Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 725-733.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2023.04.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective mechanisms of Tuina therapy against lipopolysaccharide-induced fever in young rabbits based on untargeted metabolomics analysis
LIU Di1, ZHANG Yingqi1( ), YU Tianyuan1(
), YU Tianyuan1( ), LIU Zhifeng1, JIAO Yi1, WANG Hourong1, XU Yajing1, GUAN Qian1, CHEN Lulu2, HU Hui3
), LIU Zhifeng1, JIAO Yi1, WANG Hourong1, XU Yajing1, GUAN Qian1, CHEN Lulu2, HU Hui3
- 1 School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 102401, China
2 Department of Acupuncture-Moxibustion, Beijing Massage Hospital, Beijing 100035, China
3 Department of Acupuncture-Moxibustion, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100078, China
-
Received:2022-07-22Accepted:2022-11-15Online:2023-08-15Published:2023-07-03 -
Contact:ZHANG Yingqi, School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 102401, China. zhangyingqi0305@163.com. Telephone: +86-18210220868; +86-15810409565
YU Tianyuan, School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 102401, China. yutianyuan@sina.com. -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: to Explore the Antipyretic Effects and Mechanism of the “Reducing Fever Six Methods” Technique on Infant Rabbits with Fever from the Peripheral TLR4/NF-kB Signaling Pathway to the Central Positive and Negative Mediators(81873392)
Cite this article
LIU Di, ZHANG Yingqi, YU Tianyuan, LIU Zhifeng, JIAO Yi, WANG Hourong, XU Yajing, GUAN Qian, CHEN Lulu, HU Hui. Protective mechanisms of Tuina therapy against lipopolysaccharide-induced fever in young rabbits based on untargeted metabolomics analysis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 725-733.
share this article
| Group | n | Anal temperature (℃) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 1 h | 2 h | 3 h | ||
