analyses • Next Articles
Efficacy of substances containing 3 types of active ingredients-saponins, flavones, and alkaloids in regulation of cytokines in autoimmune diseases a systematic review and Meta-analysis based on animal studies
ZHU Ruifang1,3, ZHANG Jun2, LYU Yaru2, CHEN Yulu2, HAN Shifan3( ), WANG Hongwei1(
), WANG Hongwei1( )
)
- 1 Key Laboratory for Molecular Diagnosis and Treatment of Hematologic Diseases, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi 030001, China
2 School of Nursing, Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi 030001, China
3 Editorial Office, First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi 030001, China
-
Received:2023-07-16Accepted:2023-10-31Online:2024-06-15Published:2024-04-02 -
Contact:WANG Hongwei, Haematology Department, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan City, Shanxi 030001, China.wanghw68@hotmail.com ; HAN Shifan, Editorial Office, First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan City, Shanxi 030001, China.shifan.han@sxmu.edu.cn Telephone: +86-13513639012 -
Supported by:Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province: to Explore the Material Basis and Mechanism of Codonopsis Pilosula for Preventing and Treating Immune Thrombocytopenia based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking(202203021221251);Doctor Starting Foundation of First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University: Material Basis and Mechanism of Codonopsis Pilosula for Preventing and Treating Immune Thrombocytopenia(YB2203)
Cite this article
ZHU Ruifang, ZHANG Jun, LYU Yaru, CHEN Yulu, HAN Shifan, WANG Hongwei. Efficacy of substances containing 3 types of active ingredients-saponins, flavones, and alkaloids in regulation of cytokines in autoimmune diseases a systematic review and Meta-analysis based on animal studies[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 417-426.
share this article
| Literature | Type of disease | Interventional substance | Type of animal | No. of animals (male/female) | Animal weight (g) | Outcome indicator | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saponins | |||||||
| Zhang Y 200512 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Total saponins of Jixiangcao (Pink reineckia) | Wistar rats | 70/0 | 180-220 | 1 | |
| Ma HL 200813 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | Esculentoside | BXSB mice | 24/0 | 20-25 | 4, 7 | |
| Huang Q et al 201314 | Autoimmune thyroiditis | Ginsenosides | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-200 | 2, 3 | |
| Gu SD 201315 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Chibao (Thladiantha dubia) | SD rats | 80/0 | 160-180 | 4, 5 | |
| Chen JY 201416 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Ginsenosides | SD rats | 80/0 | 100-140 | 1, 3 | |
| Feng XH et al 201517 | Autoimmune thyroiditis | Ginsenosides | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-200 | 4, 7 | |
| Cao YJ et al 201618 | Hashimoto's thyroiditis | Water-soluble total saponins of Chuanshanlong (Rhizoma Dioscoreae Nipponicae) | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-200 | 2, 3 | |
| Huang YN 201919 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Escin | SD rats | 60/0 | 180-220 | 4, 7 | |
| Zeng HL 202020 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | Esculentoside | - | 0/24 | 18-22 | 5, 6 | |
| Xu W 202121 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Ginsenosides | C57BL/6 mice | 0/30 | 16-18 | 4, 5, 8 | |
| Xia FL et al 202122 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Dioscin | C57BL/6 mice | 0/40 | 20-30 | 3, 6, 8 | |
| Ma CJ et al 202123 | Autoimmune thyroiditis | Ginsenosides | BALB/C mice | 0/30 | 16-18 | 3, 8 | |
| Flavones | |||||||
| Feng GY 200924 | Autoimmune gastritis | Dihydromyricetin | SD rats | 30/30 | 180-220 | 2, 3 | |
