Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 400-407.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220311.004
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism underlying efficacy of Shugan Sanjie decoction (疏肝散结汤) on plasma cell mastitis, based on network pharmacology and experimental verification
QIAO Nan1, WANG Qinnan2, MA Chaoqun3( ), CHEN Dexuan1, CHEN Haidong3, LU Yaoyao3
), CHEN Dexuan1, CHEN Haidong3, LU Yaoyao3
- 1 Department of general surgery, Nantong Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nantong 226001, China
2 Department of science and education, Affiliated Nantong Hospital of Shanghai University, Nantong 226000, China
3 Department of general surgery, Affiliated Hospital to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China
-
Received:2021-04-12Accepted:2021-07-25Online:2022-06-15Published:2022-03-11 -
Contact:MA Chaoqun -
About author:MA Chaoqun, Department of general surgery, Affiliated Hospital to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China. mcq_1964@sina.com.Telephone: +86-18251313699
-
Supported by:Clinical Medicine Project of Nantong University for Youth(2019LQ018);Youth Project of Nantong Municipal Health Committee(QA2020013);Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Nantong Science and Technology(MSZ18254)
Cite this article
QIAO Nan, WANG Qinnan, MA Chaoqun, CHEN Dexuan, CHEN Haidong, LU Yaoyao. Mechanism underlying efficacy of Shugan Sanjie decoction (疏肝散结汤) on plasma cell mastitis, based on network pharmacology and experimental verification[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 400-407.
share this article
| TCMSP Number | Components | TCMSP Number | Components |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | MOL003283 | (2R,3R,4S)-4-(4-Hydroxy-3-Methoxy-Phenyl)-7-Methoxy-2,3-Dimethylol-Tetralin-6-Ol |
| MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | MOL003290 | (3R,4R)-3,4-Bis[(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)Methyl]Oxolan-2-One |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | MOL003315 | 3beta-Acetyl-20,25-Epoxydammarane-24alpha-Ol |
| MOL004598 | 3,5,6,7-Tetramethoxy-2-(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl) Chromone | MOL000211 | Mairin |
| MOL004718 | Α-Spinasterol | MOL003347 | Hyperforin |
| MOL000098 | Quercetin | MOL000522 | Arctiin |
| MOL000282 | Ergosta-7,22E-Dien-3beta-Ol | MOL000006 | Luteolin |
| MOL000283 | Ergosterol Peroxide | MOL003044 | Chryseriol |
| MOL000296 | Hederagenin | MOL003542 | 8-Isopentenyl-Kaempferol |
| MOL004355 | Spinasterol | MOL004074 | Stigmasterol Glucoside_Qt |
| MOL006756 | Schottenol | MOL001406 | Crocetin |
| MOL007165 | 10α-Cucurbita-5,24-Diene-3β-Ol | MOL004561 | Sudan III |
| MOL007171 | 5-Dehydrokarounidiol | MOL003095 | 5-Hydroxy-7-Methoxy-2-(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl)Chromone |
| MOL001689 | Acacetin | MOL000797 | (22e,24r)-Ergosta-7,22-Dien-3-One |
| MOL000173 | Wogonin | MOL000798 | Ergosta-7,22-Diene-3β-Ol |
| MOL000228 | (2R)-7-Hydroxy-5-Methoxy-2-Phenylchroman-4-One | MOL000816 | Ergosta-7,22-Dien-3-One |
| MOL002714 | Baicalein | MOL000817 | Ergosta-5,7,22-Trien-3-Ol |
| MOL002928 | Oroxylin A | MOL004085 | Taraxasterol |
| MOL002933 | 5,7,4'-Trihydroxy-8-Methoxyflavone | MOL000394 | Choline |
| MOL002934 | Neobaicalein | MOL003837 | Esculetin |
| MOL000358 | Beta-Sitosterol | MOL000414 | Caffeic Acid |
| MOL000359 | Sitosterol | MOL006554 | Taraxerol |
| MOL000073 | Ent-Epicatechin | ||
| MOL001458 | Coptisine | ||
| MOL002897 | Epiberberine |
Table 1 Active components of SGSJD
| TCMSP Number | Components | TCMSP Number | Components |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | MOL003283 | (2R,3R,4S)-4-(4-Hydroxy-3-Methoxy-Phenyl)-7-Methoxy-2,3-Dimethylol-Tetralin-6-Ol |
| MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | MOL003290 | (3R,4R)-3,4-Bis[(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)Methyl]Oxolan-2-One |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | MOL003315 | 3beta-Acetyl-20,25-Epoxydammarane-24alpha-Ol |
| MOL004598 | 3,5,6,7-Tetramethoxy-2-(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl) Chromone | MOL000211 | Mairin |
| MOL004718 | Α-Spinasterol | MOL003347 | Hyperforin |
| MOL000098 | Quercetin | MOL000522 | Arctiin |
| MOL000282 | Ergosta-7,22E-Dien-3beta-Ol | MOL000006 | Luteolin |
| MOL000283 | Ergosterol Peroxide | MOL003044 | Chryseriol |
| MOL000296 | Hederagenin | MOL003542 | 8-Isopentenyl-Kaempferol |
| MOL004355 | Spinasterol | MOL004074 | Stigmasterol Glucoside_Qt |
| MOL006756 | Schottenol | MOL001406 | Crocetin |
| MOL007165 | 10α-Cucurbita-5,24-Diene-3β-Ol | MOL004561 | Sudan III |
| MOL007171 | 5-Dehydrokarounidiol | MOL003095 | 5-Hydroxy-7-Methoxy-2-(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl)Chromone |
| MOL001689 | Acacetin | MOL000797 | (22e,24r)-Ergosta-7,22-Dien-3-One |
| MOL000173 | Wogonin | MOL000798 | Ergosta-7,22-Diene-3β-Ol |
| MOL000228 | (2R)-7-Hydroxy-5-Methoxy-2-Phenylchroman-4-One | MOL000816 | Ergosta-7,22-Dien-3-One |
| MOL002714 | Baicalein | MOL000817 | Ergosta-5,7,22-Trien-3-Ol |
| MOL002928 | Oroxylin A | MOL004085 | Taraxasterol |
| MOL002933 | 5,7,4'-Trihydroxy-8-Methoxyflavone | MOL000394 | Choline |
| MOL002934 | Neobaicalein | MOL003837 | Esculetin |
| MOL000358 | Beta-Sitosterol | MOL000414 | Caffeic Acid |
| MOL000359 | Sitosterol | MOL006554 | Taraxerol |
| MOL000073 | Ent-Epicatechin | ||
| MOL001458 | Coptisine | ||
| MOL002897 | Epiberberine |

Figure 2 Network of herbal medicine-component-target-disease CRP: c-reactive protein; DHFR: dihydrofolate reductase; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; ERBB2: erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2; ESR1: estrogen receptor 1; ICAM1: intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IFNG: interferon gamma; IL6: interleukin 6; IRF1: interferon regulatory factor 1; MCL1: myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1; MUC1: Mucin 1; NOS3: nitric oxide synthase 3; NR3C1: nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group c member 1; PGR: progesterone receptor; RASA1: ras p21 protein activator 1; SELE: selectin e; SRD5A1: steroid 5 alpha-reductase 1; TP63: tumor protein p63; VCAM1: vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; ADH1B: alcohol dehydrogenase 1b (class i), beta polypeptide. CH: Chaihu (Radix Bupleuri Chinensis); FL: Fuling (Poria); GL: Gualou (Fructus et Semen Trichosanthis); HQ: Huangqin (Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis); LQ: Lianqiao (Fructus Forsythiae Suspensae); PGY: Pugongying (Herba Taraxaci Mongolici); XF: Xiangfu (Rhizoma Cyperi); ZL: Zhuling (Polyporus); ZZ: Zhizi (Fructus Gardeniae).
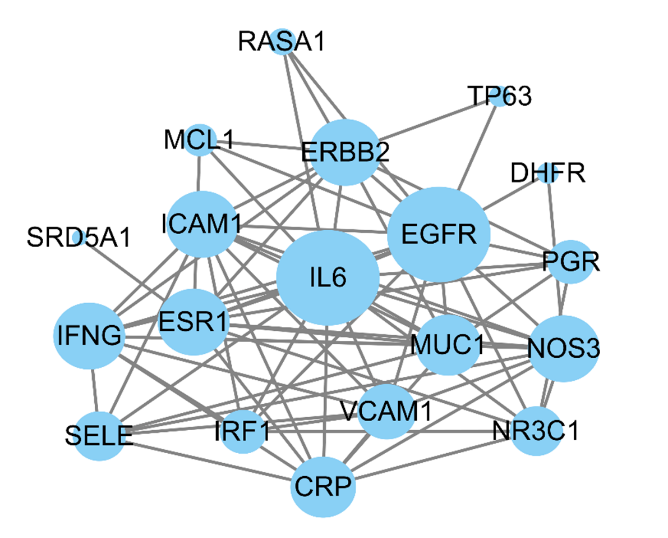
Figure 3 Network of protein protein interaction RASA1: ras p21 protein activator 1; MCL1: myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1; ERBB2: erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2; TP63: tumor protein p63; SRD5A1: steroid 5 alpha-reductase 1; ICAM1: intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IL6: interleukin 6; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; DHFR: dihydrofolate reductase; IFNG: interferon gamma; ESR1: estrogen receptor 1; PGR: progesterone receptor; MUC1: Mucin 1; NOS3: nitric oxide synthase 3; SELE: selectin e; IRF1: interferon regulatory factor 1; VCAM1: vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; NR3C1: nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group c member 1; CRP: c-reactive protein.
