Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 594-601.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230328.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Therapy of replenishing Yin and regulating Yang for manic episode in bipolar disorder: study protocol for a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial
YANG Yang1,2, YUAN Haining1,2, JIA Hongxiao3,4, NING Yanzhe3,4, WANG Di1,2, ZHANG Lei1,2, YAN Kaijuan1,2, GUO Yumeng1,2, WANG Fei1,2, SUN Weishuang1,2, CHEN Pei1,2( )
)
- 1 Beijing Key Laboratory of Mental Disorders, National Clinical Research Center for Mental Disorders and National Center for Mental Disorders, Department of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine, Beijing Anding Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
2 Advanced Innovation Center for Human Brain Protection, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100088, China
3 Beijing Key Laboratory of Mental Disorders, National Clinical Research Center for Mental Disorders and National Center for Mental Disorders, Beijing Anding Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100088, China
4 Advanced Innovation Center for Human Brain Protection, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China
-
Received:2022-03-23Accepted:2022-06-15Online:2023-06-15Published:2023-03-28 -
Contact:CHEN Pei, Department of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine, Beijing Anding Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100088, China. bettereveryday@163.com. Telephone: +86-10-58303111 -
Supported by:Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program(PZ2021031);which plays no role in the design of the study, collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, and in writing the manuscript
Cite this article
YANG Yang, YUAN Haining, JIA Hongxiao, NING Yanzhe, WANG Di, ZHANG Lei, YAN Kaijuan, GUO Yumeng, WANG Fei, SUN Weishuang, CHEN Pei. Therapy of replenishing Yin and regulating Yang for manic episode in bipolar disorder: study protocol for a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 594-601.
share this article
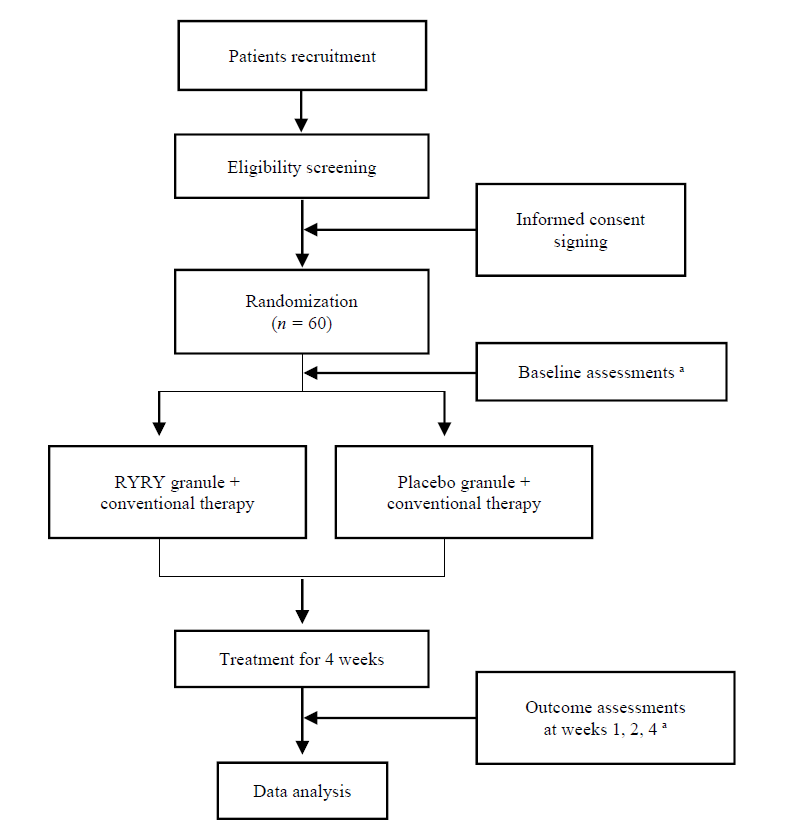
Figure 1 Study design RYRY: replenishing Yin and regulating Yang; YMRS: Young Mania Rating Scale; TESS: Treatment Emergent Symptom Scale; CRP: C-reactive protein; IL-6: interleukin-6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α. a Baseline and outcome assessments mainly include YMRS, TCM Symptom Pattern Rating Scale, TESS, levels of CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α, and the gut microbial community profile of stool samples.

