Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 463-471.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.03.012
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Transcutaneous auricular vague nerve stimulation improved brain connection activity on patients of disorders of consciousness: a pilot study
WANG Yifei1, YANG Yi2, WANG Yu1, ZHANG Jinling1, ZHAI Weihang1, LI Shaoyuan1, WU Mozheng1, HE Jianghong2( ), RONG Peijing1(
), RONG Peijing1( )
)
- 1 Institute of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
2 Department of Neurosurgery, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, 100700, Beijing, China
-
Received:2021-10-22Accepted:2022-01-29Online:2022-06-15Published:2022-05-20 -
Contact:HE Jianghong,RONG Peijing -
About author:HE Jianghong, Department of Neurosurgery, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, 100700, Beijing, China, he_jianghong@sina.cnTelephone: +86-13718482149; +86-13717951390
Prof. RONG Peijing, Institute of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China. drrongpj@163.com;
-
Supported by:Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Public Welfare Research Institutes: Brain Effects and Multimodal Imaging Mechanism of Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Patients with Disorder of Consciousness(CI2021A03305)
Cite this article
WANG Yifei, YANG Yi, WANG Yu, ZHANG Jinling, ZHAI Weihang, LI Shaoyuan, WU Mozheng, HE Jianghong, RONG Peijing. Transcutaneous auricular vague nerve stimulation improved brain connection activity on patients of disorders of consciousness: a pilot study[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 463-471.
share this article
| Number | Age | Sex | Etiology | Post-injury (Months) | CRS-R | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | Male | stroke | 8 | 6 | VS |
| 2 | 51 | Male | stroke | 3 | 6 | VS |
| 3 | 33 | Male | anoxic | 10 | 6 | VS |
| 4 | 39 | Male | stroke | 11 | 6 | VS |
| 5 | 50 | Male | stroke | 4 | 7 | VS |
| 6 | 39 | Male | stroke | 6 | 6 | VS |
| 7 | 41 | Male | anoxic | 6 | 7 | VS |
| 8 | 41 | Male | stroke | 5 | 8 | MCS |
| 9 | 24 | Male | stroke | 13 | 9 | MCS |
| 10 | 53 | Male | trauma | 13 | 10 | MCS |
| 11 | 32 | Male | trauma | 6 | 9 | MCS |
| 12 | 24 | Male | stroke | 6 | 8 | MCS |
Table 1 Characteristics of patients
| Number | Age | Sex | Etiology | Post-injury (Months) | CRS-R | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | Male | stroke | 8 | 6 | VS |
| 2 | 51 | Male | stroke | 3 | 6 | VS |
| 3 | 33 | Male | anoxic | 10 | 6 | VS |
| 4 | 39 | Male | stroke | 11 | 6 | VS |
| 5 | 50 | Male | stroke | 4 | 7 | VS |
| 6 | 39 | Male | stroke | 6 | 6 | VS |
| 7 | 41 | Male | anoxic | 6 | 7 | VS |
| 8 | 41 | Male | stroke | 5 | 8 | MCS |
| 9 | 24 | Male | stroke | 13 | 9 | MCS |
| 10 | 53 | Male | trauma | 13 | 10 | MCS |
| 11 | 32 | Male | trauma | 6 | 9 | MCS |
| 12 | 24 | Male | stroke | 6 | 8 | MCS |

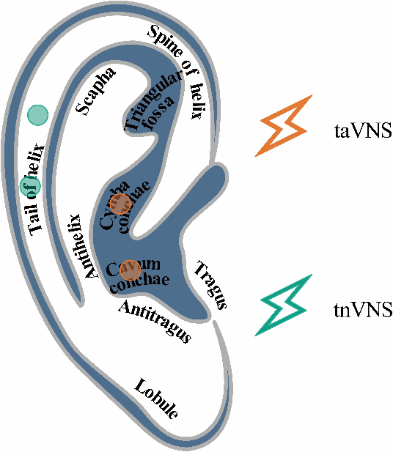
Figure 3 Consort diagram EEG: electroencephalogram; CRS-R: Coma Recovery Scale-Revised; taVNS: transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve nerve stimulation; tnVNS: transcutaneous non-auricular vague nerve stimulation.

Figure 6 Topography of spectral density In Figure 6 (a) shows that taVNS can increase the energy of Delta band and decrease the energy of Beta band of patients in VS group. (c) shows that the results are opposite in patients of MCS group after taVNS. taVNS: transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve nerve stimulation; tnVNS: transcutaneous non-auricular vague nerve stimulation; MCS: minimally conscious state.On the other hand, tnVNS can hardly cause changes in patients’ brain activities.
