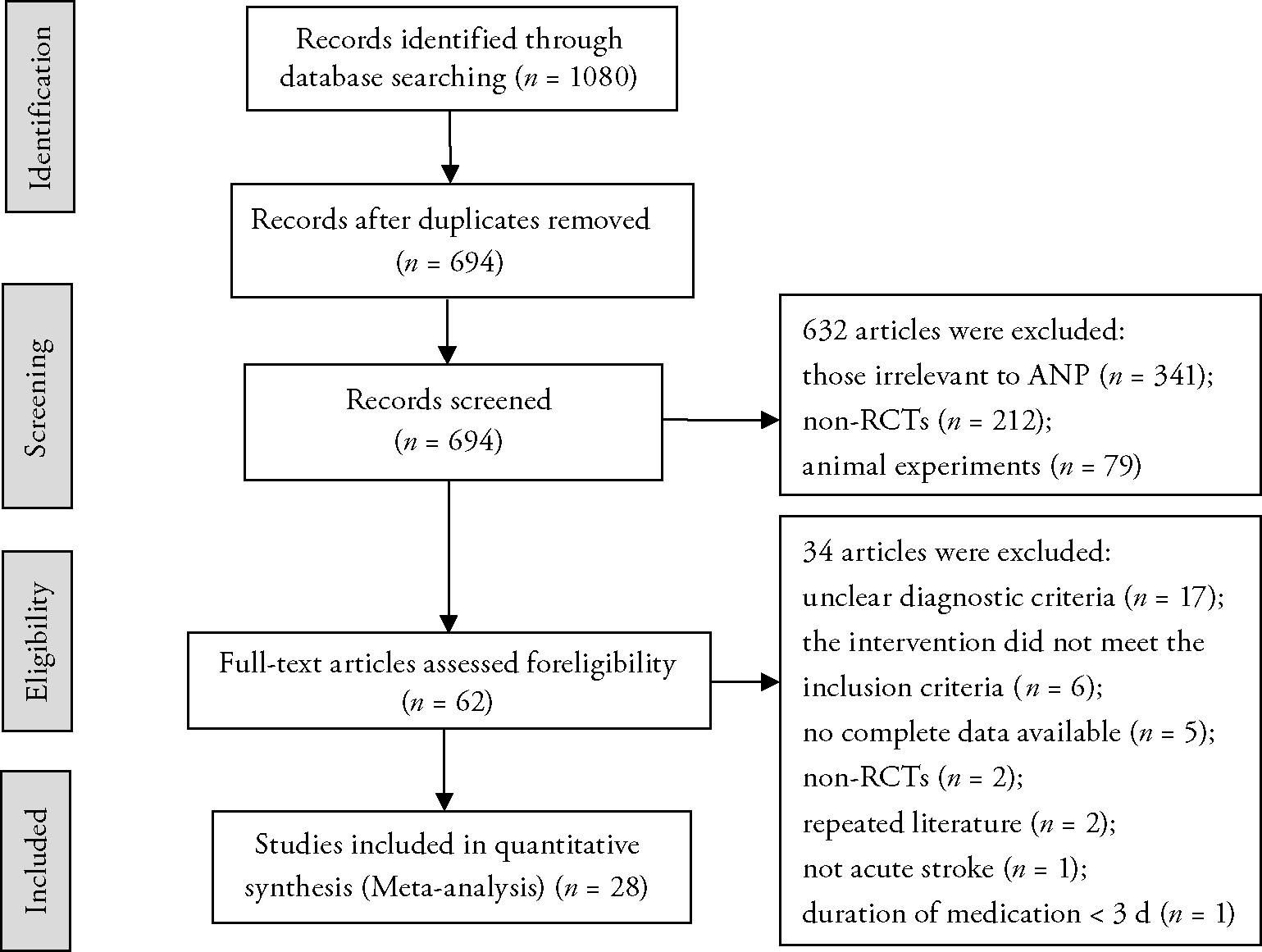
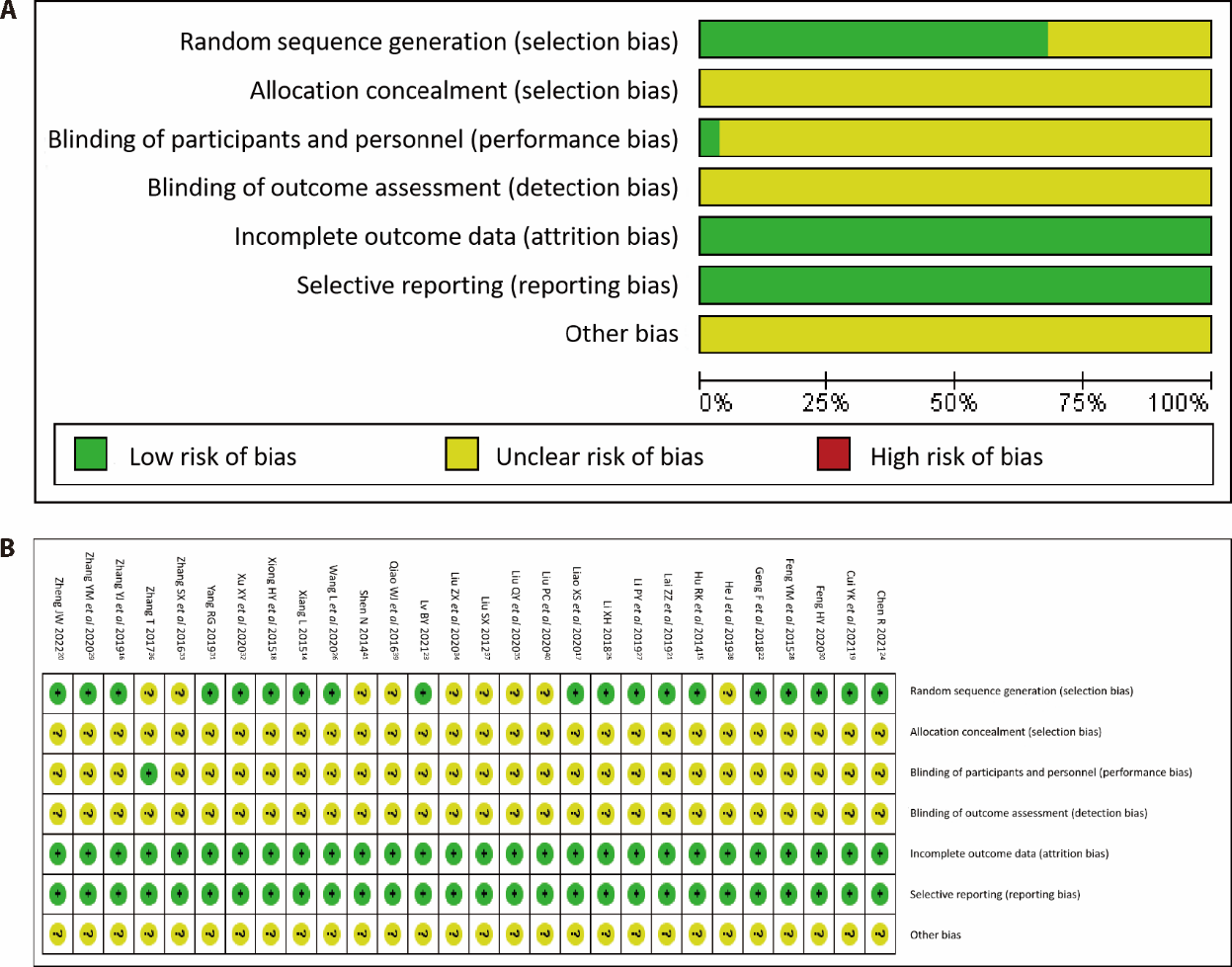
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 650-660.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230526.002
• Meta-analysises • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effectiveness and safety of Angong Niuhuang pill (安宫牛黄丸) in treatment of acute stroke: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
MENG Xiangran, CAO Xue, SUN Minglin, AI Yanke, HE Liyun( ), LIU Jia(
), LIU Jia( )
)
- Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medicine Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2022-05-06Accepted:2022-09-12Online:2023-08-15Published:2023-05-26 -
Contact:Prof. HE Liyun, Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medicine Sciences, Beijing 100700, China. hely3699@163.com. Telephone: +86-18801368925
Prof. LIU Jia, Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medicine Sciences, Beijing 100700, China. marie_liujia@sina.cn -
Supported by:Science and Technology Innovation Project of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences: Research on Key Technologies of Real-world Clinical Evaluation and Data Governance Analysis Based on Disease Research(CI2021A00702-2);Project of National Key Research and Development Program: Development of International Clinical Research Service Standard for Acupuncture and Moxibustion(2019YFC1712205)
Cite this article
MENG Xiangran, CAO Xue, SUN Minglin, AI Yanke, HE Liyun, LIU Jia. Effectiveness and safety of Angong Niuhuang pill (安宫牛黄丸) in treatment of acute stroke: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 650-660.
