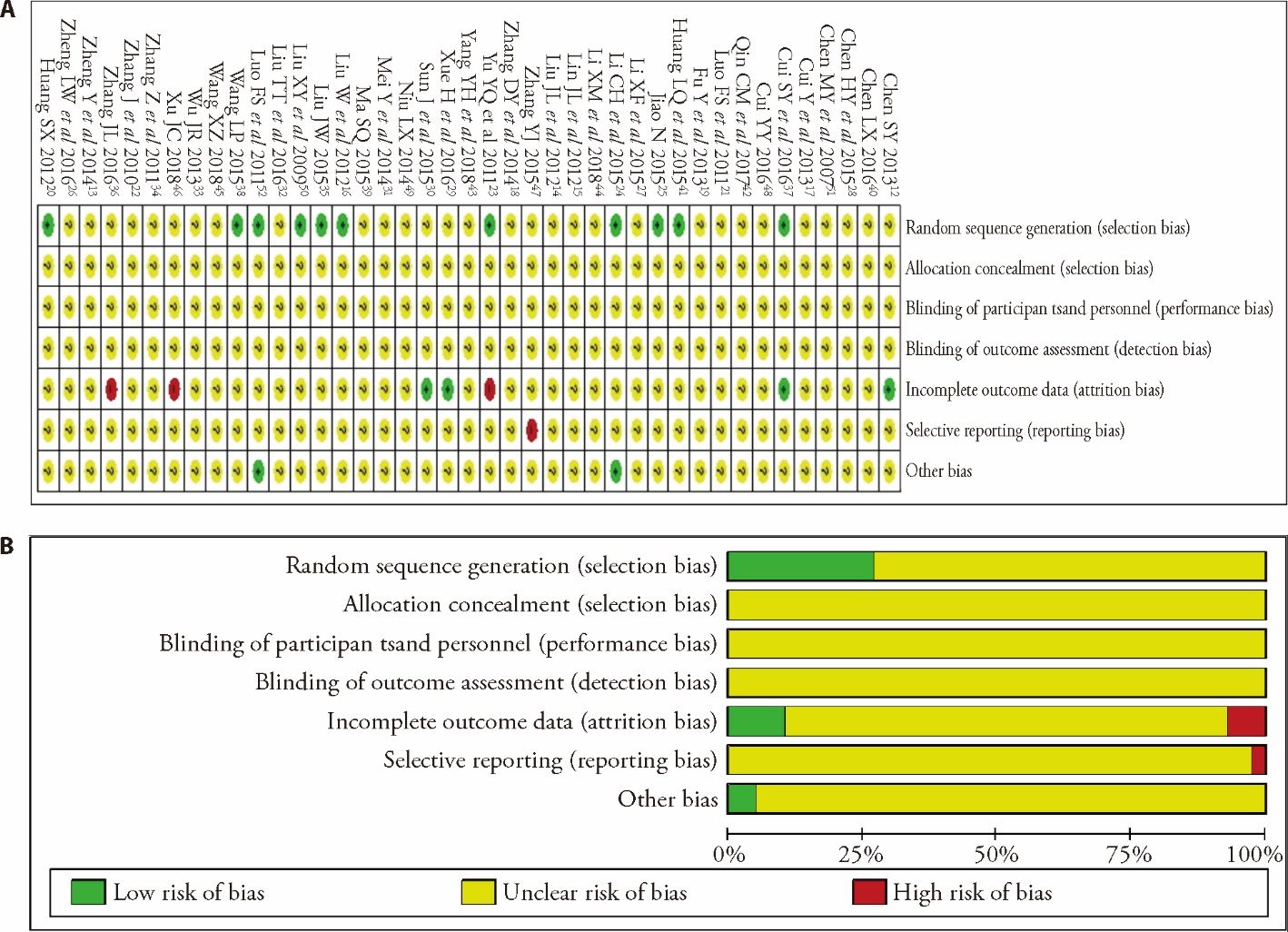
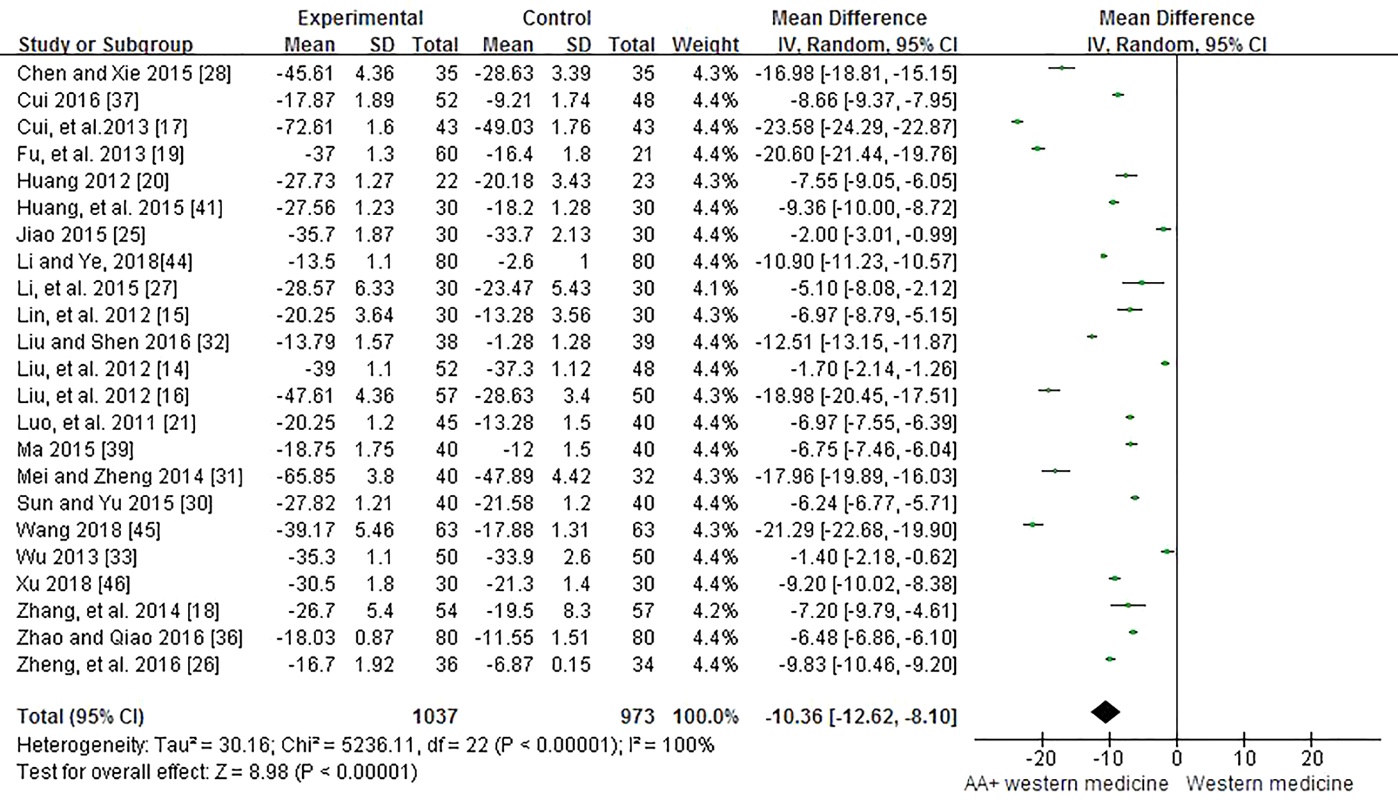
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 159-166.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.02.001
• Meta-analysis • Next Articles
Acupoint application therapies for essential hypertension: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
LIU Wei1, XIONG Xingjiang2, QIAO Lumin3, CHEN Yuyi4, LI Yixuan5, SU Xing6, CHU Fuyong1( ), LIU Hongxu1(
), LIU Hongxu1( )
)
- 1 Department of Cardiology, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100010, China
2 Department of Cardiology, Guang′anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China
3 Department of Emergency, Yinchuan Chinese Medicine Hospital, Ningxia 750001, China
4 Department of Oncology, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100010, China
5 Community Healthcare Center of Shangzhuang Town, Beijing 100053,China
6 Department of Medical Administration Division, Beijing Mentougou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing 102300, China
-
Received:2021-01-27Accepted:2021-04-09Online:2022-04-15Published:2022-04-01 -
Contact:CHU Fuyong,LIU Hongxu -
About author:lhxcardiology1@163.com, Telephone: +8601052176633
Prof. CHU Fuyong and LIU Hongxu, Department of Cardiology, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100010, China. cfy0629@126.com;
-
Supported by:Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Molecular Mechanisms of Bushen Jiangya Decoction on Hypertensive Renal Damage Based on miR-21 Induced TGF β/Smad Signal Pathway)(7194277);Key Medical Professional Development Program Fund of Beijing Municipal Hospital Administration(ZYLX201817)
Cite this article
LIU Wei, XIONG Xingjiang, QIAO Lumin, CHEN Yuyi, LI Yixuan, SU Xing, CHU Fuyong, LIU Hongxu. Acupoint application therapies for essential hypertension: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 159-166.
