Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 848-857.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.06.002
• Systematic Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Systematic review and Meta-analysis of acupuncture and acupoint catgut embedding for the treatment of abdominal obesity
YE Wujie1, XING Jingyu1, YU Zekai1, HU Xingang2( ), ZHAO Yan3(
), ZHAO Yan3( )
)
- 1 Diagnostics of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
2 Internal encephalopathy of traditional Chinese medicine, Dongfang Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100078, China
3 Diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine, Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2022-07-17Accepted:2022-09-05Online:2022-12-15Published:2022-11-01 -
Contact:HU Xingang,ZHAO Yan -
About author:ZHAO Yan, diagnostics of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China. yanzh3232@126.com,Telephone: +86-15201484830
HU Xingang, internal encephalopathy of traditional Chinese medicine, Dongfang Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100078, China. xinganghu@163.com;
-
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Project: Clinical Evaluation of the Interventional Techniques for Abdominal Obesity(2019YFC1710102)
Cite this article
YE Wujie, XING Jingyu, YU Zekai, HU Xingang, ZHAO Yan. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of acupuncture and acupoint catgut embedding for the treatment of abdominal obesity[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 848-857.
share this article
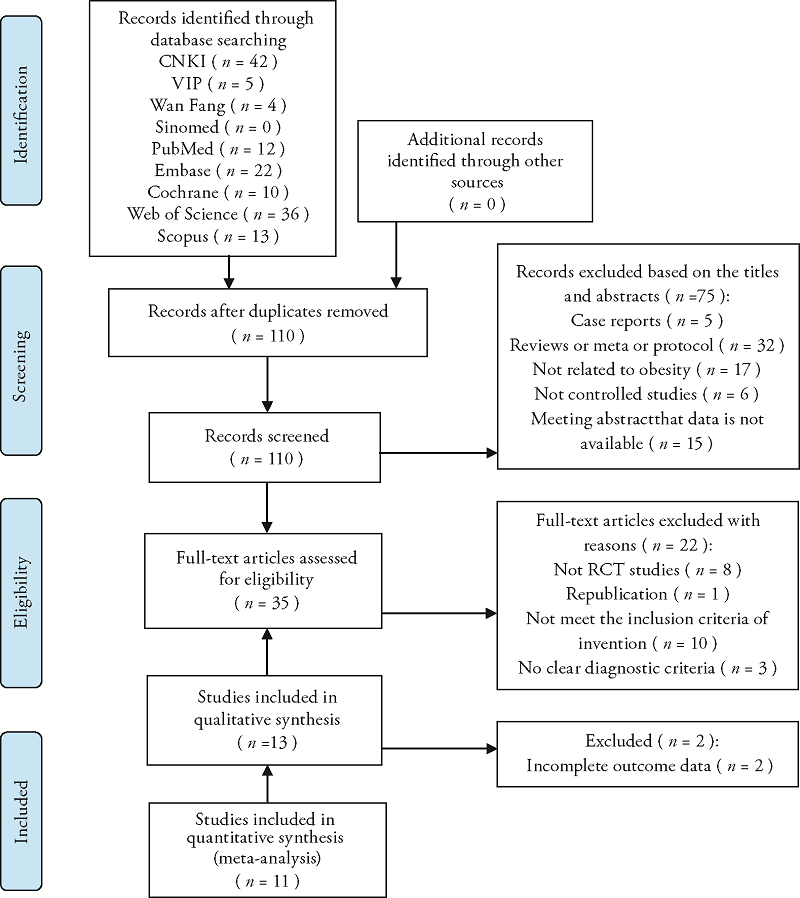
Figure 1 Flow chart CNKI: China National Knowledge Infrastructure Database; VIP: China Science and Technology Journal Database; RCT: randomized controlled trial.
