Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 695-703.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220909.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Qinghua decoction (清化饮) improves chronic nonbacterial prostatitis possibly via regulating the chromogranin A/nerve growth factor/tyrosine kinase A signaling pathway mediated by inflammatory factors
HAN Yunpeng1,2, YU Wentao1, ZHANG Ying1, XU Huazhou1, DENG Guoxing1( ), FANG Chaoyi1,2(
), FANG Chaoyi1,2( )
)
- 1 School of Basic Medical Sciences, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China
2 Hebei Key Laboratory of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine for Lung Disease Research, Shijiazhuang 050091, China
-
Received:2022-04-22Accepted:2022-07-08Online:2023-08-15Published:2022-09-09 -
Contact:Prof. FANG Chaoyi, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China. hbfcy@163.com. Telephone: +86-311-89926162; +86-311-89926015
Prof. DENG Guoxing, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China. deng6191@163.com -
Supported by:Hebei Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Project: Study on the Neuroendocrine Mechanism of Chronic Prostatitis Rats Regulated by the Method of Clearing heat and Dampness, Activating Blood and Removing Stasis(2019087);Hebei Provincial Department of Education for Postgraduate Innovation Ability Training Project: the Mechanism of Improving Pulmonary Function of COPD Rats with Lung Qi Deficiency by Regulating Intestinal Bacteria with Peitu Shengjin Formula(CXZZBS2020151);Provincial Universities Basic Research Funds Special Project: Study on the Mechanism of Shenling Baizhu Powder Based on Lung Intestine Axis to Interfere with the Deficiency of Lung and Spleen in Experimental COPD(YJZ2019010)
Cite this article
HAN Yunpeng, YU Wentao, ZHANG Ying, XU Huazhou, DENG Guoxing, FANG Chaoyi. Qinghua decoction (清化饮) improves chronic nonbacterial prostatitis possibly via regulating the chromogranin A/nerve growth factor/tyrosine kinase A signaling pathway mediated by inflammatory factors[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 695-703.
share this article

Figure 1 Diagram of the experimental protocol Control: Normal control group; Model: Model group; QLTY: Qianlie Tongyu capsule group (0.5 g·kg-1·d-1); QH-L: Qinghua decoction low-dose (1.25 g·kg-1·d-1); QH-M: Qinghua decoction medium-dose group (2.5 g·kg-1·d-1); QH-H: Qinghua decoction high-dose group (5 g·kg-1·d-1). The drug was administered by gavage once a day for 4 weeks. ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; PCR: polymerase chain reaction.

Figure 2 Effect of Qinghua decoction on pathomorphology of prostate in rats with CNP (HE, ×200) A: Normal control group; B: Model group; C: Qianlie Tongyu capsule group (0.5 g·kg-1·d-1); D: Qinghua decoction low-dose group (1.25 g·kg-1·d-1); E: Qinghua decoction medium-dose group (2.5 g·kg-1·d-1); F: Qinghua decoction high-dose group (5 g·kg-1·d-1); the scale is 1 mm. Normal control and model groups were given normal saline (10 mL·kg-1 d-1) by gavage for 28 d. The Qianlie Tongyu capsule group received Qianlie Tongyu capsules (0.5 g·kg-1·d-1) for 28 d, The Qinghua decoction low-, medium-, and high dose groups were given Qinghua decoction (1.25, 2.5, and 5 g kg-1·d-1, respectively) for 28 d. Each group received the drug by gavage once a day using an equal volume and unequal concentration method. Body weight was measured every seven days, and the dosage volume was adjusted according to the change in body weight. CNP: chronic nonbacterial prostatitis; HE: hematoxylin-eosin.
