Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 181-187.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220719.002
• Methodology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Consensus on diagnostic criteria for Yin deficiency syndrome in hypertension: a modified Delphi study
HE Yun1, HE Jing3, XU Xiangru6, LI Haixiao1, SHI Rongwei1, LIANG Junya4, ZHOU Ying5, ZHU Yao5, CHEN Xiaohu5, TANG Shuhua5, XIAO Min7, ZHAN Libin8, PEI Yinghao2( ), JIANG Weiming5(
), JIANG Weiming5( )
)
- 1 Department of General Internal Medicine, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Hospital of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China
2 Department of Intensive Care Unit, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Hospital of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China
3 Department of Hepatology, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Hospital of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China
4 Department of Institute of Hypertension, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Hospital of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China
5 Department of Cardiology, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Hospital of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China
6 Department of Emergency, Longhua Hospital affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China
7 Department of Cardiology, Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
8 School of Traditional Chinese Medicine & School of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China
-
Received:2022-01-11Accepted:2022-04-18Online:2023-02-15Published:2023-01-10 -
Contact:PEI Yinghao,JIANG Weiming -
About author:PEI Yinghao, Department of Intensive Care Unit, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Hospital of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China. piaopiao5556@sina.com.Telephone:+86-25-86617141
Prof. JIANG Weiming, Department of Cardiology, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Hospital of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China. jwm0410@njucm.edu.cn;
-
Supported by:Study on Syndrome Differentiation Standard of Yin deficiency Syndrome in Hypertension(2018YFC1704403);National Key R&D Program of China Project: Systematic Study on the Standard of Syndrome Differentiation of Yin Deficiency Syndrome(2018YFC1704400)
Cite this article
HE Yun, HE Jing, XU Xiangru, LI Haixiao, SHI Rongwei, LIANG Junya, ZHOU Ying, ZHU Yao, CHEN Xiaohu, TANG Shuhua, XIAO Min, ZHAN Libin, PEI Yinghao, JIANG Weiming. Consensus on diagnostic criteria for Yin deficiency syndrome in hypertension: a modified Delphi study[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 181-187.
share this article
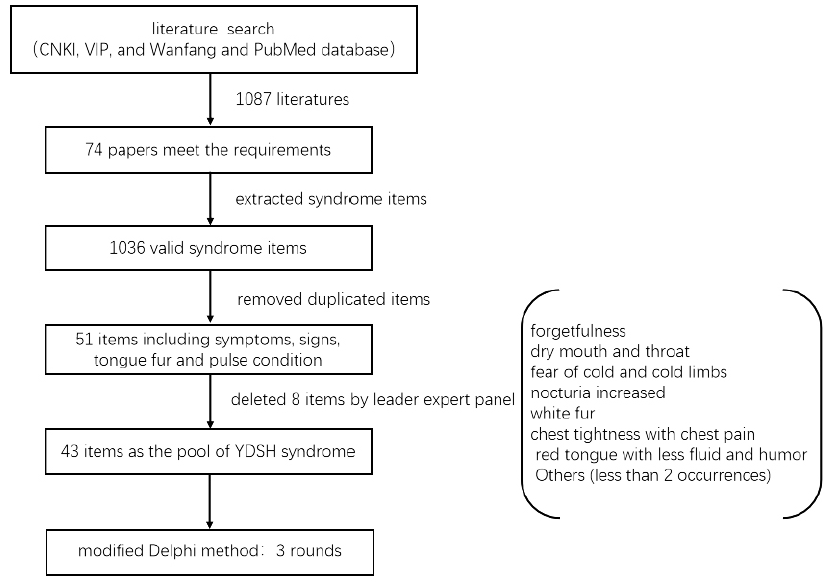
Figure 2 Workflow of Screening CNKI: China National Knowledge Infrastructure Database; VIP: China Science and Technology Journal Database; YDSH: Yin deficiency syndrome in hypertension.