| Study | Patients | Gender | Average age | Interventions | Treatment time | Outcomes | Adverse Events | Follow-up | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (T/C) | (male/female) | (years) | Treatment / Control | ||||||||
| Liang CM et al 2016 | 50/23 | 21/52 | T: 47.7±11.0 C: 49.4±11.4 | Acupuncture, 3 times a week Health education | 8 weeks | weight; BMI; WC; HC | None | None | |||
| Qin WL et al 2016 | 58/54 | 33/79 | T: 42.14±11.83 C: 39.13±11.13 | Catgut embedding, once a week Sham acupuncture | 4 weeks | weight; BMI; WC | None | None | |||
| Xiong W 2019 | 31/32 | 12/51 | T: 33.16±6.99 C: 33.00±6.75 | Acupuncture, once a day, 2 d off after 5 d Oral orlistat, 1 tablet each time, t.i.d | 28 days | weight; WHR | Mentioned | None | |||
| Wu KQ 2019 | 33/33 | 35/31 | T: 35.61±8.24 C: 32.24±6.58 | Acupuncture, twice a week Auricular point bean | 4 weeks | weight; WC; HC; BMI; WHR; WHtR | None | Mentioned | |||
| Zhang XH 2020 | 25/25 | 20/30 | T: 36.6±8.1 C: 36.4±7.9 | Catgut embedding, once every 2 weeks Oral Chinese medicine, 1 dose per day | 6 weeks | weight; WC; HC; BMI; WHR; | None | None | |||
| Song YX et al 2018 | 200/100 | 0/300 | T: 33.2±2.6 C: 33.5±2.5 | Catgut embedding, once every 2 weeks Tuina, once a day | 8 weeks | weight; WC; WHR; BMI | Mentioned | None | |||
| Jin YH 2019 | 33/32 | 13/52 | T: 34.58±9.95 C: 35.47±8.89 | Catgut embedding, once every 2 weeks Sham acupuncture | 8 weeks | weight; WC; HC | Mentioned | None | |||
| Meng JQ 2019 | 35/34 | 10/59 | T: 36.51±10.13 C: 36.44±9.66 | Catgut embedding, once every 2 weeks Sham acupuncture | 8 weeks | weight; BMI; WC; HC | Mentioned | None | |||
| Pan XW 2017 | 26/24 | 16/34 | T: 35.88±8.65 C: 37.62±8.84 | acupuncture, 3 times a week Sham acupuncture | 12 weeks | weight; WC; HC; BMI; WHR | Mentioned | Mentioned | |||
| Deng LJ, et al 2014 | 30/30 | 5/55 | T: 33±8 C: 32±7 | Catgut embedding, once a week no treatment | 9 weeks | weight; WC | None | None | |||
| Chen LS et al 2019 | 28/23 | / | T: 34.43±7.63 C: 34.60±5.21 | Catgut embedding, Once every 10 d no treatment | 10 weeks | weight; BMI; WC; HC; WHR; WtHR | None | None | |||
| Chen IJ et al 2018 | 40/40 | / | T: 39.9±9.8 C: 43.7±9.3 | Catgut embedding, once a week Sham acupuncture | 6 weeks | weight; WC; HC; WHR | None | None | |||
| Lei H et al 2017 | 15/15 | / | T: 31.6±8.2 C: 31.4±8.4 | Acupuncture, 3 times a week no treatment | 12 weeks | BMI; WC | None | None | |||
Table 1 Basic Characteristics of Included RCTs
| Study | Patients | Gender | Average age | Interventions | Treatment time | Outcomes | Adverse Events | Follow-up | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (T/C) | (male/female) | (years) | Treatment / Control | ||||||||
| Liang CM et al 2016 | 50/23 | 21/52 | T: 47.7±11.0 C: 49.4±11.4 | Acupuncture, 3 times a week Health education | 8 weeks | weight; BMI; WC; HC | None | None | |||
| Qin WL et al 2016 | 58/54 | 33/79 | T: 42.14±11.83 C: 39.13±11.13 | Catgut embedding, once a week Sham acupuncture | 4 weeks | weight; BMI; WC | None | None | |||
| Xiong W 2019 | 31/32 | 12/51 | T: 33.16±6.99 C: 33.00±6.75 | Acupuncture, once a day, 2 d off after 5 d Oral orlistat, 1 tablet each time, t.i.d | 28 days | weight; WHR | Mentioned | None | |||
| Wu KQ 2019 | 33/33 | 35/31 | T: 35.61±8.24 C: 32.24±6.58 | Acupuncture, twice a week Auricular point bean | 4 weeks | weight; WC; HC; BMI; WHR; WHtR | None | Mentioned | |||
| Zhang XH 2020 | 25/25 | 20/30 | T: 36.6±8.1 C: 36.4±7.9 | Catgut embedding, once every 2 weeks Oral Chinese medicine, 1 dose per day | 6 weeks | weight; WC; HC; BMI; WHR; | None | None | |||
| Song YX et al 2018 | 200/100 | 0/300 | T: 33.2±2.6 C: 33.5±2.5 | Catgut embedding, once every 2 weeks Tuina, once a day | 8 weeks | weight; WC; WHR; BMI | Mentioned | None | |||
| Jin YH 2019 | 33/32 | 13/52 | T: 34.58±9.95 C: 35.47±8.89 | Catgut embedding, once every 2 weeks Sham acupuncture | 8 weeks | weight; WC; HC | Mentioned | None | |||
| Meng JQ 2019 | 35/34 | 10/59 | T: 36.51±10.13 C: 36.44±9.66 | Catgut embedding, once every 2 weeks Sham acupuncture | 8 weeks | weight; BMI; WC; HC | Mentioned | None | |||
| Pan XW 2017 | 26/24 | 16/34 | T: 35.88±8.65 C: 37.62±8.84 | acupuncture, 3 times a week Sham acupuncture | 12 weeks | weight; WC; HC; BMI; WHR | Mentioned | Mentioned | |||
| Deng LJ, et al 2014 | 30/30 | 5/55 | T: 33±8 C: 32±7 | Catgut embedding, once a week no treatment | 9 weeks | weight; WC | None | None | |||