share this article
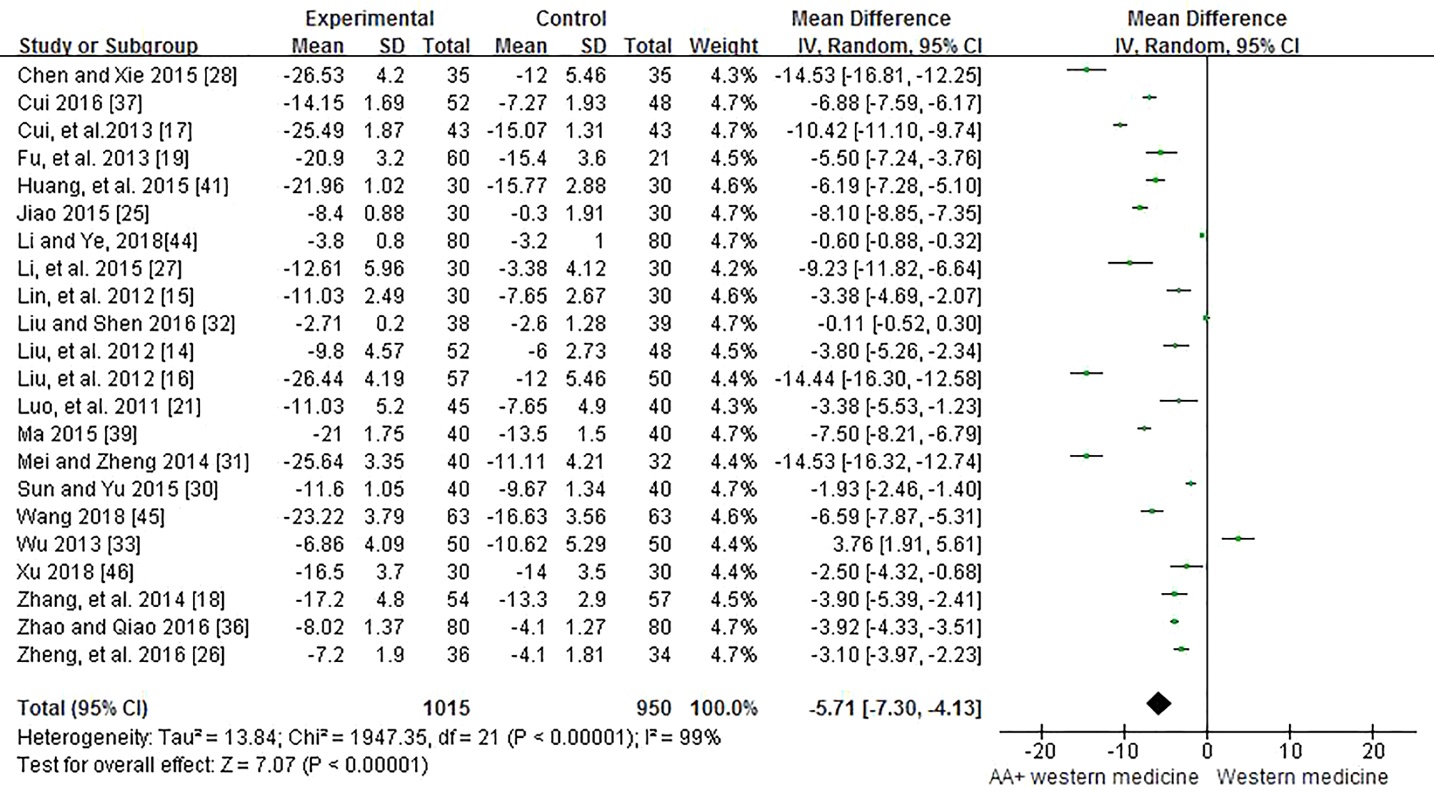
Figure 5 Forest plot of comparison: acupoint application therapies combined with Western Medicine versus Western Medicine for diastolic blood pressure
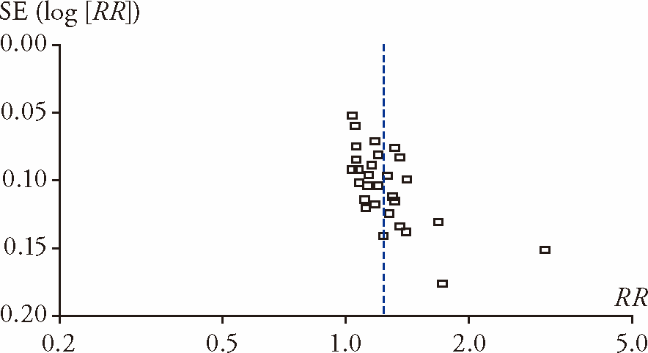
Figure 6 Funnel plot of the trials that compared AA combined with Western Medicine with Western Medicine for SBP AA: acupoint application; SBP: systolic blood pressure.
| 1. | Wiysonge CS, Bradley HA, Volmink J. Beta-blockers for hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017; 20: CD002-3. |
| 2. | Bundy JD, He J. Hypertension and related cardiovascular disease burden in China. Ann Glob Health 2016; 82: 227-33. |
| 3. | Xiong XJ, Yang XC, Liu W, et al. Trends in the treatment of hypertension from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Med-icine. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2013; 2013: 1-8. |
| 4. | Wang J, Xiong XJ. Evidence-based Chinese medicine for hypertension. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2013; 978398: 1-2. |
| 5. | Xiong XJ, Che CT, Francesca B, et al. Evidence-based TAM classic herbal formula: from myth to science. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2017; 9493076: 1-3. |
| 6. |
Kristoffersen AE, Sirois FM, Stub T, et al. Prevalence and predictors of complementary and alternative medicine use among people with coronary heart disease or at risk for this in the sixth Tromsø study: a comparative analysis using protection motivation theory. BMC Complement Altern Med 2017; 17: 324.
DOI URL |
| 7. | Yang XC, Xiong XJ, Yang GY, et al. Effectiveness of stimulation of acupoint KI 1 by artemisia vulgaris (Moxa) for the treatment of essential hypertension: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 2014: 187484. |
| 8. |
Moawia MA, Farah TS, Mai HS, et al. Evaluation of bloodletting cupping therapy in the management of hypertension. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 2018; 10: 1-6.
