Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 131-144.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20231121.003
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of Danlou tablet (丹蒌片) on myocardial ischemia/ reperfusion injury assessed by network pharmacology and experimental verification
YANG Ye1, CHEN Xiaoyang2, YAO Junkai1, HU Yueyao1, WANG Wei2( )
)
- 1 School of Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
2 School of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China
-
Received:2022-10-11Accepted:2023-01-15Online:2024-02-15Published:2023-11-21 -
Contact:Prof. WANG Wei, School of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China. wangwei26960@126.com. Telephone: +86-13120011005
Cite this article
YANG Ye, CHEN Xiaoyang, YAO Junkai, HU Yueyao, WANG Wei. Efficacy of Danlou tablet (丹蒌片) on myocardial ischemia/ reperfusion injury assessed by network pharmacology and experimental verification[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 131-144.
share this article

Figure 1 Compound-targets network The pink square nodes displayed the herb name. The circle nodes displayed the active components of each herb. The red octagonal nodes displayed the common ingredients shared by various herbs. The blue diamond nodes displayed the related targets of DLT. Their degree value analyzed by Cytoscape were represented by the node size and transparency, whose larger size and darker color indicated a higher degree value. The interaction between the compounds and the related targets was performed by the edge. DLT: Danlou tablet.

Figure 2 Process of filtering core targets and the component-target-pathway network of DLT against myocardial I/R injury A, B: process of filtering core targets of DLT against myocardial I/R injury. A: 133 intersection targets uploaded into the STRING database, followed by 129 nodes representing the potential targets and 2060 edges representing their PPI network. Their degree value analyzed by Cytoscape were represented by the node size and color depth, whose larger size and darker depth indicated a higher degree value. The interactivity between the nodes was emerged by the edge. Their combined score analyzed by Cytoscape were represented by the color depth of edge, whose darker depth indicated a higher combined score. B: after that, we applied CytoNCA plug-in to conduct the network analysis of DC. There were 28 nodes representing the core targets and 510 protein interaction. Their degree value analyzed by Cytoscape were represented by the node size, whose larger size indicated a higher degree value. The interactivity between the nodes was emerged by the edge. Their combined score analyzed by Cytoscape were represented by the color depth of edge, whose darker depth indicated a higher combined score. C: the component-target-pathway network of DLT against myocardial I/R injury. Active chemical compounds in DLT, 28 core targets, and top 10 pathways constructed the network. Among them, the circle nodes displayed active chemical compounds in DLT. The diamond nodes displayed 28 core targets of DLT against I/R. The square nodes displayed the top 10 pathways. The degree value of nodes analyzed by Cytoscape were represented by the node size and color depth, whose larger size and darker color indicated a higher degree value. The interactivity between the compounds, core targets, and pathways was brought by the edge. DLT: Danlou tablet; I/R: ischemia/reperfusion; STRING: Search tool for the retrieval of interacting genes proteins; PPI: protein-protein interaction; DC: degree centrality.
| No. | Gene symbol | Protein name | DC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AKT1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | 112 |
| 2 | STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 | 106 |
| 3 | JUN | Transcription factor AP-1 | 100 |
| 4 | TP53 | Cellular tumor antigen p53 | 98 |
| 5 | IL6 | Interleukin-6 | 98 |
| 6 | CASP3 | Caspase-3 | 88 |
| 7 | EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor | 88 |
| 8 | HSP90AA1 | Heat shock protein HSP 90 alpha family class A member 1 | 86 |
| 9 | VEGFA | Vascular endothelial growth factor A | 82 |
| 10 | RELA | Transcription factor p65 | 80 |
| 11 | IL1B | Interleukin-1 beta | 78 |
| 12 | MAPK14 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 | 74 |
| 13 | MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 | 66 |
| 14 | MYC | Myc proto-oncogene protein | 62 |
| 15 | HIF1A | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha | 60 |
| 16 | ESR1 | Estrogen receptor | 60 |
| 17 | EGF | Epidermal growth factor | 60 |
| 18 | IL10 | Interleukin-10 | 56 |