| Zhong J 201325 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Huangqin (Scutellaria baicalensis) stem-leaf total flavonoid | C57BL/6 mice | 90/0 | 16-20 | 5, 8 | |
| Zhong J 201326 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Total flavonoids from Laoyingcha (Litsea Coreana Levl) | C57BL/6 mice | 60/0 | 180-220 | 1, 7 | |
| Zhong C 201627 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Total flavonoids of Astragalus | Wistar rats | 42/0 | 200-240 | 1, 7 | |
| Li YN et al 201828 | Thromboangiitis obliterans | Total flavonoids of Guoshanjue (Camptosorus sibiricus Rupr.) | Wistar rats | 70/0 | 180-220 | 4, 7 | |
| Wang HX 202029 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside | SD rats | 72/0 | — | 2, 4, 5, 7, 8 | |
| Li QL et al 202130 | Hashimoto's thyroiditis | Total flavones of Yinyanghuo (Epimedium) | HT rats | 0/60 | 150-180 | 4, 5, 6, 8 | |
| Alkaloids | |||||||
| Guo L et al 200431 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Sinomenine | Wistar rats | 0/36 | 180-200 | 5, 7, 8 | |
| Wang LQ et al 200932 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Tetrandrine | Wistar rats | 0/30 | 180-220 | 8 | |
| Guo XB et al 201033 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Matrine | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-220 | 3, 8 | |
| Guo X et al 201034 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Oxymatrine | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-220 | 7 | |
| Zhao XY 201135 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Matrine | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-220 | 6 | |
| Liu N 201336 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Matrine | Wistar rats | 0/50 | 180-220 | 3, 5 | |
| Yang DQ 201437 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Sinomeninec | SD rats | 50/50 | 180-220 | 5, 8 | |
| Guo XB et al 201538 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Matrine | Wistar rats | 0/30 | 180-220 | 5 | |
| Zhu ZG et al 201539 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Berberine | Lewis rats | 0/24 | 150-180 | 5, 7, 8 | |
| Li N 201740 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Leonurine | DBA/1 mice | 32/0 | 18-22 | 1, 4, 7 | |
| Zhao ZM 201841 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Sinomenine | DBA/1 mice | 30/0 | 20-30 | 3, 4, 5, 7 | |
| Tan MA 201842 | Autoimmune hepatitis | Sinomenine | Wistar rats | 0/42 | 190-220 | 2, 5 | |
Table 1 Basic characteristics of 31 studies
| Literature | Type of disease | Interventional substance | Type of animal | No. of animals (male/female) | Animal weight (g) | Outcome indicator | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saponins | |||||||
| Zhang Y 200512 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Total saponins of Jixiangcao (Pink reineckia) | Wistar rats | 70/0 | 180-220 | 1 | |
| Ma HL 200813 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | Esculentoside | BXSB mice | 24/0 | 20-25 | 4, 7 | |
| Huang Q et al 201314 | Autoimmune thyroiditis | Ginsenosides | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-200 | 2, 3 | |
| Gu SD 201315 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Chibao (Thladiantha dubia) | SD rats | 80/0 | 160-180 | 4, 5 | |
| Chen JY 201416 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Ginsenosides | SD rats | 80/0 | 100-140 | 1, 3 | |
| Feng XH et al 201517 | Autoimmune thyroiditis | Ginsenosides | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-200 | 4, 7 | |
| Cao YJ et al 201618 | Hashimoto's thyroiditis | Water-soluble total saponins of Chuanshanlong (Rhizoma Dioscoreae Nipponicae) | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-200 | 2, 3 | |
