Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 200-212.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20211214.004
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Baicalin inhibits inflammation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via toll like receptor-4/myeloid differentiation primary response 88/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway
ZHU Changle1,2, FENG Cuiling2( ), FENG Feng1, Yao Xiaoqin3, WANG Guishu1, SHI Liangtian1, ZHENG Jiakun1
), FENG Feng1, Yao Xiaoqin3, WANG Guishu1, SHI Liangtian1, ZHENG Jiakun1
- 1 Department of respiration, Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100000, China
2 Department of traditional Chinese Medicine, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing, 100000, China
3 Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 100000, China
-
Received:2021-07-19Accepted:2021-10-09Online:2021-12-14Published:2021-12-14 -
Contact:FENG Cuiling -
About author:Prof. FENG Cuiling, Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100000, China. 20170941060@bucm.edu.cn, Telephone: +86-18810619976
-
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on the Intervention of Qingjin Huatan Decoction on Hypersecretion of Airway Mucus(81473655);Comparative Study about Intervention of Yupingfeng Powder and Modified Guomin Decoction on Decreased Alveolar Macrophage Phagocytosis and Immune Imbalance Leading to Pulmonary Inflammation Induced by PM2(581673921)
Cite this article
ZHU Changle, FENG Cuiling, FENG Feng, Yao Xiaoqin, WANG Guishu, SHI Liangtian, ZHENG Jiakun. Baicalin inhibits inflammation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via toll like receptor-4/myeloid differentiation primary response 88/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 200-212.
share this article
| Targeted gene | Forward primer and reverse primer |
|---|---|
| Human TLR4 F: | 5'-TTTGGACAGTTTCCCACATTGA-3' |
| Human TLR4 R: | 5'-AAGCATTCCCACCTTTGTTGG-3' |
| Human MyD88 F: | 5'-GGCTGCTCTCAACATGCGA-3' |
| Human MyD88 R: | 5'-CTGTGTCCGCACGTTCAAGA-3' |
| Human TRIF F: | 5'-TGCCTATTCTGGAGCCGGTCAA-3' |
| Human TRIF R: | 5'-AGTTGGAGTGGCGTCTGGTCTT-3' |
| Human NF-κB F: | 5'-ACTGTAACTGCTGGACCCAAGGA-3' |
| Human NF-κB R: | 5'-CGCCTCTGTCATTCGTGCTTCC-3' |
| Human GAPDH F: | 5'-AGCCTTCTCCATGGTGGTGAAGAC-3' |
| Human GAPDH R: | 5'-CGGAGTCAACGGATTTGGTCGTAT-3' |
Table 1 RT-PCR primer sequences