| Item | Appropriate (mean/median) | Uncertain (mean/median) | Inappropriate (mean/median) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Further evaluation | Inappropriate | |||
| Symptom and signs | Dizziness (7.14/8) Night sweating (6.5/7) Dry eyes (6.57/7) Heat in the palms and soles (7.36/7.5) Vexing heat in chest, palms, and soles (7.11/7) | Dizzy vision (6.04/6) Soreness and weakness of lumbus and knee (6.32/6) Tinnitus (5.93/6) Insomnia (5.64/5.5) Palpitations (5.04/5) Profuse dreaming (5.36/5) Blurred vision (5.5/5.5) Dry stool (5.86/6) Rosy cheeks (6.04/6) Flushed complexion (5.79/6) | Headache (4.93/5) Shortness of breath (4.11/4) Agitation (5.04/5) Lack of mental vigor and physical strength (4.11/4) Numbness of the limbs (4.04/4) Heavy head and light feet (4.32/4.5) Restlessness (5.04/5) Bitter taste in the mouth (3.93/4) Seminal emission or scant menstruation (4.89/5) Muscular twitching and cramp (4.32/4) Reddened complexion and eyes (4.43/5) Emaciation (5.86/6) Yellow urine (4.64/5) Dark-yellow urine (4.07/5) Deafness (4.54/4.5) | Discomfort in hypochondrium (3.18/2.5) |
| Tongue manifestation | Red tongue (7.25/8) scanty fur (7.25/8) No fur (6.75/7) | Thin fur (5.18/6) | Yellow fur (3.75/4.5) | Pale tongue (3.18/2.5) |
| Pulse condition | String-like, fine and rapid pulse (6.64/7) Fine and rapid pulse (6.54/7) | String-like, fine pulse (6/6.5) | Fine and sunken pulse (4.71/5) Fine, weak, and rapid pulse (5.75/7) Fine and weak pulse (4.54/4.5) | |
Table 1 Items in questionnaire round one
| Item | Appropriate (mean/median) | Uncertain (mean/median) | Inappropriate (mean/median) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Further evaluation | Inappropriate | |||
| Symptom and signs | Dizziness (7.14/8) Night sweating (6.5/7) Dry eyes (6.57/7) Heat in the palms and soles (7.36/7.5) Vexing heat in chest, palms, and soles (7.11/7) | Dizzy vision (6.04/6) Soreness and weakness of lumbus and knee (6.32/6) Tinnitus (5.93/6) Insomnia (5.64/5.5) Palpitations (5.04/5) Profuse dreaming (5.36/5) Blurred vision (5.5/5.5) Dry stool (5.86/6) Rosy cheeks (6.04/6) Flushed complexion (5.79/6) | Headache (4.93/5) Shortness of breath (4.11/4) Agitation (5.04/5) Lack of mental vigor and physical strength (4.11/4) Numbness of the limbs (4.04/4) Heavy head and light feet (4.32/4.5) Restlessness (5.04/5) Bitter taste in the mouth (3.93/4) Seminal emission or scant menstruation (4.89/5) Muscular twitching and cramp (4.32/4) Reddened complexion and eyes (4.43/5) Emaciation (5.86/6) Yellow urine (4.64/5) Dark-yellow urine (4.07/5) Deafness (4.54/4.5) | Discomfort in hypochondrium (3.18/2.5) |
| Tongue manifestation | Red tongue (7.25/8) scanty fur (7.25/8) No fur (6.75/7) | Thin fur (5.18/6) | Yellow fur (3.75/4.5) | Pale tongue (3.18/2.5) |
| Pulse condition | String-like, fine and rapid pulse (6.64/7) Fine and rapid pulse (6.54/7) | String-like, fine pulse (6/6.5) | Fine and sunken pulse (4.71/5) Fine, weak, and rapid pulse (5.75/7) Fine and weak pulse (4.54/4.5) | |
| Item | Appropriate (mean/median) | Uncertain (mean/median) |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms Signs | Heat in the palms and soles (7.35/8) Dizziness (7.26/8) Dry eyes (7.1/7) Soreness and weakness of lumbus and knee (6.74/7) Dizzy vision (7.26/7) Palpitations (6.55/7) Rosy cheeks (6.16/7) Tinnitus (6.81/7) Profuse dreaming (6.35/7) | Vexing heat in chest, palms, and soles (7.19/8) Insomnia (5.81/6) Night sweating (6.42/6) Blurred vision (5.52/6) Dry stool (6.29/6) Flushed complexion (5.61/6) |
| Tongue manifestation | Red tongue (7.45/8) scanty fur (7.45/8) | Thin fur (5.97/6) No fur (5.42/5) |
| Pulse condition | String-like and fine pulse (7.35/8) | String-like, fine and rapid pulse (7.13/7) fine and rapid pulse (6.94/7) |
Table 2 Items in questionnaire round two