| Huang YN 201919 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Escin | SD rats | 60/0 | 180-220 | 4, 7 | |
| Zeng HL 202020 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | Esculentoside | - | 0/24 | 18-22 | 5, 6 | |
| Xu W 202121 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Ginsenosides | C57BL/6 mice | 0/30 | 16-18 | 4, 5, 8 | |
| Xia FL et al 202122 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Dioscin | C57BL/6 mice | 0/40 | 20-30 | 3, 6, 8 | |
| Ma CJ et al 202123 | Autoimmune thyroiditis | Ginsenosides | BALB/C mice | 0/30 | 16-18 | 3, 8 | |
| Flavones | |||||||
| Feng GY 200924 | Autoimmune gastritis | Dihydromyricetin | SD rats | 30/30 | 180-220 | 2, 3 | |
| Zhong J 201325 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Huangqin (Scutellaria baicalensis) stem-leaf total flavonoid | C57BL/6 mice | 90/0 | 16-20 | 5, 8 | |
| Zhong J 201326 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Total flavonoids from Laoyingcha (Litsea Coreana Levl) | C57BL/6 mice | 60/0 | 180-220 | 1, 7 | |
| Zhong C 201627 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Total flavonoids of Astragalus | Wistar rats | 42/0 | 200-240 | 1, 7 | |
| Li YN et al 201828 | Thromboangiitis obliterans | Total flavonoids of Guoshanjue (Camptosorus sibiricus Rupr.) | Wistar rats | 70/0 | 180-220 | 4, 7 | |
| Wang HX 202029 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside | SD rats | 72/0 | — | 2, 4, 5, 7, 8 | |
| Li QL et al 202130 | Hashimoto's thyroiditis | Total flavones of Yinyanghuo (Epimedium) | HT rats | 0/60 | 150-180 | 4, 5, 6, 8 | |
| Alkaloids | |||||||
| Guo L et al 200431 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Sinomenine | Wistar rats | 0/36 | 180-200 | 5, 7, 8 | |
| Wang LQ et al 200932 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Tetrandrine | Wistar rats | 0/30 | 180-220 | 8 | |
| Guo XB et al 201033 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Matrine | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-220 | 3, 8 | |
| Guo X et al 201034 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Oxymatrine | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-220 | 7 | |
| Zhao XY 201135 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Matrine | Wistar rats | 0/40 | 180-220 | 6 | |
| Liu N 201336 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Matrine | Wistar rats | 0/50 | 180-220 | 3, 5 | |
| Yang DQ 201437 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Sinomeninec | SD rats | 50/50 | 180-220 | 5, 8 | |
| Guo XB et al 201538 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Matrine | Wistar rats | 0/30 | 180-220 | 5 | |
| Zhu ZG et al 201539 | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Berberine | Lewis rats | 0/24 | 150-180 | 5, 7, 8 | |
| Li N 201740 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Leonurine | DBA/1 mice | 32/0 | 18-22 | 1, 4, 7 | |
| Zhao ZM 201841 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Sinomenine | DBA/1 mice | 30/0 | 20-30 | 3, 4, 5, 7 | |
| Tan MA 201842 | Autoimmune hepatitis | Sinomenine | Wistar rats | 0/42 | 190-220 | 2, 5 | |
| Literature | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang Y 200512 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Ma HL 200813 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Huang Q et al 201314 | Y | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Gu SD 201315 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Chen JY 201416 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Feng XH et al 201517 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Cao YJ et al 201618 | Y | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Huang YN 201919 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zeng HL 202020 | Y | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Xu W 202121 