| Group | n | TNF-α | IL-1β | IL-6 | IL-8 | IL-10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6 | 18.1±2.0 | 25.0±3.2 | 18.4±3.3 | 18.6±1.2 | 14.8±1.2 |
| Model | 6 | 24.2±2.0a | 35.6±3.7a | 27.2±3.5a | 24.7±1.6a | 9.4±1.6a |
| QLTY | 6 | 20.6±3.0b | 30.4±5.5b | 21.4±2.3c | 21.9±2.0b | 12.2±1.8c |
| QH-L | 6 | 23.4±2.3 | 34.4±3.4 | 25.7±2.7 | 21.1±3.2b | 11.9±1.6c |
| QH-M | 6 | 21.1±1.7b | 33.0±1.3 | 22.9±2.5b | 22.5±1.5 | 12.5±1.7c |
| QH-H | 6 | 20.9±2.6b | 27.4±4.8c | 21.9±3.7c | 19.8±3.1c | 14.0±0.9cd |
Table 1 Effect of Qinghua decoction on the expression of TNF-α, IL-1 β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10 in rats with CNP (pg/mL, $\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | TNF-α | IL-1β | IL-6 | IL-8 | IL-10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6 | 18.1±2.0 | 25.0±3.2 | 18.4±3.3 | 18.6±1.2 | 14.8±1.2 |
| Model | 6 | 24.2±2.0a | 35.6±3.7a | 27.2±3.5a | 24.7±1.6a | 9.4±1.6a |
| QLTY | 6 | 20.6±3.0b | 30.4±5.5b | 21.4±2.3c | 21.9±2.0b | 12.2±1.8c |
| QH-L | 6 | 23.4±2.3 | 34.4±3.4 | 25.7±2.7 | 21.1±3.2b | 11.9±1.6c |
| QH-M | 6 | 21.1±1.7b | 33.0±1.3 | 22.9±2.5b | 22.5±1.5 | 12.5±1.7c |
| QH-H | 6 | 20.9±2.6b | 27.4±4.8c | 21.9±3.7c | 19.8±3.1c | 14.0±0.9cd |

Figure 3 Effect of Qinghua decoction on CgA, NGF and TrkA protein expression in rats with CNP A: protein bands for each group; B-D: Protein content of CgA, NGF, and TrkA, inter-group control. Control: Normal control group; Model: Model group; QLTY: Qianlie Tongyu capsule group (0.5 g kg-1· d-1); QH-L: Qinghua decoction low-dose group (1.25 g·kg-1 d-1); QH-M: Qinghua decoction medium-dose group (2.5 g· kg-1 d-1); QH-H: Qinghua decoction high-dose group (5 g· kg-1 d-1). The drug was administered by gavage once a day for 4 weeks. CgA: chromogranin A; NGF: nerve growth factor; TrkA: tyrosine kinase A; CNP: chronic nonbacterial prostatitis. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). Compared to the normal control group, aP < 0.01; compared to the model group, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.05; compared to the Qianlie Tongyu capsule group, dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01.
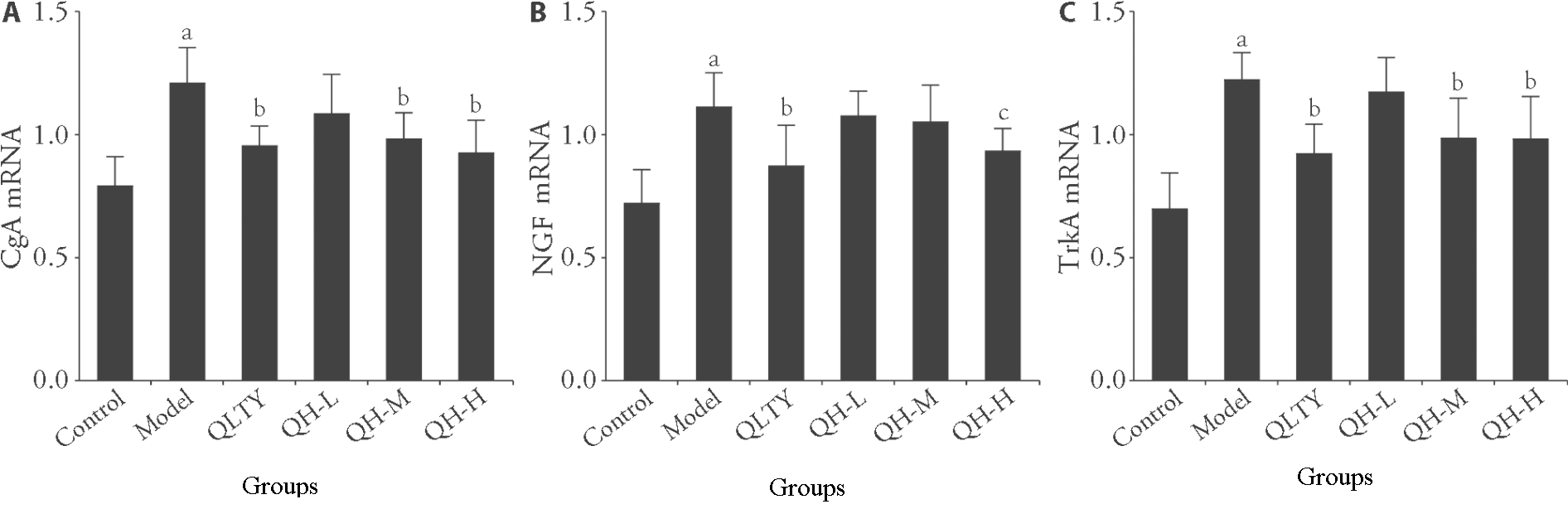
Figure 4 Effect of Qinghua decoction on CgA, NGF, and TrkA gene expression in rats with CNP A: the relative quantitative gene expression of CgA in lung tissue; B: the relative quantitative gene expression of NGF in lung tissue; C: the relative quantitative gene expression of TrkA in lung tissue. Control: Normal control group; Model: Model group; QLTY: Qianlie Tongyu capsule group (0.5 g·kg-1 d-1); QH-L: Qinghua decoction low-dose group (1.25 g·kg-1 d-1); QH-M: Qinghua decoction middle-dose group (2.5 g·kg-1 d-1); QH-H: Qinghua decoction high-dose group (5 g·kg-1 d-1). The drug was administered by gavage once a day for 4 weeks. CgA: chromogranin A; NGF: nerve growth factor; TrkA: tyrosine kinase A; CNP: chronic nonbacterial prostatitis. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). Compared with the normal control group, aP < 0.01; compared with the model group, bP <0.01, cP < 0.05.