| 19 | MAPK8 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 | 56 |
| 20 | STAT1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-alpha/beta | 56 |
| 21 | MAPK14 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 | 56 |
| 22 | CCL2 | C-C motif chemokine 2 | 56 |
| 23 | PTGS2 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 | 54 |
| 24 | CXCL8 | Interleukin-8 | 54 |
| 25 | FOS | Proto-oncogene c-Fos | 54 |
| 26 | CCND1 | G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 | 54 |
| 27 | TGFB1 | Transforming growth factor beta-1 | 52 |
| 28 | NFKBIA | NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha | 52 |
Table 1 Core targets of DLT against myocardial I/R injury
| No. | Gene symbol | Protein name | DC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AKT1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | 112 |
| 2 | STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 | 106 |
| 3 | JUN | Transcription factor AP-1 | 100 |
| 4 | TP53 | Cellular tumor antigen p53 | 98 |
| 5 | IL6 | Interleukin-6 | 98 |
| 6 | CASP3 | Caspase-3 | 88 |
| 7 | EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor | 88 |
| 8 | HSP90AA1 | Heat shock protein HSP 90 alpha family class A member 1 | 86 |
| 9 | VEGFA | Vascular endothelial growth factor A | 82 |
| 10 | RELA | Transcription factor p65 | 80 |
| 11 | IL1B | Interleukin-1 beta | 78 |
| 12 | MAPK14 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 | 74 |
| 13 | MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 | 66 |
| 14 | MYC | Myc proto-oncogene protein | 62 |
| 15 | HIF1A | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha | 60 |
| 16 | ESR1 | Estrogen receptor | 60 |
| 17 | EGF | Epidermal growth factor | 60 |
| 18 | IL10 | Interleukin-10 | 56 |
| 19 | MAPK8 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 | 56 |
| 20 | STAT1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-alpha/beta | 56 |
| 21 | MAPK14 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 | 56 |
| 22 | CCL2 | C-C motif chemokine 2 | 56 |
| 23 | PTGS2 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 | 54 |
| 24 | CXCL8 | Interleukin-8 | 54 |
| 25 | FOS | Proto-oncogene c-Fos | 54 |
| 26 | CCND1 | G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 | 54 |
| 27 | TGFB1 | Transforming growth factor beta-1 | 52 |
| 28 | NFKBIA | NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha | 52 |
| Type | No. | Term | Enrichment | Count | % InGO | Gene symbols | -Log10 (P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO MF | 1 | GO:0140297: DNA-binding transcription factor binding | 25.24 | 11 | 39.29 | MAPK14|ESR1|FOS|HIF1A|JUN|MYC| NFKBIA|RELA|STAT1|STAT3|TP53 | 12.71 |
| GO MF | 2 | GO:0061629: RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding trans-cription factor binding | 30.99 | 10 | 35.71 | MAPK14|ESR1|FOS|HIF1A|JUN|NFKBIA|RELA|STAT1|STAT3|TP53 | 12.40 |
| GO MF | 3 | GO:0005126:cytokine receptor binding | 35.69 | 9 | 32.14 | CASP3|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8|IL10|CCL2| STAT1|TGFB1|VEGFA | 11.69 |
| GO MF | 4 | GO:0008134: transcription factor binding | 19.94 | 11 | 39.29 | MAPK14|ESR1|FOS|HIF1A|JUN|MYC| NFKBIA|RELA|STAT1|STAT3|TP53 | 11.60 |
| GO MF | 5 | GO:0030235: nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity | 616.29 | 4 | 14.29 | AKT1|EGFR|ESR1|HSP90AA1 | 10.69 |
| GO MF | 6 | GO:0019900: kinase binding | 15.39 | 11 | 39.29 | AKT1|CCND1|MAPK14|EGFR| ESR1|HIF1A|HSP90AA1|MAPK8|RELA |STAT3|TP53 | 10.39 |
| GO MF | 7 | GO:0019901: protein kinase binding | 15.65 | 10 | 35.71 | AKT1|CCND1|MAPK14|ESR1| HIF1A|HSP90AA1|MAPK8|RELA| STAT3|TP53 | 9.49 |
| GO MF | 8 | GO:0044389: ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding | 27.22 | 8 | 28.57 | EGFR|HIF1A|HSP90AA1|JUN|NFKBIA|RELA|STAT1|TP53 | 9.46 |
| GO MF | 9 | GO:0001046: core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding | 128.39 | 5 | 17.86 | FOS|MYC|RELA|STAT1|TP53 | 9.41 |
| GO MF | 10 | GO:0019902: phosphatase binding | 39.12 | 7 | 25.00 | MAPK14|EGFR|MAPK1|MAPK8| STAT1|STAT3|TP53 | 9.38 |
| GO BP | 1 | GO:0032496: response to lipopolysaccharide | 50.87 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|FOS|IL1B| IL6|CXCL8|IL10|NFKBIA|MAPK1| MAPK8|PTGS2|RELA|CCL2|TGFB1 | 22.29 |
| GO BP | 2 | GO:0002237: response to molecule of bacterial origin | 47.72 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|FOS|IL1B| IL6|CXCL8|IL10|NFKBIA|MAPK1| MAPK8|PTGS2|RELA|CCL2|TGFB1 | 21.87 |
| GO BP | 3 | GO:0062197: cellular response to chemical stress | 56.55 | 14 | 50.00 | AKT1|CASP3|EGFR|FOS|HIF1A|IL6|JUN|MMP9|MYC|MAPK1|MAPK8|PTGS2 |RELA|TP53 | 21.34 |