| Saline | 8 | 39.10±0.23 | 39.06±0.16 | 39.05±0.14 | 39.09±0.11 |
| Model | 8 | 39.09±0.18 | 40.09±0.23 | 40.31±0.33 | 40.66±0.49 |
| Tuina | 8 | 39.19±0.06 | 40.10±0.05 | 39.40±0.32a | 39.64±0.46a |
Table 1 Comparison of the anal temperature of young rabbits in 3 groups ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | Anal temperature (℃) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 1 h | 2 h | 3 h | ||
| Saline | 8 | 39.10±0.23 | 39.06±0.16 | 39.05±0.14 | 39.09±0.11 |
| Model | 8 | 39.09±0.18 | 40.09±0.23 | 40.31±0.33 | 40.66±0.49 |
| Tuina | 8 | 39.19±0.06 | 40.10±0.05 | 39.40±0.32a | 39.64±0.46a |
| Group | n | TRI1 | 120 min TRI2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saline Model Tuina | 8 | 0.16±0.14 1.61±0.45a 1.49±0.22b | 0.82±0.64 9.14±2.29a 4.34±1.28ab |
| 8 | |||
| 8 |
Table 2 Comparison of TRI1 and TRI2 in 3 groups($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | TRI1 | 120 min TRI2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saline Model Tuina | 8 | 0.16±0.14 1.61±0.45a 1.49±0.22b | 0.82±0.64 9.14±2.29a 4.34±1.28ab |
| 8 | |||
| 8 |
| Group | n | Blood | Hypothalamus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saline | 8 | 587±22 667±8a 634±24ab | 635±42 730±19b 686±9ab |
| Model | 8 | ||
| Tuina | 8 |
Table 3 Comparison of PGE2 expression in the blood and hypothalamus in 3 groups (pg/mL)
| Group | n | Blood | Hypothalamus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saline | 8 | 587±22 667±8a 634±24ab | 635±42 730±19b 686±9ab |
| Model | 8 | ||
| Tuina | 8 |
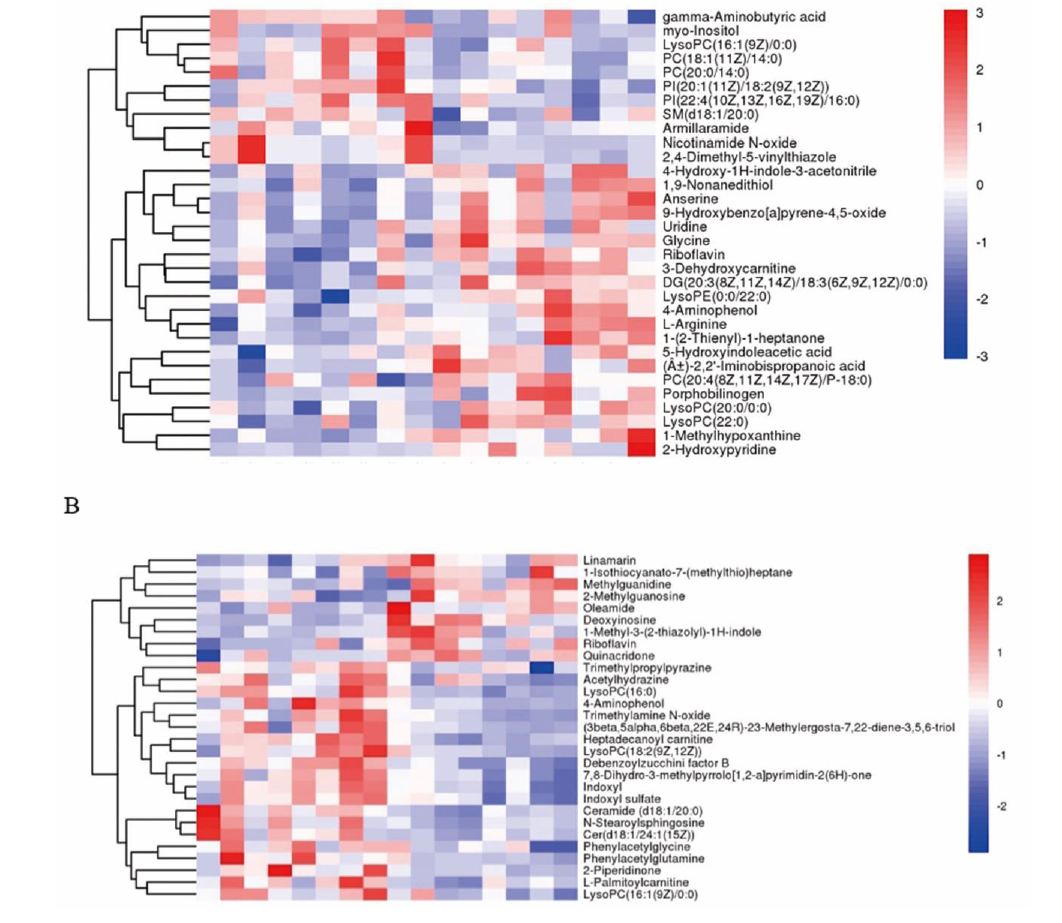
Figure 2 Analysis of the potential biomarkers A: heat map of the hierarchical cluster analysis of the Tuina group vs the model group; B: heat map of the hierarchical cluster analysis of the saline group vs the model group.