| 1. | Li HS, Wang B, Zhao B. Consensus of experts in TCM diagnosis and treatment of chronic prostatitis. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao 2015; 34: 412-5. |
| 2. | Chen XP, Wang JP, Zhao JZ. Surgical science. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2018: 541-2. |
| 3. | Zhu YX, Xu NG. Clinical treatment of chronic nonbacterial prostatitis of kidney Yang deficiency type by acupuncture of Sanhuang points. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2019; 44: 443-5, 458. |
| 4. | Fan S, Hao ZY, Zhang L, et al. Increased chromogranin A and neuron-specific enolase in rats with chronic nonbacterial prostatitis induced by 17-beta estradiol combined with castration. Inter J Clinical Exp Pathol 2014; 7: 3992-9. |
| 5. | Jiang FZ, Yu Y, Wang W, Shen C, Lv H, Yang B. Clinical efficacy of chlormethadone combined with solinacin in the treatment of type III prostatitis and its effect on nerve growth factor, macrophage inflammatory protein-1α and interferon-γ in prostatic fluid. Lin Chuang Jun Yi Za Zhi 2019; 47: 99-100. |
| 6. | Zhu YH, Xu YF, Chen YW, Meng J, Shu C. Expressions and clinical significances of nerve growth factorand inflammatory factors in serum and expressed prostatic secretionsin the elderly patients with prostatitis. Xian Dai Sheng Wu Yi Xue Jin Zhan 2018; 18: 272-5. |
| 7. |
Huang J, Yao JL, Zhang L, et al. Differential expression of interleukin-8 and its receptors in the neuroendocrine and non-neuroendocrine compartments of prostate cancer. Am J Pathol 2005; 166: 1807-15.
PMID |
| 8. |
Naslund MJ, Strandberg JD, Coffey DS. The role of androgens and estrogens in the pathogenesis of experimental nonbacterial prostatitis. J Urology 1988; 140: 1049-53.
DOI URL |
| 9. |
Robinette CL. Sex-hormone-induced inflammation and fibromuscular proliferation in the rat lateral prostate. The Prostate 1988; 12: 271-86.
DOI URL |
| 10. | Fan S. The evaluation of rats chronic prostatitis model induced by 17-beta estradiol combined with castration and preliminary research on neuroendocrine differentiation. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2014: 1-88. |
| 11. | Li GS, Chang DG, Zhang PH, et al. Theraputic effects of Qian Mi Tong on chronic nonbacterial prostatitis in rats and its mechanism. Zhong Guo Nan Ke Xue Za Zhi 2016; 30: 15-9. |
| 12. |
Suleman K, Naheam Mujtaba, Philip S. Acute and chronic prostatitis. InnovAiT 2021; 14: 33-7.
DOI URL |
| 13. |
Wang WL, Naveed M, Baig MMFA, Abbas M, Zhou XH. Experimental rodent models of chronic prostatitis and evaluation criteria. Biomed Pharmacother 2018; 108: 1894-901.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Gu JQ, Cai T, Liao B, et al. Efficacy and safety of diclofenac sodium, tamsulosin and prostaglandin in the treatment of chronic abacterial prostatitis. The first male health collaborative innovation forum of Chinese and Western Medicine and the third national andrology youth academic forum of integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine 2019: 28-9. |
| 15. | Han Q. Chinese expert consensus on clinical application of qianlieshutong capsule in chronic prostatitis. Zhong Hua Nan Ke Xue Za Zhi 2018; 24: 1142-5. |
| 16. | Ma CQ, Xiong J, Li HJ. Advances in the studies of special biomarkers for the experimental diagnosis of CP/CPPS. Zhong Hua Nan Ke Xue Za Zhi 2020; 26: 660-5. |
| 17. | Zhang HY, Zhang XY, Shi LY. Inflammatory nature of disease and its intervention with Traditional Chinese Medicine. Xi Bei Nong Ye Xue Bao 2017; 26: 1-13. |
| 18. | Zhang YL. Efficacy of the qingzhuo decoction on the expression of SIgA, IL-8 and TNF-α in the blood of patients with type Ⅲ B prostatitis of the Shire Yuzu syndrome. Zhong Yi Lin Chuang Yan Jiu 2021; 13: 101-3. |
| 19. |
Xiong YY, Zhou LL, Qiu XT, Miao CG. Anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperplastic effect of Bazhengsan in a male rat model of chronic nonbacterial prostatitis. J Pharmacol Sci 2019; 139: 201-8.
