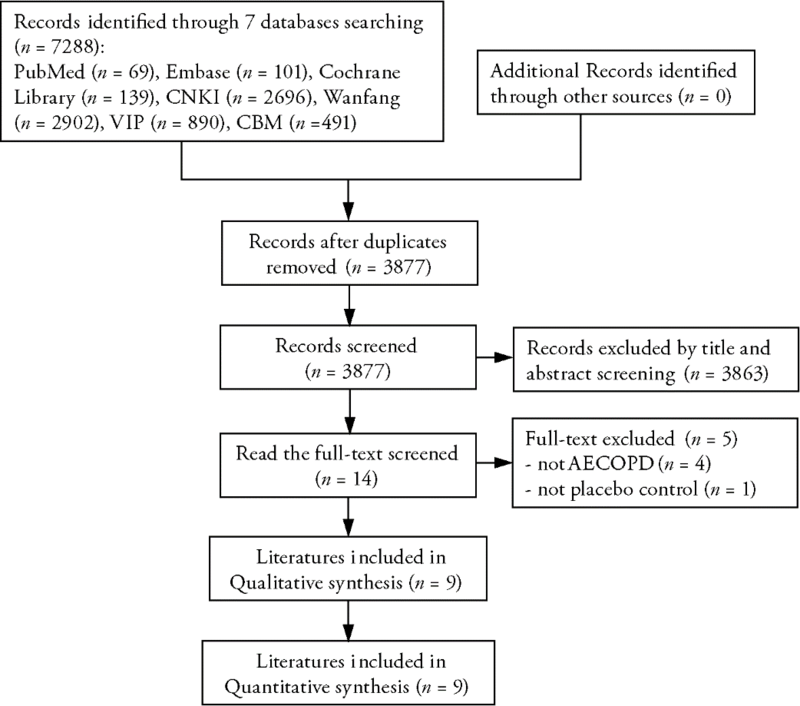
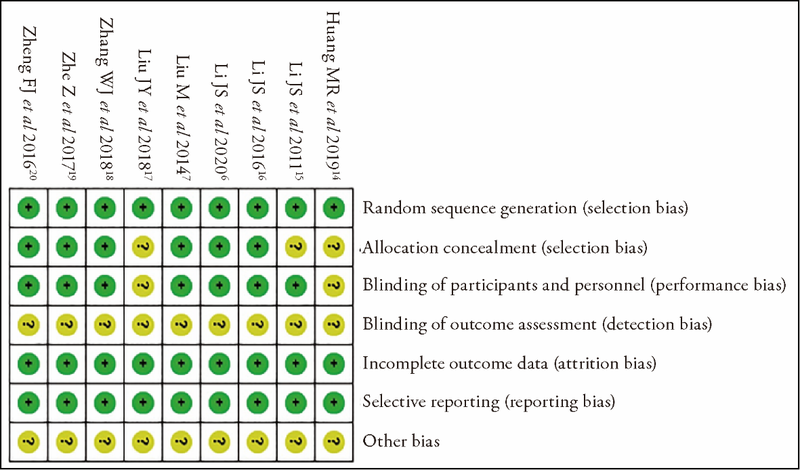
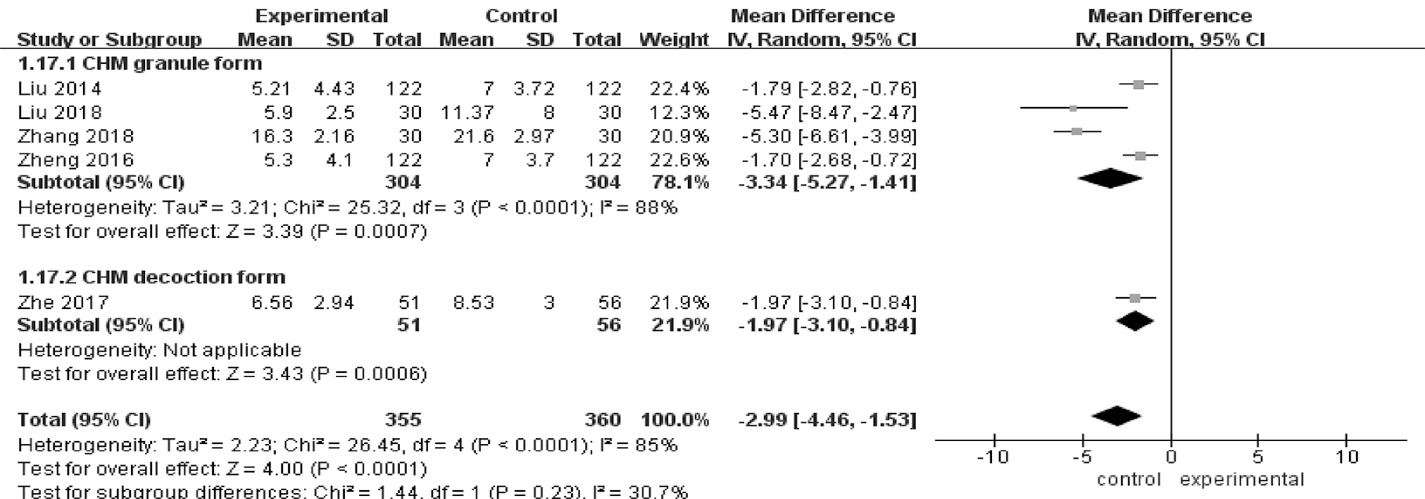
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 212-220.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2023.02.003
• Meta Analysis • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effectiveness of Chinese herbal medicine combined with conventional medicine on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
GUO Wen1, LI Xuanlin1, ZHAO Hulei2, LEI Siyuan1, XIE Yang2, LI Jiansheng1( )
)
- 1 Co-construction Collaborative Innovation Center for Respiratory Disease Diagnosis and Treatment & Chinese Medicine Development of Henan Province/ Henan Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine for Respiratory Disease, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, China
2 Department of Respiratory Diseases, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, China
-
Received:2023-01-08Accepted:2023-04-19Online:2023-04-15Published:2023-03-14 -
Contact:Prof. LI Jiansheng, Co-construction Collaborative Innovation Center for Respiratory Disease Diagnosis and Treatment & Chinese Medicine Development of Henan Province/ Henan Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine for Respiratory Disease, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, China. li_js8@163.com. Telephone: +86-371-65676568 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation Project: Research on Key Technology of Outcome Measurement and Evaluation of Syndrome Differentiation and Treatment Based on Clinical Trials of COPD(81830116);Chinese Medicine Inheritance and Innovation “Hundred and Ten Million” Talent Project-Chief Scientist of Qi-Huang Project((2020) No. 219);Zhong-yuan Scholars and Scientists Project(2018204)
Cite this article
GUO Wen, LI Xuanlin, ZHAO Hulei, LEI Siyuan, XIE Yang, LI Jiansheng. Effectiveness of Chinese herbal medicine combined with conventional medicine on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 212-220.
share this article
| Study | Sample size | Sex (M/F) | Age | Intervention | Duration (days) | Follow- up | Outcome | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | T | C | |||||||
| Huang MR et al 2019 | 40 | 40 | T: 26/14 C: 23/17 | T: 65.6±4.2 C: 64.9±4.9 | Mengshiguntan decoction+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 14 | NR | ||
| Li JS et al 2011 | 34 | 31 | T: 23/11 C: 19/12 | T: 63.90±11.37 C: 65.70±12.31 | Huoxuehuayu decoction+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 14 | NR | ⑤ | |
| Li JS et al 2016 | 173 | 180 | T: 126/47 C: 126/54 | T: 68.01±8.07 C: 67.87±8.36 | 3 CHM granules△+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 7-21 | 6 months | ⑦⑧ | |
| Li JS et al 2020 | 189 | 189 | T: 155/34 C: 163/26 | T: 65.73±8.47 C: 66.94±7.61 | 3 CHM granules△+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 14 | 3 months | ⑦⑧⑨ | |
| Liu M et al 2014 | 122 | 122 | T: 88/34 C: 82/40 | T: 70.1±9.8 C: 70.7±9.8 | Xuanbaichengqi granules+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 10 | NR | ⑤⑥⑨ | |