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Xia FL et al 202122 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Ma CJ et al 202123 | Y | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Feng GY 200924 | Y | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhong J 201325 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhong J 201326 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhong C 201627 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Li YN et al 201828 | Y | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Wang HX 202029 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Li QL et al 202130 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Guo L et al 200431 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Wang LQ et al 200932 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Guo XB et al 201033 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Guo X et al 201034 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhao XY 201135 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Liu N 201336 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Yang DQ 201437 | Y | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | Y | U |
| Guo XB et al 201538 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhu ZG et al 201539 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Li N 201740 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhao ZM 201841 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Tan MA 201842 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
Table 2 Risk of bias assessment results
| Literature | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang Y 200512 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Ma HL 200813 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Huang Q et al 201314 | Y | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Gu SD 201315 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Chen JY 201416 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Feng XH et al 201517 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Cao YJ et al 201618 | Y | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Huang YN 201919 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zeng HL 202020 | Y | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Xu W 202121 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Xia FL et al 202122 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Ma CJ et al 202123 | Y | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Feng GY 200924 | Y | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhong J 201325 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhong J 201326 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhong C 201627 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Li YN et al 201828 | Y | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Wang HX 202029 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Li QL et al 202130 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Guo L et al 200431 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Wang LQ et al 200932 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Guo XB et al 201033 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Guo X et al 201034 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhao XY 201135 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Liu N 201336 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Yang DQ 201437 | Y | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | Y | U |
| Guo XB et al 201538 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhu ZG et al 201539 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Li N 201740 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Zhao ZM 201841 | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Tan MA 201842 | U | U | U | Y | U | U | U | U | Y | U |
