Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 87-94.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2023.01.008
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Astragaloside IV plays a role in reducing radiation-induced liver inflammation in mice by inhibiting thioredoxin-interacting protein/nod-like receptor protein 3 signaling pathway
DING Yanping1, DONG Xiaoqing1, MA Yifan1, CHEN Lili1, ZHOU Jie1 , LI Xinyan1, SHAO Baoping2( )
)
- 1 College of Life Science, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou 730000, China
2 College of Life Science, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China
-
Received:2021-12-11Accepted:2022-03-28Online:2023-02-15Published:2023-01-10 -
Contact:SHAO Baoping -
About author:SHAO Baoping, College of Life Science, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China. shaobp@lzu.edu.cn. Telephone:+86-931-7971414
-
Supported by:Molecular Mechanism of the Brain AQP4 Adaptation to the Extreme Hhypoxia in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Animal(31760271)
Cite this article
DING Yanping, DONG Xiaoqing, MA Yifan, CHEN Lili, ZHOU Jie, LI Xinyan, SHAO Baoping. Astragaloside IV plays a role in reducing radiation-induced liver inflammation in mice by inhibiting thioredoxin-interacting protein/nod-like receptor protein 3 signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 87-94.
share this article

Figure 1 AS-IV alleviates radiation-induced liver injury A1: ALT levels in mice serum; A2: AST levels in mice serum; B: HE staining of liver with different amplification (B1-B5 is ×200, B6-B10 is ×400 ), B1, B5: control group; B2, B6: DMSO group; B3, B7: IR group; B4, B8: IR+AS-IV-20 group; B5, B10: IR+AS-IV-40 group; the arrow points to the hepatic sinus and the triangle points to the changes of liver structure after radiation; C: transmission electron microscopy of liver (C1-B5 is ×1000, C6-B10 is ×2500), C1, C5: Control group; C2, C6: DMSO group; C3, C7: IR group; C4, C8: IR+AS-IV-20 group; C5, C10: IR+AS-IV-40 group. DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide; IR: irradiation; IR+AS-20: irradiation +AS-IV (20 mg/kg); IR+AS-40: irradiation +AS-IV (40 mg/kg); AS-IV: astragaloside IV; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspertate aminotransferase; HE: hematoxylin-eosin. aP < 0.001 vs Control group; bP < 0.001 vs IR group.
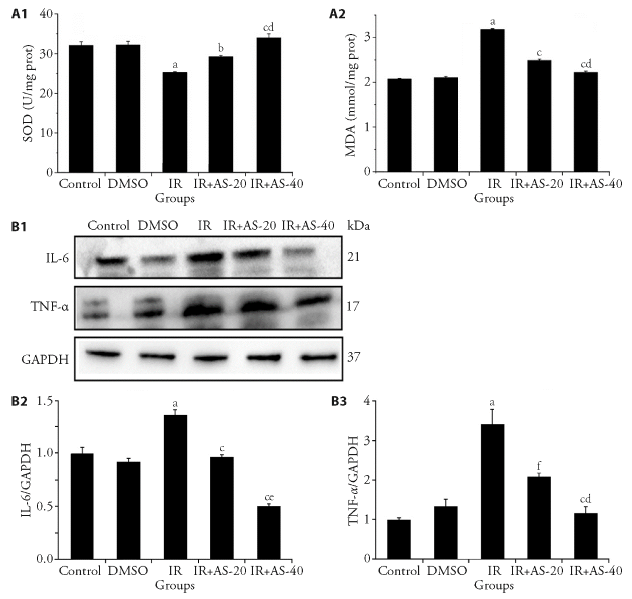
Figure 2 AS-IV alleviates the oxidative damage and the expression of inflammatory factors in radiation-induced liver injury mice A1: levels of SOD; A2: content of MDA; B1: Western blot detection of the expression levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in mice liver; B2: relative density of IL-6; B3: relative density of TNF-α. DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide; IR: irradiation; IR+AS-20: irradiation +AS-IV (20 mg/kg); IR+AS-40: irradiation +AS-IV (40 mg/kg); AS-IV: astragaloside IV; MDA: malonaldehyde; SOD: superoxide dismutase; IL-6: interleukin 6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha. aP < 0.001 vs Control group; bP < 0.05 vs IR group; cP < 0.05 vs IR+AS-20 group; dP < 0.01 vs IR group; eP < 0.01 vs IR+AS-20 group; fP < 0.001 vs IR group.
