Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 508-517.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.03.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiong's Shiwei Wendan decoction (熊氏十味温胆汤) attenuates plaque lesions and balances gut microbiota dysbiosis in ApoE-/- mice with high-fat diet
LIU Qian1( ), XIAO Liuchen2,3(
), XIAO Liuchen2,3( ), YUAN Yue1, DANG Xiaopeng1, WEN Jie1, TAN Moye4,5, LIU Yuxin1, GU Hongfeng6(
), YUAN Yue1, DANG Xiaopeng1, WEN Jie1, TAN Moye4,5, LIU Yuxin1, GU Hongfeng6( ), XIE Xuejiao7(
), XIE Xuejiao7( )
)
- 1 Graduate School of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China
2 Graduate School of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China
3 Department of preventive treatment of disease, Changde First Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changde 415099, China
4 Graduate School of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China
5 Department of Zhong jing' Theory, College of Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China
6 Hengyang Key Laboratory of Neurodegeneration and Cognitive Impairment and Institute of Neuroscience, Hengyang Medical College, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, China
7 Department of Zhong jing' Theory, College of Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China
-
Received:2024-02-22Accepted:2024-09-27Online:2025-06-15Published:2025-05-21 -
Contact:GU Hongfeng, Hengyang Key Laboratory of Neurodegeneration and Cognitive Impairment and Institute of Neuroscience, Hengyang Medical College, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, China.ghf513@sina.com ; Prof. XIE Xuejiao, Department of Zhong jing' Theory, College of Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, 410208, China.003809@hnucm.edu.cn ,Telephone: +86-15200825927 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: the Anti-Atherosclerotic Mechanism of Xiong’s Shiwei Wendan decoction based on the Regulation of Reverse Cholesterol Transport via the MicroRNA-33A Adenosine Triphosphate-binding Cassette Subfamily A Member 1/ Adenosine Triphosphate-binding Cassette Subfamily A Member 1 Pathway(81603600);Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China: the Anti-Atherosclerotic Mechanism of Xiong's Shiwei Wendan Decoction based on the Activation of Lipophagy Mediated by the AMP-activated Protein Kinase/Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Pathway(2021JJ30510);Health Research Project of Hunan Provincial Health Commission: the An-ti-Atherosclerotic Mechanism of Xiong's Shiwei Wendan Decoction based on Lipophagy Mediated by the MicroRNA-499a-3p/ Autophagy-related 5 Pathway(D202303018265)
Cite this article
LIU Qian, XIAO Liuchen, YUAN Yue, DANG Xiaopeng, WEN Jie, TAN Moye, LIU Yuxin, GU Hongfeng, XIE Xuejiao. Xiong's Shiwei Wendan decoction (熊氏十味温胆汤) attenuates plaque lesions and balances gut microbiota dysbiosis in ApoE-/- mice with high-fat diet[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 508-517.
share this article

Figure 1 Effect of XSWD-medicated serum and XSWD on THP-1 macrophages differentiation A: CCK-8 assay for THP-1 macrophages cultured in the presence of 10% XSWD-containing serum; B: ORO staining of THP-1 macrophages (× 912, scale bars = 10 μm); B1: cells of the control group; B2: cells of the model group; B3: cells of the L-XSWD group; B4: cells of the M-XSWD group; B5: cells of the H-XSWD group; C: area of Oil Red O measured from the images shown in (B) using ImageJ software. Control: normal control (incubated by complete medium); Model: model group (25 μg/mL ox-LDL + complete medium); L-XSWD: low-dose XSWD group (25 μg/mL ox-LDL + 1.25 mg/mL XSWD); M-XSWD: medium-dose XSWD group (25 μg/mL ox-LDL + 2.5 mg/mL XSWD); H-XSWD: high-dose XSWD group (25 μg/mL ox-LDL + 5 mg/mL XSWD). XSWD: Xiong's Shiwei Wendan decoction; CCK-8: cell counting kit-8; THP-1: Tsuchiya human peripheral blood mononuclear cell-1; ORO: oil red O; ANOVA: analysis of variance. Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA. All data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). aP < 0.0001, compared with the control group; bP < 0.01 and cP < 0.001, compared with the model group.