| GO BP | 4 | GO:0070848: response to growth factor | 34.65 | 16 | 57.14 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|EGFR|FOS|CXCL8|IL10|JUN|MYC|MAPK1|RELA|CCL2|STAT3|TGFB1|TP53|VEGFA | 21.22 |
| GO BP | 5 | GO:0071216: cellular response to biotic stimulus | 58.66 | 13 | 46.43 | AKT1|MAPK14|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8| IL10|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8| RELA|CCL2|TGFB1|TP53 | 19.94 |
| GO BP | 6 | GO:0071363: cellular response to growth factor stimulus | 34.57 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|EGFR|FOS|CXCL8|IL10|JUN|MYC|RELA|CCL2|STAT3|TGFB1|TP53|VEGFA | 19.75 |
| GO BP | 7 | GO:0000302: response to reactive oxygen species | 75.68 | 12 | 42.86 | AKT1|CASP3|EGFR|FOS|HIF1A|IL6|JUN|MMP9|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA|STAT1 | 19.69 |
| GO BP | 8 | GO:0006979: response to oxidative stress | 41.37 | 14 | 50.00 | AKT1|CASP3|EGFR|FOS|HIF1A|IL6|JUN|MMP9|MAPK1|MAPK8|PTGS2|RELA|STAT1|TP53 | 19.42 |
| GO BP | 9 | GO:0071396:cellular response to lipid | 32.16 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|MAPK14|EGFR|ESR1|IL1B| IL6|CXCL8|IL10|MYC|NFKBIA| MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA|CCL2|TGFB1 | 19.28 |
| GO BP | 10 | GO:0010035:response to inorganic substance | 31.05 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|CCND1|CASP3|EGFR|FOS| HIF1A|IL6|JUN|MMP9|MYC|MAPK1|MAPK8|PTGS2|RELA|STAT1 | 19.05 |
| GO CC | 1 | GO:0005667: transcription regulator complex | 21.78 | 10 | 35.71 | CCND1|ESR1|FOS|HIF1A|JUN|MYC| RELA|STAT1|STAT3|TP53 | 10.89 |
| GO BP | 9 | GO:0071396:cellular response to lipid | 32.16 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|MAPK14|EGFR|ESR1|IL1B| IL6|CXCL8|IL10|MYC|NFKBIA| MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA|CCL2|TGFB1 | 19.28 |
| GO CC | 2 | GO:0031983:vesicle lumen | 23.09 | 7 | 25.00 | MAPK14|EGF|EGFR|HSP90AA1|MAPK1|TGFB1|VEGFA | 7.80 |
| GO CC | 3 | GO:0090575:RNA polymerase Ⅱ transcription regulator complex | 26.74 | 6 | 21.43 | FOS|HIF1A|JUN|MYC|STAT1|STAT3 | 7.09 |
| GO CC | 4 | GO:0034774:secretory granule lumen | 20.10 | 6 | 21.43 | MAPK14|EGF|HSP90AA1|MAPK1|TGFB1|VEGFA | 6.36 |
| GO CC | 5 | GO:0060205: cytoplasmic vesicle lumen | 19.91 | 6 | 21.43 | MAPK14|EGF|HSP90AA1|MAPK1|TGFB1|VEGFA | 6.34 |
| GO CC | 6 | GO:0017053: transcription repressor complex | 56.76 | 4 | 14.29 | CCND1|JUN|MYC|TP53 | 6.14 |
| GO CC | 7 | GO:1904813:ficolin-1-rich granule lumen | 34.79 | 4 | 14.29 | MAPK14|HSP90AA1|MMP9|MAPK1 | 5.29 |
| GO CC | 8 | GO:0101002:ficolin-1-rich granule | 23.32 | 4 | 14.29 | MAPK14|HSP90AA1|MMP9|MAPK1 | 4.60 |
| GO CC | 9 | GO:0031093:platelet alpha granule lumen | 48.29 | 3 | 10.71 | EGF|TGFB1|VEGFA | 4.48 |
| GO CC | 10 | GO:0031091:platelet alpha granule | 35.55 | 3 | 10.71 | EGF|TGFB1|VEGFA | 4.09 |
| KEGG | 1 | hsa04933:AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications | 172.56 | 16 | 57.14 | AKT1|CCND1|CASP3|MAPK14|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8|JUN|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA| CCL2|STAT1|STAT3|TGFB1|VEGFA | 32.76 |
| KEGG | 2 | hsa04657:IL-17 signaling pathway | 172.10 | 15 | 53.57 | CASP3|MAPK14|FOS|HSP90AA1|IL1B |IL6|CXCL8| JUN|MMP9|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8| PTGS2|RELA|CCL2 | 30.55 |
| KEGG | 3 | hsa05417:Lipid and atherosclerosis | 85.28 | 17 | 60.71 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|FOS|HSP90AA1|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8|JUN|MMP9|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA|CCL2|STAT3|TP53 | 29.49 |
| KEGG | 4 | hsa04668:TNF signaling pathway | 134.81 | 14 | 50.00 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|FOS|IL1B|IL6|JUN|MMP9|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8|PTGS2|RELA|CCL2 | 26.81 |
| KEGG | 5 | hsa04010:MAPK signaling pathway | 55.03 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|EGF|EGFR|FOS|IL1B|JUN|MYC|MAPK1|MAPK8| RELA|TGFB1|TP53|VEGFA | 22.81 |
| KEGG | 6 | hsa04620:Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 124.44 | 12 | 42.86 | AKT1|MAPK14|FOS|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8| JUN|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA| STAT1 | 22.38 |
| KEGG | 7 | hsa04926:Relaxin signaling pathway | 100.33 | 12 | 42.86 | AKT1|MAPK14|EGFR|FOS|JUN|MMP9|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA|TGFB1|VEGFA | 21.20 |
| KEGG | 8 | hsa05418:Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | 93.11 | 12 | 42.86 | AKT1|MAPK14|FOS|HSP90AA1|IL1B| JUN|MMP9|MAPK8|RELA|CCL2|TP53| VEGFA | 20.80 |
| KEGG | 9 | hsa01522:Endocrine resistance | 121.06 | 11 | 39.29 | AKT1|CCND1|MAPK14|EGFR|ESR1|FOS|JUN|MMP9|MAPK1|MAPK8|TP53 | 20.32 |