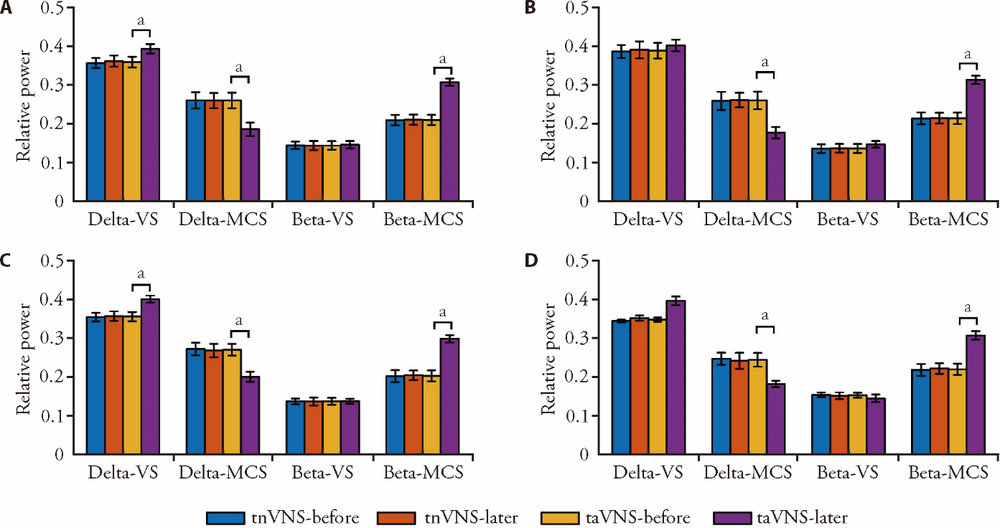
Figure 7 Spectral density As shown in Figure 7, after taVNS or tnVNS stimulation for 14 d, patients of VS group only showed significant changes in delta band energy. There were differences in whole brain, frontal lobe and parietal lobe. While in patients of MCS group, there were significant changes not only in delta and beta bands, but also in whole brain and local brain regions. taVNS: transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve nerve stimulation; tnVNS: transcutaneous non-auricular vague nerve stimulation; VS: vegetative state; MCS: minimally conscious state. Compared with VS, aP < 0.05.
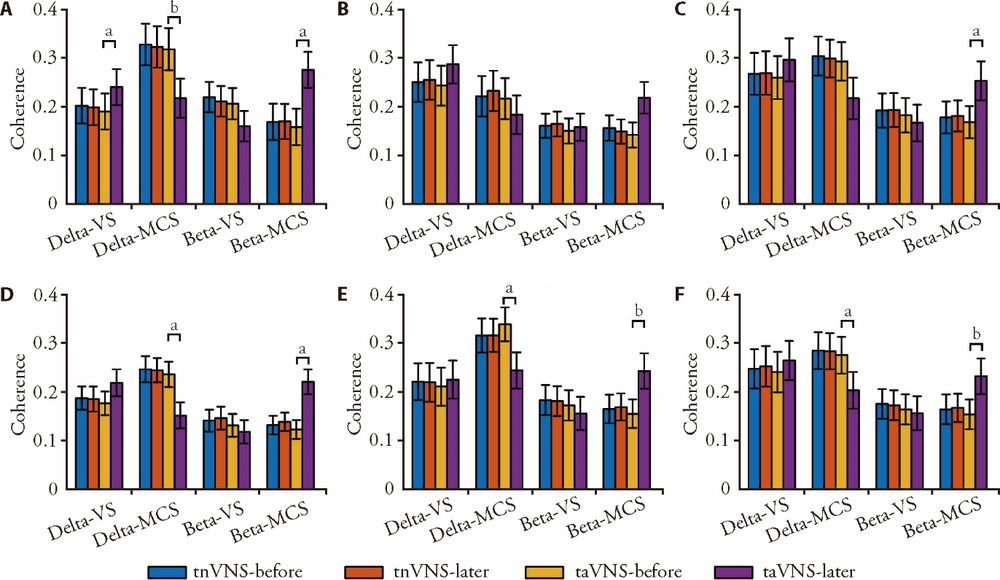
Figure 8 Region - Coherence As can be seen from Figure 8, after taVNS or tnVNS stimulation for 14 d, there is only significant channel activity between the frontal and parietal lobes in patients of VS group. In patients of MCS group, there was significant connective activity not only in the local brain regions of the frontal and occipital lobes, but also in the trans-cerebral regions of the frontal-parietal and frontal-occipital lobes. taVNS: transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve nerve stimulation; tnVNS: transcutaneous non-auricular vague nerve stimulation; VS: vegetative state; MCS: minimally conscious state. Compared with VS, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
| 1 |
Grüner ML, Terhaag D. Multimodal early onset stimulation (MEOS) in rehabilitation after brain injury. Brain injury 2000; 14:585-94.