| Liu JY et al 2018 | 30 | 30 | T: 27/3 C: 28/2 | T: 64.80±6.55 C: 65.67±5.36 | Qingfei granules+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 10 | NR | ②③⑦⑨ | |
| Zhang WJ et al 2018 | 30 | 30 | T: 19/11 C: 21/9 | T: 63.45±9.67 C: 65.76±10.42 | Gubenquyujiedu granules+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 10 | NR | ②⑤⑥⑨ | |
| Zhe Z et al 2017 | 51 | 56 | T: 26/25 C: 28/28 | T: 67.85±7.82 C: 66.87±8.65 | Compound Fo’ercao decoction +CWM | Placebo+CWM | 14 | NR | ⑨ | |
| Zheng FJ et al 2016 | 122 | 122 | T: 84/38 C: 82/40 | T: 69.9±10.3 C: 70.7±9.8 | Rhubarb granules+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 10 | NR | ②⑤⑥⑨ | |
Table 1 Characteristics of the included studies
| Study | Sample size | Sex (M/F) | Age | Intervention | Duration (days) | Follow- up | Outcome | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | T | C | |||||||
| Huang MR et al 2019 | 40 | 40 | T: 26/14 C: 23/17 | T: 65.6±4.2 C: 64.9±4.9 | Mengshiguntan decoction+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 14 | NR | ||
| Li JS et al 2011 | 34 | 31 | T: 23/11 C: 19/12 | T: 63.90±11.37 C: 65.70±12.31 | Huoxuehuayu decoction+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 14 | NR | ⑤ | |
| Li JS et al 2016 | 173 | 180 | T: 126/47 C: 126/54 | T: 68.01±8.07 C: 67.87±8.36 | 3 CHM granules△+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 7-21 | 6 months | ⑦⑧ | |
| Li JS et al 2020 | 189 | 189 | T: 155/34 C: 163/26 | T: 65.73±8.47 C: 66.94±7.61 | 3 CHM granules△+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 14 | 3 months | ⑦⑧⑨ | |
| Liu M et al 2014 | 122 | 122 | T: 88/34 C: 82/40 | T: 70.1±9.8 C: 70.7±9.8 | Xuanbaichengqi granules+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 10 | NR | ⑤⑥⑨ | |
| Liu JY et al 2018 | 30 | 30 | T: 27/3 C: 28/2 | T: 64.80±6.55 C: 65.67±5.36 | Qingfei granules+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 10 | NR | ②③⑦⑨ | |
| Zhang WJ et al 2018 | 30 | 30 | T: 19/11 C: 21/9 | T: 63.45±9.67 C: 65.76±10.42 | Gubenquyujiedu granules+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 10 | NR | ②⑤⑥⑨ | |
| Zhe Z et al 2017 | 51 | 56 | T: 26/25 C: 28/28 | T: 67.85±7.82 C: 66.87±8.65 | Compound Fo’ercao decoction +CWM | Placebo+CWM | 14 | NR | ⑨ | |
| Zheng FJ et al 2016 | 122 | 122 | T: 84/38 C: 82/40 | T: 69.9±10.3 C: 70.7±9.8 | Rhubarb granules+CWM | Placebo+CWM | 10 | NR | ②⑤⑥⑨ | |
| Outcome | Number of studies | Number of patients | RR/MD | 95%CI | I2 value (%) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | ||||||
| CAT scores | 3 | 373 | 355 | ?2.08 | ?2.85, ?1.31 | 10 | <0.000 01 |
| PaO2 | 4 | 279 | 281 | 4.51 | 1.97, 7.04 | 0 | 0.0005 |
| PaCO2 | 3 | 274 | 274 | ?2.87 | ?4.28, ?1.46 | 0 | <0.0001 |
| Length of hospitalization | 3 | 392 | 399 | ?1.87 | ?3.33, ?0.42 | 86 | 0.01 |
| Acute exacerbation rate | 2 | 343 | 325 | 0.60 | 0.43, 0.83 | 0 | 0.002 |
Table 2 Meta-analysis outcomes
| Outcome | Number of studies | Number of patients | RR/MD | 95%CI | I2 value (%) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | ||||||
| CAT scores | 3 | 373 | 355 | ?2.08 | ?2.85, ?1.31 | 10 | <0.000 01 |