Figure 2 Schedule of enrollment, intervention and assessments of this study protocol TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine; TESS: Treatment emergent symptom scale; YMRS: Young mania rating scale; CRP: C-reactive protein; IL-6: interleukin-6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α. a Blood samples for CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α testing and stool samples for gut microbial community profile.
| [1] |
Vieta E, Berk M, Schulze TG, et al. Bipolar disorders. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018; 4: 18008.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Sanchez-Moreno J, Martinez-Aran A, Tabarés-Seisdedos R, Torrent C, Vieta E, Ayuso-Mateos JL. Functioning and disability in bipolar disorder: an extensive review. Psychother Psychosom 2009; 78: 285-97.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Miller JN, Black DW. Bipolar disorder and suicide: a review. Curr Psychiatry Rep 2020; 22: 6.
DOI |
| [4] |
Aldinger F, Schulze TG. Environmental factors, life events, and trauma in the course of bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2017; 71: 6-17.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Van der Schot AC, Vonk R, Brouwer RM, et al. Genetic and environmental influences on focal brain density in bipolar disorder. Brain 2010; 133: 3080-92.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Pacchiarotti I, Anmella G, Colomer L, Vieta E. How to treat mania. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2020; 142: 173-92.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Vieta E, Sanchez-Moreno J. Acute and long-term treatment of mania. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 2008; 10: 165-79.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Harrison PJ, Cipriani A, Harmer CJ, et al. Innovative approaches to bipolar disorder and its treatment. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2016; 1366: 76-89.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Baldessarini RJ, Tondo L, Vázquez GH. Pharmacological treatment of adult bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2019; 24: 198-217.
DOI |
| [10] | Li ZY, Cao Y, Jia HX. Clinical experience of JIA Hong-xiao in the treatment of bipolar disorder by coordinating Yin and Yang. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2019; 34: 3087-90. |
| [11] |
Dickerson F, Severance E, Yolken R. The microbiome, immunity, and schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Brain Behav Immun 2017; 62: 46-52.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Halverson T, Alagiakrishnan K. Gut microbes in neurocognitive and mental health disorders. Ann Med 2020; 52: 423-43.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Fries GR, Walss-Bass C, Bauer ME, Teixeira AL. Revisiting inflammation in bipolar disorder. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2019; 177: 12-9.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Round JL, Mazmanian SK. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 313-23.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Nguyen TT, Kosciolek T, Eyler LT, Knight R, Jeste DV. Overview and systematic review of studies of microbiome in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. J Psychiatr Res 2018; 99: 50-61.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Evans SJ, Bassis CM, Hein R, et al. The gut microbiome composition associates with bipolar disorder and illness severity. J Psychiatr Res 2017; 87: 23-9.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Goldsmith DR, Rapaport MH, Miller BJ. A meta-analysis of blood cytokine network alterations in psychiatric patients: comparisons between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. Mol Psychiatry 2016; 21: 1696-709.
DOI |
| [18] |
Luo Y, He H, Zhang M, Huang X, Fan N. Altered serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-18 in manic, depressive, mixed state of bipolar disorder patients. Psychiatry Res 2016; 244: 19-23.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Solmi M, Suresh Sharma M, Osimo EF, et al. Peripheral levels of C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-1β across the mood spectrum in bipolar disorder: a Meta-analysis of mean differences and variability. Brain Behav Immun 2021; 97: 193-203.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Kim YK, Jung HG, MYint AM, Kim H, Park SH. Imbalance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord 2007; 104: 91-5..