| KEGG | 10 | hsa04621:NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 70.34 | 12 | 42.86 | MAPK14|HSP90AA1|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8|JUN|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA| CCL2|STAT1 | 19.29 |
Table 2 The top 10 GO and KEGG terms of the therapeutic efficacy of DLT on myocardial I/R injury
| Type | No. | Term | Enrichment | Count | % InGO | Gene symbols | -Log10 (P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO MF | 1 | GO:0140297: DNA-binding transcription factor binding | 25.24 | 11 | 39.29 | MAPK14|ESR1|FOS|HIF1A|JUN|MYC| NFKBIA|RELA|STAT1|STAT3|TP53 | 12.71 |
| GO MF | 2 | GO:0061629: RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding trans-cription factor binding | 30.99 | 10 | 35.71 | MAPK14|ESR1|FOS|HIF1A|JUN|NFKBIA|RELA|STAT1|STAT3|TP53 | 12.40 |
| GO MF | 3 | GO:0005126:cytokine receptor binding | 35.69 | 9 | 32.14 | CASP3|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8|IL10|CCL2| STAT1|TGFB1|VEGFA | 11.69 |
| GO MF | 4 | GO:0008134: transcription factor binding | 19.94 | 11 | 39.29 | MAPK14|ESR1|FOS|HIF1A|JUN|MYC| NFKBIA|RELA|STAT1|STAT3|TP53 | 11.60 |
| GO MF | 5 | GO:0030235: nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity | 616.29 | 4 | 14.29 | AKT1|EGFR|ESR1|HSP90AA1 | 10.69 |
| GO MF | 6 | GO:0019900: kinase binding | 15.39 | 11 | 39.29 | AKT1|CCND1|MAPK14|EGFR| ESR1|HIF1A|HSP90AA1|MAPK8|RELA |STAT3|TP53 | 10.39 |
| GO MF | 7 | GO:0019901: protein kinase binding | 15.65 | 10 | 35.71 | AKT1|CCND1|MAPK14|ESR1| HIF1A|HSP90AA1|MAPK8|RELA| STAT3|TP53 | 9.49 |
| GO MF | 8 | GO:0044389: ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding | 27.22 | 8 | 28.57 | EGFR|HIF1A|HSP90AA1|JUN|NFKBIA|RELA|STAT1|TP53 | 9.46 |
| GO MF | 9 | GO:0001046: core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding | 128.39 | 5 | 17.86 | FOS|MYC|RELA|STAT1|TP53 | 9.41 |
| GO MF | 10 | GO:0019902: phosphatase binding | 39.12 | 7 | 25.00 | MAPK14|EGFR|MAPK1|MAPK8| STAT1|STAT3|TP53 | 9.38 |
| GO BP | 1 | GO:0032496: response to lipopolysaccharide | 50.87 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|FOS|IL1B| IL6|CXCL8|IL10|NFKBIA|MAPK1| MAPK8|PTGS2|RELA|CCL2|TGFB1 | 22.29 |
| GO BP | 2 | GO:0002237: response to molecule of bacterial origin | 47.72 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|FOS|IL1B| IL6|CXCL8|IL10|NFKBIA|MAPK1| MAPK8|PTGS2|RELA|CCL2|TGFB1 | 21.87 |
| GO BP | 3 | GO:0062197: cellular response to chemical stress | 56.55 | 14 | 50.00 | AKT1|CASP3|EGFR|FOS|HIF1A|IL6|JUN|MMP9|MYC|MAPK1|MAPK8|PTGS2 |RELA|TP53 | 21.34 |
| GO BP | 4 | GO:0070848: response to growth factor | 34.65 | 16 | 57.14 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|EGFR|FOS|CXCL8|IL10|JUN|MYC|MAPK1|RELA|CCL2|STAT3|TGFB1|TP53|VEGFA | 21.22 |
| GO BP | 5 | GO:0071216: cellular response to biotic stimulus | 58.66 | 13 | 46.43 | AKT1|MAPK14|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8| IL10|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8| RELA|CCL2|TGFB1|TP53 | 19.94 |
| GO BP | 6 | GO:0071363: cellular response to growth factor stimulus | 34.57 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|EGFR|FOS|CXCL8|IL10|JUN|MYC|RELA|CCL2|STAT3|TGFB1|TP53|VEGFA | 19.75 |
| GO BP | 7 | GO:0000302: response to reactive oxygen species | 75.68 | 12 | 42.86 | AKT1|CASP3|EGFR|FOS|HIF1A|IL6|JUN|MMP9|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA|STAT1 | 19.69 |
| GO BP | 8 | GO:0006979: response to oxidative stress | 41.37 | 14 | 50.00 | AKT1|CASP3|EGFR|FOS|HIF1A|IL6|JUN|MMP9|MAPK1|MAPK8|PTGS2|RELA|STAT1|TP53 | 19.42 |
| GO BP | 9 | GO:0071396:cellular response to lipid | 32.16 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|MAPK14|EGFR|ESR1|IL1B| IL6|CXCL8|IL10|MYC|NFKBIA| MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA|CCL2|TGFB1 | 19.28 |
| GO BP | 10 | GO:0010035:response to inorganic substance | 31.05 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|CCND1|CASP3|EGFR|FOS| HIF1A|IL6|JUN|MMP9|MYC|MAPK1|MAPK8|PTGS2|RELA|STAT1 | 19.05 |
| GO CC | 1 | GO:0005667: transcription regulator complex | 21.78 | 10 | 35.71 | CCND1|ESR1|FOS|HIF1A|JUN|MYC| RELA|STAT1|STAT3|TP53 | 10.89 |
| GO BP | 9 | GO:0071396:cellular response to lipid | 32.16 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|MAPK14|EGFR|ESR1|IL1B| IL6|CXCL8|IL10|MYC|NFKBIA| MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA|CCL2|TGFB1 | 19.28 |
| GO CC | 2 | GO:0031983:vesicle lumen | 23.09 | 7 | 25.00 | MAPK14|EGF|EGFR|HSP90AA1|MAPK1|TGFB1|VEGFA | 7.80 |
| GO CC | 3 | GO:0090575:RNA polymerase Ⅱ transcription regulator complex | 26.74 | 6 | 21.43 | FOS|HIF1A|JUN|MYC|STAT1|STAT3 | 7.09 |