| Targeted gene | Forward primer and reverse primer |
|---|---|
| Human TLR4 F: | 5'-TTTGGACAGTTTCCCACATTGA-3' |
| Human TLR4 R: | 5'-AAGCATTCCCACCTTTGTTGG-3' |
| Human MyD88 F: | 5'-GGCTGCTCTCAACATGCGA-3' |
| Human MyD88 R: | 5'-CTGTGTCCGCACGTTCAAGA-3' |
| Human TRIF F: | 5'-TGCCTATTCTGGAGCCGGTCAA-3' |
| Human TRIF R: | 5'-AGTTGGAGTGGCGTCTGGTCTT-3' |
| Human NF-κB F: | 5'-ACTGTAACTGCTGGACCCAAGGA-3' |
| Human NF-κB R: | 5'-CGCCTCTGTCATTCGTGCTTCC-3' |
| Human GAPDH F: | 5'-AGCCTTCTCCATGGTGGTGAAGAC-3' |
| Human GAPDH R: | 5'-CGGAGTCAACGGATTTGGTCGTAT-3' |
| Group | n | W/D lung weight ratio | Protein concentration (ng/μL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5 | 4.18±0.67a | 2.09±0.26a |
| Model | 5 | 9.61±0.72 | 5.34±0.05 |
| L-baicalin | 5 | 8.42±0.35b | 2.76±0.12a |
| H-baicalin | 5 | 5.67±0.49a | 2.67±0.04a |
| CAM | 5 | 5.99±0.55a | 2.51±0.10a |
Table 2 Alterations in the permeability of the alveolocapillary membrane ($\bar{x}± s$)
| Group | n | W/D lung weight ratio | Protein concentration (ng/μL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5 | 4.18±0.67a | 2.09±0.26a |
| Model | 5 | 9.61±0.72 | 5.34±0.05 |
| L-baicalin | 5 | 8.42±0.35b | 2.76±0.12a |
| H-baicalin | 5 | 5.67±0.49a | 2.67±0.04a |
| CAM | 5 | 5.99±0.55a | 2.51±0.10a |
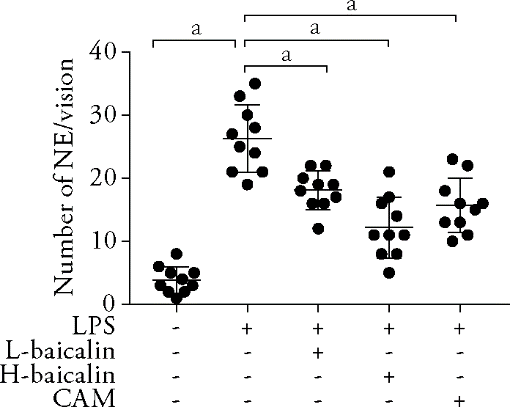
Figure 1 Tissue injury and inflammatory infiltration L-baicalin: low-dose baicalin group, H-baicalin: high-dose baicalin group, CAM: Clarithromycin group, LPS: Model group, Lipopolysaccharide, NE: neutrophil. The rats in the low-dose baicalin (L-baicalin), high-dose baicalin (H-baicalin), and CAM groups were administered baicalin 50 mg·kg–1·d–1, baicalin 100 mg·kg–1·d–1, and CAM 45 mg·kg–1·d–1 by gavage, respectively, as described previously. The control and model groups were administered normal saline 0.1 mL·kg–1·d–1 by gavage. On the second day, the model and the drug groups were administered LPS 10 mg/mL (100 μL) by airway instillation. The number of neutrophils in control, LPS, L-baicalin, H-baicalin, and CAM groups. Count neutrophils in the high-power field (× 400) in at least ten random fields (n = 10); aP < 0.01 compared to the model group. The data were represented as mean ± standard deviation.
| Group | n | BALF-CXCL1 (pg/mL) | BALF-IL6 (pg/mL) | BALF-IL-1β (pg/mL) | BALF-TNF-α (pg/mL) | BALF-MPO (U/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6 | 33.8±2.1a | 39.8±17.7a | 6.8±1.4b | 62.8±5.0a | 113.1±8.5a |