DOI URL |
| [21] | Tong X, Xu J, Lian F, et al. Structural Alteration of gut microbiota during the amelioration of human type 2 diabetes with hyperlipidemia by metformin and a traditional Chinese herbal formula: a multicenter, randomized, open label clinical trial. mBio 2018; 9: e02392-17. |
| [22] | Zheng Y, Ding Q, Wei Y, et al. Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on gut microbiota in adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytomedicine 2021; 88: 153455. |
| [23] |
Jia Q, Wang L, Zhang X, et al. Prevention and treatment of chronic heart failure through traditional Chinese medicine: role of the gut microbiota. Pharmacol Res 2020; 151: 104552.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Hu Y, Huang W, Luo Y, et al. Assessment of the anti-inflammatory effects of three rhubarb anthraquinones in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages using a pharmacodynamic model and evaluation of the structure-activity relationships. J Ethnopharmacol 2021; 273: 114027. |
| [25] |
Dinda B, Dinda S, DasSharma S, Banik R, Chakraborty A, Dinda M. Therapeutic potentials of baicalin and its aglycone, baicalein against inflammatory disorders. Eur J Med Chem 2017; 131: 68-80.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Wang J, Wang L, Lou GH, et al. Coptidis Rhizoma: a comprehensive review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Pharm Biol 2019; 57: 193-225.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Habtemariam S. Berberine pharmacology and the gut microbiota: a hidden therapeutic link. Pharmacol Res 2020; 155: 104722. |
| [28] | Han F, Li HQ, Cao KG, Li B. Selection and evaluation of placebo in clinical research of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao 2020; 39: 846-50. |
| [29] |
Young RC, Biggs JT, Ziegler VE, Meyer DA. A rating scale for mania: reliability, validity and sensitivity. Br J Psychiatry 1978; 133: 429-35.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Hamilton M. General problems of psychiatric rating scales (especially for depression). Mod Probl Pharmacopsychiatry 1974; 7: 125-38. |
| [31] |
Patel NC, Patrick DM, Youngstrom EA, Strakowski SM, Delbello MP. Response and remission in adolescent mania: signal detection analyses of the young mania rating scale. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2007; 46: 628-35.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Lukasiewicz M, Gerard S, Besnard A, et al. Young mania rating scale: how to interpret the numbers? Determination of a severity threshold and of the minimal clinically significant difference in the EMBLEM cohort. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 2013; 22: 46-58.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Shan X, Zhao W, Qiu Y, et al. Preliminary clinical investigation of combinatorial pharmacogenomic testing for the optimized treatment of depression: a randomized single-blind study. Front Neurosci 2019; 13: 960.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Zheng W, Xiang YQ, Ng CH, Ungvari GS, Chiu HF, Xiang YT. Extract of Ginkgo biloba for tardive dyskinesia: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacopsychiatry 2016; 49: 107-11.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Garvey CA, Gross D, Freeman L. Assessing psychotropic medication side effects among children. A reliability study. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs 1991; 4: 127-31.
PMID |
| [36] | Li CP, Zhang JP, Wu RL. Observation on the therapeutic effect of Baihu Chengqi Decoction combined with magnesium valproate sustained-release tablet in the treatment of recurrent mania. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2010; 19: 2248-9. |
| [37] | Wang ZY. Dachengqi Decoction cure mania of Yangming fu-viscera excess through the clinical observation. Taiyuan, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine. Taiyuan, Shanxi, China: Taiyuan, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine; 2016: 6-7. |
| [38] |
Luo Y, Wang CZ, Hesse-Fong J, Lin JG, Yuan CS. Application of Chinese medicine in acute and critical medical conditions. Am J Chin Med 2019; 47: 1223-35.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Feng W, Ao H, Peng C, Yan D. Gut microbiota, a new frontier to understand Traditional Chinese Medicines. Pharmacol Res 2019; 142: 176-91.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Lu Q, Lai J, Lu H, et al. Gut microbiota in bipolar depression and its relationship to brain function: An advanced exploration. Front Psychiatry 2019; 10: 784.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Bioque M, González-Rodríguez A, Garcia-Rizo C, et al. Targeting the microbiome-gut-brain axis for improving cognition in schizophrenia and major mood disorders: a narrative review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2021; 105: 110130.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