| PaO2 | 4 | 279 | 281 | 4.51 | 1.97, 7.04 | 0 | 0.0005 |
| PaCO2 | 3 | 274 | 274 | ?2.87 | ?4.28, ?1.46 | 0 | <0.0001 |
| Length of hospitalization | 3 | 392 | 399 | ?1.87 | ?3.33, ?0.42 | 86 | 0.01 |
| Acute exacerbation rate | 2 | 343 | 325 | 0.60 | 0.43, 0.83 | 0 | 0.002 |
| Certainty assessment | No. of patients | Effect | Certainty | Importance | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of studies | Study design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | publication bias | T | C | Relative (95% CI) | Absolute (95% CI) | ||||
| Clinical total effective rate | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | RCTs | seriousa | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 123/134 (91.8%) | 91/131 (69.5%) | RR 1.29 (1.07 to 1.56) | 201 more per 1,000 (from 49 more to 389 more) | ⊕⊕?? LOW | CRITICAL | ||
| TCM symptom scores | ||||||||||||||
| 5 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 355 | 360 | - | MD 2.99 lower (4.46 lower to 1.53 lower) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | CRITICAL | ||
| CAT scores | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 373 | 355 | - | MD 2.08 lower (2.85 lower to 1.31 lower) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | CRITICAL | ||
| PaO2 | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 279 | 281 | - | MD 4.51 higher (1.97 higher to 7.04 higher) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | IMPORTANT | ||
| PaCO2 | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 274 | 274 | - | MD 2.87 lower (4.28 lower to 1.46 lower) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | IMPORTANT | ||
| Length of hospitalization | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 392 | 399 | - | MD 1.87 lower (3.33 lower to 0.42 lower) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | IMPORTANT | ||
| Acute exacerbation rate | ||||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 48/343 (14.0%) | 77/325 (23.7%) | RR 0.60 (0.43 to 0.83) | 95 fewer per 1000 (from 135 fewer to 40 fewer) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | IMPORTANT | ||
Table 3 Quality of evidence
| Certainty assessment | No. of patients | Effect | Certainty | Importance | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of studies | Study design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | publication bias | T | C | Relative (95% CI) | Absolute (95% CI) | ||||
| Clinical total effective rate | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | RCTs | seriousa | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 123/134 (91.8%) | 91/131 (69.5%) | RR 1.29 (1.07 to 1.56) | 201 more per 1,000 (from 49 more to 389 more) | ⊕⊕?? LOW | CRITICAL | ||
| TCM symptom scores | ||||||||||||||
| 5 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 355 | 360 | - | MD 2.99 lower (4.46 lower to 1.53 lower) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | CRITICAL | ||
| CAT scores | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 373 | 355 | - | MD 2.08 lower (2.85 lower to 1.31 lower) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | CRITICAL | ||
