Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 552-560.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.03.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Intervention and mechanism of Xiaoyin Anshen Yin (消银安神饮) in treatment of psoriasis combined with sleep disorders
DIAO Ruohan1,2, DUAN Xingwu3( ), LI Lingling3, QU Tiange3(
), LI Lingling3, QU Tiange3( ), FENG Huishang3, CHEN Guangshan3
), FENG Huishang3, CHEN Guangshan3
- 1 Department of Dermatology, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
2 Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
3 Department of Dermatology, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2024-10-26Accepted:2025-01-14Online:2025-06-15Published:2025-05-21 -
Contact:Prof. Duan Xingwu, Department of Dermatology, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China. xwduan@sina.com;QU Tiange, Department of Dermatology, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China. 122367278@qq.com,Telephone: +86-10-84013167 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on the Mechanism of Cooling Blood and Tranquilizing Mind in the Treatment of Psoriasis with Sleep Disorder based on the Regulation of Oxidative Stress by Melatonin(82074436)
Cite this article
DIAO Ruohan, DUAN Xingwu, LI Lingling, QU Tiange, FENG Huishang, CHEN Guangshan. Intervention and mechanism of Xiaoyin Anshen Yin (消银安神饮) in treatment of psoriasis combined with sleep disorders[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 552-560.
share this article

Figure 1 Effect of drug-containing serum on oxidative stress indexes A: cells of each group were stained with 2', 7'-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate probe, the average fluorescence intensity was used to represent the level of intracellular ROS for statistical analysis. A1: flow cytometry analysis results; A2: relative levels of ROS. B: cells of each group were stained using JC-1 probe, Q2 is JC-1 multimer and its percentage, Q3 is JC-1 monomer and its percentage, and mitochondrial membrane potential was statistically analyzed by multimer/monomer to represent mitochondrial membrane potential. B1: NC; B2: Model; B3: XYAS; B4: QXAS; B5: LXJD; B6: mitochondrial membrane potential levels. C: The expression levels of SOD2 and Cyt-c in each group was detected via western blot method. C1: immunoblot bands for SOD2 and Cyt-c; C2: relative protein levels of SOD2; C3: relative protein levels of Cyt-c. NC: 10% NC serum; Model: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% NC serum; XYAS: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% XYAS serum; QXAS: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% QXAS serum; LXJD: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% LXJD serum. SOD2: superoxide dismutase 2; Cyt-c: Cytochrome-c; NC: Negative control; XYAS: Xiaoyin Anshen; QXAS: Qinxin Anshen; LXJD: Liangxue Jiedu; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor‐α. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance for multiple comparisons. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n ≥ 3). Compared with the Model group, aP < 0.001, cP < 0.01, dP < 0.05; compared with the NC group, bP < 0.001, eP < 0.05.
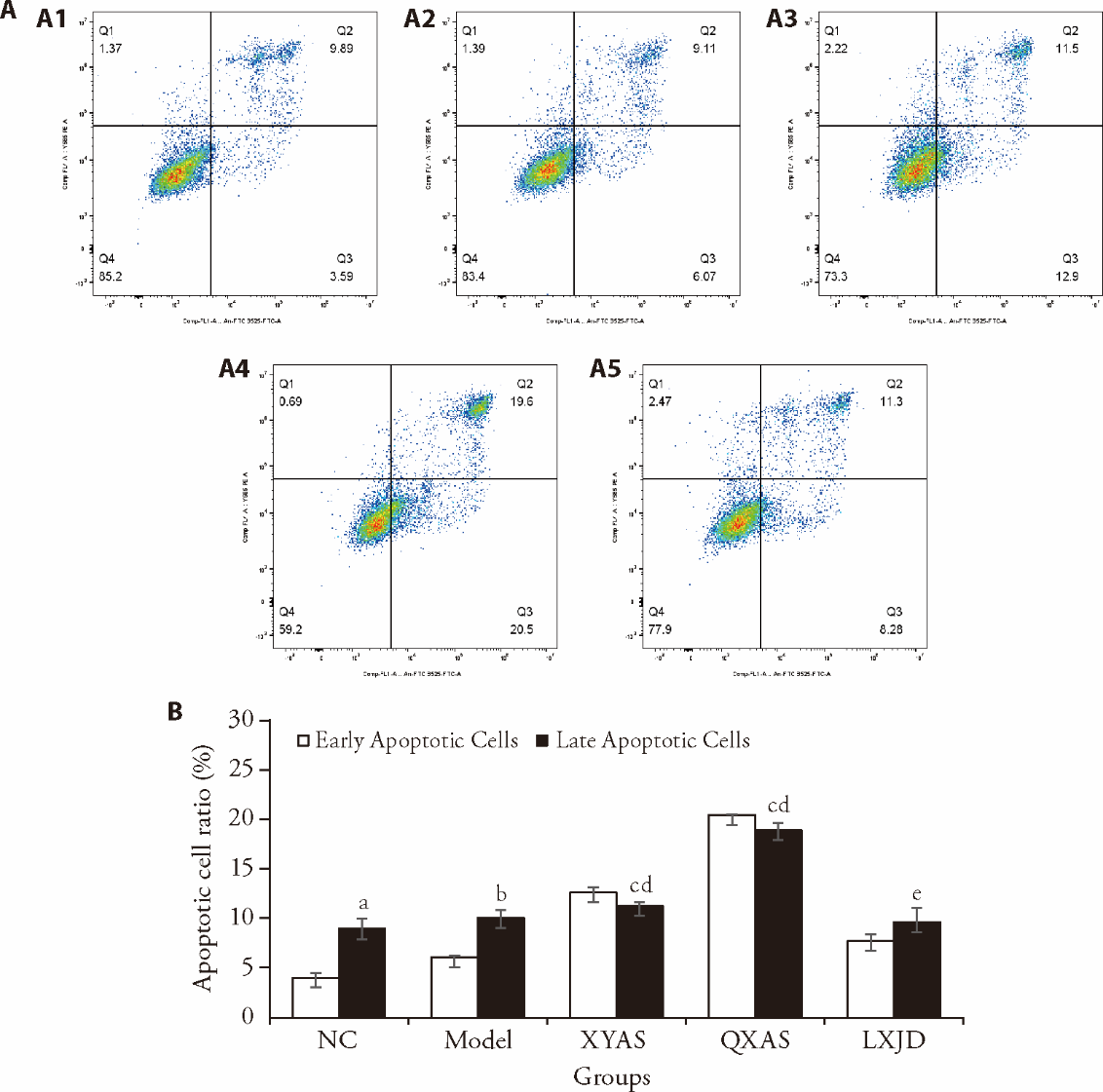
Figure 2 Effect of drug-containing serum on apoptosis A: the cells of each group were stained using AnnexinV-FITC/PI double staining. Q1-Q4 represented cell debris and necrotic cells, late apoptotic cells, early apoptotic cells, non-apoptotic cells and the percentage of apoptotic cells respectively. A1: NC; A2: Model; A3: XYAS; A4: QXAS; A5: LXJD. B: The percentage of Q2 + Q3 (early apoptotic cells + late apoptotic cells) was used for statistical analysis. NC: 10% NC serum; Model: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% NC serum; XYAS: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% XYAS serum; QXAS: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% QXAS serum; LXJD: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% LXJD serum. NC: Negative control; XYAS: Xiaoyin Anshen; QXAS: Qinxin Anshen; LXJD: Liangxue Jiedu; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor‐α; FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate; PI: propidium iodide. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance for multiple comparisons. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Compared with the Model group, aP < 0.05, cP < 0.001; compared with the NC group, bP < 0.05, dP < 0.001, eP < 0.01.

Figure 3 Effect of drug-containing serum on the activation of NF-κB pathway A: immunoblot bands for p-p65, p65 and IκBα; B: ratios of p-p65 to p65; C: relative protein levels of IκBα. NC: 10% NC serum; Model: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% NC serum; XYAS: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% XYAS serum; QXAS: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% QXAS serum; LXJD: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% LXJD serum. NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-B; p-p65: phosphorylated p65; IκBα: inhibitor of kappa-B alpha; NC: Negative control; XYAS: Xiaoyin Anshen; QXAS: Qinxin Anshen; LXJD: Liangxue Jiedu; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor‐α. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance for multiple comparisons. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n ≥ 3). Compared with the Model group, aP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, eP < 0.05; compared with the NC group, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.05.