DOI URL |
| 9. | Lee SH, Chang GT, Zhang XY, et al. Acupoint herbal patching for asthma: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine 2016; 95: 1-12. |
| 10. | Wang WH, Zhang LX, Li LF. Therapeutic effect of acupoint application with fructus evodiae rutaecarpae on patients with hyp-ertension. Shenzhen Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2013; 23: 375-7. |
| 11. | Yin ZF, Wang SY. Preliminary clinical study on the treatment of refractory hypertension by acupuncture plus point application. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2005; 24: 16-8. |
| 12. | Chen SY. The clinical observation and nursing care of acupoint application combined valsartan capsule for hypertension. Neimenggu Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2013; 26: 147. |
| 13. | Zheng Y, Liu L, Le D. Clinical observation on the treatment of 40 cases of hypertension by Yongquan acupoint application combined medicine. Zhong Yi Wai Zhi Za Zhi 2014; 23: 42. |
| 14. | Liu JL, Zheng QL, Zhu W. Clinical observation of acupoint application combined valsartan capsule for hypertension. Hubei Zhony Yi Za Zhi 2012; 34: 65-66. |
| 15. | Lin JL, Gong JQ, Zhang XQ. Clinical observation on the treatment of 30 cases of hypertension with using Chinese combined western and medicine therapy. Jiangsu Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2012; 44: 36-7. |
| 16. | Liu W, Feng Q, Li LT, et al. The clinical analysis of the treatment of 57 cases of hypertension by acupoint application. Guizhou Yi Yao 2012; 36: 1114-5. |
| 17. | Cui Y, Cui MY, Jin Y. Effect analysis of acupoint application of Chinese herbs in the treatment of hypertension. Zhong Guo Dang Dai Yi Yao 2013; 20: 107-8. |
| 18. | Zang DY, Wei ZX, Kong YL, et al. Clinical observation on the Traditional Chinese Medicine acupoint sticking therapy for the treatment of primary hypertension. Zhen Jiu Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2014: 30: 1-5. |
| 19. | Fu Y, Zhang XJ, Chen Y. Clinical observation on the acupoint sticking therapy for the treatment of hypertension. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xin Nao Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2013; 11: 1521-1522. |
| 20. | Huang SX. Clinical observation on the combined with acupoint sticking therapy for the treatment of elderly isolated systolic hypertension. Guangxi Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2012; 35: 23-24. |
| 21. | Luo FS, Li GH, Li QL, et al. Clinical observation on the acupoint application for elderly patients with hypertension. Zhong Wai Yi Liao 2011; 30: 149-150. |
| 22. | Zhang J, Li JF. Clinical observation on the treatment of 101 cases of primary hypertension in the community by acupoint application. Zhong Yi Wai Zhi Za Zhi 2010; 19: 22-23. |
| 23. | Yu HQ, Zhao QY. Clinical observation on the treatment of 120 cases of hypertension by acupoint application. Guang Ming Zhong Yi 2011; 26: 1184-1186. |
| 24. | Li CH, Teng J. Clinical curative effect analysis of acupoint application for elderly with hypertension. Shi Jie Zui Xin Yi Xue Xin Xi Wen Zhai 2015; 15: 137-138. |
| 25. | Jiao N. Clinical observation on treating primary hypertension with the acupoint sticker of the Sanzi Yangyin prescription. Zhong Yi Lin Chuang Yan Jiu 2015; 7: 6-8. |
| 26. | Zheng LW, Liu XZ, Yu XL. The influence of Tianma Gouteng Yin on blood pressure and syndrome in hyperactivity of liver-YANG syndrome of hypertensive patients. Fujian Zhong Yi Yao 2016; 47: 3-5. |
| 27. | Li XF, Yang BH, Wu YN, et al. Clinical observation on treating mild hypertension with the acupoint sticker of Tianma Gouteng Yin combined with levamlodipine besylate tablets. Neimenggu Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2015; 4: 87-9. |
| 28. | Chen HY, Xie LZ. Clinical observation on treating hypertension with the acupoint sticker Yongquan point of Wuzhuyu powder mixed honey. J Bethune Med Sci 2015; 13: 647-648. |