| Model | 6 | 47.4±4.6 | 309.6±25.1 | 10.8±0.9 | 116.1±9.3 | 181.5±14.5 |
| L-baicalin | 6 | 40.7±5.5b | 294.2±21.5 | 10.3±0.8 | 93.2±9.7a | 140.6±14.3a |
| H-baicalin | 6 | 23.9±2.0a | 166.6±28.3a | 5.5±0.3b | 58.1±5.5a | 111.6±4.2a |
| CAM | 6 | 19.6±0.8a | 148.0±37.3a | 3.3±0.2a | 46.1±2.3a | 65.2±8.2a |
Table 3 Infiltration of inflammatory factors and MPO in BALF ($\bar{x}± s$)
| Group | n | BALF-CXCL1 (pg/mL) | BALF-IL6 (pg/mL) | BALF-IL-1β (pg/mL) | BALF-TNF-α (pg/mL) | BALF-MPO (U/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6 | 33.8±2.1a | 39.8±17.7a | 6.8±1.4b | 62.8±5.0a | 113.1±8.5a |
| Model | 6 | 47.4±4.6 | 309.6±25.1 | 10.8±0.9 | 116.1±9.3 | 181.5±14.5 |
| L-baicalin | 6 | 40.7±5.5b | 294.2±21.5 | 10.3±0.8 | 93.2±9.7a | 140.6±14.3a |
| H-baicalin | 6 | 23.9±2.0a | 166.6±28.3a | 5.5±0.3b | 58.1±5.5a | 111.6±4.2a |
| CAM | 6 | 19.6±0.8a | 148.0±37.3a | 3.3±0.2a | 46.1±2.3a | 65.2±8.2a |
| Group | n | serum-CXCL1 (pg/mL) | serum -IL6 (pg/mL) | serum -IL-1β (pg/mL) | serum-TNF-α (pg/mL) | Serum-MPO (U/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5 | 27.0±2.5a | 17.3±2.4a | 5.8±0.5a | 71.5±4.8a | 107.8±13.4a |
| Model | 5 | 41.2±3.8 | 61.7±3.7 | 10.5±1.6 | 101.4±5.7 | 162.9±13.3 |
| L-baicalin | 5 | 36.3±3.8b | 56.7±4.0 | 8.7±0.7b | 96.4±7.3 | 121.7±8.7a |
| H-baicalin | 5 | 20.9±1.8a | 41.1±1.6a | 4.5±0.8a | 53.1±7.6a | 91.4±8.7a |
| CAM | 5 | 16.5±1.0a | 36.9±1.2a | 2.5±0.4a | 38.8±3.7a | 62.3±6.0a |
Table 4 Secretion of inflammatory cytokines and MPO in the serum ($\bar{x}± s$)
| Group | n | serum-CXCL1 (pg/mL) | serum -IL6 (pg/mL) | serum -IL-1β (pg/mL) | serum-TNF-α (pg/mL) | Serum-MPO (U/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5 | 27.0±2.5a | 17.3±2.4a | 5.8±0.5a | 71.5±4.8a | 107.8±13.4a |
| Model | 5 | 41.2±3.8 | 61.7±3.7 | 10.5±1.6 | 101.4±5.7 | 162.9±13.3 |
| L-baicalin | 5 | 36.3±3.8b | 56.7±4.0 | 8.7±0.7b | 96.4±7.3 | 121.7±8.7a |
| H-baicalin | 5 | 20.9±1.8a | 41.1±1.6a | 4.5±0.8a | 53.1±7.6a | 91.4±8.7a |
| CAM | 5 | 16.5±1.0a | 36.9±1.2a | 2.5±0.4a | 38.8±3.7a | 62.3±6.0a |
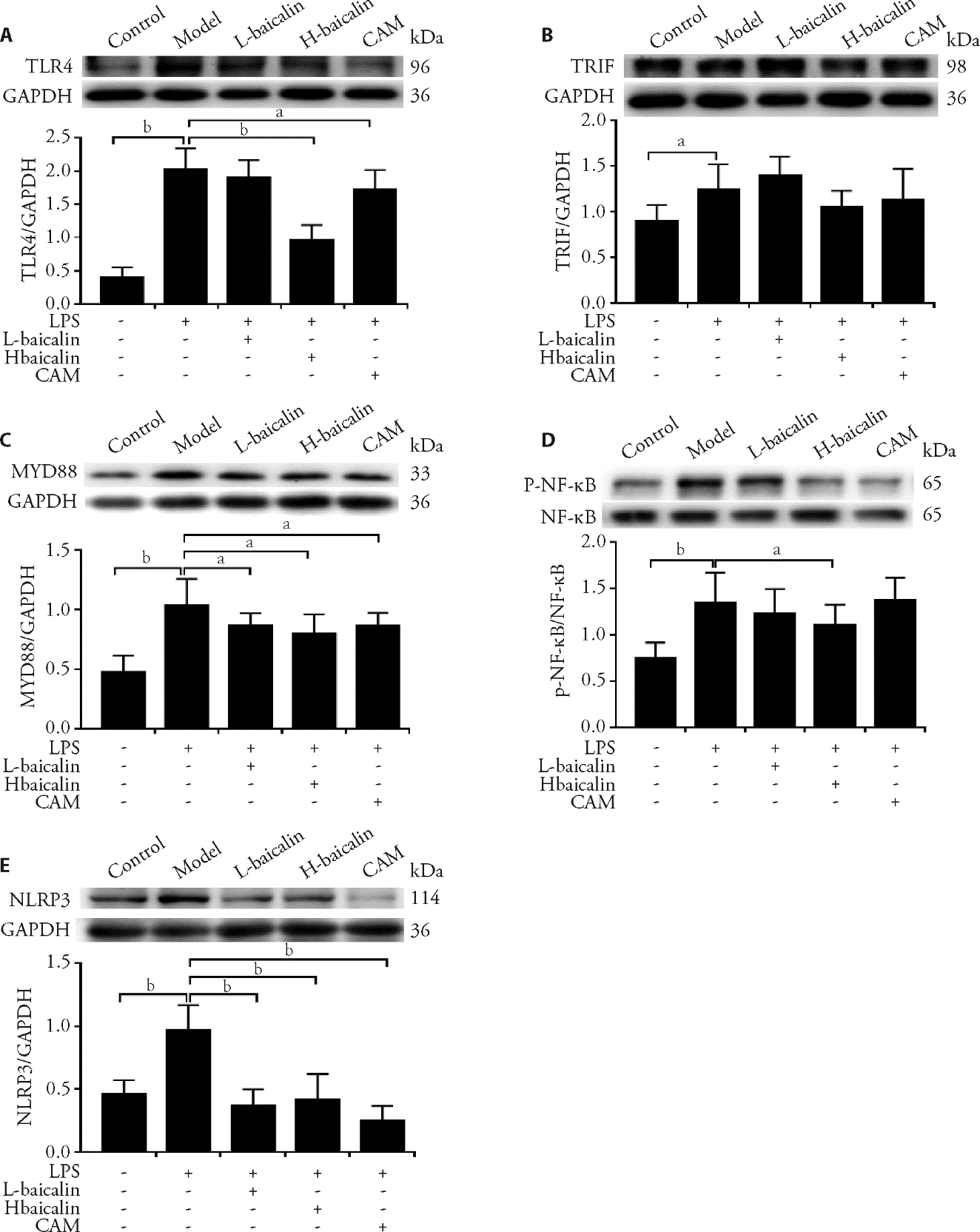