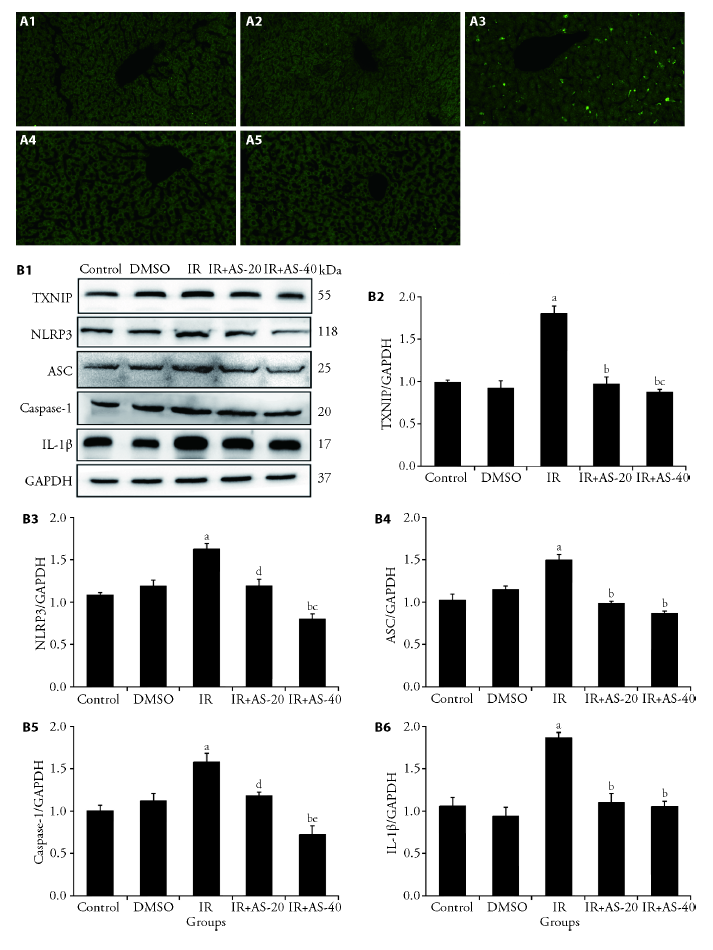
Figure 3 AS-IV blocks radiation-induced activation in TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway A: immunofluorescence expression of NLRP3 inflammasome in each group. A1: Control group; A2: DMSO group; A3: IR group; A4: IR+AS-IV-20 group; A5: IR+AS-IV-40 group; B1: the expressions of TXNIP, NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1 and IL-1β in liver were measured by Western blot; B2: relative density of TXNIP; B3: relative density of NLRP3; B4: relative density of ASC. B5: relative density of Caspase-1; B6: relative density of IL-1β. DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide; IR: irradiation; IR+AS-20: irradiation+AS-IV (20 mg/kg); IR + AS-40: irradiation +AS-IV (40 mg/kg); AS-IV: astragaloside IV; TXNIP: Thioredoxin-interacting protein; NLRP3: nod-like receptor protein 3; ASC: apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; Caspase-1: cysteinyl aspartate-specific proteinase 1; IL-1β: interleukin 1beta. aP < 0.001 vs Control group; bP < 0.001 vs IR group; cP < 0.05 vs IR + AS-20 group; dP < 0.01 vs IR group; eP < 0.01 vs IR + AS-20 group.
| 1 |
Najafi M, Shirazi A, Motevaseli E, Rezaeyan AH, Salajegheh A, Rezapoor S. The melatonin immunomodulatory actions in radiotherapy. Biophys rev 2017; 9: 139-48.