Figure 2 Effects of XSWD on AS lesions in ApoE-/- mice A: en face analysis of the aorta; A1: aorta of the control group; A2: aorta of the model group; A3: aorta of the atorvastatin group; A4: aorta of the L-XSWD group; A5: aorta of the M-XSWD group; A6: aorta of the H-XSWD group. B: ORO staining and analysis of aortic root plaque lesions (× 40, scale bars = 300 μm); B1: aortic root plaque lesions of the control group; B2: aortic root plaque lesions of the model group; B3: aortic root plaque lesions of the atorvastatin group; B4: aortic root plaque lesions of the L-XSWD group; B5: aortic root plaque lesions of the M-XSWD group; B6: aortic root plaque lesions of the H-XSWD group. C: lipid area of ORO in aortic root plaque. Control: normal control (fed by normal chow); Model: model group (fed by HFD); Atorvastatin: atorvastatin group (2.6 mg/kg atorvastatin + HFD); L-XSWD: low-dose XSWD group (9 g/kg XSWD + HFD); M-XSWD: medium-dose XSWD group (18 g/kg XSWD + HFD); H-XSWD: high-dose XSWD group (36 g/kg XSWD + HFD). XSWD: Xiong’s Shiwei Wendan decoction; ORO: oil red O; HFD: high-fat diet; ANOVA: analysis of variance. The statistical significance of lipid area was assessed by Welch’s ANOVA. All data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). aP < 0.001, compared with the control group; bP < 0.05, compared with the model group.
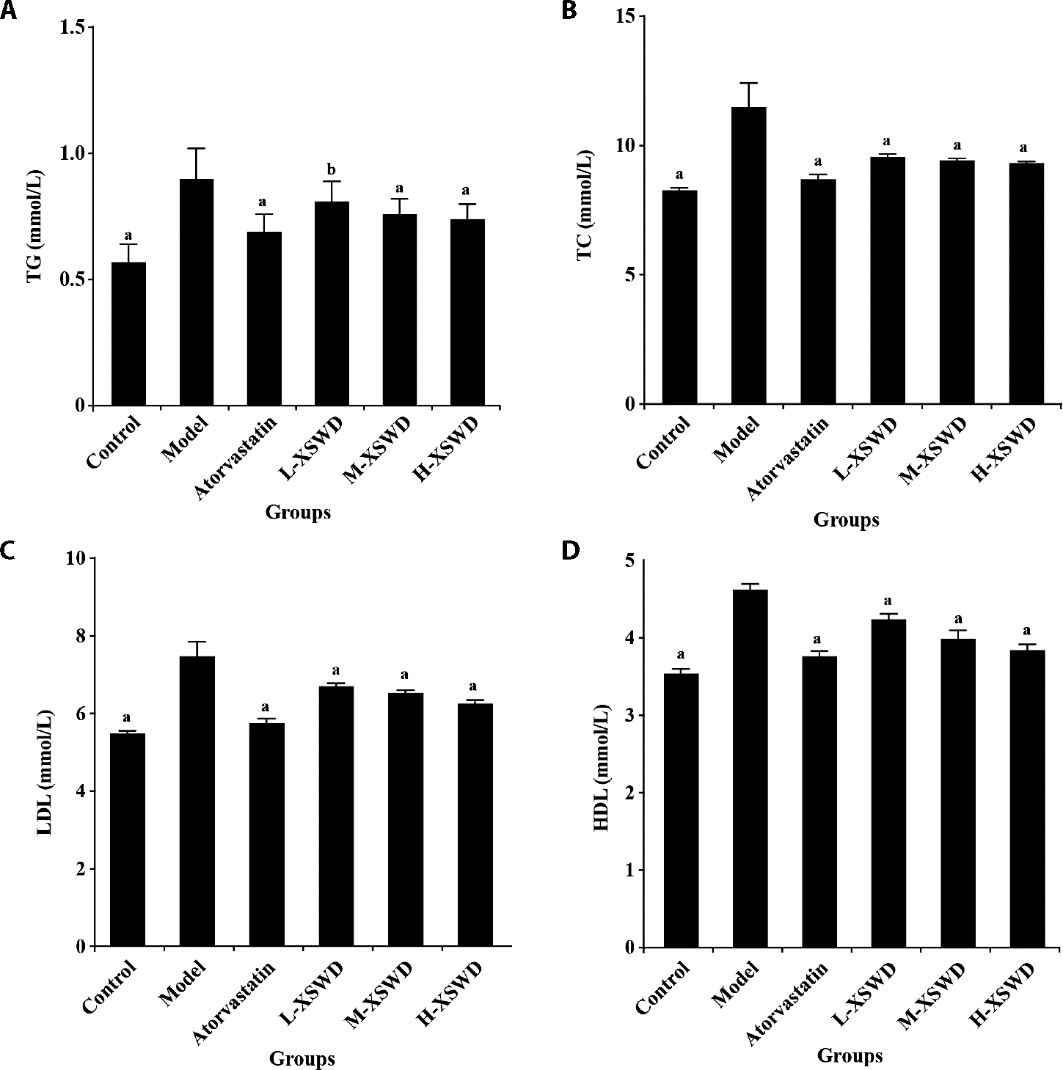
Figure 3 Effect of XSWD on serum lipid profile in ApoE-/- mice A: serum TG level. B: serum TC level. C: serum LDL level. D: serum HDL level. Control: normal control (fed by normal chow); Model: model group (fed by HFD); Atorvastatin: atorvastatin group (2.6 mg/kg atorvastatin + HFD); L-XSWD: low-dose XSWD group (9 g/kg XSWD + HFD); M-XSWD: medium-dose XSWD group (18 g/kg XSWD + HFD); H-XSWD: high-dose XSWD group (36 g/kg XSWD + HFD). XSWD: Xiong’s Shiwei Wendan decoction; TG: triglycerides; TC: total cholesterol; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; HFD: high-fat diet; ANOVA: analysis of variance. Statistical significance of all data was assessed using one-way ANOVA. All data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). aP < 0.01 and bP < 0.05, compared with the model group.

Figure 4 GM composition in AS mice after XSWD administration A: top 15 colonic gut microorganisms at phylum level; B: top 15 colonic gut microorganisms at genus level; C: Chao1 index of Alpha diversity; D: Shannon index of Alpha diversity; E: un-weighted unifrac PcoA plot. Control: normal control (fed by normal chow); Model: model group (fed by HFD); Atorvastatin: atorvastatin group (2.6 mg/kg