| GO CC | 4 | GO:0034774:secretory granule lumen | 20.10 | 6 | 21.43 | MAPK14|EGF|HSP90AA1|MAPK1|TGFB1|VEGFA | 6.36 |
| GO CC | 5 | GO:0060205: cytoplasmic vesicle lumen | 19.91 | 6 | 21.43 | MAPK14|EGF|HSP90AA1|MAPK1|TGFB1|VEGFA | 6.34 |
| GO CC | 6 | GO:0017053: transcription repressor complex | 56.76 | 4 | 14.29 | CCND1|JUN|MYC|TP53 | 6.14 |
| GO CC | 7 | GO:1904813:ficolin-1-rich granule lumen | 34.79 | 4 | 14.29 | MAPK14|HSP90AA1|MMP9|MAPK1 | 5.29 |
| GO CC | 8 | GO:0101002:ficolin-1-rich granule | 23.32 | 4 | 14.29 | MAPK14|HSP90AA1|MMP9|MAPK1 | 4.60 |
| GO CC | 9 | GO:0031093:platelet alpha granule lumen | 48.29 | 3 | 10.71 | EGF|TGFB1|VEGFA | 4.48 |
| GO CC | 10 | GO:0031091:platelet alpha granule | 35.55 | 3 | 10.71 | EGF|TGFB1|VEGFA | 4.09 |
| KEGG | 1 | hsa04933:AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications | 172.56 | 16 | 57.14 | AKT1|CCND1|CASP3|MAPK14|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8|JUN|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA| CCL2|STAT1|STAT3|TGFB1|VEGFA | 32.76 |
| KEGG | 2 | hsa04657:IL-17 signaling pathway | 172.10 | 15 | 53.57 | CASP3|MAPK14|FOS|HSP90AA1|IL1B |IL6|CXCL8| JUN|MMP9|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8| PTGS2|RELA|CCL2 | 30.55 |
| KEGG | 3 | hsa05417:Lipid and atherosclerosis | 85.28 | 17 | 60.71 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|FOS|HSP90AA1|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8|JUN|MMP9|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA|CCL2|STAT3|TP53 | 29.49 |
| KEGG | 4 | hsa04668:TNF signaling pathway | 134.81 | 14 | 50.00 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|FOS|IL1B|IL6|JUN|MMP9|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8|PTGS2|RELA|CCL2 | 26.81 |
| KEGG | 5 | hsa04010:MAPK signaling pathway | 55.03 | 15 | 53.57 | AKT1|CASP3|MAPK14|EGF|EGFR|FOS|IL1B|JUN|MYC|MAPK1|MAPK8| RELA|TGFB1|TP53|VEGFA | 22.81 |
| KEGG | 6 | hsa04620:Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 124.44 | 12 | 42.86 | AKT1|MAPK14|FOS|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8| JUN|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA| STAT1 | 22.38 |
| KEGG | 7 | hsa04926:Relaxin signaling pathway | 100.33 | 12 | 42.86 | AKT1|MAPK14|EGFR|FOS|JUN|MMP9|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA|TGFB1|VEGFA | 21.20 |
| KEGG | 8 | hsa05418:Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | 93.11 | 12 | 42.86 | AKT1|MAPK14|FOS|HSP90AA1|IL1B| JUN|MMP9|MAPK8|RELA|CCL2|TP53| VEGFA | 20.80 |
| KEGG | 9 | hsa01522:Endocrine resistance | 121.06 | 11 | 39.29 | AKT1|CCND1|MAPK14|EGFR|ESR1|FOS|JUN|MMP9|MAPK1|MAPK8|TP53 | 20.32 |
| KEGG | 10 | hsa04621:NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 70.34 | 12 | 42.86 | MAPK14|HSP90AA1|IL1B|IL6|CXCL8|JUN|NFKBIA|MAPK1|MAPK8|RELA| CCL2|STAT1 | 19.29 |
| Term | No. | Symbol | Name | Degree | Chemical structure /PDB ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active components | 1 | A1 | Quercetin (MOL000098) | 24 | 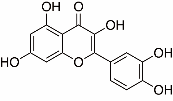 |
| Active components | 2 | M2 | Luteolin (MOL000006) | 15 |  |
| Active components | 3 | CS4 | Baicalein (MOL002714) | 10 | 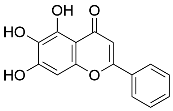 |
| Gene | 1 | PTGS2 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 | 90 | 5IKV |
| Gene | 2 | HSP90AA1 | Heat shock protein HSP 90 alpha family class A member 1 | 55 | 4EGK |
| Gene | 3 | ESR1 | Estrogen receptor | 35 | 4J24 |
Table 3 Top3 active components and core targets of DLT against myocardial I/R injury
| Term | No. | Symbol | Name | Degree | Chemical structure /PDB ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active components | 1 | A1 | Quercetin (MOL000098) | 24 |  |
| Active components | 2 | M2 | Luteolin (MOL000006) | 15 |  |
| Active components | 3 | CS4 | Baicalein (MOL002714) | 10 |  |
| Gene | 1 | PTGS2 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 | 90 | 5IKV |
| Gene | 2 | HSP90AA1 | Heat shock protein HSP 90 alpha family class A member 1 | 55 | 4EGK |
| Gene | 3 | ESR1 | Estrogen receptor | 35 | 4J24 |
| Component | Target: gene symbol | Contacting residue | Binding distance | Binding energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin (A1, MOL000098) | PTGS2 (5IKV) | LYS-83/ LY-S83/ MET-471 | 2.8/ 2.7/ 2.5 | -1.89 |
| Quercetin (A1, MOL000098) | HSP90AA1 (4EGK) | LYS-185/ ARG-182/ ARG-182/ ARG-182/ GLY-181/ | 2.1/ 1.9/ 1.8/ 1.8/ 2.5 | -3.05 |
| Quercetin (A1, MOL000098) | ESR1 (4J24) | ASN-483/ LYS-480/ VAL-487/ VAL-487/ VAL-487 | 2.2/ 2.6/ 2.6/ 2.4/ 3.1 | -0.63 |
| Luteolin (M2, MOL000006) | PTGS2 (5IKV) | ASN-570/ ASN-570/ GLY-574/ MET-261 | 2.4/ 2.9/ 2.0/ 2.5 | -2.64 |