| Metabolite name | mz | VIP value | P value | Fold Change | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myo-inositol | 203.05 | 1.66 | 0.04 | 1.40 | ↑ |
| Nicotinamide N-oxide | 139.05 | 2.44 | 0.03 | 2.42 | ↑ |
| 2, 4-Dimethyl-5-vinylthiazole | 140.05 | 2.40 | 0.03 | 3.27 | ↑ |
| Gamma-aminobutyric acid | 104.07 | 1.58 | 0.05 | 1.23 | ↑ |
| PC [20:4(8Z, 11Z, 14Z, 17Z)/P-18:0] | 794.61 | 1.90 | 0.03 | 0.80 | ↓ |
| PC [18:1(11Z)/14:0] | 732.55 | 1.79 | 0.04 | 1.79 | ↑ |
| PC (20:0/14:0) | 762.59 | 1.57 | 0.04 | 1.39 | ↑ |
| SM (d18:1/20:0) | 759.64 | 1.63 | 0.04 | 1.19 | ↑ |
| Armillaramide | 556.53 | 1.83 | 0.04 | 1.33 | ↑ |
| PI [20:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z, 12Z)] | 889.57 | 2.08 | 0.01 | 1.34 | ↑ |
| PI [22:4(10Z, 13Z, 16Z, 19Z)/16:0] | 887.56 | 1.84 | 0.02 | 1.24 | ↑ |
| DG [20:3(8Z, 11Z, 14Z)/18:3(6Z, 9Z, 12Z)/0:0] | 641.51 | 1.90 | 0.02 | 0.71 | ↓ |
| 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid | 192.06 | 1.60 | 0.04 | 0.73 | ↓ |
| LysoPC(22:0) | 580.43 | 1.71 | 0.04 | 0.74 | ↓ |
| (?±)-2, 2'-Iminobispropanoic acid | 162.08 | 1.93 | 0.02 | 0.72 | ↓ |
| Porphobilinogen | 227.10 | 1.72 | 0.04 | 0.73 | ↓ |
Table 4 Results of differential metabolite screening of the Tuina group versus the model group
| Metabolite name | mz | VIP value | P value | Fold Change | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myo-inositol | 203.05 | 1.66 | 0.04 | 1.40 | ↑ |
| Nicotinamide N-oxide | 139.05 | 2.44 | 0.03 | 2.42 | ↑ |
| 2, 4-Dimethyl-5-vinylthiazole | 140.05 | 2.40 | 0.03 | 3.27 | ↑ |
| Gamma-aminobutyric acid | 104.07 | 1.58 | 0.05 | 1.23 | ↑ |
| PC [20:4(8Z, 11Z, 14Z, 17Z)/P-18:0] | 794.61 | 1.90 | 0.03 | 0.80 | ↓ |
| PC [18:1(11Z)/14:0] | 732.55 | 1.79 | 0.04 | 1.79 | ↑ |
| PC (20:0/14:0) | 762.59 | 1.57 | 0.04 | 1.39 | ↑ |
| SM (d18:1/20:0) | 759.64 | 1.63 | 0.04 | 1.19 | ↑ |
| Armillaramide | 556.53 | 1.83 | 0.04 | 1.33 | ↑ |
| PI [20:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z, 12Z)] | 889.57 | 2.08 | 0.01 | 1.34 | ↑ |
| PI [22:4(10Z, 13Z, 16Z, 19Z)/16:0] | 887.56 | 1.84 | 0.02 | 1.24 | ↑ |
| DG [20:3(8Z, 11Z, 14Z)/18:3(6Z, 9Z, 12Z)/0:0] | 641.51 | 1.90 | 0.02 | 0.71 | ↓ |
| 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid | 192.06 | 1.60 | 0.04 | 0.73 | ↓ |
| LysoPC(22:0) | 580.43 | 1.71 | 0.04 | 0.74 | ↓ |
| (?±)-2, 2'-Iminobispropanoic acid | 162.08 | 1.93 | 0.02 | 0.72 | ↓ |
| Porphobilinogen | 227.10 | 1.72 | 0.04 | 0.73 | ↓ |

Figure 3 Analysis of the metabolic pathway A: graph of the pathway analysis of the saline group versus the model group; B: graph of the pathway analysis of the Tuina group versus the model group. Each bubble in the bubble diagram represents a metabolic pathway. The bubble's horizontal coordinates and bubble size indicate the influence factor size of the pathway in the topological analysis; the vertical coordinates of the bubble and the bubble color indicate the P-value of the enrichment analysis.
| 1. |
Evans SS, Repasky EA, Fisher DT. Fever and the thermal regulation of immunity: the immune system feels the heat. Nat Rev Immunol 2015; 15: 335-49.