Figure 2 Effects of baicalin on inhibiting the protein expression of TLR4-TRIF/MyD88-NF-κB pathway signaling and NLRP3 in lung tissues detected by Western blotting A-E: expression of TLR4, TRIF, MyD88, NLRP3, and p-NF-κB proteins of control group, LPS group, baicalin group, CAM group in lung tissues from rats detected by WB. L-baicalin: low-dose baicalin group, H-baicalin: high-dose baicalin group, CAM: Clarithromycin group, LPS: model group, lipopolysaccharide. The rats in the low-dose baicalin (L-baicalin), high-dose baicalin (H-baicalin), and CAM groups were administered baicalin 50 mg·kg–1·d–1, baicalin 100 mg·kg–1·d–1, and CAM 45 mg·kg–1·d–1 by gavage, respectively, as described previously. The control and model groups were administered normal saline 0.1 mL·kg–1·d–1 by gavage. On the second day, the model and the drug groups were administered LPS 10 mg/mL (100 μL) by airway instillation. TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; TRIF: toll-receptor-associated activator of interferon; MyD88: myeloid differentiation factor 88; p-NF-κB: phospho-nuclear factor-kappa B; NLRP3: nod-like receptor pyrin containing 3. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, compared to the model group (n = 5) for each group. The data were represented as mean ± standard deviation.

Figure 3 Effects of baicalin on inhibiting the expression of TLR4-TRIF/MyD88-NF-κB pathway and NLRP3 protein in lung tissues detected by immune-ohistochemistry analysis A-D: expression of TLR4, MyD88, p-NF-κB, and NLRP3 proteins in the control group, LPS group, baicalin group, and CAM group in lung tissues from rats detected by immunohistochemistry. L-baicalin: low-dose baicalin group, H-baicalin: high-dose baicalin group, CAM: Clarithromycin group, LPS: Model group, Lipopolysaccharide. The rats in the low-dose baicalin (L-baicalin), high-dose baicalin (H-baicalin), and CAM groups were administered baicalin 50 mg·kg–1·d–1, baicalin 100 mg·kg–1·d–1, and CAM 45 mg·kg–1·d–1 by gavage, respectively, as described previously. The control and model groups were administered normal saline 0.1 mL·kg–1·d–1 by gavage. On the second day, the model and the drug groups were administered LPS 10 mg/mL (100 μL) by airway instillation. TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; TRIF: toll-receptor-associated activator of interferon; MyD88: myeloid differentiation factor 88; p-NF-κB: phospho-nuclear factor-kappa B; NLRP3: nod-like receptor pyrin containing 3. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, compared to the model group (n = 5) for each group. The data were represented as mean ± standard deviation.