| Luteolin (M2, MOL000006) | HSP90AA1 (4EGK) | GLY-181/ GLY-181/ ARG-182/ | 2.2/ 2.4/ 1.9/ | -3.22 |
| Luteolin (M2, MOL000006) | ESR1 (4J24) | ASN-483 | 2.2 | -0.01 |
| Baicalein (CS4, MOL002714) | PTGS2 (5IKV) | ASP-158/ ASP-158/ CYS-159/ CYS-159 | 2.2/ 2.0/ 1.9/ 2.7 | -3.24 |
| Baicalein (CS4, MOL002714) | HSP90AA1 (4EGK) | GLU-178/ GLU-178 | 2.0/ 2.3 | -3.13 |
| Baicalein (CS4, MOL002714) | ESR1 (4J24) | - | - | - |
Table 4 Results of molecular docking
| Component | Target: gene symbol | Contacting residue | Binding distance | Binding energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin (A1, MOL000098) | PTGS2 (5IKV) | LYS-83/ LY-S83/ MET-471 | 2.8/ 2.7/ 2.5 | -1.89 |
| Quercetin (A1, MOL000098) | HSP90AA1 (4EGK) | LYS-185/ ARG-182/ ARG-182/ ARG-182/ GLY-181/ | 2.1/ 1.9/ 1.8/ 1.8/ 2.5 | -3.05 |
| Quercetin (A1, MOL000098) | ESR1 (4J24) | ASN-483/ LYS-480/ VAL-487/ VAL-487/ VAL-487 | 2.2/ 2.6/ 2.6/ 2.4/ 3.1 | -0.63 |
| Luteolin (M2, MOL000006) | PTGS2 (5IKV) | ASN-570/ ASN-570/ GLY-574/ MET-261 | 2.4/ 2.9/ 2.0/ 2.5 | -2.64 |
| Luteolin (M2, MOL000006) | HSP90AA1 (4EGK) | GLY-181/ GLY-181/ ARG-182/ | 2.2/ 2.4/ 1.9/ | -3.22 |
| Luteolin (M2, MOL000006) | ESR1 (4J24) | ASN-483 | 2.2 | -0.01 |
| Baicalein (CS4, MOL002714) | PTGS2 (5IKV) | ASP-158/ ASP-158/ CYS-159/ CYS-159 | 2.2/ 2.0/ 1.9/ 2.7 | -3.24 |
| Baicalein (CS4, MOL002714) | HSP90AA1 (4EGK) | GLU-178/ GLU-178 | 2.0/ 2.3 | -3.13 |
| Baicalein (CS4, MOL002714) | ESR1 (4J24) | - | - | - |

Figure 3 Specific docking details between the top three core components and core proteins The green ribbon-like structures or grey surface structure displayed target proteins, the pink rod-like structures displayed chemical compounds, the purple rod-like structures displayed amino acid residues linking to the corresponding compounds, and the yellow dashed strip displayed connection distance between compounds and residues. A: quercetin (A1, MOL000098)-PTGS2 (PDB ID: 5IKV); B: quercetin (A1, MOL000098)-HSP90AA1 (PDB ID: 4EGK); C: quercetin (A1, MOL000098)-ESR1 (PDB ID: 4J24); D: luteolin (M2, MOL000006)-PTGS2 (PDB ID: 5IKV); E: luteolin (M2, MOL000006)-HSP90AA1 (PDB ID: 4EGK); F: luteolin (M2, MOL000006)-ESR1 (PDB ID: 4J24); G: baicalein (CS4, MOL002714)-PTGS2 (PDB ID: 5IKV); H: baicalein (CS4, MOL002714)-HSP90AA1 (PDB ID: 4EGK); I: baicalein (CS4, MOL002714)-ESR1 (PDB ID: 4J24). PTGS2: prostaglandin G/H synthase 2; HSP90AA1: heat shock protein HSP 90 alpha family class A member 1; ESR1: estrogen receptor 1.

Figure 4 Efficacy verification of 3 active compounds in DLT on the three core proteins in OGD/R-induced H9c2 cardiomyocytes A-C: the protective effects of the active compounds in DLT on cell viabilities in OGD/R injured H9c2 cells. The cell viabilities were detected by the CCK-8 assay. A: the effective range of Quercetin (A1, MOL000098) in OGD/R induced H9c2 cardiomyocytes, among which 20 μΜ concentration was applied to subsequent compound-pathway exploration. B: the effective range of Luteolin (M2, MOL000006) in OGD/R induced H9c2 cardiomyocytes, among which 10 μΜ concentration was applied to subsequent compound-pathway exploration. C: the effective range of Baicalein (CS4, MOL002714) in OGD/R induced H9c2 cardiomyocytes, among which 5 μΜ concentration was applied to subsequent compound-pathway exploration. D-G: Expression of PTGS2, HSP90AA1, and ESR1 were detected by Western blot, after intervention with Quercetin (20 μM), Luteolin (10 μM), or Baicalein (5 μM). D: representative images of bands detected by Western blot. E: expression of PTGS2 were detected by Western blot, after intervention with Quercetin (20 μM), Luteolin (10 μM), or Baicalein (5 μM). F: expression of HSP90AA1 were detected by Western blot, after intervention with Quercetin (20 μM), Luteolin (10 μM), or Baicalein (5 μM). G: expression of ESR1 were detected by Western blot, after intervention with Quercetin (20 μM), Luteolin (10 μM), or Baicalein (5 μM). DLT: Danlou tablet; OGD/R: oxygen-glucose deprivation/recovery; CCK-8: cell counting kit-8. PTGS2: prostaglandin G/H synthase 2; HSP90AA1: heat shock protein HSP 90 alpha family class A member 1; ESR1: estrogen receptor 1. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). aP < 0.001 vs the control group; bP < 0.001, cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, vs the OGD/R group.
| 1. |
Hausenloy DJ, Botker HE, Engstrom T, et al. Targeting reperfusion injury in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: trials and tribulations. Eur Heart J 2017; 38: 935-41.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Heusch G. Myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in perspective. Nat Rev Cardiol 2020; 17: 773-89.