| Outcome indicator | Subtype and total | No. of studies included | Sample size (animals) | Heterogeneity tests | Effect model | Meta-analysis results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention group | Model group | I 2 (%) | P value | SMD (95% CI) | P value | |||||
| IL-1β | Saponins | 1 | 8 | 8 | - | - | Random | -1.03 (-2.09, 0.03) | 0.06 | |
| Flavones | 2 | 17 | 17 | 0 | 0.42 | Fixed | -1.69 (-2.51, -0.87) | <0.0001 | ||
| Alkaloids | 1 | 8 | 8 | - | - | Random | -3.98 (-5.85, -2.11) | <0.0001 | ||
| Total | 4 | 33 | 33 | 62 | 0.05 | Random | -1.94 (-2.99, -0.90) | 0.0003 | ||
| IL-2 | Saponins | 2 | 16 | 16 | 0 | 0.32 | Fixed | -0.74 (-1.47, -0.01) | 0.05 | |
| Flavones | 2 | 34 | 34 | 64 | 0.10 | Random | 0.63 (-0.29, 1.55) | 0.18 | ||
| Alkaloids | 1 | 7 | 7 | - | - | Random | -4.97 (-7.38, -2.56) | <0.0001 | ||
| Total | 5 | 57 | 57 | 86 | <0.0001 | Random | -0.63 (-1.82, 0.57) | 0.30 | ||
| IL-4 | Saponins | 5 | 44 | 44 | 87 | <0.00001 | Random | 0.49 (-0.87, 1.85) | 0.48 | |
| Flavones | 2 | 34 | 34 | 74 | 0.05 | Random | -0.57 (-1.68,0.53) | 0.31 | ||
| Alkaloids | 3 | 25 | 25 | 83 | 0.002 | Random | 5.37 (1.78,8.95) | 0.003 | ||
| Total | 10 | 103 | 103 | 90 | <0.00001 | Random | 1.30 (0.15, 2.44) | 0.03 | ||
| IL-6 | Saponins | 5 | 40 | 40 | 78 | 0.001 | Random | -1.71 (-2.92, -0.51) | 0.005 | |
| Flavones | 3 | 40 | 40 | 48 | 0.14 | Fixed | -0.93 (-1.40, -0.45) | 0.0001 | ||
| Alkaloids | 2 | 13 | 13 | 58 | 0.12 | Random | -2.65 (-4.81, -0.49) | 0.02 | ||
| Total | 10 | 93 | 93 | 70 | 0.0005 | Random | -1.65 (-2.33, -0.97) | <0.00001 | ||
| IL-10 | Saponins | 3 | 24 | 24 | 0 | 0.79 | Fixed | 4.19 (3.06, 5.31) | <0.00001 | |
| Flavones | 3 | 38 | 38 | 18 | 0.30 | Fixed | 0.91 (0.43, 1.40) | 0.0002 | ||
| Alkaloids | 7 | 53 | 51 | 32 | 0.19 | Fixed | 1.67 (1.18, 2.15) | <0.00001 | ||
| Total | 13 | 115 | 113 | 70 | <0.0001 | Random | 2.05 (1.39, 2.70) | <0.00001 | ||
| IL-17 | Saponins | 2 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 0.72 | Fixed | -3.62 (-4.47, -2.47) | <0.00001 | |
| Flavones | 1 | 6 | 6 | - | - | Random | -1.29 (-2.59, 0.00) | 0.05 | ||
| Alkaloids | 1 | 10 | 10 | - | - | Random | -1.57 (-2.60, -0.54) | 0.003 | ||
| Total | 4 | 34 | 34 | 68 | 0.03 | Random | -2.41 (-3.61, -1.20) | <0.0001 | ||
| TNF-α | Saponins | 3 | 26 | 26 | 0 | 0.37 | Fixed | -0.78 (-1.36, -0.21) | 0.008 | |
| Flavones | 4 | 51 | 51 | 90 | <0.00001 | Random | -1.68 (-3.35, -0.02) | 0.05 | ||
| Alkaloids | 5 | 37 | 37 | 74 | 0.004 | Random | -2.83 (-4.24, -1.42) | <0.0001 | ||
| Total | 12 | 114 | 114 | 84 | <0.00001 | Random | -1.86 (-2.69, -1.03) | <0.0001 | ||
| IFN-γ | Saponins | 3 | 26 | 26 | 84 | 0.002 | Random | -3.27 (-5.68, -0.87) | 0.008 | |
| Flavones | 3 | 38 | 38 | 89 | 0.0001 | Random | 0.73 (-1.57, 3.03) | 0.54 | ||
| Alkaloids | 5 | 41 | 39 | 70 | 0.009 | Random | -1.70 (-2.73, -0.68) | 0.001 | ||
| Total | 11 | 105 | 103 | 82 | 0.00001 | Random | -1.54 (-2.43, -0.65) | 0.0007 | ||
Table 3 Meta-analysis results
| Outcome indicator | Subtype and total | No. of studies included | Sample size (animals) | Heterogeneity tests | Effect model | Meta-analysis results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention group | Model group | I 2 (%) | P value | SMD (95% CI) | P value | |||||
| IL-1β | Saponins | 1 | 8 | 8 | - | - | Random | -1.03 (-2.09, 0.03) | 0.06 | |
| Flavones | 2 | 17 | 17 | 0 | 0.42 | Fixed | -1.69 (-2.51, -0.87) | <0.0001 | ||
| Alkaloids | 1 | 8 | 8 | - | - | Random | -3.98 (-5.85, -2.11) | <0.0001 | ||
| Total | 4 | 33 | 33 | 62 | 0.05 | Random | -1.94 (-2.99, -0.90) | 0.0003 | ||
| IL-2 | Saponins | 2 | 16 | 16 | 0 | 0.32 | Fixed | -0.74 (-1.47, -0.01) | 0.05 | |
| Flavones | 2 | 34 | 34 | 64 | 0.10 | Random | 0.63 (-0.29, 1.55) | 0.18 | ||