| PaO2 | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 279 | 281 | - | MD 4.51 higher (1.97 higher to 7.04 higher) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | IMPORTANT | ||
| PaCO2 | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 274 | 274 | - | MD 2.87 lower (4.28 lower to 1.46 lower) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | IMPORTANT | ||
| Length of hospitalization | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 392 | 399 | - | MD 1.87 lower (3.33 lower to 0.42 lower) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | IMPORTANT | ||
| Acute exacerbation rate | ||||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | not serious | seriousb | not serious | not serious | none | 48/343 (14.0%) | 77/325 (23.7%) | RR 0.60 (0.43 to 0.83) | 95 fewer per 1000 (from 135 fewer to 40 fewer) | ⊕⊕⊕? MODERATE | IMPORTANT | ||
| 1. | Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of COPD. 2019. Available from URL: https://www.goldcopd.com |
| 2. |
GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016; 388: 1459-544.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Suissa S, Dell'Aniello S, Ernst P. Long-term natural history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: severe exacerbations and mortality. Thorax 2012; 67: 957-63.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Ko FW, Chan KP, Hui DS, et al. Acute exacerbation of COPD. Respirology 2016; 21: 1152-65.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Aaron SD. Management and prevention of exacerbations of COPD. BMJ 2014; 349: g5237.
DOI URL |
| 6. |
Li JS, Zhang HL, Ruan HR, et al. Effects of Chinese herbal medicine on acute exacerbations of COPD: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2020; 15: 2901-12.
DOI URL |
| 7. |
Liu M, Zhong XG, Li YH, et al. Xuan Bai Cheng Qi formula as an adjuvant treatment of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease of the syndrome type phlegm-heat obstructing the lungs: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-con-trolled clinical trial. BMC Complement Altern Med 2014; 14: 239.
DOI URL |
| 8. | Coyle M, Shergis JL, Liu S, et al. Safety of Chinese herbal medicine for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015; 2015: 380678. |
| 9. | Wu RH, Zheng FJ, Li YH, et al. Modified Dachengqi decoction combined with conventional treatment for treating acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review based on randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013; 2013: 323715. |
| 10. | Liu SN, Shergis J, Chen XK, et al. Chinese herbal medicine (Weijing decoction) combined with pharmacotherapy for the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 2014: 257012. |
| 11. |
Gao Z, Jing J, Liu Y. Xiaoqinglong decoction (a Traditional Chinese Medicine) combined conventional treatment for acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020; 99: e19571.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Zabor EC, Kaizer AM, Hobbs BP. Randomized Controlled Trials. Chest 2020; 158: S79-87.