share this article
| Study | Type of stroke | Sample size (E/C) | Sex (M/F) | Mean age (years) | Intervention (E) | Duration (d) | Outcome | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | C | E | C | |||||||
| Xiang L 2015 | ACI | 86 (43/43) | 27/16 | 24/19 | 62.1±10.3 | 62.7±9.5 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 10 | ①②③ | 3 |
| Hu RK | AIH | 53 (28/25) | 19/9 | 17/8 | 55.8±10.7 | 53.6±11.3 | ANP 3 g, qd (nasal feeding) | 5 | ①②③⑧ | 3 |
| et al 2014 | +CT | |||||||||
| Zhang YJ et al 2019 | AIH | 98 (49/49) | 29/20 | 27/22 | 64±5 | 63±5 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral or nasal feeding)+CT | 14 | ①②③ | 4 |
| Liao XS | AIH | 87 (45/42) | 27/18 | 24/18 | 60.53±10.71 | 59.31±8.67 | ANP 3 g, bid (nasal feeding)+CT | 7 | ③⑥⑧ | 3 |
| et al 2020 | ||||||||||
| Xiong HY et al 2015 | AIH | 32 (16/16) | 7/9 | 6/11 | 62.70±3.32 | 40.19±4.35 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral or nasal feeding)+CT | 10 | ③ | 3 |
| Cui YK | ACI | 103 (51/52) | NA | NA | NA | NA | ANP 3 g, qd (oral or nasal feeding)+CT | 7 | ①②③⑧ | 4 |
| et al 2021 | ||||||||||
| Zheng JW 2022 | ACI | 86 (43/43) | 25/18 | 23/20 | 65.89±4.32 | 65.82±4.36 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral)+CT | 14 | ①②③ | 3 |
| Lai ZZ | ACI | 70 (35/35) | 24/11 | 26/9 | 69.6±13.0 | 66.3±11.3 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 14 | ①② | 3 |
| et al 2019 | ||||||||||
| Geng F | AIH | 120 (60/60) | 37/23 | 35/25 | 54.9±11.8 | 55.6±11.3 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral)+CT | 14 | ①②⑤⑧ | 3 |
| et al 2018 | ||||||||||
| Lü BY 2021 | AIH | 200 (100/100) | 54/46 | 57/43 | 63.5±10.7 | 62.9±11.2 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral or nasal feeding)+CT | 14 | ①②⑥ | 3 |
| Chen R 2021 | AIH | 90 (45/45) | 32/13 | 30/15 | 58.74±10.96 | 57.86±5.72 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 14 | ①②④⑦ | 3 |
| Li XH 2018 | AIH | 100 (50/50) | 25/25 | 27/23 | 45.01±2.15 | 45.21±2.06 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 7 | ②⑤⑧ | 4 |
| Wang L | AIH | 124 (62/62) | 32/30 | 33/29 | 51.33±10.41 | 51.29±10.52 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 7 | ①⑤⑧ | 3 |
| et al 2020 | ||||||||||
| Li PY | AIH | 110 (55/55) | 31/24 | 29/26 | 12.7±3.4 | 12.3±3.0 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral or nasal feeding) +CT | 14 | ①②⑦ | 3 |
| et al 2019 | ||||||||||
| Feng YM | ACI | 80 (40/40) | 24/16 | 22/18 | 62.3±10.9 | 61.4±10.2 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 7 | ①②③ | 3 |
| et al 2015 | ||||||||||
| Zhang YM et al 2020 | ACI | 90 (45/45) | 26/19 | 25/20 | 67.3±2.4 | 65.7±2.3 | ANP 6-9g, bid (oral or nasal feeding) +CT | 21 | ①② | 3 |
| Feng HY 2020 | AIH | 40 (20/20) | 13/7 | 13/7 | 60.35±8.60 | 62.00±10.46 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 10 | ①②③⑧ | 4 |
| Yang RG 2019 | AIH | 120 (60/60) | 37/23 | 36/24 | 73.61±5.89 | 71.26±5.85 | ANP 3 g, qd (nasal feeding) +CT | 28 | ②④ | 3 |
| Xu XY | ACI | 94 (47/47) | 24/23 | 27/20 | 71.76±8.13 | 70.38±8.09 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 14 | ①②④⑧ | 3 |