atorvastatin + HFD); L-XSWD: low-dose XSWD group (9 g/kg XSWD + HFD); M-XSWD: medium-dose XSWD group (18 g/kg XSWD + HFD); H-XSWD: high-dose XSWD group (36 g/kg XSWD + HFD). GM: gut microbiota; AS: atherosclerosis; XSWD: Xiong’s Shiwei Wendan decoction; PcoA: principal coordinates analysis; HFD: high-fat diet. The statistical significance of Chao1 index and Shannon index were assessed by kruskal-wallis. All data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 5).
| 1. | Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation 2021; 143e254-743. |
| 2. |
Libby P, Buring JE, Badimon L, et al. Atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2019; 5: 56.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Fan L, Huang X, Xue W, et al. Effects of ruanmailing in blocking early stages of atherosclerosis by TNF- regulation via kir2.1. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022; 2022: 2836880. |
| 4. | Zhang X, Gao R, Zhou Z, et al. Uncovering the mechanism of huanglian-wuzhuyu herb pair in treating nonalcoholic steatohe-patitis based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. J Ethnopharmacol 2022; 296: 115405. |
| 5. | Wang ZY, Ouyang QL, Tan C. Medication rules of TCM master Xiong Jibo in treating chest bi-impediment and heartache by data mining. Hunan Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2023; 43: 189-96. |
| 6. | Xie XJ, Liu L. Clinical study on the treatment of chest stuffiness and pains with Shiwei Wendan decoction by Professor Xiong Jibai. Shi Yong Zhong Yi Nei Ke Za Zhi 2012; 26: 1-2. |
| 7. | Nogal A, Valdes AM, Menni C. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between gut microbiota and diet in cardio-metabolic health. Gut Microbes 2021; 13: 1-24. |
| 8. |
Wang Z, Zhao Y. Gut microbiota derived metabolites in cardiovascular health and disease. Protein Cell 2018; 9: 416-31.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Aja F, Stakheev D, Chernyavskiy O, Kían J, Akov HK. Immune activation by microbiome shapes the colon mucosa: comparison between healthy rat mucosa under conventional and germ-free conditions. J Immunotoxicol 2021; 181: 37-49. |
| 10. | Chase CCL. Enteric immunity: happy gut, healthy animal. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract 2018; 34: 1-18. |
| 11. | Chen L, Ishigami T, Doi H, Arakawa K, Tamura K. 2020; 98: 1235-44. |
| 12. | Chen JH, Yu L, Liu Y, Wu SW, Ding GA, Liao XZ. Efficacy of the wendan decoction on glucose and lipid metabolism and intestinal flora in patients with metabolic syndrome caused by olanzapine. Zhong Yi Lin Chuang Yan Jiu 2021; 13: 99-102. |