| Chen LS et al 2019 | 28/23 | / | T: 34.43±7.63 C: 34.60±5.21 | Catgut embedding, Once every 10 d no treatment | 10 weeks | weight; BMI; WC; HC; WHR; WtHR | None | None | |||
| Chen IJ et al 2018 | 40/40 | / | T: 39.9±9.8 C: 43.7±9.3 | Catgut embedding, once a week Sham acupuncture | 6 weeks | weight; WC; HC; WHR | None | None | |||
| Lei H et al 2017 | 15/15 | / | T: 31.6±8.2 C: 31.4±8.4 | Acupuncture, 3 times a week no treatment | 12 weeks | BMI; WC | None | None | |||

Figure 4 Meta-analysis A: weight: acupuncture or acupoint catgut embedding versus comparator; B: waist circumference: acupuncture or acupoint catgut embedding versus comparator; C: body mass index: acupuncture or acupoint catgut embedding versus comparator; D: hip circumference: acupuncture or acupoint catgut embedding versus comparator; E: Waist/Hip ratio: acupuncture or acupoint catgut embedding versus comparator; F: waist/height ratio: acupuncture or acupoint catgut embedding versus comparator.
| Quality assessment | No of patients | Effect | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No of studies | Design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | Summary | Control | Relative (95%CI) | Absolute | Quality | Importance | |||
| Weight (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 11 | Randomized Trials | No serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | None | 539 | 427 | - | MD 1.45 higher (1.4 to 1.5 higher) | LOW | IMPORTANT | |||
| Waist circumference (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 10 | Randomized Trials | no serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | None | 508 | 395 | - | MD 3.9 higher (2.43 to 5.36 higher) | LOW | IMPORTANT | |||
| Hip circumference (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 7 | Randomized Trials | no serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | Seriousb | None | 220 | 211 | - | MD 0.54 higher (0.2 lower to 1.27 higher) | VERY LOW | IMPORTANT | |||
| BMI (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 7 | Randomized Trials | no serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | None | 405 | 293 | - | MD 1.37 higher (0.2 to 2.54 higher) | LOW | IMPORTANT | |||
| WHR (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 7 | Randomized Trials | no serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | Seriousb | None | 383 | 277 | - | MD 0.03 higher (0.03 to 0.04 higher) | VERY LOW | NOT IMPORTANT | |||
| WtHR (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 3 | Randomized Trials | no serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | Very seriousb | None | 119 | 110 | - | MD 0.07 higher (0.04 lower to 0.19 higher) | VERY LOW | NOT IMPORTANT | |||
Table 2 GRADE analysis: acupuncture or acupoint catgut embedding for abdominal obesity
| Quality assessment | No of patients | Effect | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No of studies | Design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | Summary | Control | Relative (95%CI) | Absolute | Quality | Importance | |||
| Weight (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 11 | Randomized Trials | No serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | None | 539 | 427 | - | MD 1.45 higher (1.4 to 1.5 higher) | LOW | IMPORTANT | |||
| Waist circumference (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 10 | Randomized Trials | no serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | None | 508 | 395 | - | MD 3.9 higher (2.43 to 5.36 higher) | LOW | IMPORTANT | |||
| Hip circumference (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 7 | Randomized Trials | no serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | Seriousb | None | 220 | 211 | - | MD 0.54 higher (0.2 lower to 1.27 higher) | VERY LOW | IMPORTANT | |||
| BMI (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 7 | Randomized Trials | no serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | None | 405 | 293 | - | MD 1.37 higher (0.2 to 2.54 higher) | LOW | IMPORTANT | |||
| WHR (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 7 | Randomized Trials | no serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | Seriousb | None | 383 | 277 | - | MD 0.03 higher (0.03 to 0.04 higher) | VERY LOW | NOT IMPORTANT | |||
| WtHR (better indicated by lower values) | |||||||||||||||