DOI |
| 3. |
Heusch G, Bøtker HE, Przyklenk K, Redington A, Yellon D. Remote ischemic conditioning. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015; 65: 177-95.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Ye T, Xiong D, Li Y, et al. Inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B as a mechanism of Danshensu during toll-like receptor 2-triggered inflammation in macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 2020; 83: 106419.
DOI URL |
| 5. |
Wang L, Wu T, Si C, et al. Danlou tablet activates autophagy of vascular adventitial fibroblasts through PI3K/Akt/mTOR to protect cells from damage caused by atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol 2021; 12: 730525.
DOI URL |
| 6. |
Li Z, Yang L, Liu Y, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects of Danlou tablets in the treatment of coronary heart disease revealed by metabolomics integrated with molecular mechanism studies. J Ethnopharmacol 2019; 240: 111911.
DOI URL |
| 7. |
Wei M, Guo M, Meng X, et al. PPARγ mediates the cardioprotective roles of Danlou tablet after acute myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022; 9: 858909.
DOI URL |
| 8. | Ru J, Li P, Wang J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform 2014; 6: 13. |
| 9. | Ji ZL, Zhou H, Wang JF, Han LY, Zheng CJ, Chen YZ. Traditional Chinese Medicine information database. J Ethnopharmacol 2006; 103: 501. |
| 10. |
Liu Z, Guo F, Wang Y, et al. BATMAN-TCM: a bioinformatics analysis tool for molecular mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Sci Rep 2016; 6: 21146.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Fang S, Dong L, Liu L, et al. HERB: a high-throughput experiment- and reference-guided database of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Nucleic Acids Res 2021; 49: D1197-206. |
| 12. |
Song W, Ni S, Fu Y, Wang Y. Uncovering the mechanism of Maxing Ganshi decoction on asthma from a systematic perspective: a network pharmacology study. Sci Rep 2018; 8: 17362.
DOI PMID |
| 13. |
UniProt Consortium. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res 2021; 49: D480-9.
DOI PMID |
| 14. |
Kohl M, Wiese S, Warscheid B. Cytoscape: software for visualization and analysis of biological networks. Methods Mol Biol 2011; 696: 291-303.
DOI PMID |
| 15. |
Rasmussen SA, Hamosh A. What's in a name? Issues to consider when naming Mendelian disorders. Genet Med 2020; 22: 1573-5.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Safran M, Dalah I, Alexander J, et al. GeneCards Version 3: the human gene integrator. Database. Oxford 2010; 2010: baq020. |
| 17. | Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Lian X, et al. Therapeutic target database update 2022: facilitating drug discovery with enriched comparative data of targeted agents. Nucleic Acids Res 2022; 50: D1398-407. |
| 18. |
Piñero J, Saüch J, Sanz F, Furlong LI. The DisGeNET cytoscape app: exploring and visualizing disease genomics data. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2021; 19: 2960-7.
DOI URL |
| 19. | Jia C, Pan X, Wang B, Wang P, Wang Y, Chen R. Mechanism prediction of against cisplatin-induced kidney damage by network pharmacology and molecular docking. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2021; 2021: 9516726. |
| 20. | Wei Y, Ren S, Wang R, et al. Based on network pharmacology to explore the potential bioactive compounds and mechanisms of Zuojin pill for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2021; 2021: 7567025. |
| 21. | Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC, et al. The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res 2021; 49: D605-12. |
| 22. | Ding Z, Xu F, Sun Q, et al. Exploring the mechanism of action of herbal medicine (decoction) for poststroke depression based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2021; 2021: 2126967. |
| 23. |
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, et al. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun 2019; 10: 1523.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Dedhia M, Kohetuk K, Crusio WE, Delprato A. Introducing high school students to the Gene Ontology classification system. F1000Res 2019; 8: 241.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Burenbatu, Wang Y, Wang S, et al. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics analysis of immune thrombocytopenia patients before and after Qishunbaolier treatment. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2021; 35: e8993.
DOI URL |
| 26. |
Seeliger D, de Groot BL. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMOL and autodock/vina. J Comput Aided Mol Des 2010; 24: 417-22.
DOI URL |
| 27. |
Trott O, Olson AJ. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 2010; 31: 455-61.
DOI PMID |
| 28. |
Chang H, Li C, Wang Q, et al. QSKL protects against myocardial apoptosis on heart failure via PI3K/Akt-p 53 signaling pathway. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 16986.
DOI PMID |
| 29. | Raja-Khan N, Stener-Victorin E, Wu X, Legro RS. The physiological basis of complementary and alternative medicines for polycystic ovary syndrome. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2011; 301. |
| 30. |
Perry E, Howes M-JR. Medicinal plants and dementia therapy: herbal hopes for brain aging? CNS Neurosci Ther 2011; 17: 683-98.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Ding M, Ma W, Wang X, et al. A network pharmacology integrated pharmacokinetics strategy for uncovering pharmacological mechanism of compounds absorbed into the blood of Danlou tablet on coronary heart disease. J Ethnopharmacol 2019; 242: 112055.
DOI URL |
| 32. |
Li Y, Zhao H, Du J, et al. Clinical metabolomic analysis of Danlou tablets with antioxidant effects for treating stable angina pectoris. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2022; 219: 114922.
DOI URL |
| 33. |
Qi JY, Wang L, Gu DS, Guo LH, Zhu W, Zhang MZ. Protective effects of Danlou tablet against murine myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury in vivo. Chin J Integr Med 2018; 24: 613-20.
DOI URL |
| 34. |
Piot C, Croisille P, Staat P, et al. Effect of cyclosporine on reperfusion injury in acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 473-81.