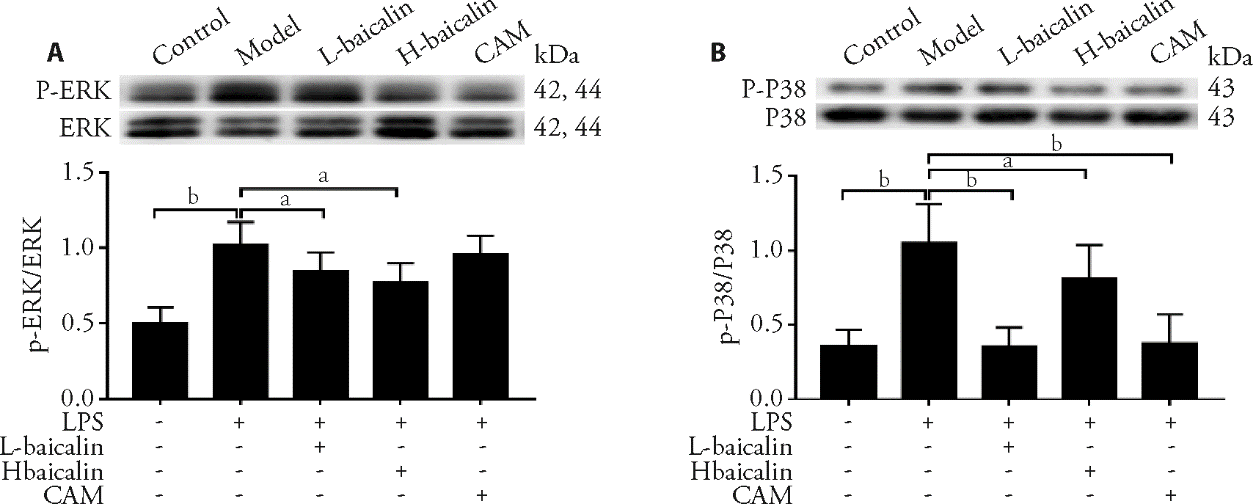
Figure 4 Effects of baicalin on inhibiting MAPK pathway protein expression in lung tissues detected by Western blotting A-B: expression of p-ERK (Phospho-p44/42 Mitogen-activated protein kinase) and p-P38 (Phospho-p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase) in lung tissues from rats detected by WB. L-baicalin: low-dose baicalin group, H-baicalin: high-dose baicalin group, CAM: clarithromycin group, LPS: model group, lipopolysaccharide. MAPK pathway: mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. The rats in the low-dose baicalin (L-baicalin), high-dose baicalin (H-baicalin), and CAM groups were administered baicalin 50 mg·kg–1·d–1, baicalin 100 mg·kg–1·d–1, and CAM 45 mg·kg–1·d–1 by gavage, respectively, as described previously. The control and model groups were administered normal saline 0.1 mL·kg–1·d–1 by gavage. On the second day, the model and the drug groups were administered LPS 10 mg/mL (100 μL) by airway instillation. In A and B, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, compared to the model group (n = 5) for each group. The data were represented as mean ± standard deviation.

Figure 5 Effects of baicalin on inhibiting MAPK pathway protein expression in lung tissues detected by immunohistochemical A, B: protein expression of p-ERK (phospho-p44/42 Mitogen-activated protein kinase) and p-P38 (phospho-p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase) in lung tissues from rats detected by immunohistochemistry. L-baicalin: low-dose baicalin group, H-baicalin: high-dose baicalin group, CAM: Clarithromycin group, LPS: model group, lipopolysaccharide. MAPK pathway: Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. The rats in the low-dose baicalin (L-baicalin), high-dose baicalin (H-baicalin), and CAM groups were administered baicalin 50 mg·kg–1·d–1, baicalin 100 mg·kg–1·d–1, and CAM 45 mg·kg–1·d–1 by gavage, respectively, as described previously. The control and model groups were administered normal saline 0.1 mL·kg–1·d–1 by gavage. On the second day, the model and the drug groups were administered LPS 10 mg/mL (100 μL) by airway instillation. aP < 0.01 compared to the model group (n = 5) for each group. The data were represented as mean ± standard deviation.