PMID |
| 2 |
Septien S, Rubin MA. Disorders of consciousness: Ethical issues of diagnosis, treatment, and prognostication. Seminars in neurology 2018; 38:548-54.
DOI URL |
| 3 |
Johnson DA, Roethig-Johnston K, Richards D. Biochemical and physiological parameters of recovery in acute severe head injury: responses to multisensory stimulation. Brain Inj 1993; 7:491-9.
PMID |
| 4 |
Jennett B, Plum F: persistent vegetative state after brain damage. A syndrome in search of a name. Lancet 1972; 1:734-37.
PMID |
| 5 |
Bernat JL. Chronic disorders of consciousness. Lancet 2006; 367:1181-92.
PMID |
| 6 |
Bao W, Li X, Luo B: A novel prognostic approach to predict recovery in patients with chronic disorders of consciousness. Neuroscience bulletin 2019; 35:953-4.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
Schiff ND. Central thalamic contributions to arousal regulation and neurological disorders of consciousness. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2008; 1129:105-18.
DOI URL |
| 8 |
Manganotti P, Formaggio E, Storti SF, et al. Effect of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on brain excitability in severely brain-injured patients in minimally conscious or vegetative state. Brain Stimul 2013; 6:913-21.
DOI PMID |
| 9 |
Shi C, Flanagan SR, Samadani U. Vagus nerve stimulation to augment recovery from severe traumatic brain injury impeding consciousness: a prospective pilot clinical trial. Neurol Res 2013; 35:263-76.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
Rush AJ, George MS, Sackeim HA, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) for treatment-resistant depressions: a multicenter study. Biol Psychiatry 2000; 47:276-86.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Oleson T. Auriculotherapy stimulation for neuro-rehabilitation. NeuroRehabilitation 2002; 17:49-62.
PMID |
| 12 |
Shiozawa P, Silva ME, Carvalho TC, et al. Transcutaneous vagus and trigeminal nerve stimulation for neuropsychiatric disorders: a systematic review. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2014; 72:542-7.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Butt MF, Albusoda A, Farmer AD, Aziz Q. The anatomical basis for transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. Journal of anatomy 2020; 236:588-611.
DOI |
| 14 |
Noé E, Ferri J, Colomer C, Moliner B, et al. Feasibility, safety and efficacy of transauricular vagus nerve stimulation in a cohort of patients with disorders of consciousness. Brain stimulation 2020; 13:427-9.
DOI URL |
| 15 |
Wang Y, Li SY, Wang D, et al. Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation: From concept to application. Neurosci Bull 2021; 37:853-62.
DOI PMID |
| 16 |
Bernat JL. Chronic disorders of consciousness. Lancet 2006; 367:1181-92
PMID |
| 17 |
Gosseries O, Pistoia F, Charland-Verville V, et al. The role of neuroimaging techniques in establishing diagnosis, prognosis and therapy in disorders of consciousness. Open Neuroimag J 2016; 10:52-68.
DOI PMID |
| 18 |
Schnakers C, Vanhaudenhuyse A, Giacino J, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the vegetative and minimally conscious state: clinical consensus versus standardized neurobehavioral assessment. BMC Neurol 2009; 9:35.
DOI PMID |
| 19 |
Laureys S, Schiff ND. Coma and consciousness: paradigms (re)framed by neuroimaging. Neuroimage 2012; 61:478-91.
DOI PMID |
| 20 |
Stender J, Gosseries O, Bruno MA, et al. Diagnostic precision of PET imaging and functional MRI in disorders of consciousness: a clinical validation study. Lancet 2014; 384(9942):514-22.
DOI PMID |
| 21 |
Derakhshan I. Voluntary brain processing in disorders of consciousness. Neurology 2009; 73:1712-3.
DOI PMID |
| 22 |
Hermann DM, Gunzer M. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils play a decisive role for brain injury and neurological recovery poststroke. Stroke 2019; 50:e40-1.
DOI |
| 23 |
Kondziella D, Bender A, Diserens K, et al. European academy of neurology guideline on the diagnosis of coma and other disorders of consciousness. Eur J Neurol 2020; 27:741-56.
DOI PMID |
| 24 |
Curley WH, Forgacs PB, Voss HU, et al. Characterization of EEG signals revealing covert cognition in the injured brain. Brain 2018; 141:1404-21.
