Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 552-558.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2023.03.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
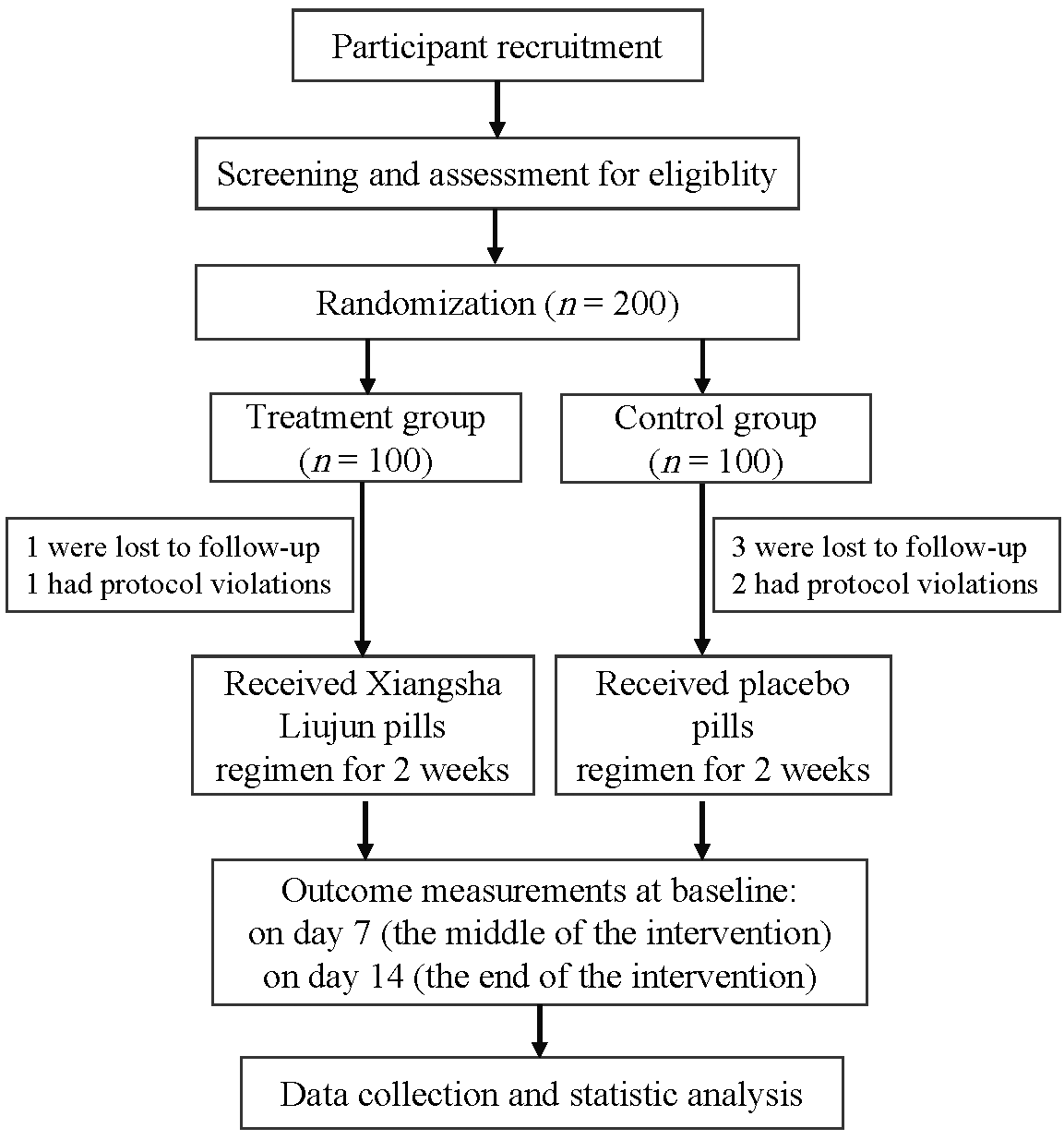
Effectiveness of Xiangsha Liujun pills (香砂六君丸) on decreased digestive function in convalescent patients of coronavirus disease 2019: a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial
ZHANG Yuehong1, SHAO Xianzhi2, ZHAO Qianlong2, ZHAN Hualong2, ZHANG Jianhua2, DU Sisi2, CHEN Jing2, LIU Yingfang2, ZHOU Haiwang2, CHEN Xinsheng2, HONG Ying2, LIAN Fengmei1, TONG Xiaolin1( ), BA Yuanming3(
), BA Yuanming3( )
)
- 1 Department of Endocrinology, Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China
2 Department of Gastroenterology, Ezhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ezhou 436000, China
3 Department of Nephrology, Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, China
-
Received:2022-02-12Accepted:2022-06-10Online:2023-06-15Published:2023-04-28 -
Contact:BA Yuanming, Department of Nephrology, Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, China. 1723426138@qq.com. Telephone: +86-27-87748195; +86-13986179621
TONG Xiaolin, Department of Endocrinology, Guang’anmen Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China. tongxiaolin@vip.163.com -
Supported by:Special Fund of the Technology Division of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine: a Randomized, Double Blinded, Controlled Clinical Trial to Improve the Symptoms of Decreased Digestive Function During the Convalescence of COVID-19(2020ZYLCYJ08-5)
Cite this article
ZHANG Yuehong, SHAO Xianzhi, ZHAO Qianlong, ZHAN Hualong, ZHANG Jianhua, DU Sisi, CHEN Jing, LIU Yingfang, ZHOU Haiwang, CHEN Xinsheng, HONG Ying, LIAN Fengmei, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Effectiveness of Xiangsha Liujun pills (香砂六君丸) on decreased digestive function in convalescent patients of coronavirus disease 2019: a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 552-558.