| 3 | Randomized Trials | no serious risk of bias | Very seriousa | No serious indirectness | Very seriousb | None | 119 | 110 | - | MD 0.07 higher (0.04 lower to 0.19 higher) | VERY LOW | NOT IMPORTANT | |||
| [1] |
Smith U. Abdominal obesity: a marker of ectopic fat accumulation. J Clin Invest 2015; 125: 1790-2.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Jin WS, Pan CY. Global consensus on the definition of metabolic syndrome by the International Diabetes Federation. Zhong Hua Nei Fen Mi Dai Xie Za Zhi 2005; 21: 412-3. |
| [3] |
Duclos M. Osteoarthritis, obesity and type 2 diabetes: the weight of waist circumference. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 2016; 59: 157-60.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Heymsfield SB, Wadden TA. Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and management of obesity. N Engl J Med 2017; 376: 254-66.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bhattacharya PK, Barman B, Jamil M, et al. Metabolic syndrome and atherogenic indices in rheumatoid arthritis and their relationship with disease activity: a hospital-based study from northeast India. J Transl Intern Med 2020; 8: 99-105.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Yuan F, Zhang Q, Dong H, et al. Effects of des-acyl ghrelin on insulin sensitivity and macrophage polarization in adipose tissue. J Transl Intern Med 2021; 9: 84-97.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Yu PL, Zhou JT, Hu SL. Study on the relationship between abdominal obesity and blood pressure, blood sugar, insulin and blood lipids. Guangxi Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2001; 18: 371-3. |
| [8] |
Azzopardi PS, Hearps SJC, Francis KL, et al. Progress in adolescent health and wellbeing: tracking 12 headline indicators for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2016. Lancet 2019; 393: 1101-1118.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Collaborators GBDO, Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH, et al. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med 2017; 377: 13-27.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet (London, England) 2014; 384: 766-81. |
| [11] | Abarca-Gómez L, Abdeen ZA, Hamid ZA, et al. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017; 390: 2627-42. |
| [12] |
Stefan N, Häring H-U, Hu FB, et al. Metabolically healthy obesity: epidemiology, mechanisms, and clinical implication. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2013; 1: 152-62.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Sun BY, Zhang B, Lin ZJ, et al. Advances in abdominal obesity. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2015; 33: 80-3. |
| [14] |
Kesztyus D, Erhardt J, Schonsteiner D, et al. Therapeutic treatment for abdominal obesity in adults. Dtsch Arztebl Int 2018; 115: 487-93.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Scarsella C, Després JP. Treatment of obesity: the need to target attention on high-risk patients characterized by abdominal obesity. Cadernos de saude publica 2003; 19 Suppl 1: S7-19.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Apovian CM, Aronne LJ, Bessesen DH, et al. Pharmacological management of obesity: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015; 100: 342-62.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Knowler WC, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, et al. 10-year follow-up of diabetes incidence and weight loss in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Lancet (London, England) 2009; 374: 1677-86.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Look ARG. Eight-year weight losses with an intensive lifestyle intervention: the look AHEAD study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2014; 22: 5-13.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Cardiology/ACo, Force AHAT, On Practice Guidelines OE, et al. Expert Panel Report: Guidelines (2013) for the management of overweight and obesity in adults. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2014; 22 Suppl 2: S41-410. |
| [20] |