| Item | Appropriate (mean/median) | Uncertain (mean/median) |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms Signs | Heat in the palms and soles (7.35/8) Dizziness (7.26/8) Dry eyes (7.1/7) Soreness and weakness of lumbus and knee (6.74/7) Dizzy vision (7.26/7) Palpitations (6.55/7) Rosy cheeks (6.16/7) Tinnitus (6.81/7) Profuse dreaming (6.35/7) | Vexing heat in chest, palms, and soles (7.19/8) Insomnia (5.81/6) Night sweating (6.42/6) Blurred vision (5.52/6) Dry stool (6.29/6) Flushed complexion (5.61/6) |
| Tongue manifestation | Red tongue (7.45/8) scanty fur (7.45/8) | Thin fur (5.97/6) No fur (5.42/5) |
| Pulse condition | String-like and fine pulse (7.35/8) | String-like, fine and rapid pulse (7.13/7) fine and rapid pulse (6.94/7) |
| No. | Item | Weight score | Unadjusted | 10-adjusted | 8-adjusted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red tongue and scanty fur | 22.8 | 23 | 24 | 26 |
| 2 | Heat in the palms and soles | 20.1 | 20 | 21 | 23 |
| 3 | Dry eyes | 10.6 | 11 | 11 | 12 |
| 4 | String-like and fine pulse | 8.8 | 9 | 9 | 10 |
| 5 | Soreness and weakness of lumbus and knees | 8.0 | 8 | 9 | 9 |
| 6 | Rosy cheeks | 8.3 | 8 | 8 | 9 |
| 7 | Dizziness | 5.1 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| 8 | Tinnitus | 4.9 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| 9 | Dizzy vision | 4.4 | 4 | 5 | |
| 10 | Profuse dreaming | 3.6 | 4 | 4 | |
| 11 | Palpitations | 3.4 | 3 |
Table 3 Weight score of each item (%)
| No. | Item | Weight score | Unadjusted | 10-adjusted | 8-adjusted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red tongue and scanty fur | 22.8 | 23 | 24 | 26 |
| 2 | Heat in the palms and soles | 20.1 | 20 | 21 | 23 |
| 3 | Dry eyes | 10.6 | 11 | 11 | 12 |
| 4 | String-like and fine pulse | 8.8 | 9 | 9 | 10 |
| 5 | Soreness and weakness of lumbus and knees | 8.0 | 8 | 9 | 9 |
| 6 | Rosy cheeks | 8.3 | 8 | 8 | 9 |
| 7 | Dizziness | 5.1 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| 8 | Tinnitus | 4.9 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| 9 | Dizzy vision | 4.4 | 4 | 5 | |
| 10 | Profuse dreaming | 3.6 | 4 | 4 | |
| 11 | Palpitations | 3.4 | 3 |
| No. | Expert Name | Institute Specialty Professional title |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lin Qian | Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 2 | Xie Haibo | Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 3 | Deng Bing | Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 4 | Wang Zhentao | Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 5 | Zhang Junru | Shanxi Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 6 | Zhang Yan | Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 7 | Wang LiYing | Institute of Clinical Basic Medicine of Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences; Internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine; Associate Researcher |
| 8 | Li Rong | The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 9 | An Dongqing | Xingjiang Medical College; Pharmacology and Internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine; Chief Physician |
| 10 | Zhao Mingfen | Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 11 | Chen Xiaohu | Jiangsu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 12 | Ge Jinwen | Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 13 | Zhou Duan | Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 14 | Han Xuejie | Clinical Institute of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 15 | Zhang Jing | Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 16 | Lu Feng | Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 17 | Liu Zhongyong | Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 18 | Deng Yue | Affiliated Hospital of Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 19 | Dai Xiaohua | The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 20 | Fu Deyu | YueYang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 21 | Shen Chundi | Changzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 22 | Hu Yuanhui | Guang'anmen Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences'; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 23 | Lu Jianqi | The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 24 | Tang Shuhua | Jiangsu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 