| et al 2020 | ||||||||||
| Zhang SX et al 2016 | ACI | 122 (61/61) | 35/26 | 37/24 | 63.5±9.9 | 64.7±10.2 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 14 | ①②③⑧ | 2 |
| Liu ZX | ACI | 80 (40/40) | 24/16 | 29/11 | 71.43±6.12 | 70.51±6.09 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral) +CT | 7 | ①②④⑧ | 2 |
| et al 2020 | ||||||||||
| Liu QY | ACI | 120 (60/60) | 32/28 | 33/27 | 53.32±6.97 | 53.20±6.91 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 28 | ①②⑥⑧ | 2 |
| et al 2020 | ||||||||||
| Zhang T 2017 | AIH | 92(46/46) | 28/18 | 27/19 | 52.6±9.7 | 53.7±9.4 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral)+CT | 14 | ① | 2 |
| Liu SX 2012 | ACI | 160 (80/80) | NA | NA | NA | NA | ANP 3 g, qd (oral)+CT | 5 | ①②⑧ | 2 |
| He J | AIH | 100(50/50) | NA | NA | 46.12±6.24 | 48.44±5.53 | ANP 3 g, bid+CT | 15 | ③ | 2 |
| et al 2019 | ||||||||||
| Qiao WJ | AIH | 88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 10 | ③⑥ | 2 |
| et al 2016 | (44/44) | |||||||||
| Liu PC | AIH | 120 | 28/32 | 27/33 | 62.18±10.18 | 58.47±11.21 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | >3 | ①②⑧ | 2 |
| et al 2020 | (60/60) | |||||||||
| Shen N 2014 | ACI | 80 | 25/15 | 23/17 | 65.2±9.3 | 64.5±8.7 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 7 | ①②⑧ | 2 |
| (40/40) | ||||||||||
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the included literature
| Study | Type of stroke | Sample size (E/C) | Sex (M/F) | Mean age (years) | Intervention (E) | Duration (d) | Outcome | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | C | E | C | |||||||
| Xiang L 2015 | ACI | 86 (43/43) | 27/16 | 24/19 | 62.1±10.3 | 62.7±9.5 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 10 | ①②③ | 3 |
| Hu RK | AIH | 53 (28/25) | 19/9 | 17/8 | 55.8±10.7 | 53.6±11.3 | ANP 3 g, qd (nasal feeding) | 5 | ①②③⑧ | 3 |
| et al 2014 | +CT | |||||||||
| Zhang YJ et al 2019 | AIH | 98 (49/49) | 29/20 | 27/22 | 64±5 | 63±5 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral or nasal feeding)+CT | 14 | ①②③ | 4 |
| Liao XS | AIH | 87 (45/42) | 27/18 | 24/18 | 60.53±10.71 | 59.31±8.67 | ANP 3 g, bid (nasal feeding)+CT | 7 | ③⑥⑧ | 3 |
| et al 2020 | ||||||||||
| Xiong HY et al 2015 | AIH | 32 (16/16) | 7/9 | 6/11 | 62.70±3.32 | 40.19±4.35 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral or nasal feeding)+CT | 10 | ③ | 3 |
| Cui YK | ACI | 103 (51/52) | NA | NA | NA | NA | ANP 3 g, qd (oral or nasal feeding)+CT | 7 | ①②③⑧ | 4 |
| et al 2021 | ||||||||||
| Zheng JW 2022 | ACI | 86 (43/43) | 25/18 | 23/20 | 65.89±4.32 | 65.82±4.36 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral)+CT | 14 | ①②③ | 3 |
| Lai ZZ | ACI | 70 (35/35) | 24/11 | 26/9 | 69.6±13.0 | 66.3±11.3 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 14 | ①② | 3 |
| et al 2019 | ||||||||||
| Geng F | AIH | 120 (60/60) | 37/23 | 35/25 | 54.9±11.8 | 55.6±11.3 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral)+CT | 14 | ①②⑤⑧ | 3 |
| et al 2018 | ||||||||||
| Lü BY 2021 | AIH | 200 (100/100) | 54/46 | 57/43 | 63.5±10.7 | 62.9±11.2 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral or nasal feeding)+CT | 14 | ①②⑥ | 3 |