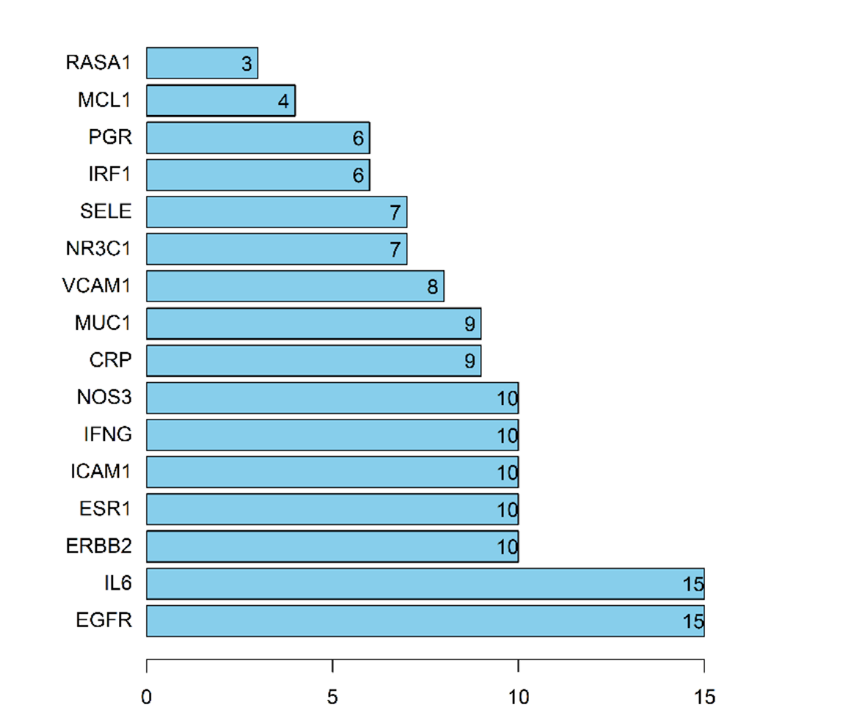
Figure 4 Ranking of key targets EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; IL6: interleukin 6; ERBB2: erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2; ESR1: estrogen receptor 1; ICAM1: intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IFNG: interferon gamma; NOS3: nitric oxide synthase 3; CRP: c-reactive protein; MUC1: Mucin 1; VCAM1: vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; NR3C1: nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group c member 1; SELE: selectin e; IRF1: interferon regulatory factor 1; PGR: progesterone receptor; MCL1: myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1; RASA1: ras p21 protein activator 1.
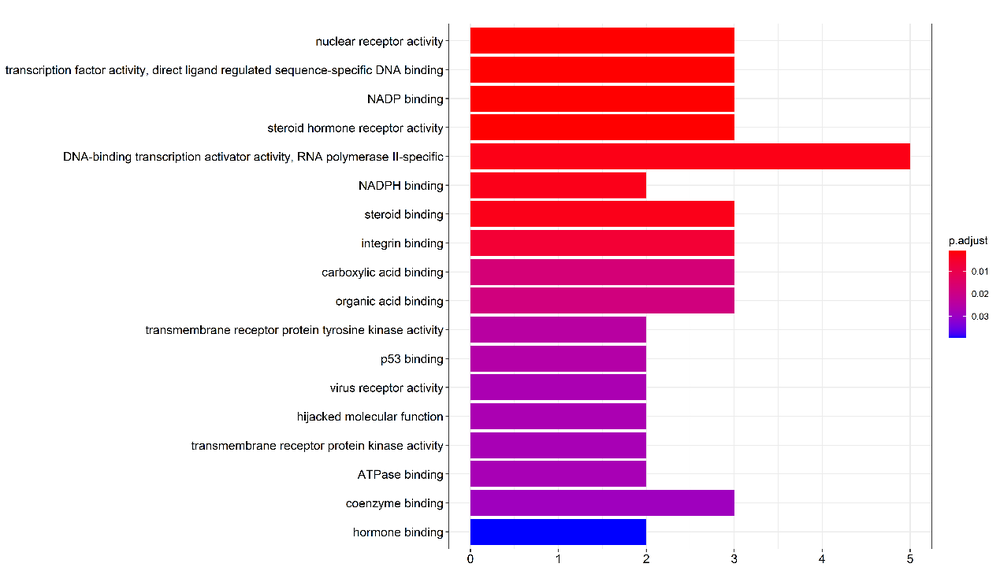
Figure 5 Analysis of GO function DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid; RNA: ribonucleic acid;NADP: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (reduced state).