25 | Wu Wei | The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 26 | Zhu Mingjun | The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 27 | Huang Shuwei | The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 28 | Wang Xianliang | The First Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 29 | Chen Lianfa | Xiamen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 30 | Wang Xiaofeng | Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 31 | Zhu Cuiling | Heart Center of the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 32 | Yang Xia | The Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Sichuan Province; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 33 | Zhao Yingqiang | The Second Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
Table S1 List of panel members
| No. | Expert Name | Institute Specialty Professional title |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lin Qian | Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 2 | Xie Haibo | Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 3 | Deng Bing | Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 4 | Wang Zhentao | Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 5 | Zhang Junru | Shanxi Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 6 | Zhang Yan | Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 7 | Wang LiYing | Institute of Clinical Basic Medicine of Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences; Internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine; Associate Researcher |
| 8 | Li Rong | The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 9 | An Dongqing | Xingjiang Medical College; Pharmacology and Internal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine; Chief Physician |
| 10 | Zhao Mingfen | Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 11 | Chen Xiaohu | Jiangsu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 12 | Ge Jinwen | Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 13 | Zhou Duan | Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 14 | Han Xuejie | Clinical Institute of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 15 | Zhang Jing | Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 16 | Lu Feng | Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 17 | Liu Zhongyong | Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 18 | Deng Yue | Affiliated Hospital of Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 19 | Dai Xiaohua | The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 20 | Fu Deyu | YueYang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 21 | Shen Chundi | Changzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 22 | Hu Yuanhui | Guang'anmen Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences'; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 23 | Lu Jianqi | The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 24 | Tang Shuhua | Jiangsu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 25 | Wu Wei | The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 26 | Zhu Mingjun | The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 27 | Huang Shuwei | The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 28 | Wang Xianliang | The First Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 29 | Chen Lianfa | Xiamen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 30 | Wang Xiaofeng | Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 31 | Zhu Cuiling | Heart Center of the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 32 | Yang Xia | The Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Sichuan Province; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 33 | Zhao Yingqiang | The Second Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Cardiovascular of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine; Chief Physician |
| 1 |
Yang MX, Lao LX. Emerging applications of metabolomics in Traditional Chinese Medicine treating hypertension: biomarkers, pathways and more. Front Pharmacol 2019; 10: 158.