DOI PMID |
| 13. |
Gerdesmeyer L, Klueter T, Rahlfs VW, et al. Randomized placebo-controlled placebo trial to determine the placebo effect size. Pain Physician 2017; 20: 387-96.
PMID |
| 14. | Huang MR, Yang YP, Xu ZB, He F. Effect of modified mengshi guntan pill on IL-17, IL-10 and 8-iso-pg in exhaled condensate of patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Zhong Yi Yao Tong Bao 2019; 18: 40-3+18. |
| 15. | Li JS, Li B, Yu XQ, et al. Clinical effect evaluation on herbs for promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis in treatment of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with blood stasis syndrome. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Ji Jiu Za Zhi 2011; 18: 9-13. |
| 16. |
Li JS, Wang HF, Li SY, et al. Effect of sequential treatment with TCM syndrome differentiation on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and AECOPD risk window. Complement Ther Med 2016; 29: 109-15.
DOI PMID |
| 17. | Liu JY, Zhe Z, Lu JJ, Shi KH. Clinical observation of Qingfei granule in the treatment of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with phlegm-heat obstructing lung syndrome. Hebei Zhong Yi 2018; 40: 1458-62. |
| 18. | Zhang WJ, Fan CZ, Zhang Q, Guo DH, Wang B, Xu ZW. Clinical study of Guben Quyu Jiedu formula combined with Western Medicine on patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2018; 38: 1040-4. |
| 19. | Zhe Z, Li FS, Zhao ZX, et al. Effects of compound Fo’ercao mixture on inflammatory factors in peripheral blood and expression of Toll like receptors in monocytes of AECOPD patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Shanghai Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2017; 51: 38-41. |
| 20. | Zheng FJ, Sun Y, Zhong XG, et al. A multicenter randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of rhubarb in treating acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease of the syndrome type phlegm-heat obstructing the lungs. J Trad Chin Med Sci 2016; 3: 71-80. |
| 21. |
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and Meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009; 339: b2535.
DOI URL |
| 22. | Xie Y, Zhao HL, Li XL, Han WH, Li JS. Chinese herbal medicine for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of high quality randomized controlled trials. PROSPERO 2021 CRD42021257385. Available from URL: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/#recordDetails. |
| 23. |
Rabe KF, Hurd S, Anzueto A, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2007; 176: 532-55.
DOI URL |
| 24. | Chinese Society of Respiratory Diseases. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease diagnostic and treatment guidelines (revised 2013). Zhong Hua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 2013; 36: 255-64. |
| 25. | Vogelmeier CF, Criner GJ, Martinez FJ, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease 2017 report. GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2017; 195: 557-82. |
| 26. | Zheng XY. Guiding principle of clinical research on new drugs of Traditional Chinese Medicine (trial implementation). Beijing: Chinese Medical Science and Technology Press, 2002: 54-66. |
| 27. |
Taylor KS, Mahtani KR, Aronson JK. Summarising good practice guidelines for data extraction for systematic reviews and Meta-analysis. BMJ Evid Based Med 2021; 26: 88-90.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from URL: https://www.cochrane-handbook.org. |
| 29. |
Aguayo-Albasini JL, Flores-Pastor B, Soria-Aledo V. GRADE system: classification of quality of evidence and strength of recommendation. Cir Esp 2014; 92: 82-8.
DOI URL |
| 30. |
Martinez FJ, Han MK, Flaherty K, Curtis J. Role of infection and antimicrobial therapy in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2006; 4: 101-24.
PMID |
| 31. |
Make B. How can we assess outcomes of clinical trials: the MCID approach. COPD 2007; 4: 191-4.
PMID |
| 32. |
Tu YH, Zhang Y, Fei GH. Utility of the CAT in the therapy assessment of COPD exacerbations in China. BMC Pulm Med 2014; 14: 42.
DOI URL |
| 33. |
Kon SS, Canavan JL, Jones SE, et al. Minimum clinically important difference for the COPD assessment test: a prospective analysis. Lancet Respir Med 2014; 2: 195-203.
DOI URL |
| 34. |
Raoufy MR, Eftekhari P, Gharibzadeh S, Masjedi MR. Predicting arterial blood gas values from venous samples in patients with acute exacerbation chronic obstructive pulmonary disease using artificial neural network. J Med Syst 2011; 35: 483-8.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Cazzola M, Macnee W, Martinez FJ, et al. Outcomes for COPD pharmacological trials: from lung function to biomarkers. Eur Respir J 2008; 31: 416-69.
DOI PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||