| Chen R 2021 | AIH | 90 (45/45) | 32/13 | 30/15 | 58.74±10.96 | 57.86±5.72 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 14 | ①②④⑦ | 3 |
| Li XH 2018 | AIH | 100 (50/50) | 25/25 | 27/23 | 45.01±2.15 | 45.21±2.06 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 7 | ②⑤⑧ | 4 |
| Wang L | AIH | 124 (62/62) | 32/30 | 33/29 | 51.33±10.41 | 51.29±10.52 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 7 | ①⑤⑧ | 3 |
| et al 2020 | ||||||||||
| Li PY | AIH | 110 (55/55) | 31/24 | 29/26 | 12.7±3.4 | 12.3±3.0 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral or nasal feeding) +CT | 14 | ①②⑦ | 3 |
| et al 2019 | ||||||||||
| Feng YM | ACI | 80 (40/40) | 24/16 | 22/18 | 62.3±10.9 | 61.4±10.2 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 7 | ①②③ | 3 |
| et al 2015 | ||||||||||
| Zhang YM et al 2020 | ACI | 90 (45/45) | 26/19 | 25/20 | 67.3±2.4 | 65.7±2.3 | ANP 6-9g, bid (oral or nasal feeding) +CT | 21 | ①② | 3 |
| Feng HY 2020 | AIH | 40 (20/20) | 13/7 | 13/7 | 60.35±8.60 | 62.00±10.46 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 10 | ①②③⑧ | 4 |
| Yang RG 2019 | AIH | 120 (60/60) | 37/23 | 36/24 | 73.61±5.89 | 71.26±5.85 | ANP 3 g, qd (nasal feeding) +CT | 28 | ②④ | 3 |
| Xu XY | ACI | 94 (47/47) | 24/23 | 27/20 | 71.76±8.13 | 70.38±8.09 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 14 | ①②④⑧ | 3 |
| et al 2020 | ||||||||||
| Zhang SX et al 2016 | ACI | 122 (61/61) | 35/26 | 37/24 | 63.5±9.9 | 64.7±10.2 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 14 | ①②③⑧ | 2 |
| Liu ZX | ACI | 80 (40/40) | 24/16 | 29/11 | 71.43±6.12 | 70.51±6.09 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral) +CT | 7 | ①②④⑧ | 2 |
| et al 2020 | ||||||||||
| Liu QY | ACI | 120 (60/60) | 32/28 | 33/27 | 53.32±6.97 | 53.20±6.91 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 28 | ①②⑥⑧ | 2 |
| et al 2020 | ||||||||||
| Zhang T 2017 | AIH | 92(46/46) | 28/18 | 27/19 | 52.6±9.7 | 53.7±9.4 | ANP 3 g, qd (oral)+CT | 14 | ① | 2 |
| Liu SX 2012 | ACI | 160 (80/80) | NA | NA | NA | NA | ANP 3 g, qd (oral)+CT | 5 | ①②⑧ | 2 |
| He J | AIH | 100(50/50) | NA | NA | 46.12±6.24 | 48.44±5.53 | ANP 3 g, bid+CT | 15 | ③ | 2 |
| et al 2019 | ||||||||||
| Qiao WJ | AIH | 88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 10 | ③⑥ | 2 |
| et al 2016 | (44/44) | |||||||||
| Liu PC | AIH | 120 | 28/32 | 27/33 | 62.18±10.18 | 58.47±11.21 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | >3 | ①②⑧ | 2 |
| et al 2020 | (60/60) | |||||||||
| Shen N 2014 | ACI | 80 | 25/15 | 23/17 | 65.2±9.3 | 64.5±8.7 | ANP 3 g, qd+CT | 7 | ①②⑧ | 2 |
| (40/40) | ||||||||||
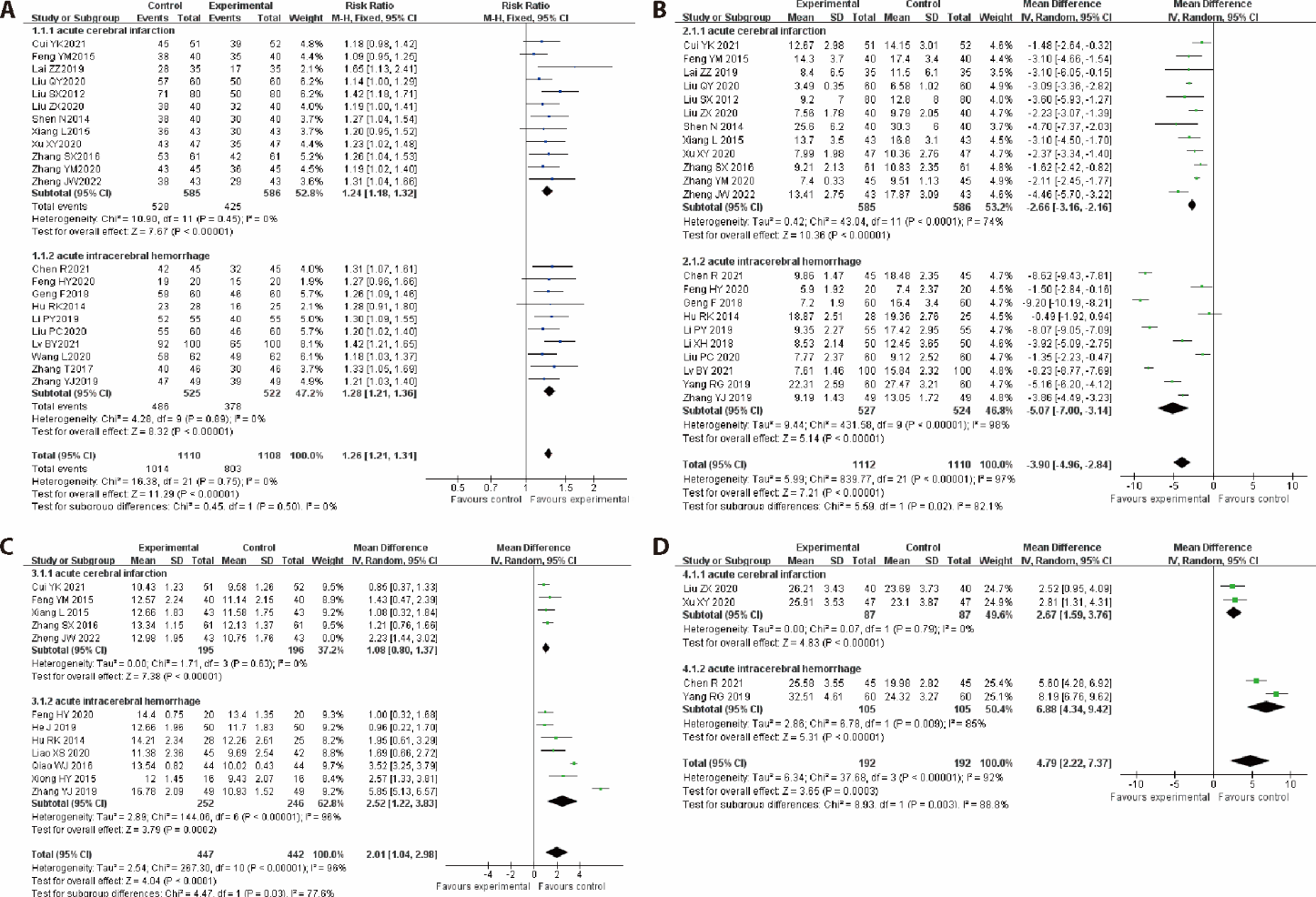
Figure 3 Results of the Meta-analysis A: forest plot of effective rate; B: forest plot of NIHSS; C: forest plot of GCS; D: forest plot of MMSE. NIHSS: National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; GCS: Glasgow Coma Scale; MMSE: Mini-mental State Examination; SD: standard deviation; CI: confidence interval; Random: random-effects model; Fixed: fixed-effects model.