| 29. | Xue H, Zhang YG. Curative effect observation of acupoint sticker Yongquan point for hypertension. Shi Jie Zui Xin Yi Xue Xin Xi Wen Zhai 2016; 16: 171-3. |
| 30. | Sun J, Yu L. Clinical observation on the treatment of 40 cases of hypertension by acupoint application on Yongquan point. Yunnan Zhong Yi Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2015; 36: 26-7. |
| 31. | Mei Y, Zheng R. The effect of acupoint paste on blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Neimenggu Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2014; 1: 87-8. |
| 32. | Liu TT, Shen CZ. Effect of point application on quality of life of hypertension patients with phlegm dampness type. Hu Li Yan Jiu 2016; 30: 1216-8. |
| 33. | Wu JR. Efficacy observation on treating hypertension by plastering on acupoint combined with Shengtongping. Zhong Yi Lin Chuang Yan Jiu 2013; 5: 68-9. |
| 34. | Zhang Z, Chen M. Effect of antihypertensive drug combined with acupoint mounting on quality of life in elderly hypertension. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xin Nao Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2011; 9: 531-2. |
| 35. | Liu JW. Clinical observation on the treatment of 50 cases of hypertension in by acupoint application combined with antihypertensive drugs. Guang Ming Zhong Yi 2015; 30: 807-9. |
| 36. | Zhao JL, Qiao JM. Effect of antihypertensive drug combined with acupoint on hypertension. Xin Zhong Yi 2016; 48: 5-6. |
| 37. | Cui SY, Sheng Y. Clinical observation on the acupoint plastering in the treatment of hypertension. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Yuan Cheng Jiao Yu 2016; 14: 104-5. |
| 38. | Wang LP. Observations on the therapeutic effect of acupoint application on senile hypertension of Yin Deficiency and Yang Excess. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2015; 34: 421-422. |
| 39. | Ma SQ. Clinical observation on the treatment of 80 cases of hypertension of hyperaction of liver Yang by acupoint application on Yongquan point. Guang Ming Zhong Yi 2015; 30: 1028-9. |
| 40. | Chen LX. Clinical observation on treating hypertension with the acupoint sticker Yongquan point. Mod Diagn Treat 2016; 5: 836-7. |
| 41. | Huang LQ, He QX, Liu SY, et al. Clinical observation on the acupoint plastering in the treatment of hypertension of hyperaction of liver Yang. J Mod Med Health 2015; 31: 2504-5. |
| 42. | Qin CM, Yang YH, Huang CY, et al. To observe the curative effect of compound antihypertensive formula of acupoint application in the treatment of liver-yang hyperactivity type hypertension. Zhong Guo Ji Xu Yi Xue Jiao Yu 2017; 9: 186-8. |
| 43. | Yang YH, Qin CM, Huang CH. Efficacy of antihypertensive point acupoint in treating hypertension of liver-Yang hypertension. Zhong Guo Dang Dai Yi Yao 2018; 25: 114-6. |
| 44. | Li XM, Ye JF. Antihypertensive drugs combined with acupoint application in the treatment of patients with hypertension due to Yin deficiency and Yang hyperactivity. Jilin Zhong Yi Yao 2018; 38: 853-5. |
| 45. | Wang XZ. The clinical efficacy of acupoint sticking therapy of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of hypertension. Zhong Guo Ji Xu Yi Xue Jiao Yu 2018; 10: 141-143. |
| 46. | Xu JC. Therapeutic observation of acupoint sticking for hypertension due to hyperactivity of liver fire. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2018; 37: 874-6. |
| 47. | Zhang YJ. Clinical observation on the acupoint plastering in the treatment of hypertension. Lin Chuang He Li Yong Yao 2015; 8: 122-3. |
| 48. | Cui YY. Efficacy observation on treating hypertension by plastering on acupoint. Shi Jie Zui Xin Yi Xue Xin Xi Wen Zhai 2016; 16: 37-38. |
| 49. | Niu LX. Clinical observation on the treatment of 50 cases of senile hypertension by acupoint application. Henan Zhong Yi 2014; 34: 344-345. |
| 50. | Liu XY, Nie R. Point application therapy treatment 60 cases of essential hypertension. Shi Yong Zhong Yi Nei Ke Za Zhi 2009; 23: 120-121. |
| 51. | Chen MY, Zhang CZ. The effects of acupoint application therapy on hypertension. Li Shi Zhen Guo Yi Guo Yao 2007; 18: 2788-2789. |