Yanovski SZ, Yanovski JA. Long-term drug treatment for obesity: a systematic and clinical review. JAMA 2014; 311: 74-86.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N Engl J Med 2015; 373: 11-22.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Angrisani L, Santonicola A, Iovino P, et al. Bariatric surgery worldwide 2013. Obes Surg 2015; 25: 1822-32.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Sturm R, Hattori A. Morbid obesity rates continue to rise rapidly in the United States. Int J Obes (Lond) 2013; 37: 889-91.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Puzziferri N, Roshek TB, Mayo HG, et al. Long-term follow-up after bariatric surgery: a systematic review. JAMA 2014; 312: 934-42.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Chen YY. Diagnosis and treatment of abdominal obesity by acupuncture and moxibustion. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ke Xue Yuan 2019; 1-68. |
| [26] | Liu Q, Li JL. Clinical research progress of acupuncture and moxibustion in the treatment of abdominal obesity. Xian Dai Lin Chuang Yi Xue 2019; 5: 392-5. |
| [27] |
Zheng HD, Wang ZQ, Li SS, et al. Effect of acupoints on acupuncture-moxibustion and its therapeutic mechanism. World J Tradit Chin Med 2020; 6: 239-48.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Zhou Y, Ma ZB, Liu AG, et al. Classification of and advances in clinical operational techniques of acupoint catgut embedding. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2019; 8: 948-52. |
| [29] | Du HM, Zhang W. The application development process of thread of acupoint catgut embedding. Zhong Yi Yao Dao Bao 2019; 25: 121-4. |
| [30] | Zhao WP, Li J, Zhang YS, et al. Efficacy of acupuncture therapy for improving anorexia in tumor patients: a Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2021; 41: 507-14. |
| [31] | Liang CM, Hu H, Wang CX, et al. Randomized controlled clinical trials for acupuncture treatment of abdominal obesity. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2016; 41: 159-62+74. |
| [32] | Qin WL, Wang CX, Yang WJ, et al. Clinical study on abdominal type of simple obesity treated with acupoint catgut embedding therapy. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao 2016; 35: 207-10. |
| [33] | Xiong W. Clinical research on acupuncture manipulation of “reinforcing spleen and reducing dampness” for simple obesity. Chengdu: Chengdu Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2019; 1-66. |
| [34] | Ng Hoi Kei (Wu KQ). The study of clinical study on treatment of abdominal obesity by Lai’s Tongyuan therapy. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2019; 1-68 |
| [35] | Zhang XH. Comparison of acupoint catgut embedding method and Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of abdominal obesity with spleen deficiency and dampness obstruction. Zhong Guo Xiang Cun Yi Yao 2020; 27: 34-5. |
| [36] | Song YX, Wang L, Ma Z. Clinical study on acupoint catgut embedding combined with abdominal massage in treatment of female abdominal obesity with spleen deficiency and dampness retention syndrome. Guo Ji Zhong Yi Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2018; 40: 1150-3. |
| [37] | Jin YH. Study on the clinical efficacy of Shumu acupoint buried line in the treatment of obesity in the abdomen that spleen deficiency and the body very wet. Yunnan: Yunnan Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2019; 1-48. |
| [38] | Meng JQ. The clinical study of curative effect of Shumu points catgut embedding therapy for abdominal obesity with stomach-heat and dampness-stagnation type. Yunnan: Yunnan Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2019; 1-47. |
| [39] | Pan XW. Study on acupuncture therapy for prevention and treatment of abdominal obesity and related complications. Beijing: Beijing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2017; 1-53. |
| [40] |
Deng LJ, Lun ZJ, Ma XW, et al. Clinical observation on regulating the three energizer by acupoint catgut embedding combined with abdominal acupuncture in treating abdominal obesity: a randomized controlled trial. World J Acupunct Moxibustion 2014; 24: 29-34.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Chen LS, Li YY, Chen H, et al. Polyglycolic acid sutures embedded in abdominal acupoints for treatment of simple obesity in adults: a randomized control trial. Chin Med 2019; 14: 32.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Chen IJ, Yeh YH, Hsu CH. Therapeutic effect of acupoint catgut embedding in abdominally obese women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2018; 27: 782-90.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Lei H, Chen X, Liu S, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on visceral and hepatic fat in women with abdominal obesity: a randomized controlled study based on magnetic resonance imaging. J Altern Complement Med 2017; 23: 285-94.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Zhang YJ. Clinical research of acupoint catgut embedding combined with Yin-Yang Tiao Li moxibustin on improving Qi-deficiency constitution for the treatment of abdominal obesity. Hubei: Hubei Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2021; 1-57. |