| Alkaloids | 1 | 7 | 7 | - | - | Random | -4.97 (-7.38, -2.56) | <0.0001 | ||
| Total | 5 | 57 | 57 | 86 | <0.0001 | Random | -0.63 (-1.82, 0.57) | 0.30 | ||
| IL-4 | Saponins | 5 | 44 | 44 | 87 | <0.00001 | Random | 0.49 (-0.87, 1.85) | 0.48 | |
| Flavones | 2 | 34 | 34 | 74 | 0.05 | Random | -0.57 (-1.68,0.53) | 0.31 | ||
| Alkaloids | 3 | 25 | 25 | 83 | 0.002 | Random | 5.37 (1.78,8.95) | 0.003 | ||
| Total | 10 | 103 | 103 | 90 | <0.00001 | Random | 1.30 (0.15, 2.44) | 0.03 | ||
| IL-6 | Saponins | 5 | 40 | 40 | 78 | 0.001 | Random | -1.71 (-2.92, -0.51) | 0.005 | |
| Flavones | 3 | 40 | 40 | 48 | 0.14 | Fixed | -0.93 (-1.40, -0.45) | 0.0001 | ||
| Alkaloids | 2 | 13 | 13 | 58 | 0.12 | Random | -2.65 (-4.81, -0.49) | 0.02 | ||
| Total | 10 | 93 | 93 | 70 | 0.0005 | Random | -1.65 (-2.33, -0.97) | <0.00001 | ||
| IL-10 | Saponins | 3 | 24 | 24 | 0 | 0.79 | Fixed | 4.19 (3.06, 5.31) | <0.00001 | |
| Flavones | 3 | 38 | 38 | 18 | 0.30 | Fixed | 0.91 (0.43, 1.40) | 0.0002 | ||
| Alkaloids | 7 | 53 | 51 | 32 | 0.19 | Fixed | 1.67 (1.18, 2.15) | <0.00001 | ||
| Total | 13 | 115 | 113 | 70 | <0.0001 | Random | 2.05 (1.39, 2.70) | <0.00001 | ||
| IL-17 | Saponins | 2 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 0.72 | Fixed | -3.62 (-4.47, -2.47) | <0.00001 | |
| Flavones | 1 | 6 | 6 | - | - | Random | -1.29 (-2.59, 0.00) | 0.05 | ||
| Alkaloids | 1 | 10 | 10 | - | - | Random | -1.57 (-2.60, -0.54) | 0.003 | ||
| Total | 4 | 34 | 34 | 68 | 0.03 | Random | -2.41 (-3.61, -1.20) | <0.0001 | ||
| TNF-α | Saponins | 3 | 26 | 26 | 0 | 0.37 | Fixed | -0.78 (-1.36, -0.21) | 0.008 | |
| Flavones | 4 | 51 | 51 | 90 | <0.00001 | Random | -1.68 (-3.35, -0.02) | 0.05 | ||
| Alkaloids | 5 | 37 | 37 | 74 | 0.004 | Random | -2.83 (-4.24, -1.42) | <0.0001 | ||
| Total | 12 | 114 | 114 | 84 | <0.00001 | Random | -1.86 (-2.69, -1.03) | <0.0001 | ||
| IFN-γ | Saponins | 3 | 26 | 26 | 84 | 0.002 | Random | -3.27 (-5.68, -0.87) | 0.008 | |
| Flavones | 3 | 38 | 38 | 89 | 0.0001 | Random | 0.73 (-1.57, 3.03) | 0.54 | ||
| Alkaloids | 5 | 41 | 39 | 70 | 0.009 | Random | -1.70 (-2.73, -0.68) | 0.001 | ||
| Total | 11 | 105 | 103 | 82 | 0.00001 | Random | -1.54 (-2.43, -0.65) | 0.0007 | ||
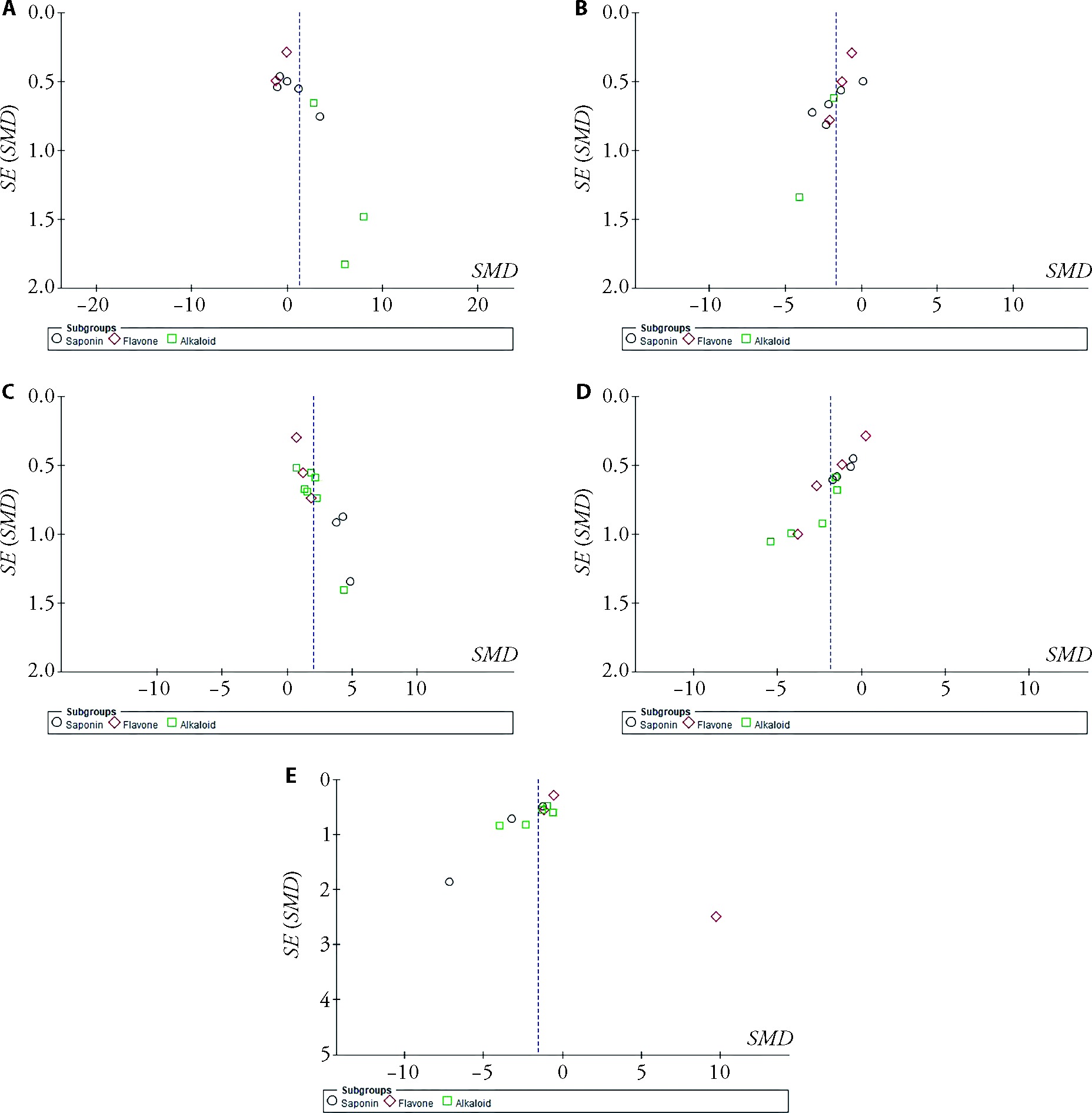
Figure 2 Funnel plot of serum IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α and INF-γ A: IL-4: interleukin 4; B: IL-6: interleukin 6; C: IL-10: interleukin 10; D: TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; E: IFN-γ: interferon γ; SMD: standardized mean difference.
| 1. |
Wang L, Wang FS, Gershwin ME. Human autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive update. J Inter Med 2015; 278: 369-95.
DOI URL |
| 2. |
Yasunaga M. Antibody therapeutics and immunoregulation in cancer and autoimmune disease. Semin Cancer Biol 2020; 64: 1-12.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Ma YX, Zhang JP. Autoantibodies and their detection and application in systemic autoimmune diseases. Guo Ji Jian Yan Yi Xue Za Zhi 2011; 32: 2087-9. |
| 4. | Pi XM, Li H, Long JW, Jin J. The application of the immunosuppressive effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine in dermatology. Chongqing 2010: Processing of treatment of skin and venereal diseases with integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; 2010 Sep 1; Chongqing, China. 2010: 131-3. |
| 5. |
Wahren-Herlenius M, Döener T. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of systemic autoimmune disease. Lancet 2013; 382: 819-31.
DOI PMID |
| 6. | Gouirand V, Habrylo I, Rosenblum MD. Regulatory T cells and inflammatory mediators in autoimmune disease. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 2022; 14: 774-80. |
| 7. |
Raphael I, Nalawade S, Eagar TN, Forsthuber TG. T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine 2015; 74: 5-17.