DOI URL |
| 25 | Sitt JD, King JR, El Karoui I, et al. Large scale screening of neural signatures of consciousness in patients in a vegetative or minimally conscious state. Brain 2014; 137:2258270. |
| 26 |
Rosanova M, Gosseries O, Casarotto S, et al. Recovery of cortical effective connectivity and recovery of consciousness in vegetative patients. Brain 2012; 135:1308-20.
DOI PMID |
| 27 |
Gosseries O, Schnakers C, Ledoux D, et al. Automated EEG entropy measurements in coma, vegetative state/unresponsive wakefulness syndrome and minimally conscious state. Funct Neurol 2011; 26:25-30.
PMID |
| 28 |
Williams ST, Conte MM, Goldfine AM, et al. Common resting brain dynamics indicate a possible mechanism underlying zolpidem response in severe brain injury. Elife 2013; 2:e01157.
DOI URL |
| 29 | Farzan F, Barr MS, Wong W, et al. Suppression of gamma-oscillations in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex following long interval cortical inhibition: a TMS-EEG study. Neurop-sychopharmacology 2009; 34:1543-51. |
| 30 |
Jensen KB, Berna C, Loggia ML, et al. The use of functional neuroimaging to evaluate psychological and other non-pharmacological treatments for clinical pain. Neurosci Lett 2012; 520:156-64.
DOI PMID |
| 31 |
Pavuluri MN, Herbener ES, Sweeney JA. Affect regulation: a systems neuroscience perspective. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2005; 1:9-15.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Laureys S, Owen AM, Schiff ND. Brain function in coma, vegetative state, and related disorders. Lancet Neurol 2004; 3:537-46.
PMID |
| 33 |
Monti MM, Rosenberg M, Finoia P, et al. Thalamo-frontal connectivity mediates top-down cognitive functions in disorders of consciousness. Neurology 2015; 84:167-73.
DOI URL |
| 34 |
Schiff ND, Nauvel T, Victor JD. Large-scale brain dynamics in disorders of consciousness. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2014; 25:7-14.
DOI URL |
| 35 |
Kondziella D, Friberg CK, Frokjaer VG, et al. Preserved consciousness in vegetative and minimal conscious states: systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2016; 87:485-92.
DOI PMID |
| 36 |
Li J, Shen J, Liu S, et al. Responses of patients with disorders of consciousness to habit stimulation: a quantitative EEG study. Neurosci Bull 2018; 34:691-9.
DOI URL |
| 37 | Wallis JD. Cross-species studies of orbitofrontal cortex and value-based decision-making. Nat Neurosci 2011; 15:13-9. |
| 38 |
Corazzol M, Lio G, Lefevre A, et al. Restoring consciousness with vagus nerve stimulation. Curr Biol 2017; 27:R994-6.
DOI URL |
| 39 |
Dietrich S, Smith J, Scherzinger C, et al. A novel transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation leads to brainstem and cerebral activations measured by functional MRI. Biomed Tech (Berl) 2008; 53:104-11.
DOI URL |
| 40 | Kleim JA, Jones TA. Principles of experience-dependent neural plasticity: implications for rehabilitation after brain damage. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2008; 51:S225-39. |
| 41 |
Sattin D, Giovannetti AM, Ciaraffa F, et al. Assessment of patients with disorder of consciousness: do different Coma Recovery Scale scoring correlate with different settings? J Neurol 2014; 261:2378-86.
DOI URL |
| 42 |
Wannez S, Heine L, Thonnard M, et al. Coma science group collaborators. The repetition of behavioral assessments in diagnosis of disorders of consciousness. Ann Neurol 2017; 81:883-9.
DOI PMID |
| 43 |
Giacino JT, Ashwal S, Childs N, et al. The minimally conscious state: definition and diagnostic criteria. Neurology 2002; 58:349-53.