| 13. |
Jie Z, Xia H, Zhong SL, et al. The gut microbiome in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Commun 2017; 8: 845.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Li A, Wang N, Li N, et al. Modulation effect of chenpi extract on gut microbiota in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice. J Food Biochem 2021; 45: e13541. |
| 15. | Sun S, Wang K, Sun L, et al. Therapeutic manipulation of gut microbiota by polysaccharides of Wolfi Poria cocos reveals the contribution of the gut fungi-induced PGE(2) to alcoholic hepatic steatosis. Gut Microbes 2020; 12: 1830693. |
| 16. | National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. Beijing: China Medical Science Press 2015: 74-591. |
| 17. | Huang J, Huang X, Chen Z, Zheng Q, Sun R. Dose conversion among different animals and healthy volunteers in pharmacological study. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Yao Li Xue Yu Zhi Liao Xue 2004; 9: 1069-72. |
| 18. | Yang X, Zeng B. Effect of Qiyin granules on FFA, LEP and RETN levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease cell models. Xin Jiang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2019; 42: 676-80. |
| 19. | Duttaroy AK. Role of gut microbiota and their metabolites on atherosclerosis, hypertension and human blood platelet function: a review. Nutrients 2021; 13: 144. |
| 20. | Kang Y, Kang X, Yang H, et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates obesity in mice through modulation of gut microbiota dysbiosis and intestinal permeability. Pharmacol Res 2022; 175: 106020. |
| 21. | Chen XJ, Zhong BY, Wu HL, Xu DP. Inhibitory effect of wendan decoction on formation of foam cells induced by ox-LDL. Zhong Guo Bing Li Sheng Li Za Zhi 2020; 36: 1952. |
| 22. |
Gao H, Li L, Li L, et al. Danshensu promotes cholesterol efflux in RAW264.7 macrophages. Lipids 2016; 51: 1083.
DOI PMID |
| 23. | Hao D, Danbin W, Maojuan G, et al. Ethanol extracts of danlou tablet attenuate atherosclerosis via inhibiting inflammation and promoting lipid effluent. Pharmacol Res 2019; 146: 104306. |
| 24. | Wang PX, Deng XR, Zhang CH, Yuan HJ. Gut microbiota and metabolic syndrome. Chin Med J (Engl) 2020; 133: 808. |
| 25. |
Brandsma E, Kloosterhuis NJ, Koster M, et al. A proinflammatory gut microbiota increases systemic inflammation and accelerates atherosclerosis. Circ Res 2019; 124: 94.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Caesar R, Fåk F, Bäckhed F. Effects of gut microbiota on obesity and atherosclerosis via modulation of inflammation and lipid metabolism. J Intern Med 2010; 268: 320.