Figure 4 Effects of drug-containing serum on melatonin and RORα A: The melatonin content in the drug-containing serum of each group tested by ELISA method; B: immunoblot bands for RORα; C: relative protein levels of RORα. NC: 10% NC serum; Model: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% NC serum; XYAS: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% XYAS serum; QXAS: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% QXAS serum; LXJD: 25 ng/mL TNF-α + 10% LXJD serum. MLT: melatonin; RORα: retinoid related orphan receptor alpha; NC: Negative control; XYAS: Xiaoyin Anshen; QXAS: Qinxin Anshen; LXJD: Liangxue Jiedu; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor‐α; ELISA: enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance for multiple comparisons. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n ≥ 3). Compared with the NC serum, aP < 0.001; compared with the Model group, bP < 0.05; compared with the NC group, cP < 0.05.
| 1. |
Griffiths CEM, Armstrong AW, Gudjonsson JE, Barker JNWN. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021; 397: 1301-15.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Korman NJ. Management of psoriasis as a systemic disease: what is the evidence? Br J Dermatol 2020; 182: 840-8.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Menter A, Strober BE, Kaplan DH, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol 2019; 80: 1029-72.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Baranwal N, Yu PK, Siegel NS. Sleep physiology, pathophysiology, and sleep hygiene. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2023; 77: 59-69.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Smith MP, Ly K, Thibodeaux Q, et al. Factors influencing sleep difficulty and sleep quantity in the citizen pscientist psoriatic cohort. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2019; 9: 511-23. |
| 6. | Luna PC, Chu CY, Fatani M, et al. Psychosocial burden of psoriasis: a systematic literature review of depression among patients with psoriasis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2023; 13: 3043-55. |
| 7. | Spencer RK, Jin JQ, Elhage KG, et al. Association between poor sleep and myocardial infarction in patients with psoriasis: findings from a cross-sectional study with the national psoriasis foundation. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2023; 13: 2903-9. |
| 8. | Halioua B, Chelli C, Misery L, Taieb J, Taieb C. Sleep disorders and psoriasis: an update. Ucta Derm Venereol 2022; 102: adv00699. |
| 9. | Nowowiejska J, Baran A, Flisiak I. Mutual relationship between sleep disorders, quality of life and psychosocial aspects in patients with psoriasis. Front Psychiatry 2021; 12: 674460. |
| 10. | Gao YX, Duan XW, Wu ZM, et al. Xiaoyin Anshen Beverage (消银安神饮) in the treatment of 34 psoriasis vulgaris patients of blood-heat syndrome complicated with sleep disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2023; 64: 909-15. |
| 11. | Zhu Z, Yin Q, Duan X. Xiaoyin-anshen formula alleviates psoriasis complicated by sleep disturbances by regulating melatonin, antioxidant enzymes, and pro-inflammatory cytokines in mice. Front Pharmacol 2024; 15: 1427985. |
| 12. |
Chen X, Zhang R, Duan X, et al. Effectiveness of Xiaoyin Jiedu granules in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris in patients with blood-heat symptom patterns in terms of Traditional Chinese Medicine. J Tradit Chin Med 2020; 40: 863-9.
DOI |
| 13. | Lin L, Huang Z, Jianchi M, et al. Artesunate alleviates psoriasis-like dermatitis by reducing interleukin-23 expression in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced HaCaT cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2023; 50: 903-13. |
| 14. | Zhang S, Zhang J, Yu J, et al. Hyperforin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like murine skin inflammation by modulating IL-17A-producing γδ T cells. Front Immunol 2021; 12: 635076. |
| 15. | Tang ZL, Zhang K, Lyu SC, Xu GW, Zhang JF, Jia HY. LncRNA MEG3 suppresses PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway to enhance autophagy and inhibit inflammation in TNF-α-treated keratinocytes and psoriatic mice. Cytokine 2021; 148: 155657. |
| 16. | Pleńkowska J, Gabig-Cimińska M, Mozolewski P. Oxidative stress as an important contributor to the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 6206. |
| 17. | Agrawal S, Singh V, Singh C, Singh A. A review on pathophysiological aspects of sleep deprivation. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2023; 22: 1194-208. |
| 18. | Krawczyk A, Miśkiewicz J, Strzelec K, Wcisło-Dziadecka D, Strzalka-Mrozik B. Apoptosis in autoimmunological diseases, with particular consideration of molecular aspects of psoriasis. Med Sci Monit 2020; 26: e922035. |
| 19. |
Goldminz AM, Au SC, Kim N, Gottlieb AB, Lizzul PF. NF-κB: an essential transcription factor in psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci 2013; 69: 89-94.
DOI PMID |
| 20. | Kim IW, Jeong HS, Yun HY, et al. Efficacy of horse oil on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in human keratinocyte. J Tradit Chin Med 2021; 41: 355-9. |
| 21. | Chitimus DM, Popescu MR, Voiculescu SE, et al. Melatonin's impact on antioxidative and anti-inflammatory reprogramming in homeostasis and disease. Biomolecules 2020; 10: 1211. |
| 22. |
Calvo JR, González-Yanes C, Maldonado MD. The role of melatonin in the cells of the innate immunity: a review. J Pineal Res 2013; 55: 103-20.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
Kumar N, Kojetin DJ, Solt LA, et al. Identification of SR3335 (ML-176): a synthetic RORα selective inverse agonist. ACS Chem Biol 2011; 6: 218-22.