DOI PMID |
| 20. | Sun HB, Wang M, Liu YZ, Dang RM, Xie HS, Li ZC. Swimming plus medication reduces the expressions of cytokines in rats with chronic abacterial prostatitis. Zhong Hua Nan Ke Xue Za Zhi 2017; 23: 21-6. |
| 21. | Zhang ZN, Zhou Q. Effect of Qianliqingyu decoction on NGF, MIP-1α and IFN-γ of prostatic fluid in the treatment of type Ⅲ prostatitis. Man Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2021; 22: 923-4, 927. |
| 22. | Li Q, Shen JW, Lü SX, Shao KQ, Zeng FX, Gao Z. Data mining research on herbal administration of Zhang Guangsheng in treatment of chronic prostatitis. Liaoning Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2017; 44: 2490-3. |
| 23. | Yu JW, Zhang TQ. Clinical observation on 86 cases of chronic prostatitis treated with huoxue qushi tongluo decoction. Xinjiang Zhong Yi Yao 2017; 35: 5-7. |
| 24. | Sun Y, Lenon GB, Yang AWH. Phellodendri cortex: a phytochemical, pharmacological, and pharmacokinetic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019; 7621929. |
| 25. | Yan YX, Yang Y, Chi LK, Zheng P. Berberine-type alkaloids from phellodendron Chinense and their anti-tumor activities. Yunnan Shi Fan Da Xue Xue Bao (Zi Ran Ke Xue Ban) 2022; 42: 46-9. |
| 26. |
Linn YC, Lu J, Lim LC, et al. Berberine-induced haemolysis revisited: safety of rhizoma coptidis and cortex phellodendri in chronic haematological diseases. Phytother Res 2012; 26: 682-6.
DOI URL |
| 27. | Mao X, Yao RM, Bao YY, et al. Effect of polysaccharides from seeds of vaccaria segetalis in alleviating urinary tract infection induced bladder injury by inhibiting NLRP 3 inflammasome. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2021; 46: 3388-93. |
| 28. |
Xie FS, Cai WW, Liu YL, et al. Vaccarin attenuates the human EA. hy 926 endothelial cell oxidative stress injury through inhibition of notch signaling. Int J Mol Med 2015; 35: 135-42.
DOI URL |
| 29. |
Tian M, Huang YW, Wang X, et al. Vaccaria segetalis: a review of ethnomedicinal, phytochemical, pharmacological, and toxicological findings. Front Chem 2021; 9: 666280.
DOI URL |
| 30. |
Nikolaev SM, Nikolaeva GG, Mondodoev AG, Markaryan AA, Nikolaeva IG, Nagaslaeva OV. Anti-inflammatory action of polyextract of orthosiphon stamineus (leaves), arctostaphylos uva-ursi (leaves), polygonum aviculare (herbs), calendula officinalis (flowers), and glycyrrhiza uralensis (root) on the rat prostate. Pharm Chem J 2018; 52: 117-21.
DOI |
| 31. | Li L. Simultaneous determination of eight active components in polygonum aviculare L. by HPLC. Tai Shan Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2021; 42: 61-5. |
| 32. |
Subhawa S, NaikiIto A, Kato H, et al. Suppressive effect and molecular mechanism of houttuynia cordata thunb. extract against prostate carcinogenesis and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancers 2021; 13: 3403.
DOI URL |
| 33. | Li H, Hung A, Yang A. Herbal formula (danggui beimu kushen wan) for prostate disorders: a systematic review of classical literature. Int Med Res 2019; 8: 240-6. |
| 34. | Xie PY, Cui LL, Yuan S, Kang WY. Antithrombotic effect and mechanism of radix paeoniae rubra. Biomed Res Int 2017: 9475074. |
| 35. |
Cheng HJ, Sha XX, Luo YY, et al. Acute and subacute toxicity evaluation of houttuynia cordata ethanol extract and plasma metabolic profiling analysis in both male and female rats. J Appl Toxicol JAT 2021; 41: 2068-82.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