DOI PMID |
| 2. | Urbane UN, Likopa Z, Gardovska D, et al. Beliefs, practices and health care seeking behavior of parents regarding fver in children. Medicina (Kaunas) 2019; 55: 398. |
| 3. | Li HP, Chen ZG, Liu GP, et al. Clinical efficacy of Lingnan characteristic Tuina in treating 60 cases of pediatric exogenous fever. Sichuan Zhong Yi 2020; 38: 211-4. |
| 4. | Wei LZ, Xu L. Central inhibitory effect of Qingtianheshui on endotoxic fever in infant rabbits and its related clinical application. Xin Zhong Yi 2020; 52: 148-51. |
| 5. |
Geng C, Guo Y, Wang C, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of lipopolysaccharide-induced changes in rats based on metabolomics. J Inflamm Res 2020; 13: 477-86.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Liu HY, Zhang L, Zhao BS, et al. Hypothalamus metabolomic profiling to elucidate the tissue-targeted biochemical basis of febrile response in yeast-induced pyrexia rats. Chem Biol Interact 2015; 231: 61-70.
DOI URL |
| 7. |
Cao H, Zhang A, Zhang H, et al. The application of metabolomics in Traditional Chinese Medicine opens up a dialogue between Chinese and Western medicine. Phytother Res 2015; 29: 159-66.
DOI PMID |
| 8. | Yang GJ, Chen XL, Shao P, et al. Study on the endotoxin method of rabbit fever animal model and its standardization. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Dong Wu Xue Bao 2001; 9: 57-60. |
| 9. | Wu XL. Study on the time-effect relationship of Qingtianheshui on the reduction of fever in pediatric exogenous fever. Chengdu: Chengdu university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015: 16. |
| 10. | Jiao Y, Liu ZF, Yu TY, et al. Effect of “Six Methods of Antipyretic” on TLR4/NF-κB and inflammatory factors LPS-induced fever rabbits. Huan Qiu Zhong Yi Yao 2022; 15, 7-12. |
| 11. |
Milton AS, Wendlandt S. Effects on body temperature of prostaglandins of the A, E and F series on injection into the third ventricle of unanaesthetized cats and rabbits. J Physiol 1971; 218: 325-36.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Johnson CH, Ivanisevic J, Siuzdak G. Metabolomics: beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2016; 17: 451-9.
DOI |
| 13. | Liang WS, Liu YL, Li ZY, et al. Study on antipyretic effect and mechanism of Ban-lian Bai-du Oral-liquid (BBQ). Dong Wu Yi Xue Jin Zhan 2019; 40: 74-8. |
| 14. | Yang JZ. The great compendium of acupuncture and moxibustion. Tianjin: scientific and technical publishers, 2017: 175. |
| 15. | Yao X. The Effect on the rabbits’body temperature by pushing down or up Ji (spine). Jinan: Shandong university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2001: 7. |
| 16. |
Oren R, Farnham AE, Saito K, et al. Metabolic patterns in three types of phagocytizing cells. J Cell Biol 1963; 17: 487-501.
PMID |
| 17. |
Toyosawa T, Suzuki M, Kodama K, et al. Effects of intravenous infusion of highly purified vitamin B2 on lipopolysaccharide-induced shock and bacterial infection in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2004; 492: 273-80.
PMID |
| 18. |
Korbecki J, Bajdak-Rusinek K. The effect of palmitic acid on inflammatory response in macrophages: an overview of molecular mechanisms. Inflamm Res 2019; 68: 915-32.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Liu J, Zong ZY, Zhang WH, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide alleviates LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative stress via decreasing COX-2 expression in macrophages. Front Mol Biosci 2021; 8: 702107.
DOI URL |
| 20. |
Yien YY, Ringel AR, Paw BH. Mitochondrial transport of protoporphyrinogen IX in erythroid cells. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 20742-3.
PMID |
| 21. | Dutra FF, Alves LS, Rodrigues D, et al. Hemolysis-induced lethality involves inflammasome activation by heme. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: E4110-8. |
| 22. |
Zhang C, He J, Wang X, et al. Dietary gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) improves non-specific immunity and alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced immune overresponse in juvenile Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Fish Shellfish Immunol 2022; 124: 480-9.