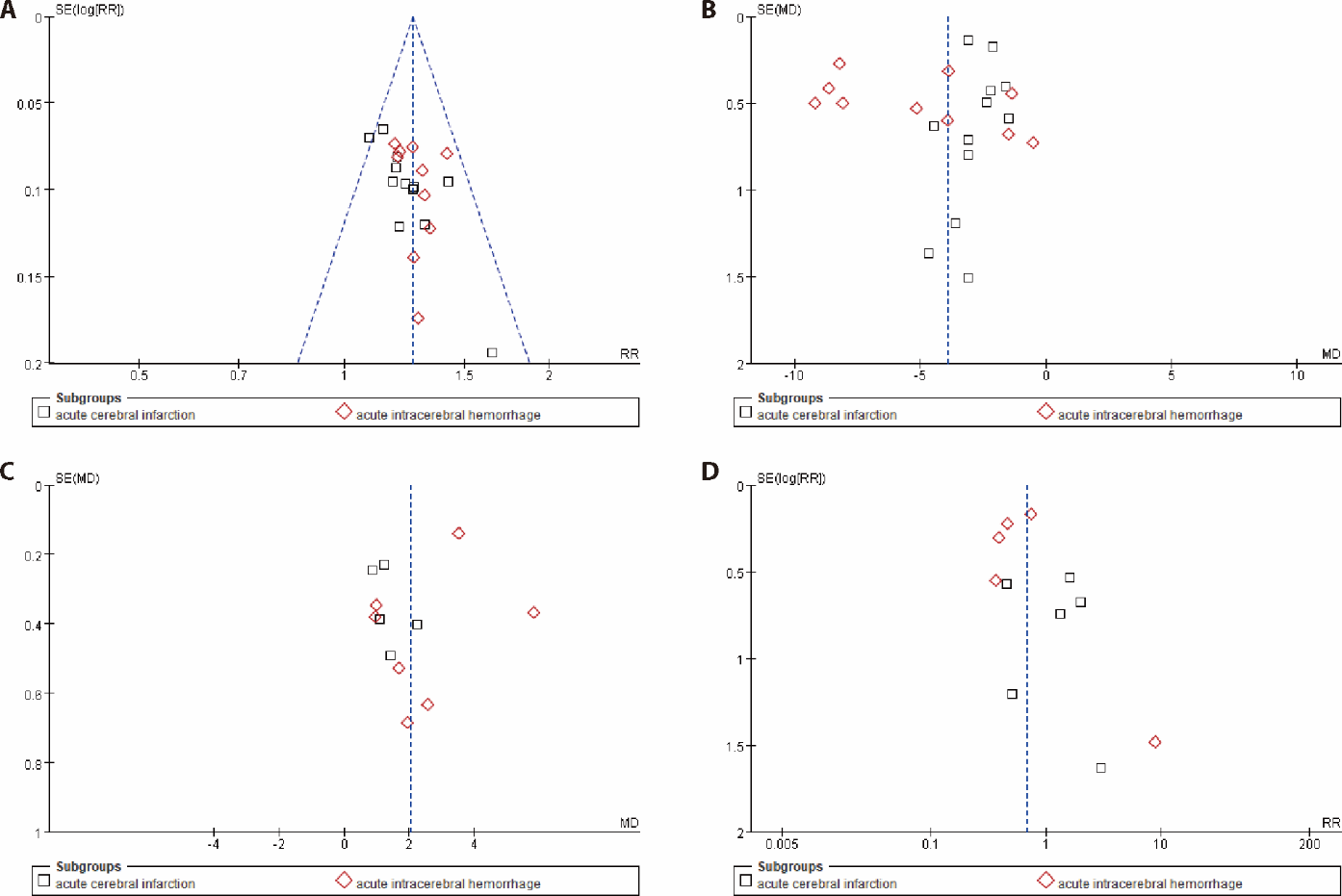
Figure 4 Results of publication bias A: funnel plot of effective rate; B: funnel plot of NIHSS; C: funnel plot of GCS; D: funnel plot of adverse reactions or their incidence. NIHSS: National Institutes of Health stroke scale; GCS: Glasgow Coma Scale.
| 1. | Zhou ZY. Internal Medicine of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2007: 304-13. |
| 2. | GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol 2021; 20: 795-820. |
| 3. | Wang LD, Peng B, Zhang HQ, et al. Summary of Chinese stroke prevention report 2020. Zhong Guo Nao Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2022; 19: 136-44. |
| 4. |
Rimmele DL, Thomalla G. Langzeitfolgen von Schlaganfällen [Long-term consequences of stroke]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung-Gesundheitsschutz 2022; 65: 498-502.
DOI |
| 5. | Yang Y, Man XW, Yu Z, et al. Managing urban stroke health expenditures in China: role of payment method and hospital level. Int J Health Policy Manag 2022; 11: 2698-706. |
| 6. | Jírů-Hillmann S, Gabriel KMA, Schuler M, et al. Experiences of family caregivers 3-months after stroke: results of the prospective trans-regional network for stroke intervention with telemedicine registry (TRANSIT-Stroke). BMC Geriatr 2022; 22: 228. |
| 7. |
Wu YX, Yang YH, Guo XL, et al. Effect of pre-hospital early intervention combined with an in-hospital emergency model in the emergency care of patients with acute stroke. Am J Transl Res 2022; 14: 672-8.