DOI PMID |
| 27. | Wang RR, Zhang LF, Chen LP, et al. Structural and functional modulation of gut microbiota by Jiangzhi granules during the amelioration of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021; 2021: 2234695. |
| 28. | Sui H, Zhang L, Gu K, et al. YYFZBJS ameliorates colorectal cancer progression in Apc (Min/+) mice by remodeling gut microbiota and inhibiting regulatory T-cell generation. Cell Commun Signal 2020; 18: 113. |
| 29. | Li S, Wang N, Tan HY, et al. Modulation of gut microbiota mediates berberine-induced expansion of immuno-suppressive cells to against alcoholic liver disease. Clin Transl Med 2020; 10: e112. |
| 30. | Yue C, Li M, Li J, et al. Medium-, long- and medium-chain-type structured lipids ameliorate high-fat diet-induced atherosclerosis by regulating inflammation, adipogenesis, and gut microbiota in ApoE(-/-) mice. Food Funct 2020; 11: 5142. |
| 31. | Liu J, Hefni ME, Witthöft CM, et al. Effects of whole brown bean and its isolated fiber fraction on plasma lipid profile, atherosclerosis, gut microbiota, and microbiota-dependent metabolites in Apoe(-/-) mice. Nutrients 2022; 14: 937. |
| 32. | Duan M, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Zou R, Guo M, Zheng H. Characteristics of gut microbiota in people with obesity. PLoS One 2021; 16: e0255446. |
| 33. | Sze MA, Schloss PD. Looking for a signal in the noise: revisiting obesity and the microbiome. mBio 2016; 7: e01018. |
| 34. |
Tang WH, Kitai T, Hazen SL. Gut microbiota in cardiovascular health and disease. Circ Res 2017; 120: 1183.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Carmody RN, Gerber GK, Luevano JM, et al. Diet dominates host genotype in shaping the murine gut microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2015; 17: 72.
DOI PMID |
| 36. | Beam A, Clinger E, Hao L. Effect of diet and dietary components on the composition of the gut microbiota. Nutrients 2021; 13: 2795. |
| 37. |
Wu J, Wei Z, Cheng P, et al. Rhein modulates host purine metabolism in intestine through gut microbiota and ameliorates experimental colitis. Theranostics 2020; 10: 10665.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Nilsson A, Akrami R, et al. Dietary fiber-induced improvement in glucose metabolism is associated with increased abundance of prevotella. Cell Metab 2015; 22: 971.
DOI PMID |
| 39. |
Miyamoto J, Igarashi M, Watanabe K, et al. Gut microbiota confers host resistance to obesity by metabolizing dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids. Nat Commun 2019; 10: 4007.
DOI PMID |
| 40. |
Cummings JH, Pomare EW, Branch WJ, Naylor CP, Macfarlane GT. Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood. Gut 1987; 28: 1221.
DOI PMID |
| 41. | Green M, Arora K, Prakash S. Microbial medicine: prebiotic and probiotic functional foods to target obesity and metabolic syndrome. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 2890. |
| 42. |
Bartolomaeus H, Balogh A, Yakoub M, et al. Short-chain fatty acid propionate protects from hypertensive cardiovascular damage. Circulation 2019; 139: 1407.
DOI PMID |
| 43. | Gasaly N, de Vos P, Hermoso MA. Impact of bacterial metabolites on gut barrier function and host immunity: a focus on bacterial metabolism and its relevance for intestinal inflammation. Front Immunol 2021; 12: 658354. |
| 44. |
Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Bäckhed F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016; 165: 1332.
DOI PMID |
| 45. | Popeijus HE, Zwaan W, Tayyeb JZ, Plat J. Potential contribution of short chain fatty acids to hepatic apolipoprotein A-I production. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 5986. |
| 46. | Kimberley L, Varun S, Ayesha R, et al. Bridging the gap between gut microbial dysbiosis and cardiovascular diseases. Nutrients 2017; 9: 859. |
| 47. |
Hosomi K, Saito M, Park J, et al. Oral administration of blautia wexlerae ameliorates obesity and type 2 diabetes via metabolic remodeling of the gut microbiota. Nat Commun 2022; 13: 4477.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | LI Yue, PAN Jiaxiang, YANG Guanlin, YU Jiajia, WU Xize, MIN Dongyu, CHENG Meijia, YU Dongdong, NAN Minghua, GAO Xiaoyu, PANG Linlin, GONG Lihong, JIA Lianqun. Mechanism of Huayu Qutan recipe (化瘀祛痰方) anti-atherosclerosis mediates lipophagy via mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1/ transcription factor EB signaling pathway in ApoE-/-mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 291-302. |