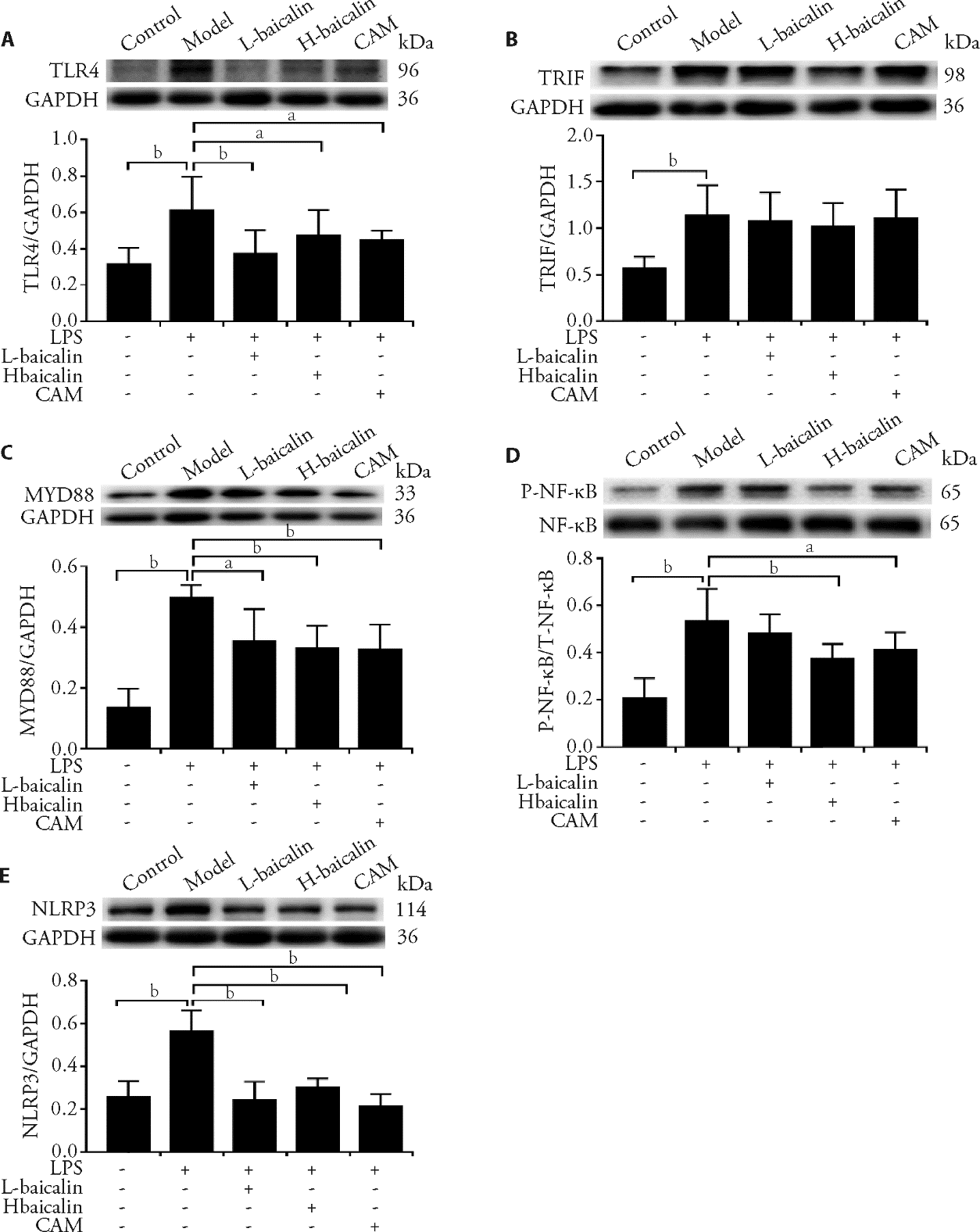
Figure 6 Effects of baicalin on inhibiting TLR4-TRIF/MyD88-NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway protein expression in epithelial cells A-E: expression of TLR4, TRIF, MyD88, p-NF-κB, and NLRP3 proteins in the epithelial cells in the control group, LPS group, L-baicalin group, H-baicalin group, and CAM group. Control: epithelial cells cultured with BEGM for 48 h. LPS: model group, epithelial cells treated with LPS (lipopolysaccharide) 50 μg/mL for 48 h. L-baicalin: low-dose baicalin group, epithelial cells treated with LPS 50 μg/mL for 48 h and baicalin 5 μg/mL for 24 h. H-baicalin: high-dose baicalin group, epithelial cells treated with LPS 50 μg/mL for 48 h and baicalin 10 μg/mL for 24 h. CAM: Clarithromycin group, epithelial cells treated with LPS 50 μg/mL for 48 h and CAM 10 μg/mL for 24 h. TLR4: toll like receptor-4; TRIF: toll-receptor-associated activator of interferon; MyD88: myeloid differentiation factor 88; p-NF-κB: phospho-nuclear factor-kappa B; NLRP3: Nod-like receptor pyrin containing 3. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, compared to the model group (n = 4 for each group). The data were represented as mean ± standard deviation.