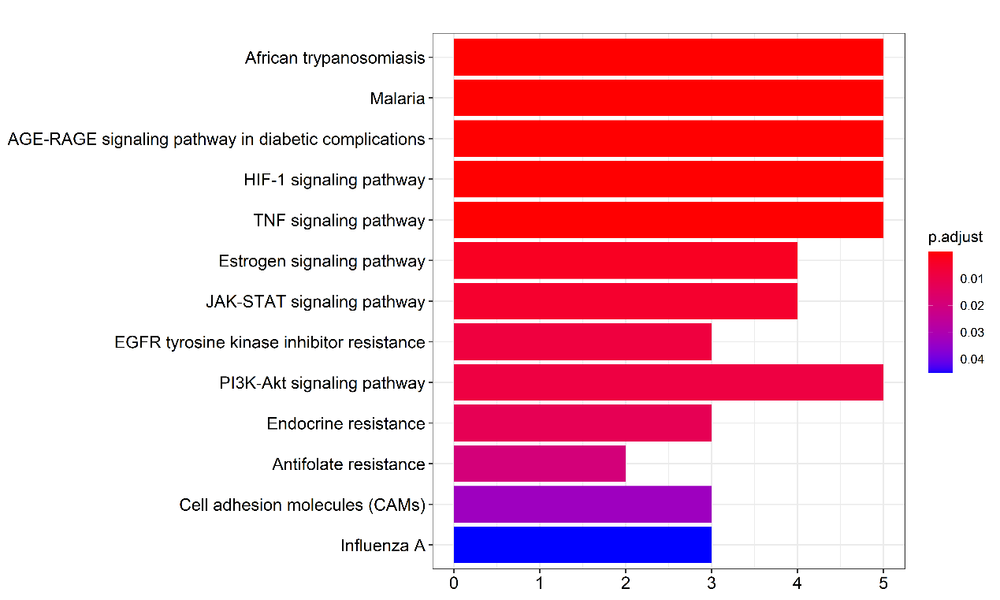
Figure 6 Analysis of KEGG pathway enrichment KEGG:Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes; AGE-RAGE: advanced glycation end products/receptor for advanced glycation end products; HIF-1: hypoxia inducible factor 1; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; JAK-STAT: janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; PI3K-Akt: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt.
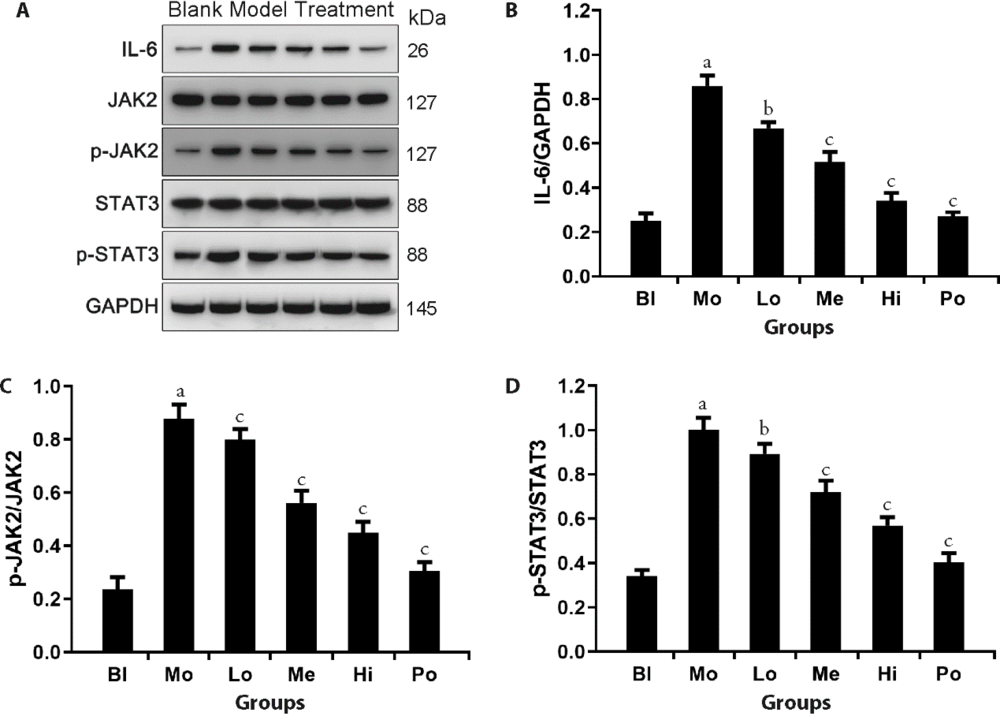
Figure 7 Western blot analyses A: Western blot picture. Bl: culture solution. Mo: culture solution and LPS, 1.0 μg/mL; Lo: LPS, 1.0 μg/mL and SGSJD extract, 250 μg/mL; Me: LPS, 1.0 μg/mL and SGSJD extract, 500 μg/mL; Hi: LPS, 1.0 μg/mL and SGSJD extract, 750 μg/mL; Po: dexamethasone, 50 μg/mL. B: comparison of the relative content of IL-6 in each group. C: comparison of relative expression of JAK2. D: comparison of relative expression of STAT3. LPS: lipopolysaccharide; Bl: blank group; Mo: model group; Lo: low group; Me: medium group; Hi: high group; Po: positive group; SGSJD: Shugan Sanjie decoction; JAK: janus kinase. Compared with Blank, aP < 0.01; compared with Model, cP < 0.01, bP < 0.05.
| 1 |
Ortiz-Mendoza CM, Sánchez NAA, Dircio AC. Fine-needle aspiration cytology to identify a rare mimicker of breast cancer: plasma cell mastitis. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2018; 40:491-3.
DOI URL |
| 2 | Ren FL, Cai XJ. Progress in research of Traditional Chinese And Western Medicine in plasma cell mastitis. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2018; 27:3303-6. |
| 3 | Liu YF, An T, Wang CH, Zhang XM, Xiao JH, Pei XH. Progress on Traditional Chinese Medicine in treatment of plasma cell mastitis. Zhong Yi Xue Bao 2019; 34:289-93. |
| 4 | Ding XW, Fang Y. 92 Cases of mammary duct dilatation treated with Shugan Sanjie decoction. Jiangxi Zhong Yi Yao 2015; 46:54-6. |
| 5 | Qiao N, Ding XW, Shen H, Ni YS, Fang Y. Clinical observation on the treatment of non-puerperal mastitis in tumor stage by Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Wai Ke Za Zhi 2020; 26:941-4. |