DOI PMID |
| 2 | Weng WQ. Clinical study on “liver Yang exuberance syndrome”. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 1989; 5: 266-9, 259. |
| 3 | Wu LN, Xie YM, Liu H, Zhang Y, Lu Q, Zhuang Y. Real-world study on syndrome distribution and medication characteristics of colonic malignant tumors. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2020; 5: 1174-79. |
| 4 | Yu G, He QY. Combination analysis of syndrome elements and syndrome response in 7213 patients with hypertension. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao 2013; 8: 2284-6. |
| 5 | Zhang LF. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension in TCM. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Yuan cheng Jiao Yu 2011; 23: 108-9. |
| 6 | Zheng XY. Guiding principles for clinical research of new chinese medicines. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2002: 73-7. |
| 7 | Zhang BY. Chinese internal medicine. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1984: 204-7. |
| 8 | Zhou ZY. Practical Chinese internal medicine. Beijing: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press, 2012: 602-12. |
| 9 | Hou PH, Chen GL, Gu WL, et al. Distribution laws of chinese medical syndrome types and analyses of risk factors in senile hypertension patients: a clinical study. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2014; 5: 536-40. |
| 10 | Ma N, Hou YZ, Wang XL, Mao JY. Analysis of medication laws for chinese medicine treating hypertension patients with Yin deficiency Yang hyperactivity syndrome based on literatures. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2016; 4: 403-10. |
| 11 | Du J, Zhong MF, Liu D, et al. Reduced mlh3 expression in the syndrome of gan-shen Yin deficiency in patients with different diseases. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017; 2017: 4109828. |
| 12 | van Helsdingen CP, Jongen AC, de Jonge WJ, Bouvy ND, Derikx JP. Consensus on the definition of colorectal anastomotic leakage: a modified delphi study. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 23: 3293-303. |
| 13 | Sinha IP, Smyth RL, Williamson PR. Using the delphi technique to determine which outcomes to measure in clinical trials: recommendations for the future based on a systematic review of existing studies. PLoS Med 2011; 1: e1000393. |
| 14 | Moossdorff M, van Roozendaal LM, Strobbe LJ, et al. Maastricht delphi consensus on event definitions for classification of recur-rence in breast cancer research. J Natl Cancer Inst 2014; 12: dju288. |
| 15 | Jin Y, Hu S, Yan D. Study on molecular mechanism of Ganyang Shangkang syndrome in hypertension. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2000; 2: 87-90. |
| 16 | Qing YZ, Zhang X, Zhao JX, Tian YX. Visual analysis of liver and kidney Yin deficiency syndrome diagnostic criteria based on citespace software. Shi Jie Ke Xue Ji Shu-Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Hua 2017; 4: 556-62. |
| 17 | Wang J, Xiong XJ, Liu W. Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes for essential hypertension: a literature analysis of 13, 272 patients. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 2014: 418206. |
| 18 | Wang JB, Jia LQ, Li N, Qu Y, Song N, Zhan LB. Exploration on construction of animal model of combining hypertension and Yin deficiency syndrome. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2020; 8: 90-2. |
| 19 | Wei JP, Wu R, Zhao DD. Analysis on Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome elements and relevant factors for senile diabetes. J Tradit Chin Med 2013; 4: 473-8. |
| 20 | Dong HY, Zhang SQ, Du WX, Cong HL, Zhang LH. Pharmacodynamics and metabonomics study of tianma gouteng decoction for treatment of spontaneously hypertensive rats with liver-Yang hyperactivity syndrome. J Ethnopharmacol 2020; 253: 112661. |
| 21 | McMillan SS, King M, Tully MP. How to use the nominal group and delphi techniques. Int J Clin Pharm 2016; 3: 655-62. |
| 22 | Luo H, Liao X, Wang Q. Application of chinese medical syndrome scores in effectiveness evaluation: a critical appraisal of 240 randomized controlled trials. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2015; 10: 1261-6. |
| 23 | Wu ZC, Zhang FY, Yu HY, J XM, Liu GW, Ouyang B. Literature analysis on the symptom characteristics of liver-kidney Yin deficiency syndrome in hypertensive patients. Shi Zhen Guo Yi Guo Yao 2015; 3: 746-8. |