| [2] | WU Jiaman, NING Yan, TAN Liya, MA Fei, LIN Yanting, ZHUO Yuanyuan. Difference of the gut microbiota of premature ovarian insufficiency in two traditional Chinese syndromes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 132-139. |
| [3] | XU Jian, LIU Yuntao, LUO Zhihao, ZHAO Zhen, WANG Dawei, LIU Qing. Chinese patent medicine for atherosclerosis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1082-1090. |
| [4] | WANG Yiying, LIU Jianjun, XIONG Yongjian, ZHANG Yongli, WEN Yuqi, XUE Mengli, GUO Huishu, QIU Juanjuan. Analysis of composition of gut microbial community in a rat model of functional dyspepsia treated with Simo Tang (四磨汤) [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1168-1176. |
| [5] | LIAO Mengting, LI Tao, CHU Fuhao, CHEN Yan, LOU Ni, ZHUANG Yuan, BO Rongqiang, DING Xia. Weichang’ an pill (胃肠安丸) alleviates functional dyspepsia through modulating brain-gut peptides and gut microbiota [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1177-1186. |
| [6] | HUANG Xiaona, LI Yuzhen, ZHU Chenyang, ZHU Hengzhou, JIANG Chenyu, ZHU Xiaodan, ZHANG Chencen, JIN Chunhui. Weitiao No. 3 (微调3号方) enhances the efficacy of anti-programmed cell death protein-1 immunotherapy by modulating the intestinal microbiota in an orthotopic model of gastric cancer mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 906-915. |
| [7] | SUN Chuanbo, XU Guangpei, JIANG Ping, HUANG Shipping, CHEN Cunwu, HE Yanfei. Protective effect of Zhizi Huangqi Shanzha formula (栀子黄芪山楂方) on aflatoxin poisoning in mice and its effect on intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 926-933. |
| [8] | REN Li, HAI Yang, YANG Xue, LUO Xianqin. Yemazhui (Herba Eupatorii Lindleyani) ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via modulation of the toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor kappa-B/nod-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 protein signaling pathway and intestinal flora in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 303-314. |
| [9] | HENG Xianpei, WANG Zhita, LI Liang, YANG Liuqing, HUANG Suping, JIN Lang, HE Weidong. Mechanisms of Dangua Fang (丹瓜方) in multi-target and multi-method regulation of glycolipid metabolism based on phosphoproteomics [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 334-344. |
| [10] | CHANG Fengjin, ZHOU Peng, LI Guoying, ZHANG Weizhi, ZHANG Yanyan, PENG Daiyin, CHEN Guangliang. Taohong Siwu decoction (桃红四物汤) ameliorates atherosclerosis in rats possibly through toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88/nuclear factor-κB signal pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 103-112. |
| [11] | LIU Huihui, FENG Jun, LIU Jianhe, CHENG Choufu, HU Guoheng. Efficacy of Jiangzhi Xiaoban tablet (降脂消斑片) on toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa B/nod-like receptor protein 3 signaling pathway in mice with atherosclerosis induced by high-fat diet [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 88-94. |
| [12] | LIU Yue, ZHANG Fan, HAN Xiaomeng, XU Ningyang, ZHAO Yu, WANG Qige, WANG Jianan, LU Bingjiu, Zhang Yan. Jianpi Qutan Fang (健脾祛痰方) induces anti-atherosclerosis and ameliorates endothelial cell injury in high-fat diet rats via an anti-inflammatory and inhibiting Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1168-1175. |
| [13] | LI Chaoran, YANG Yan, FENG Chuwen, LI Heng, QU Yuanyuan, WANG Yulin, WANG Delong, WANG Qingyong, GUO Jing, SHI Tianyu, SUN Xiaowei, WANG Xue, HOU Yunlong, SUN Zhongren, YANG Tiansong. Integrated 'omics analysis for the gut microbiota response to moxibustion in a rat model of chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1176-1189. |
| [14] | ZHOU Jun, WANG Junhua, LI Xiaobing, WAN Chenyi, LI Fangjun, Lü Yanni, CHEN Hao, SUN Meiying. Efficacy of Heshouwu (Radix Polygoni Multiflori) on gut mircobiota in mice with autoimmune encephalomyelitis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 676-685. |
| [15] | JIANG Yiqian, ZHOU Xibin, PU Wenyuan, ZHOU Chunxiang. Sanwu Baisan decoction (三物白散) inhibits colorectal cancer progression in mice by remodeling gut microbiota and tumorigenesis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 466-473. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