DOI PMID |
| 2 | Stoecklein VM, Osuka A, Ishikawa S, Lederer MR, Wanke-Jellinek L, Lederer JA. Radiation exposure induces inflammasome pathway activation in immune cells. J immunol 2015; 194: 178-89. |
| 3 | Zhou R, Yazdi A, Menu P, Tschopp J. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature 2011; 469: 221-5. |
| 4 | Liang H, Liu K, Zhuang Z, et al. Potential of Forsythoside I as a therapeutic approach for acute lung injury: involvement of TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome. Mol Immunol 2021; 134: 192-201. |
| 5 | Zhang H, Zahid A, Ismail H, Tang Y, Jin T, Tao J. An overview of disease models for NLRP3 inflammasome over-activation. Expert Opin Drug Discov 2021; 16: 429-46. |
| 6 | Wei J, Wang H, Wang H, et al. The role of NLRP 3 inflammasome activation in radiation damage. Biomed Pharmacother 2019; 118: 109217. |
| 7 | Cao Z, Fang Y, Lu Y, et al. Melatonin alleviates cadmium-induced liver injury by inhibiting the TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome. J Pineal Res 2017; 62: e12389. |
| 8 | Lin J, Fang L, Li H, et al. Astragaloside IV alleviates doxorubicin induced cardiomyopathy by inhibiting NADPH oxidase derived oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol 2019; 859: 172490. |
| 9 |
Ren S, Zhang H, Mu Y, Sun M, Liu P. Pharmacological effects of Astragaloside IV: a literature review. J Tradit Chin Med 2013; 33: 413-6.
DOI PMID |
| 10 | Qu X, Gao H, Tao L, et al. Astragaloside IV protects against cisplatin-induced liver and kidney injury via autophagy-mediated inhibition of NLRP3 in rats. J Toxicol Sci 2019; 44: 167-75. |
| 11 |
Wei R, Liu H, Chen R, Sheng Y, Liu T. Astragaloside IV combating liver cirrhosis through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med 2019; 17: 393-7.
DOI PMID |
| 12 | Li L, Huang W, Wang S, et al. Astragaloside IV attenuates acetaminophen-induced liver injuries in mice by activating the Nrf 2 signaling pathway. Molecules 2018; 23: 2032. |
| 13 | Zhou B, Zhou D, Wei XH, Zhong RY, Xu J, Sun L. Astragaloside IV attenuates free fatty acid-induced ER stress and lipid accumulation in hepatocytes via AMPK activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2017; 38: 998-1008. |
| 14 | Leng B, Zhang Y, Liu X, et al. Astragaloside IV suppresses high glucose-induced NLRP 3 inflammasome activation by inhibiting TLR4/NF- κ B and CaSR. Mediators Inflamm 2019; 2019: 1-16. |
| 15 | Jin YR. Astragaloside IV inhibits radiation-induced brain injury through NLRP3 and TLR4 signaling pathway. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2019: 23-40. |
| 16 | Liu X, Shang S, Chu W, et al. Astragaloside IV ameliorates radiation-induced senescence via antioxidative mechanism. J Pharm Pharmacol 2020; 72: 1110-8. |
| 17 | Su CM, Wang HC, Hsu FT, et al. Astragaloside IV induces aoptosis, G-Phase arrest and inhibits anti-apoptotic signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. In Vivo 2020, 34: 631-8. |
| 18 | Liu X, Chu W, Shang S, et al. Preliminary study on the anti-apoptotic mechanism of Astragaloside IV on radiation-induced brain cells. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2020; 34: 1-12. |
| 19 | Postaci I, Coskun O, Senol N, Aslankoc R, Comlekci S.The physiopathological effects of quercetin on oxidative stress in radiation of 4.5 g mobile phone exposed liver tissue of rat. Bratisl Lek Listy 2018, 119: 481-9. |
| 20 | Holovská K, Almášiová V, Cigánková V, Beňová K, Račeková E, Martončíková M. Structural and ultrastructural study of rat liver influenced by electromagnetic radiation. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2015; 78: 353-6. |
| 21 |
Lysek-Gladysinska M, Wieczorek A, Walaszczyk A, et al. Long-term effects of low-dose mouse liver irradiation involve ultrastructural and biochemical changes in hepatocytes that depend on lipid metabolism. Radiat Environ Biophys 2018; 57: 123-32.