| Group | n | TLR4 mRNA | TRIF mRNA | MYD88 mRNA | NF-ΚB mRNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5 | 0.76±0.18a | 0.56±0.10a | 1.72±0.24a | 4.36±0.77a |
| Model | 5 | 3.45±0.36 | 3.84±0.45 | 6.20±0.74 | 1.06±0.21 |
| L-baicalin | 5 | 2.49±0.37b | 3.73±0.40 | 5.82±0.31 | 1.74±0.42b |
| H-baicalin | 5 | 2.32±0.27a | 3.62±0.26 | 3.95±0.30a | 3.01±0.24a |
| CAM | 5 | 1.06±0.18a | 3.08±0.23b | 4.88±0.25b | 2.55±0.23a |
Table 5 Effects of baicalin on inhibiting TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway mRNA expression in LPS-induced epithelial cells ($\bar{x}± s$)
| Group | n | TLR4 mRNA | TRIF mRNA | MYD88 mRNA | NF-ΚB mRNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5 | 0.76±0.18a | 0.56±0.10a | 1.72±0.24a | 4.36±0.77a |
| Model | 5 | 3.45±0.36 | 3.84±0.45 | 6.20±0.74 | 1.06±0.21 |
| L-baicalin | 5 | 2.49±0.37b | 3.73±0.40 | 5.82±0.31 | 1.74±0.42b |
| H-baicalin | 5 | 2.32±0.27a | 3.62±0.26 | 3.95±0.30a | 3.01±0.24a |
| CAM | 5 | 1.06±0.18a | 3.08±0.23b | 4.88±0.25b | 2.55±0.23a |
| 1. |
Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1685-93.
DOI URL |
| 2. |
Wheeler AP, Bernard GR. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: a clinical review. Lancet 2007; 369: 1553-64.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Matthay MA, Zimmerman GA. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: four decades of inquiry into pathogenesis and rational management. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2005; 33: 319-27.
DOI URL |
| 4. |
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006; 124: 783-801.
DOI URL |
| 5. |
Aderem A, Ulevitch RJ. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature 2000; 406: 782-7.
DOI URL |
| 6. |
Litvak V, Ramsey SA, Rust AG, et al. Function of C/EBPdelta in a regulatory circuit that discriminates between transient and persistent TLR4-induced signals. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 437-43.
DOI URL |
| 7. |
Medzhitov R, Horng T. Transcriptional control of the inflammatory response. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 692-703.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Akira S, Hemmi H. Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. Immunol Lett 2003; 85: 85-95.
DOI URL |
| 9. | Natoli G, Chiocca S. Nuclear ubiquitin ligases, NF-kappa B deg-radation, and the control of inflammation. Sci Signal 2008; 1: pe1. |
| 10. |
Ivashkiv LB. Inflammatory signaling in macrophages: transitions from acute to tolerant and alternative activation states. Eur J Immunol 2011; 41: 2477-81.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Beutler B, Hoebe K, Du X, Ulevitch RJ. How we detect microbes and respond to them: the toll-like receptors and their transducers. J Leukoc Biol 2003; 74: 479-85.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Matute-Bello G, Downey G, Moore BB, et al. An official American Thoracic Society workshop report: features and measurements of experimental acute lung injury in animals. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2011; 44: 725-38.
DOI URL |
| 13. |
Matute-Bello G, Frevert CW, Martin TR. Animal models of acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2008; 295: L379-99.
DOI URL |
| 14. |
Guo LT, Wang SQ, Su J, et al. Baicalin ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behavior through inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 expression via the PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway. J Neuroinflammation 2019; 16: 95.
DOI URL |
| 15. |
Amado-Rodríguez L, González-López A, López-Alonso I, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of clarithromycin in ventilator-induced lung injury. Respir Res 2013; 14: 52.
DOI URL |
| 16. |
Calfee CS, Matthay MA. Nonventilatory treatments for acute lung injury and ARDS. Chest 2007; 131: 913-20.