| 52. | Luo FS, Li GH, Li QL, et al. Clinical research on syndrome differentiation of point application in the treatment of primary hypertension. Zhong Guo Yi Yao Dao Bao 2011; 8: 108-110. |
| [1] | LIU Tingting, LIU Tongou, LIU Mingfu. Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture in treatment of pregnancy-related symptoms: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 16-26. |
| [2] | WANG Jiabao, ZHANG Lishuang, NIU Baihan, YU Yajun, YANG Fengwen, MIAO Lin, CHAI Lijuan, DING Xinya, SUN Yingjie, WANG Yujing, WANG Lin, ZHANG Han, WANG Yi, LI Lin. Efficacy and safety of Weichang’ an pill (胃肠安丸) combined with Western Medicine on gastrointestinal diseases: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1057-1067. |
| [3] | FAN Rong, HE Haoyu, TANG Tao, CUI Hanjin. Long-term effects of Qingfei Paidu decoction (清肺排毒汤) in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 acute pneumonia after treatment: a protocol for systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1068-1071. |
| [4] | ZHAO HuiYan, JUN Purumea, LEE Chaewon, HAN Chang-Hyun. Acupoint catgut embedding for simple obesity in animal studies: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 860-867. |
| [5] | SUN Wu, ZHAO Yuwei, LIAO Liang, ZHAO Zhonghui, CHEN Shiqi, YAN Xiaoling, WANG Xueyao, CHAO Guojun, ZHOU Jian. Effectiveness and safety of Xuebijing injection for patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 631-639. |
| [6] | MENG Xiangran, CAO Xue, SUN Minglin, AI Yanke, HE Liyun, LIU Jia. Effectiveness and safety of Angong Niuhuang pill (安宫牛黄丸) in treatment of acute stroke: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 650-660. |
| [7] | SHENG Song, ZHANG Yanhong, GAO Hongyang, MA Hangkun, HUANG Ye, LI Qingna, GAO Rui, XU Fengqin. Effectiveness of acupoint application of Xiaozhong Zhitong Tie on diarrhea in patients: a retrospective cohort study in China [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 809-814. |
| [8] | LUO Xin, XIE Jing, HUANG Li, GAN Wenfan, CHEN Ming. Efficacy and safety of activating blood circulation and removing blood stasis of Traditional Chinese Medicine for managing renal fibrosis in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 429-440. |
| [9] | GUO Wen, LI Xuanlin, ZHAO Hulei, LEI Siyuan, XIE Yang, LI Jiansheng. Effectiveness of Chinese herbal medicine combined with conventional medicine on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 212-220. |
| [10] | ZHANG Junli, HE Ying, ZHANG Xia, FU Hongfang, HU Xiaoyu. Fuzheng Huayu preparation (扶正化瘀胶囊/片) combined with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate on hepatitis B: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 221-230. |
| [11] | YAO Yao, ZHAO Zhenni, CHEN Fengqin, LENG Yufei, PANG Xiangtian, XU Xiao, SUN Zhiling. Effectiveness of moxibustion alone on lumbar disc herniation: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 14-26. |
| [12] | HE Yun, HE Jing, XU Xiangru, LI Haixiao, SHI Rongwei, LIANG Junya, ZHOU Ying, ZHU Yao, CHEN Xiaohu, TANG Shuhua, XIAO Min, ZHAN Libin, PEI Yinghao, JIANG Weiming. Consensus on diagnostic criteria for Yin deficiency syndrome in hypertension: a modified Delphi study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 181-187. |
| [13] | YOU Jianyu, LI Haiyan, XIE Dingyi, CHEN Mingren, CHEN Rixin. Efficacy of acupuncture therapy for post-stroke fatigue: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 27-33. |
| [14] | LI Wei, XIA Ping, SUN Wei, ZHAO Jing, LIU Qiong, GENG Lianyi, ZHOU Yao, GAO Kun. Effects of the Huangkui capsule (黄葵胶囊) on chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 6-13. |
| [15] | YE Wujie, XING Jingyu, YU Zekai, HU Xingang, ZHAO Yan. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of acupuncture and acupoint catgut embedding for the treatment of abdominal obesity [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 848-857. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||