PMID |
| 8. | Cerebrovascular Group, Chinese Society of Neurology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of cerebral hemorrhage (2019). Zhong Hua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi 2019; 52: 994-1005. |
| 9. | Peng B, Wu B. The diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke in China guidelines 2018. Zhong Hua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi 2018; 51: 666-82. |
| 10. | Zhu XY, Guo SY, Xu YQ, Yang H, Li P, Li CQ. Effects of Angong Niuhuang pill on the prevention of cerebrovascular disease. Yao Wu Ping Jiao Yan Jiu 2017; 40: 1067-72. |
| 11. | The Fourth National Academic Conference on Cerebrovascular Diseases. Scoring criteria for the degree of clinical neurological deficit in patients with stroke (1995). Zhong Hua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi 1996; 62-4. |
| 12. | Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 1996; 17: 1-12. |
| 13. |
Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011; 343: d5928.
DOI URL |
| 14. | Xiang L. The effect of Angong Niuhuang pill on acute cerebral infarction patients with disturbance of consciousness. Xin Zhong Yi 2015; 47: 19-21. |
| 15. | Hu RK, Peng RH, Yang QW. Clinical efficacy and safety of Angong Niuhuang pill in the treatment of severe cerebral hemorrhage. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2014; 32: 266-8. |
| 16. | Zhang YJ, Sha CH, Wang J. Effect of Angong Niuhuang pill assisted Western Medicine on acute cerebral hemorrhage patients with phlegm-heat internal closure and Qinqiao syndrome and its influence on oxidative stress index. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2019; 28: 3101-4+13. |
| 17. | Liao XS, Luo Y, Yu L, Lu GH. Effect of Angong Niuhuang pill on postoperative hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage patients. Guang Xi Yi Xue 2020; 42: 1314-6. |
| 18. | Xiong HY, Wu ZY, Zhou XJ, Wang QL. Clinical study of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with hard channel catheterization in the treatment of hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage. Zhong Wai Yi Xue Yan Jiu 2015; 57-8. |
| 19. | Cui YK, Fu Q, Gao YY, Li J. Angong Niuhuang pill combined with butylphthalide in the treatment of ischemic stroke. Chang Chun Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2021; 37: 318-21. |
| 20. | Zheng JW. Clinical effect of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with butylphthalide on patients with severe cerebral infarction. Zhong Hua Yang Sheng Bao Jian 2022; 40: 5-6. |
| 21. | Lai ZZ, Cao YY, Hong WW, Xu JY. Effect of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with butylphthalide in the treatment of severe stroke. Zhong Guo Xiang Cun Yi Yao 2019; 26: 29-30. |
| 22. | Geng F, Yu L. Clinical efficacy and safety of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with nerve growth factor in the treatment of acute cerebral hemorrhage. Shi Yong Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018; 34: 2790-3. |
| 23. | Lü BY. Clinical study of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with Western Medicine in the treatment of cerebral hemorrhage. Xin Zhong Yi 2021; 53: 53-6. |
| 24. | Chen R. Effect of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with Western Medicine on symptomatic treatment of severe cerebral hemorrhage and its influence on cognitive function of patients. Xin Zhong Yi 2021; 53: 51-5. |
| 25. | Li XH. A randomized parallel controlled study of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with edaravone in the treatment of acute hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Shi Yong Zhong Yi Nei Ke Za Zhi 2018; 32: 14-6. |
| 26. | Wang L, Wang L. Effect of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with edaravone on oxidative stress in patients with hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xin Nao Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2020; 18: 3105-8. |
| 27. | Li PY, Wang XP. Effect of Angong Niuhuang pill on acute cerebral hemorrhage and its influence on serum BNP and hs-CRP levels. Wei Liang Yuan Su Yu Jian Kang Yan Jiu 2019; 36: 37-8. |
| 28. | Feng YM, Yang H. Observation on the effect of Angong Niuhuang pill in the treatment of coma patients with acute cerebral infarction. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2015; 21: 179-82. |
| 29. | Zhang YM, Zhao GS, Yang C. Effect of Angong Niuhuang pill on ischemic stroke and its effect on serum Hcy, hs-CRP and blood lipid levels. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2020; 29: 3028-30. |
| 30. | Feng HY. Clinical observation of Angong Niuhuang pill in the treatment of patients with cerebral hemorrhage in basal ganglia of phlegm-heat internal closure syndrome. Hunan: Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 2020: 1-50. |
| 31. | Yang RG. Effect of minimally invasive intracranial hematoma removal combined with Angong Niuhuang pill on hypertensive brainstem hemorrhage. Zhong Guo He Li Yong Yao Tan Suo 2019; 16: 72-4. |
| 32. | Xu XY, Zhu YT, Zhang XM, Cao XH. Effects of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with conventional Western Medicine on neurological function and coagulation function in elderly patients with acute cerebral infarction. Shi Yong Zhong Yi Nei Ke Za Zhi 2020; 34: 31-4. |
| 33. | Zhang SX, Chen JY. Effects of Angong Niuhuang pill on serum nitric oxide and asymmetric dimethylarginine in patients with acute cerebral infarction and coma and its clinical efficacy. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2016; 25: 1873-5+84. |