DOI URL |
| 17. | Zhao Q, Chen XY, Martin C. Scutellaria baicalensis, the golden herb from the garden of Chinese medicinal plants. Sci Bull (Beijing) 2016; 61: 1391-8. |
| 18. |
Wang Z, Ma L, Su M, et al. Baicalin induces cellular senescence in human colon cancer cells via upregulation of DEPP and the activation of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling. Cell Death Dis 2018; 9: 217.
DOI URL |
| 19. |
Li MH, Huang KL, Wu SY, et al. Baicalin attenuates air embolism-induced acute lung injury in rat isolated lungs. Br J Pharmacol 2009; 157: 244-51.
DOI URL |
| 20. |
Xu J, Li Y, Lou M, et al. Baicalin regulates SirT1/STAT3 pathway and restrains excessive hepatic glucose production. Pharmacol Res 2018; 136: 62-73.
DOI URL |
| 21. |
Caucheteux SM, Hu-Li J, Mohammed RN, Ager A, Paul WE. Cytokine regulation of lung Th17 response to airway immu-nization using LPS adjuvant. Mucosal Immunol 2017; 10: 361-72.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Patel KB, Xuan D, Tessier PR, Russomanno JH, Quintiliani R, Nightingale CH. Comparison of bronchopulmonary pharm-acokinetics of clarithromycin and azithromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1996; 40: 2375-9.
PMID |
| 23. |
Shinkai M, Foster GH, Rubin BK. Macrolide antibiotics modulate ERK phosphorylation and IL-8 and GM-CSF production by human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2006; 290: L75-85.
DOI URL |
| 24. |
Ye J, Guan M, Lu Y, et al. Protective effects of hesperetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by targeting MD2. Eur J Pharmacol 2019; 852: 151-8.
DOI URL |
| 25. |
Peng LY, Yuan M, Song K, et al. Baicalin alleviated APEC-induced acute lung injury in chicken by inhibiting NF-κB pathway activation. Int Immunopharmacol 2019; 72: 467-72.
DOI URL |
| 26. |
An X, Sun X, Hou Y, et al. Protective effect of oxytocin on LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Sci Rep 2019; 9: 28-36.
DOI URL |
| 27. |
Dong SJ, Zhong YQ, Lu WT, Li GH, Jiang HL, Mao B. Baicalin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through signaling NF-κB pathway in HBE16 airway epithelial cells. Inflammation 2015; 38: 1493-501.
DOI URL |
| 28. |
Manfroi B, McKee T, Mayol JF, et al. CXCL-8/IL8 produced by diffuse large B-cell lymphomas recruits neutrophils expressing a proliferation-inducing ligand APRIL. Cancer Res 2017; 77: 1097-107.
DOI PMID |
| 29. |
Liu J, Lin A. Wiring the cell signaling circuitry by the NF-kappa B and JNK1 crosstalk and its applications in human diseases. Oncogene 2007; 26: 3267-78.
PMID |
| 30. |
O'Neill LA, Bowie AG. The family of five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 353-64.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Oshikawa K, Sugiyama Y. Gene expression of Toll-like receptors and associated molecules induced by inflammatory stimuli in the primary alveolar macrophage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 305: 649-55.
DOI URL |
| 32. |
Abraham E. NF-kappa B activation. Crit Care Med 2000; 28: N100-4.
DOI PMID |
| 33. | Palová-Jelínková L, Dáňová K, Drašarová H, et al. Pepsin digest of wheat gliadin fraction increases production of IL-1β via TLR4/MyD88/TRIF/MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway and an NLRP3 inflammasome activation. PLoS One 2013; 8: 624-26. |
| 34. |
Kahlenberg JM, Lundberg KC, Kertesy SB, Qu Y, Dubyak GR. Potentiation of caspase-1 activation by the P2X7 receptor is dependent on TLR signals and requires NF-kappaB-driven protein synthesis. J Immunol 2005; 175: 7611-22.
PMID |
| 35. |
Sun JY, Li DL, Dong Y, et al. Baicalin inhibits toll-like receptor 2/4 expression and downstream signaling in rat experimental periodontitis. Int Immunopharmacol 2016; 36: 86-93.
DOI URL |
| 36. |
Guha M, Mackman N. LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cell Signal 2001; 13: 85-94.
PMID |
| 37. |
Wu Y, Wang F, Fan L, et al. Baicalin alleviates atherosclerosis by relieving oxidative stress and inflammatory responses via inactivating the NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother 2018; 97: 1673-9.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