| [45] | Xu WM, Hu JQ, Peng J, et al. Relationship between obesity and the pathogenesis of intermingled phlegm-blood stasis syndrome. Huan Qiu Zhong Yi Yao 2015; 8: 654-7. |
| [46] | Zhang GY, Yan SX. Discussion on the etiology and pathogenesis of abdominal obesity from wujing. Zhong Yi Lin Chuang Yan Jiu 2020; 12: 18-21. |
| [47] | Liu ZY. Clinical study on the treatment of abdominal obesity with phlegm dampness syndrome by five-element medicinal moxibustion cupping. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2021; 23: 24-7. |
| [48] | Gu TT. MRI imaging of hypothalamus and abdomen to explore the therapeutic effect and mechanism of miao fire on simple obesity. Shenzhen Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2016; 26: 5-7. |
| [49] | Wang JJ, Huang W, Wei D, et al. Comparison of therapeutic effects of electroacupuncture and acupoint catgut embedding in reducing serum leptin and insulin levels in simple obesity patients. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2019; 44: 57-61. |
| [50] |
Guillemot-Legris O, Muccioli GG. Obesity-induced neuro-inflammation: beyond the hypothalamus. Trends Neurosci 2017; 40: 237-53.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
Seong J, Kang JY, Sun JS, et al. Hypothalamic inflammation and obesity: a mechanistic review. Arch Pharm Res 2019; 42: 383-92.
DOI PMID |
| [52] | Tang LJ. Clinical comparative study of different acupuncture and moxibustion in the treatment of simple obesity. Hubei: Hubei Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2020; 1-63. |
| [53] | He GF. Clinical study on the treatment of simple obesity by acupu-ncture and body therapy. Shanxi: Shanxi Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2018; 1-37. |
| [54] |
Mazloomy-Mahmoodabad SS, Navabi ZS, Ahmadi A, et al. The effect of educational intervention on weight loss in adolescents with overweight and obesity: application of the theory of planned behavior. ARYA atherosclerosis 2017; 13: 176-83.
PMID |
| [55] |
Lu P, Ji X, Wan J, et al. Activity of group 2 innate lymphoid cells is associated with chronic inflammation and dysregulated metabolic homoeostasis in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Scand J Immunol 2018; 87: 99-107.
DOI PMID |
| [56] | Chen XQ, Zhang Y, Huang CL, et al. Efficacy of huanglian root decoction on kidney injury in rat’s model of metabolic syndrome. J Tradit Chin Med 2021; 41: 117-24. |
| [57] |
Izquierdo AG, Crujeiras AB, Casanueva FF, et al. Leptin, obesity, and leptin resistance: where are we 25 years later? Nutrients 2019; 11: 2704.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Kohno D, Nakata M, Maekawa F, et al. Leptin suppresses ghrelin-induced activation of neuropeptide Y neurons in the arcuate nucleus via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase- and phosphodiesterase 3-mediated pathway. Endocrinology 2007; 148: 2251-63.
PMID |
| [59] |
Rousset S, Alves-Guerra MC, Mozo J, et al. The biology of mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. Diabetes 2004; 53 Suppl 1: S130-5.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Yang C, Aye CC, Li X, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in insulin resistance: differential contributions of chronic insulin and saturated fatty acid exposure in muscle cells. Bioscience reports 2012; 32: 465-78.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | Fan JG, Zheng XY, Tian LY, et al. Dynamic changes of plasma levels of prostacycline and thromboxane A2 and their correlation with the severity of hepatic injury in rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Zhong Hua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2004; 12: 681-3. |
| [62] |
Mexitalia M, Yamauchi T, Utari A, et al. The role of uncoupling protein 2 and 3 genes polymorphism and energy expenditure in obese Indonesian children. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2013; 26: 441-7.