DOI PMID |
| 24. | Rendon A, Schäkel K. Psoriasis pathogenesis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 1475. |
| 25. | Medovic MV, Jakovljevic VL, Zivkovic VI, et al. Psoriasis between autoimmunity and oxidative stress: changes induced by different therapeutic approaches. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022; 2022: 2249834. |
| 26. |
Hu J, Bian Q, Ma X, Xu Y, Gao J. A double-edged sword: ROS related therapies in the treatment of psoriasis. Asian J Pharm Sci 2022; 17: 798-816.
DOI PMID |
| 27. | Wroński A, Wójcik P. Impact of ROS-dependent lipid metabolism on psoriasis pathophysiology. Int J Mol Sci 2022; 23: 12137. |
| 28. | Hartmann C, Kempf A. Mitochondrial control of sleep. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2023; 81: 102733. |
| 29. |
Vaccaro A, Kaplan Dor Y, Nambara K, et al. Sleep loss can cause death through accumulation of reactive oxygen species in the Gut. Cell 2020; 181: 1307-28.e15.
DOI PMID |
| 30. | Rohleder N, Aringer M, Boentert M. Role of interleukin-6 in stress, sleep, and fatigue. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2012; 1261: 88-96. |
| 31. | Irwin MR, Olmstead R, Carroll JE. Sleep disturbance, sleep duration, and inflammation: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of cohort studies and experimental sleep deprivation. Biol Psychiatry 2016; 80: 40-52. |
| 32. |
Xue R, Wan Y, Sun X, Zhang X, Gao W, Wu W. Nicotinic mitigation of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress after chronic sleep deprivation. Front Immunol 2019; 10: 2546.
DOI PMID |
| 33. | Queiro R, Coto P, González-Lara L, Coto E. Genetic variants of the NF-κB pathway: unraveling the genetic architecture of psoriatic disease. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 13004. |
| 34. | Gao T, Wang Z, Dong Y, et al. Role of melatonin in sleep deprivation-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction in mice. J Pineal Res 2019; 67: e12574. |
| 35. | Mozzanica N, Tadini G, Radaelli A, et al. Plasma melatonin levels in psoriasis. Acta Derm Venereol 1988; 68: 312-6. |
| 36. | Kartha LB, Chandrashekar L, Rajappa M, Menon V, Thappa DM, Ananthanarayanan PH. Serum melatonin levels in psoriasis and associated depressive symptoms. Clin Chem Lab Med 2014; 52: e123-5. |
| 37. | Mohammadi F, Harofteh FZ, Sahebnasagh A, Ghaneei N, Ardakani MEZ, Saghafi F. Efficacy and safety of topical rosuvastatin & melatonin vs placebo in patients with mild to moderate plaque psoriasis: a preliminary randomized double-blinded clinical trial. Skin Res Technol 2024; 30: e13689. |
| 38. |
Shen Z, Jiang J, Zhou X, et al. Melatonin attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like inflammation and restores the Th17/Treg Immune Balance. Inflammation 2024; 47: 2027-40.
DOI PMID |
| 39. | Scuderi SA, Cucinotta L, Filippone A, et al. Effect of melatonin on psoriatic phenotype in human reconstructed skin model. Biomedicines 2022; 10: 752. |
| 40. | Emet M, Ozcan H, Ozel L, Yayla M, Halici Z, Hacimuftuoglu A. A review of melatonin, its receptors and dugs. Eurasian J Med 2016; 48: 135-41. |
| 41. | Cook DN, Kang HS, Jetten AM. Retinoic acid-related orphan receptors (RORs): regulatory functions in immunity, development, circadian rhythm, and metabolism. Nucl Receptor Res 2015; 2: 101185. |
| 42. |
Hall JA, Pokrovskii M, Kroehling L, et al. Transcription factor RORα enforces stability of the Th17 cell effector program by binding to a Rorc cis-regulatory element. Immunity 2022; 55: 2027-43.e9.
DOI PMID |
| 43. | Journiac N, Jolly S, Jarvis C, et al. The nuclear receptor ROR (alpha) exerts a bi-directional regulation of IL-6 in resting and reactive astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009; 106: 21365-70. |
| 44. |
Boukhtouche F, Vodjdani G, Jarvis CI, et al. Human retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor alpha1 overexpression protects neurones against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. J Neurochem 2006; 96: 1778-89.
DOI PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