| 34. | Liu ZX, Cai DX. Effects of Angong Niuhuang pill on nerve and coagulation function in acute cerebral infarction. Changchun Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2020; 36: 930-3. |
| 35. | Liu QY, Yang HJ, Yang CJ. Clinical study of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with agatroban in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Xian Dai Yao Wu Yu Lin Chuang 2020; 35: 1327-31. |
| 36. | Zhang T. Therapeutic effect of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with oxiracetam in the treatment of acute cerebral hemorrhage. Shi Yong Lin Chuang Yi Xue 2017; 18: 3-5. |
| 37. | Liu SX. Clinical observation of Angong Niuhuang pill combined with naloxone injection in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Zhong Guo Yi Yuan Yao Xue Za Zhi 2012; 32: 962-5. |
| 38. | He J, Gu YJ, Liu YZ, Deng BC. Clinical effect of Angong Niuhuang pill on hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage and its effect on serum S100β protein. Shi Jie Zui Xin Yi Xue Xin Xi Wen Zhai 2019; 19: 29-30. |
| 39. | Qiao WJ, Liu YG. Clinical study of Angong Niuhuang pill in treatment of 44 patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage after operation. Xian Dai Zhong Yi Yao 2016; 36: 10-2. |
| 40. | Liu PC, Fang WJ, Wu YH. Clinical observation of Angong Niuhuang pill in the treatment of cerebral hemorrhage complicated with non-infectious fever. Chengdu Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2020; 43: 51-4+64. |
| 41. | Shen N. Effect analysis of Angong Niuhuang pill on phlegm-heat syndrome in acute phase of ischemic stroke. Dang Dai Yi Xue 2014; 20: 79-80. |
| 42. | Traditional, Complementary and Integrative Medicine World Health Organization. .int/publications/m/item/who-expert-meeting-on-evaluation-of-traditional-chinese-medicine-in-the-treatment-of-covid-19. |
| 43. | Huang B. Representative of Chen Xiangmei: improving the policy and medical service system of integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. Beijing: Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Bao, 2021: 2. |
| 44. | Zhao X, Zhou M. Research progress of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of ischemic stroke. Yi Xue Zong Shu 2021; 27: 4548-52. |
| 45. | Wang YH. Drug therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Yi Xue Xin Xi 2022; 35: 44-6+59. |
| 46. | Fang BJ, Yu XZ, Guo LH, et al. Expert consensus on clinical application of Angong Niuhuang pill in acute and critical cases. Zhong Guo Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2019; 39: 726-30. |
| 47. | China Medical Education Association. Expert consensus on clinical application of Angong Niuhuang pill. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2022; 42: 933-46. |
| 48. | Zhang WJ, Huang Y. Current status of Angong Niuhuang pill in the treatment of acute cerebral apoplexy. Zhong Cheng Yao 2015; 37: 2019-22. |
| 49. | Fang F, Feng SY, Sun JN. Effects of Angong Niuhuang pill on expression of MMP-9 and AQP-4 in perihematoma tissues of rats with experimental cerebral hemorrhage. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2011; 34: 535-8+78. |
| 50. | Li JZ, Jiang Y, Zeng Y, Yan XG, Yan JW. Effects of Angong Niuhuang pill on expression of MMP9 and AQP4 in rats with acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Zun Yi Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2019; 42: 412-5. |
| 51. | Zeng S, Xu SL, Pan HZ, Qin YA. Research progress of Angong Niuhuang pill in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases. Zhong Yi Lin Chuang Yan Jiu 2020; 12: 53-5. |
| 52. |
Zhou YY, Liang HS, Yan JY, et al. Effectiveness and safety of tripterygium glycosides tablet for lupus nephritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2022; 42: 671-80.
DOI PMID |
| 53. |
Yin XF, Cheng NC, Zhu J. Xuanbai Chengqi decoction plus Western Medicine in treatment of severe pneumonia with symptom pattern of phlegm-heat obstructing lung: a Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2021; 41: 17-25.
DOI PMID |
| 54. | Yan LZ, Mao FW, Cao YH, Xie M. Clinical effects of the combination of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicines on coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2021; 41: 499-506. |
| 55. | Ma LH, Li DM, Li KJ. Randomized controlled trial systematic review of Angong Niuhuang pill in the treatment of hemorrhagic stroke in acute phase. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2013; 15: 60-1. |
| 56. | Liu FF, Zhou YB, Lu YK, Yang JH. Systematic review of the efficacy and safety of Angong Niuhuang pill in the adjuvant treatment of cerebral hemorrhage. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2021; 46: 5428-35. |
| 57. | Hou M, Wang XF, Chen JH. Effect of Angong Niuhuang pill on acute ischemic stroke: a Meta-analysis. Zhong Guo Yao Fang 2016; 27: 5104-7. |
| 58. |
Liu HW, Yan Y, Pang PF, et al. Angong Niuhuang pill as adjuvant therapy for treating acute cerebral infarction and intracerebral hemorrhage: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Ethnopharmacol 2019; 237: 307-13.
DOI PMID |
| 59. | Xie QW, Xiao JM, Deng XY, et al. A preliminary study on the establishment of core outcome index set of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of ischemic stroke. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2022; 63: 220-8. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||