DOI PMID |
| [63] | Yan RH. Study on clinical efficacy and molecular mechanism of acupoint catgut embedding in the treatment of simple obesity. Dalian: Dalian Yi Ke Da Xue 2013; 1-67. |
| [64] | Lan DC, Xu NG, Sun J, et al. Randomized controlled trial of electro-acupuncture combined with acupoint thread-embedding for treatment of abdominal obesity. Guangzhou Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2016; 33: 189-93. |
| [65] | Lai SY. Observation on the clinical effect of abdominal acupuncture in the treatment of central obesity. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2009; 1-38. |
| [66] | Li YY, Hu H, Liang CM. Therapeutic observation of acupoint thread-embedding for abdominal obesity. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2014; 33: 44-6. |
| [67] | Deng LJ. Clinical study on adjusting the triple energizers by the acupoint catgut embedding for the treatment of the middle aged person’s abdominal obesity. Guangzhou Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2006; 1-33. |
| [1] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [2] | SUN Qianhui, CHENG Kai, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, WU Xiaoling, XU Chang, QIU Xinghua, GAO Xiaofeng, LIU Daonan, YANG Qirui. Effect of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) at different time points on myocardial ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 113-121. |
| [3] | LIU Tingting, LIU Tongou, LIU Mingfu. Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture in treatment of pregnancy-related symptoms: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 16-26. |
| [4] | YANG Yi, YE Huijun, ZHENG Huiling, JIN Lihua. Clinical observation on 90 cases of primary dysmenorrhea treated by buccal acupuncture therapy: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 172-181. |
| [5] | LI Menghan, WANG Yu, RAN Dawei, YANG Xinming, DENG Shizhe, SHI Lei, MENG Zhihong. Effects of anterior sciatic nerve acupuncture on lower limb paralysis after cerebral infarction: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 205-211. |
| [6] | WANG Jiabao, ZHANG Lishuang, NIU Baihan, YU Yajun, YANG Fengwen, MIAO Lin, CHAI Lijuan, DING Xinya, SUN Yingjie, WANG Yujing, WANG Lin, ZHANG Han, WANG Yi, LI Lin. Efficacy and safety of Weichang’ an pill (胃肠安丸) combined with Western Medicine on gastrointestinal diseases: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1057-1067. |
| [7] | FAN Rong, HE Haoyu, TANG Tao, CUI Hanjin. Long-term effects of Qingfei Paidu decoction (清肺排毒汤) in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 acute pneumonia after treatment: a protocol for systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1068-1071. |
| [8] | DU Zhongheng, CONG Wenjie, TANG Kejing, ZHENG Qiqi, SONG Zhiwei, CHEN Yong, YANG Su, ZHANG Chunwu, YE Tianshen. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) in mice with collagen-induced arthritis leads to adenosine A2A receptor-mediated alteration of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1103-1109. |
| [9] | QIN Xihui, PANG Jianli, XIONG Guan, FENG Jie. Bo′s abdominal acupuncture improves disordered metabolism in obese type 2 diabetic rats through regulating fibroblast growth factor 21 and its related adipokines [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1200-1208. |
| [10] | XU Yani, ZHANG Yutong, HE Weile, DAI Linglin, TANG Ding, WANG Jialing, ZHANG Xufen, CHEN Qin, CHEN Lifang, WANG Zhanglian, ZHAN Mingjie. Efficiency and safety of acupuncture for women with premature ovarian insufficiency: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1268-1274. |
| [11] | LI Menghan, YAN Yan, DENG Shizhe, WANG Yu, FU Yu, SHI Lei, YANG Jin, ZHANG Chunhong. Contralateral needling at the foot of unaffected side combining with rehabilitation treatment for motor dysfunction of hand after ischemic stroke: study protocol for a randomized controlled pilot trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 1034-1039. |
| [12] | YANG Yuqing, CHEN Yuhuan, LI Chunxiao, LING Xiao, WANG Panpan, GUO Jing, ZHANG Yingying. Effectiveness and safety of Pingxiao capsule (平消胶囊) as adjuvant therapy in treatment of breast cancer: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 851-859. |
| [13] | ZHAO HuiYan, JUN Purumea, LEE Chaewon, HAN Chang-Hyun. Acupoint catgut embedding for simple obesity in animal studies: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 860-867. |
| [14] | WANG Kun, ZHOU Jie, CUI Shuai, WU Xin, ZHU Guoqi, WU Shengbing, ZHOU Meiqi. Electroacupuncture ameliorates cardiac dysfunction in myocardial ischemia model rats: a potential role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 944-954. |
| [15] | JIANG Jianzhen, ZHANG Xin, LUO Zhenguo, SU Chengguo, ZHOU Haiyan, JIANG Yuqing, XIAO Xianjun, CHEN Yunfei, ZHU Jun. Efficacy of electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36) and Xuanzhong (GB39) on synovial angiogenesis in rats with adjuvant arthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 955-962. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||