DOI PMID |
| 8. | Wang CN, Zhao DQ, Wang LS, Wang J. Study on the two-way immune regulation mechanism and clinical application of Ginseng and compound preparation. Shi Zhen Guo Yi Guo Yao 2021; 32: 177-80. |
| 9. | Wang YH, Yang M, Cheng XD. Effect and mechanism of natural compounds in treatment of EAE. Zhong Cao Yao 2019; 50: 1012-21. |
| 10. | Xu P, Lyu ZG, Chang TY, et al. Systematic review of qnimal experiment study on Chinese medicine intervention for autoimmune myasthenia gravis. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2018; 59: 1420-5. |
| 11. | Ban QL. A Meta-analysis on the efficacy of Buyang Huanwu Decoction in the treatment of atherosclerotic plaques, blood lipids and related inflammatory factors. Youjiang: Youjiang Medical University Nationalities, 2022: 1-83. |
| 12. | Zhang Y. The effect of total saponins of Pink Reineckia on the expression of ICAM-1 in the foot joint synovium of rats with adjuvant arthritis. Guiyang: Guiyang College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2005: 1-66. |
| 13. | Ma HL. Experimental study on the treatment of mice with BXSB lupus nephritis with Esculentoside. Zunyi: Zunyi Medical College, 2008: 1-38. |
| 14. | Huang Q, Feng XH, Zhang YX, Zhao Yl, Miao Q, Lin XJ. Effect of Ginsenosides on Th1/Th2-related cytokines in rats with experimental autoimmune thyroiditi. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2013; 54: 2132-4. |
| 15. | Gu SD. Regulation mechanism of saponins of Thladiantha Dubia on the pathway of OPG/RANKL/NF-κB in rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Chengde: Chengde Medical University, 2013: 1-59. |
| 16. | Chen JY. Antiinflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of Ginsenoside CK in treatment of experimental arthritis. Anhui: Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, 2014: 1-116. |
| 17. | Feng XH, Huang Q, Zhang YX, Chen J, Wang D, Yuan X. Effects of Ginsenoside Rg1 on TNF-α and IL-6 levels in experimental rats with autoimmune thyroiditis. Xin Zhong Yi 2015; 47: 217-9. |
| 18. | Cao YJ, Luo YP, Xu ZJ, Li H, Jiang SS. The effect of water-soluble total saponins of Rhizoma Dioscoreae Nipponicae on the expression of Th1/Th2 cytokines in experimental rats with Hashimoto's thyroiditi. Jiangsu Zhong Yi Yao 2016; 48: 81-2+85. |
| 19. | Huang YN. Protective effect and mechanism of ESCIN combined with Glucocorticoid on adjuvant arthritis in rats. Yantai: Yantai University, 2019: 1-77. |
| 20. | Zeng HL. Effect of Esculentoside A on nephritis in MRL/lpr mice and expression of CD19+IL-35+breg cells and IL-35. Zunyi: Zunyi Medical College, 2020: 1-56. |
| 21. | Xu W, Zhou Y, Zhu GQ. Role and immune mechanism of Ginsenoside Rg1 in inhibiting experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Anhui Zhong Yi Da Xue Xue Bao 2021; 40: 76-81. |
| 22. | Xia FL, Shen LY, Cao Y, Lin ZJ. Study on the protective effect and mechanism of Dioscin on the injury of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in mice. Zhong Yi Yao Dao Bao 2021; 27: 13-8. |
| 23. | Ma CJ, Chen M, Zhang Q, Zhang JF. Effects of Ginsenoside RG3 on thyroid function and helper T cell subsets in mice with autoimmune thyroiditis and related mechanisms. Lin Chuang He Shi Yan Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021; 20: 1464-7. |
| 24. | Chen LF, Zhang Q, Dong QQ. Protective effect and mechanism of dihydromyricetin on gastric mucosal injury of autoimmune chronic gastritis rats. Zhong Guo Yao Li Xue Yu Du Li Xue Za Zhi 2009; 23: 381-7. |
| 25. | Feng GY. Effects of the Scutellaria Baicalensis stem-leaf total flavonoid on the cellular immune function of mouse with collagen-induced arthritis. Chengde: Chengde Medical University, 2013: 1-71. |
| 26. | Zhong J. Effects of total flavonoids from Litsea Coreana Levl on adjuvant-induced arthritis and the relationship between ER stress. Anhui: Anhui Medical University, 2013: 1-74. |
| 27. | Zhang C. Study of the regulatory effects of total flavonoids of Astragalus on OPG/RANKL/NF-κB pathway in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Yanbian: Yanbian University, 2016: 1-52. |
| 28. | Li YN, Liu XY, Song ZH. The effect of total flavonoids of Camptosorus sibiricus Rupr. on the endothelial function and thrombosis factor in rat with thromboangitis obliteran. Zhong Guo Yao Li Yu Lin Chuang 2018; 34: 80-4. |
| 29. | Wang HX. Investigating the therapeutic effects of Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside on rheumatoid arthritis. Shandong: Shandong University, 2020: 1-96. |
| 30. | Li QL, Zhang HJ, Ge MH, Zheng CM. Study of mechanism of total flavonoids of epimedium on prevention and treatment of Hashimoto's thyroiditis based on Th17/Treg balance and IL-23/IL-17 inflammatory axis. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2021; 39: 71-7+266-7. |