DOI URL |
| 35. | Tóth Š, Jonecová Z, Čurgali K, et al. Quercetin attenuates the ischemia reperfusion induced COX-2 and MPO expression in the small intestine mucosa. Biomed Pharmacother 2017; 95: 346-54. |
| 36. |
Gutiérrez-Venegas G, Torras-Ceballos A, Gómez-Mora JA, Fernández-Rojas B. Luteolin, quercetin, genistein and quercetagetin inhibit the effects of lipopolysaccharide obtained from in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts. Cell Mol Biol Lett 2017; 22: 19.
DOI PMID |
| 37. |
Qin L, Chen Z, Yang L, et al. Luteolin-7-O-glucoside protects dopaminergic neurons by activating estrogen-receptor-mediated signaling pathway in MPTP-induced mice. Toxicology 2019; 426: 152256.
DOI URL |
| 38. |
Zheng N, Yuan P, Li C, Wu J, Huang J. Luteolin reduces BACE1 expression through NF-κB and through estrogen receptor mediated pathways in HEK293 and SH-SY5Y cells. J Alzheimers Dis 2015; 45: 659-71.
PMID |
| 39. |
Ji Y, Han J, Lee N, et al. Neuroprotective effects of Baicalein, Wogonin, and Oroxylin A on amyloid beta-induced toxicity via NF-κB/MAPK pathway modulation. Molecules 2020; 25: 5087.
DOI URL |
| 40. |
Fan GW, Zhang Y, Jiang X, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of baicalein in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via estrogen receptor and NF-κB-dependent pathways. Inflammation 2013; 36: 1584-91.
DOI URL |
| [1] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [2] | CHANG Fengjin, ZHOU Peng, LI Guoying, ZHANG Weizhi, ZHANG Yanyan, PENG Daiyin, CHEN Guangliang. Taohong Siwu decoction (桃红四物汤) ameliorates atherosclerosis in rats possibly through toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88/nuclear factor-κB signal pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 103-112. |
| [3] | SUN Qianhui, CHENG Kai, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, WU Xiaoling, XU Chang, QIU Xinghua, GAO Xiaofeng, LIU Daonan, YANG Qirui. Effect of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) at different time points on myocardial ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 113-121. |
| [4] | ZHI Guoguo, SHAO Bingjie, ZHENG Tianyan, JI Shaoxiu, LI Jingwei, DANG Yanni, LIU Feng, WANG Dong. Efficacy of Ganshuang granules (肝爽颗粒) on non-alcoholic fatty liver and underlying mechanism: a network pharmacology and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 122-130. |
| [5] | ZHANG Qi, CHEN Dexuan, ZHU Guixiang, ZHANG Shihu, FENG Xiao, MA Chaoqun, ZHANG Yi. Efficacy of Tounongsan decoction (透脓散方) on pyogenic liver abscess: network pharmacology and clinical trial validation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 145-155. |
| [6] | SHI Xiao, WANG Lina, HU Jianpeng, ZHANG Limiao, WANG Jin. Effect of Naoluoxintong formula (脑络欣通方) and its split prescriptions on cerebral vascular regeneration in rats with the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1140-1149. |
| [7] | REN Hui, ZHAO Lintao, GAO Kai, YANG Yuanyuan, CUI Xiaomin, HU Jing, CHEN Zhiyong, LI Ye. Deciphering the chemical profile and pharmacological mechanism of Jinlingzi powder (金铃子散) against bile reflux gastritis using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with Q exactive focus mass spectrometry, network pharmacology, and molecular docking [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1209-1218. |
| [8] | YANG Xirui, ZHAO Hui, SHAN Muhammad, DONG Feixue, ZHANG Dandan, WANG Jixue, YUAN Xingxing. Efficacy of bioactive compounds of Chaihu (Radix Bupleuri Chinensis) on glaucomatous optic atrophy through interleukin-6/hypoxia inducible factor-1α signal pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1219-1226. |
| [9] | HAN Huagang, LI Ziqiang, OUYANG Jingfeng, WANG Tianquan, DONG Lingyan, CAO Junling. Mechanism of Lingbao Huxin Dan (灵宝护心丹) in the treatment of bradyarrhythmia complicated with coronary heart disease: a network pharmacology analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 1001-1009. |
| [10] | WANG Kun, ZHOU Jie, CUI Shuai, WU Xin, ZHU Guoqi, WU Shengbing, ZHOU Meiqi. Electroacupuncture ameliorates cardiac dysfunction in myocardial ischemia model rats: a potential role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 944-954. |
| [11] | PANG Fengtao, LI Kesong, ZHANG Yi, TANG Xiaopo, ZHOU Xinyao. Efficacy of Lushi Runzao decoction (路氏润燥汤) on ameliorating Sjogren's syndrome: a network pharmacology and experimental verification-based study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 751-759. |
| [12] | JIA Lihua, KUANG Haodan, XU Yuan. Efficacy of Buzhong Yiqi decoction (补中益气汤) on benign prostatic hyperplasia and its possible mechanism [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 533-541. |
| [13] | JIA Lihong, TIE Defu, FAN Zhaohui, CHEN Dan, CHEN Qizhu, CHEN Jun, BO Huaben. Mechanism underlying Fanmugua (Fructus Caricae) leaf multicomponent synergistic therapy for anemia: data mining based on hematopoietic network [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 542-551. |
| [14] | PENG Wan, NI Hengfan, GUO Dale, DENG Yun, DAI Manyun. Farnesoid X receptor regulators from natural products and their biological function [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 618-626. |
| [15] | LI Yue, WEN Shuting, ZHAO Runyuan, FAN Dongmei, ZHAO Dike, LIU Fengbin, MI Hong. Efficacy of active ingredients in Qingdai (Indigo Naturalis) on ulcerative colitis: a network pharmacology-based evaluation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 124-133. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