DOI URL |
| 23. |
Mota CMD, Rodrigues-Santos C, Fernández RAR, et al. Central serotonin attenuates LPS-induced systemic inflammation. Brain Behav Immun 2017; 66: 372-81.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Zhong Z, Wheeler MD, Li X, et al. L-Glycine: a novel antiinflammatory, immunomodulatory, and cytoprotective agent. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2003; 6: 229-40.
DOI URL |
| 25. | Zhang Y, Ma X, Jiang D, et al. Glycine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome and NRF2 signaling. Nutrients 2020; 12: 611. |
| 26. | Zhang YQ, Liu ZF, Yu TY, et al. Effects of six antipyretic methods of Tuina on COX-2/PGE2 expression in peripheral of LPS-induced infant rabbits. Huan Qiu Zhong Yi Yao 2022; 15: 211-16. |
| 27. |
Cheng ZX, Guo C, Chen ZG, et al. Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism confounds efficacy of complement-mediated killing. Nat Commun 2019; 10: 3325.
DOI |
| 28. |
Xiao N, Nie M, Pang H, et al. Integrated cytokine and metabolite analysis reveals immunometabolic reprogramming in COVID-19 patients with therapeutic implications. Nat Commun 2021; 12: 1618.
DOI PMID |
| 29. | Qiu Y, Yang X, Wang L, et al. L-arginine inhibited inflammatory response and oxidative stress induced by lipopolysaccharide via arginase-1 signaling in IPEC-J2 cells. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 1800. |
| 30. |
Bronte V, Zanovello P. Regulation of immune responses by L-arginine metabolism. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5: 641-54.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Rath M, Müller I, Kropf P, et al. Metabolism via arginase or nitric oxide synthase: two competing arginine pathways in macrophages. Front Immunol 2014; 5: 532. |
| [1] | LI Chaoran, YANG Yan, FENG Chuwen, LI Heng, QU Yuanyuan, WANG Yulin, WANG Delong, WANG Qingyong, GUO Jing, SHI Tianyu, SUN Xiaowei, WANG Xue, HOU Yunlong, SUN Zhongren, YANG Tiansong. Integrated 'omics analysis for the gut microbiota response to moxibustion in a rat model of chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1176-1189. |
| [2] | WANG Miao, ZHU Yan, ZHAO Hui, ZHAO Hongfang. Moxibustion enables protective effects on rheumatoid arthritis-induced myocardial injury via transforming growth factor beta1 signaling and metabolic reprogramming [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1190-1199. |
| [3] | JIANG Wenjing, JIANG Huaying, YUAN Lihua, SA Yuanhong, XIAO Jimei, SUN Hongqi, SONG Jingyan, SUN Zhengao. Xiaoyi Yusi decoction (消异育嗣汤) improves in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer outcomes in patients with endometriosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 1026-1033. |
| [4] | HONG Zongchao, CAI Quan, DUAN Xueyun, YANG Yanfang, WU Hezhen, JIANG Nan, FAN Heng. Effect of compound Sophorae decoction in the treatment of ulcerative colitis by tissue extract metabolomics approach [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 414-423. |
| [5] | Liu Mi, Shen Jiacheng, Liu Caichun, Zhong Huan, Yang Qing, Shu Wenna, Ma Mingzhu, Dong Jiyang, Yang Zongbao, Chang Xiaorong, She Chang, Yu Shu. Effects of moxibustion and acupuncture at Zusanli(ST 36) and Zhongwan(CV 12) on chronic atrophic gastritis in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 827-835. |
| [6] | Feng Xuanchao, Yang Zheng, Chu Yuguang, Du Bai, Su Mei, Li Yi, Wang Yinghong, Jiang Chunying, Hu Yuanhui. ~1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic study on efficacy of Qingrehuatan decoction against abundant phlegm-heat syndrome in young adults with essential hypertension [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(01): 28-35. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||