PMID |
| 44 |
Cavinato M, Genna C, Manganotti P, et al. Coherence and consciousness: study of fronto-parietal gamma synchrony in patients with disorders of consciousness. Brain Topogr 2015; 28:570-9.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHANG Meizhen, HAO Xiaohui, TANG Yiting, CHEN Yupeng, HE Puyu, ZHAO Liming, PANG Bing, NI Qing. Efficacy and safety of Buyang Huanwu decoction (补阳还五汤) for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 841-850. |
| [2] | SUN Wu, ZHAO Yuwei, LIAO Liang, ZHAO Zhonghui, CHEN Shiqi, YAN Xiaoling, WANG Xueyao, CHAO Guojun, ZHOU Jian. Effectiveness and safety of Xuebijing injection for patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 631-639. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yuehong, SHAO Xianzhi, ZHAO Qianlong, ZHAN Hualong, ZHANG Jianhua, DU Sisi, CHEN Jing, LIU Yingfang, ZHOU Haiwang, CHEN Xinsheng, HONG Ying, LIAN Fengmei, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Effectiveness of Xiangsha Liujun pills (香砂六君丸) on decreased digestive function in convalescent patients of coronavirus disease 2019: a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 552-558. |
| [4] | HE Jiakai, ZHANG Jinling, WANG Yu, LI Shaoyuan, FANG Jiliang, ZHANG Shuai, ZHAO Yanan, ZHAI Weihang, GAO Deqiang, LI Ran, JIANG Yuhang, CHEN Zehao, JIA Baohui, RONG Peijing. Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation would be an alternative to implantable cervical vagus nerve stimulation in some situation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 627-630. |
| [5] | ZHOU Yingyan, LIANG Huasheng, YAN Jingyao, HE Xiaohong, PAN Lili, LI Xue, CHEN Xianghong, CHEN Xiumin, YANG Aicheng, HUANG Qingchun. Effectiveness and safety of tripterygium glycosides tablet (雷公藤多苷片) for lupus nephritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 671-680. |
| [6] | CHEN Limei, SUN Jifei, GUO Chunlei, LI Xiaojiao, WANG Zhi, Hong Yang, FANG Jiliang. Preliminary single-arm study of brain effects during transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation treatment of recurrent depression by resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 818-824. |
| [7] | LIN Yi, LI Xun, WANG Zi, ZHENG Xiaoran, HANG Haiyan, LI Lingling. Efficacy and safety of external application of Chinese herbal medicine for psoriasis vulgaris: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 493-504. |
| [8] | HUANG Yusi, YANG Jiju, LI Xinyi, HAO Huifeng, LI Chong, ZHANG Fan, LIN Haiming, XIE Xianfei, HE Ke, TIAN Guihua. Effectiveness and safety of electroacupuncture for the treatment of pain after laparoscopic surgery: a systematic review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 505-512. |
| [9] | LIU Ying, ZOU Wen, XIAN Qingfei, DENG Xin, ZHANG Fuchun, WANG Li, LI Yonghong, LUN Wenhui, WANG Jian. Efficacy and safety of Mianyi granules (+mianyi+) for reversal of immune nonresponse following antiretroviral therapy of human immunodeficiency virus-1: a randomized, double-blind, multi-center, placebo-controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 432-438. |
| [10] | CHEN Yunhu, FAN Lihua, ZHANG Tao, LIU Xueqian. Effectiveness of Zhuling decoction (猪苓汤) on diuretic resistance in patients with heart failure: a randomized, controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 439-445. |
| [11] | MA Tingting, WU Jie, YANG Lijie, FENG Fen, YANG Huilin, ZHANG Jinhua, ZHONG Yanjin, NING Qing, HUANG Lirong, LIN Youbing, YAN Jue, CHEN Guiquan, HOU Tianshu, WANG Li, REN Yuanfang, TAN Jing. Ginger-indirect moxibustion plus acupuncture versus acupuncture alone for chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 242-249. |
| [12] | Rina SHA, Lu TANG, Yawei DU, Shengxian WU, Huawei SHI, Hongxin ZOU, Xuran ZHANG, Xinglu DONG, Li ZHOU. Effectiveness and safety of Ginkgo biloba extract (GBE50) in the treatment of dizziness caused by cerebral arteriosclerosis: a multi-center, double-blind, randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 83-89. |
| [13] | ZHAO Weipeng, LI Jing, ZHANG Yushuang, LI He, HUANG Jinchang, BAI Jing, LI Jianbo. Efficacy of acupuncture therapy for improving anorexia in tumor patients: a Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 507-514. |
| [14] | Li Zhengjie, Zhou Jun, Cheng Shirui, Lan Lei, Sun Ruirui, Liu Mailan, Yang Jie, Gao Yujie, Guo Taipin, Gong Qiyong, Zeng Fang, Liang Fanrong. Cerebral fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations may predict headache intensity improvement following acupuncture treatment in migraine patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(6): 1041-1051. |
| [15] | Liu Zengli, Li Xiuhui, Gou Chunyan, Li Li, Luo Xiaolan, Zhang Chun, Zhang Yin, Zhang Jiaying, Jin Aihua, Li Hongyan, Zeng Yuan, Li Tongzeng, Wang Xiaojun. Effect of Jinhua Qinggan granules on novel coronavirus pneumonia in patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(3): 467-472. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||