| 6 | Long HP, Lin XY, Wang YH, Ren WQ, Tan YS. Explore mechanism of compound uncaria hypotensive tablet for hypertension based on network pharmacology. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2018; 43:1360-5. |
| 7 | Wang J, Chen YW, Zhao K, Zhao GY, Jiang WW. Study on the molecular mechanism of Zuojin pills in the treatment of hypertension based on network pharmacology. Zhong Cheng Yao 2019; 41:1976-81. |
| 8 | Malley MJ. Isolation,culture and analysis of mouse mammary epithelial cells. Methods Mol Biol 2010; 633:139-70. |
| 9 | Lin J, Wu G, Chen J, et al. Electroacupuncture inhibits sodium nitroprusside-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway Mol Med Rep 2018; 18:4922-30. |
| 10 | Ma N, Li YJ, Fan JP. Research progress on pharmacological action of quercetin. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2018; 20:221-4. |
| 11 | Yu Q, Wu GZ. Research progress of anti-inflammatory properties of luteolin. Yao Xue Yan Jiu 2019; 38:108-11. |
| 12 | Xiao WM, Bo P, Gong WJ. Advance in studies on antitumor and immunomodulatory effects of wogonin. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2014; 39:3004. |
| 13 | Zhang WJ, Zhen H. Progress of IL-6-mediated immuno-inflammatory response and its relationship with diseases. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2017; 33:699-703. |
| 14 | Li L, Zhang HC. Progress on the relationship between IL-6 and its JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway and myocardial remodeling. Kong Jun Yi Xue Za Zhi 2009; 25:23-5. |
| 15 | Huang TY, Li QZ, Hou XM. Progress on JAK-STAT function in mammary gland. Zhong Guo Ru Pin Gong Ye 2010; 38:41-4. |
| 16 | Yu B, Huang SH, Zhang TS, Wang Y. Interleukin-6 as a therapeutic target on inflammatory disease and Castleman's disease. Wu Jing Hou Qin Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2017; 26:634-6. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||