DOI PMID |
| 22 | Tekın S, Türker H, Güven T, Yel M. The effects of ultraviolet C radiation on the ultrastructure of the liver cells of mole rats. Ultrastruct Pathol 2016; 40: 51-6. |
| 23 |
Ragy MM. Effect of exposure and withdrawal of 900-MHz-electromagnetic waves on brain, kidney and liver oxidative stress and some biochemical parameters in male rats. Electromagn Biol Med 2015, 34: 279-84.
DOI PMID |
| 24 |
Najafi M, Motevaseli E, Shirazi A, et al. Mechanisms of inflammatory responses to radiation and normal tissues toxicity: clinical implications. Int J Radiat Biol 2018; 94: 335-56.
DOI PMID |
| 25 |
Lyu Z, Ji X, Chen G, An B. Atractylodin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide and d-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure via the suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress. Int Immunopharmacol 2019; 72: 348-57.
DOI PMID |
| 26 | Han M, Li S, Li L. Verapamil inhibits early acute liver failure through suppressing the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. J Cell Mol Med 2021; 25: 5963-75. |
| 27 | Zhou X, Sun X, Gong X, et al. Astragaloside IV from Astragalus membranaceus ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis by inhibiting inflammation via TLR4/NF-кB in vivo and in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol 2017; 42: 18-24. |
| 28 |
Guarda G, Zenger M, Yazdi AS, et al. Differential expression of NLRP3 among hematopoietic cells. J Immunol 2011; 186: 2529-34.
DOI PMID |
| 29 |
Davis BK, Wen H, Ting JP. The inflammasome NLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated diseases. Annu Rev Immunol 2011; 29: 707-35.
DOI PMID |
| 30 |
De ND, Latz Eicke. NLRP 3 inflammasomes link inflammation and metabolic disease. Trends Immunol 2011; 32: 373-9.
DOI PMID |
| 31 | Qian W, Cai X, Qian Q, et al. Astragaloside IV protects endothelial progenitor cells from the damage of ox-LDL via the LOX-1/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther 2019; 13: 2579-89. |
| 32 | Song MT, Ruan J, Zhang RY, Deng J, Ma ZQ, Ma SP.Astragaloside IV ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behaviors in mice via the PPARγ/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2018; 39: 1559-70. |
| 33 |
Nasoohi S, Ismael S, Ishrat T. Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) in cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases: regulation and implication. Mol Neurobiol 2018; 55: 7900-20.
DOI PMID |
| 34 | Chen Y, Ning J, Cao W, et al. Research progress of TXNIP as a tumor suppressor gene participating in the metabolic reprogramming and oxidative stress of cancer cells in various cancers. Front Oncol 2020, 10: 568574. |
| 35 | Tsubaki H, Tooyama I, Walker DG. Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) with focus on brain and neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 9357. |
| 36 | Yodoi J, Matsuo Y, Tian H, Masutani H, Inamoto T. Anti-inflammatory thioredoxin family proteins for medicare, healthcare and aging care. Nutrients 2017; 9: 1081. |
| 37 | Fang YL. The role of TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome activation in cadmium exposure induced liver injury and the antagonistic effect of melatonin. Chongqin: Third Military Medical University, 2017: 32-65. |
| 38 |
Kumar A, Mittal R. Mapping Txnip: Key connexions in progression of diabetic nephropathy. Pharmacol Rep 2018; 70: 614-22.
DOI PMID |
| 39 |
Zhao Y, Li Q, Zhao W, et al. Astragaloside IV and cycloastragenol are equally effective in inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the endothelium. J Ethnopharmacol 2015, 169: 210-8.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | YE Xiaomei, XING Xiaowei, YUAN Kangrui, WANG Dongming, WU Dudu, CHEN Zhi, YU Zhiqiang. Astragaloside IV ameliorates insulin induced insulin resistance in HepG2 cells through reactive oxygen species mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 60-67. |
| [2] | YIN Xiuping, ZHANG Xiaotong, ZHU Rongjia, SONG Ping. Effect of astragaloside IV on the immunoregulatory function of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from patients with psoriasis vulgaris [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 513-519. |
| [3] | Shuang Ren, Hua Zhang, Yongping Mu, Mingyu Sun, Ping Liu. Pharmacological effects of Astragaloside IV: a literature review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(03): 413-416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