| 31. | Guo L, Li YH, Ji XH, et al. The treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rats by Sinomenin. Nanjing Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2004; 2: 100-2+192. |
| 32. | Wang LQ, Wang SJ, Song YF, Guo XB, Wang B. Preventive and therapeutic effect of tetrandrine on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rats. Zhong Guo Yao Fang 2009; 20: 894-6. |
| 33. | Guo XB, Kan QC, Song YF, Zhu L, Li X, Zhang GX. Prevention and treatment of autoimmune encephalomyelitis in experimental rats using matrine. Shandong Yi Yao 2010; 50: 30-1. |
| 34. | Guo X, Kan Q, Song Y, et al. Effect of Oxymatrine on interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha serum levels in an experimental rat model of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neural Regen Res 2010; 5: 6. |
| 35. | Zhao XY. The preventive treatment of EAE in Wistar rats by using matrine and the mechanism of action. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2011: 1-62. |
| 36. | Liu N. The Immunologic mechanism of action of EAE in Wistar rats by using matrine and the preventive treatment. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2013: 1-72. |
| 37. | Yang DQ. Experimental study on the effects of Sinomenine on rheumatoid arthritis rats pattern recognition receptor TLR8. Chengdu: Chengdu University Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014: 1-62. |
| 38. | Guo XB, Li WY, Zhang Y, Liu XL. Research on matrine in promoting the expressions of interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-β1 in EAE rat. Zhong Guo Yao Ye 2015; 24: B11. |
| 39. | Zhu ZG, Huang YJ, Zhang YT, Li JM. Effects of Berberine on microglia and cytokines in rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Zhong Guo Xian Dai Ying Yong Yao Xue 2015; 32: 141-4. |
| 40. | Li N. Leonurine regulates activation, migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University Chinese Medicine, 2017: 1-89. |
| 41. | Zhao ZM. The possible mechanism of PAD enzyme in rheumatoid arthritis induced by lung injury in CIA mice and the effect of Sinomenine. Nanjing: Nanjing University Chinese Medicine, 2018: 1-118. |
| 42. | Tan MA. Effect of Sinomenine and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on immune liver injury of rats induced by Con A. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University Chinese Medicine, 2018: 1-58. |
| 43. |
Stojanovich L, Marisavljevich D. Stress as a trigger of autoimmune disease. Autoimmun Rev 2008; 7: 209-13.
DOI PMID |
| 44. |
Darif D, Hammi I, Kihel A, Saik IEl, Guessous F, Akarid K. The pro-inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 pathogenesis: what goes wrong? Microb Pathog 2021; 153: 104799.
DOI URL |
| 45. |
Liu E, Perl A. Pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2019; 31: 307-15.
DOI PMID |
| 46. |
Chen Z, Bozec A, Ramming A, Schett G. Anti-inflammatory and immune-regulatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumato 2019; 15: 9-17.
DOI |
| 47. | Su SM. Studies on the effects of warming stomach on rats with cold syndrome of gastric ulcer and chemical constituents of different parts of five Alpinia herbs. Guangxi: Guangxi Tradititonal Chinese Medical University, 2019: 1-109. |
| 48. |
Yu L, Wan H, Jin W, et al. Protective effects of effective ingredients of Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) and Honghua (Flos Carthami) compatibility after rat hippocampal neurons induced by hypoxia injury. J Tradit Chin Med 2018; 38: 685-97.
DOI URL |
| 49. | Jia DW, Xu DR, Li R. Study of the immunoregulatory effect of sanguis draconis flavones on the spleen lymphocytes of mice. Ya Tai Chuan Tong Yi Yao 2018; 14: 20-3. |
| 50. | Huang WK, Liu RJ, Jia N, et al. The effect of total flavonoids from ammopiptanthus mongolicus on the immune function and ultrastructure of thymus and spleen in immunosuppressed mice. Shou Mu Shou Yi Xue Bao 2018; 49: 1752-60. |
| 51. |
Gaffen SL, Liu KD. Overview of interleukin-2 function, production and clinical applications. Cytokine 2004; 28: 109-23.
DOI PMID |
| 52. |
D'hennezel E, Kornete M, Piccirillo CA. IL-2 as a therapeutic target for the restoration of Foxp3+ regulatory T cell function in organ-specific autoimmunity: implications in pathophysiology and translation to human disease. J Transl Med 2010; 8: 113.
DOI PMID |
| 53. | Cruz-Muñoz JR, Barrios-García T, Valdez-Morales EE, et al. Ethanolic extract from Lepidium virginicum L. ameliorates DNBS-induced colitis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2022; 289: 115056. |
| 54. | Lyu GY, Li LW, Chen SH, et al. Effect of Huangqi Shengmai polysaccharide in two administration routines on mice immune function. Zhong Yao Xin Yao Yu Lin Chuang Yao Li 2006: 402-4. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||