| [1] | LIU Wei, XIONG Xingjiang, QIAO Lumin, CHEN Yuyi, LI Yixuan, SU Xing, CHU Fuyong, LIU Hongxu. Acupoint application therapies for essential hypertension: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 159-166. |
| [2] | ZHAO Zhiyue, SHI Zhenyu, ZHANG Zhenzhen, LI Yinghong, ZENG Xiaohui, CHEN Yuxing, YAO Nan, ZHOU Min, SU Hui, WANG Qinghai, JIN LiLi. Anti-hypertensive and endothelia protective effects of Fufang Qima capsule(复方芪麻胶囊) on primary hypertension via adiponectin/adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 919-926. |
| [3] | ZHU Guohua, SUN Xipeng, DING Cuntao, ZHAO Huan, LI Jing, HUA Qi. Effect of Songlingxuemaikang(松龄血脉康) on mild essential hypertension in patients: a randomized parallel-controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 799-805. |
| [4] | An Xing, Li Songtao, Weng Xiangwen, Wang Xian, Wu Hao, Zhang Xinyue, Gao Jian, Yang Renxu, Peng Bo. Maxingxiongting mixture attenuates hypoxia pulmonary arterial hypertension to improve right ventricular hypertrophy by inhibiting the rho-kinase signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(6): 992-998. |
| [5] | Bumjung Kim, Cheolmin Jo, Somin Lee, Hanna Choi, Kwang-Woo Kim, Inhye Ham, Ho-Young Choi, Kyungjin Lee. Vasorelaxant effects of 50 commonly used traditional herbal prescriptions on isolated rat aortic rings [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(4): 629-639. |
| [6] | Pei Lixin, Shu Shengnan, Wang Xuanying, Ji Baoyu. Effect of chrysanthemum extract on myocardial fibrosis in rats with renovascular hypertension [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(04): 542-549. |
| [7] | Vilaval Termklinchan, Sasinan Wasin, Mayuree Choesomboon, Chananun Praditbatuka, Somchai Sukareechai. Effect of acupuncture on blood pressure control in hypertensive patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(02): 246-250. |
| [8] | Luo Xiaozhou, Huang Jianting, Yu Juan, Tang Chunzhi. Effect of Taichong(LR 3) acupuncture in spontaneously hypertensive rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(01): 74-80. |
| [9] | Zhang Lu, Wu Lili, Liu Ximing, Yoshitomi Hisae, Ikeda Katsumi, Negishi Hiroko, Pan Yajing, Sun Wen, Qin Lingling, Li Juan-E, Xu Tunhai, Liu Tonghua, Gao Ming. Trans-cinnamaldehyde promotes nitric oxide release via the protein kinase-B/v-Akt murine thymoma viral oncogene-endothelial nitric oxide synthase pathway to alleviate hypertension in SHR.Cg-Lepr~(cp)/NDmcr rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(04): 548-555. |
| [10] | Guo Qiulei, Liu Qingguo, Sun Dongmei, Nie Binbin. Twirling reinforcing-reducing manipulation——central mechanism underlying antihypertensive effect on spontaneous hypertension in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(03): 391-398. |
| [11] | Guo Yan, Lu Juan, Liang Jingrong, Zhao Ruili, Xu Jing, Zhang Wei, Park Kibeum, Zhu Shipeng, Chen Huan, Ma Liangxiao. Effect of acupuncture at Renying(ST 9) on gene expression profile of hypothalamus in spontaneously hypertensive rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(02): 227-241. |
| [12] | Zhu Jie, Wang Baoqin, Liu Changan, Tong Xiangli, Li Zegeng. Qibai Pingfei capsule medicated serum inhibits the proliferation of hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells via the Ca~(2+)/calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T-cells 3 pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(04): 466-474. |
| [13] | Wonseok Chung, Jimi Ryu, Seokhee Chung, Sungsoo Kim. Effect of Qingxue Dan on obesity and metabolic biomarker: a double-blind randomized-controlled pilot study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(03): 291-298. |
| [14] | He Ling, Fang Meixia, Chen Liguo, Zhou Jianhua, Yuan Jing, Xu Jing, Shan Yan, Xu Qingyun, Xiong Tingting. Transcriptome analysis of blood stasis syndrome in subjects with hypertension [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(02): 173-180. |
| [15] | Yeh Tsui-Yun, Lin Jen-Chien, Liu Chi-Feng. Effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation through acupoints of Pucan(BL 61) and Shenmai(BL 62) on intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(01): 51-56. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||