share this article
| TCM Symptom | Group | Mean | Min-Max | Median | Mean±SD | F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Treatment | 3 | 0-10 | 2 | 2.7±2.2 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Control | 3 | 0-7 | 3 | 2.7±1.9 | |||
| Poor appetite | Treatment | 3 | 0-9 | 3.5 | 2.8±2.2 | ﹣0.745 | 0.457 |
| Control | 3 | 0-7 | 4 | 3.0±2.0 | |||
| Abdominal distension | Treatment | 4 | 0-8 | 4 | 3.8±2.0 | ﹣0.754 | 0.451 |
| Control | 4 | 0-7 | 3 | 3.6±2.0 | |||
| Loose stools | Treatment | 2 | 0-9 | 0 | 1.6±2.3 | ﹣1.518 | 0.131 |
| Control | 2 | 0-7 | 0 | 2.1±2.5 |
Table 1 TCM symptoms scores before the treatment
| TCM Symptom | Group | Mean | Min-Max | Median | Mean±SD | F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Treatment | 3 | 0-10 | 2 | 2.7±2.2 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Control | 3 | 0-7 | 3 | 2.7±1.9 | |||
| Poor appetite | Treatment | 3 | 0-9 | 3.5 | 2.8±2.2 | ﹣0.745 | 0.457 |
| Control | 3 | 0-7 | 4 | 3.0±2.0 | |||
| Abdominal distension | Treatment | 4 | 0-8 | 4 | 3.8±2.0 | ﹣0.754 | 0.451 |
| Control | 4 | 0-7 | 3 | 3.6±2.0 | |||
| Loose stools | Treatment | 2 | 0-9 | 0 | 1.6±2.3 | ﹣1.518 | 0.131 |
| Control | 2 | 0-7 | 0 | 2.1±2.5 |
| TCM Symptom | Group | Treatment time | Total number | Effective number | Ineffective number | Effective rate (%) | Ineffective rate (%) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Treatment | 1 week | 80 | 48 | 32 | 60.00 | 40.00 | 0.174 |
| Control | 83 | 41 | 42 | 49.40 | 50.60 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 80 | 70 | 10 | 87.50 | 12.50 | 0.006a | |
| Control | 83 | 58 | 25 | 69.88 | 30.12 | |||
| Poor appetite | Treatment | 1 week | 75 | 48 | 27 | 64.00 | 36.00 | 0.408 |
| Control | 80 | 46 | 34 | 57.50 | 42.50 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 75 | 72 | 3 | 96.00 | 4.00 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 80 | 62 | 18 | 77.50 | 22.50 | |||
| Abdominal distension | Treatment | 1 week | 90 | 61 | 29 | 67.78 | 32.22 | 0.016a |
| Control | 88 | 44 | 44 | 50.00 | 50.00 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 90 | 81 | 9 | 90.00 | 10.00 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 88 | 52 | 36 | 59.09 | 40.91 | |||
| Loose stools | Treatment | 1 week | 40 | 29 | 11 | 72.50 | 27.50 | 0.001a |
| Control | 52 | 20 | 32 | 38.46 | 61.54 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 40 | 37 | 3 | 92.50 | 7.50 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 52 | 25 | 27 | 48.08 | 51.92 |
Table 2 Comparison of the efficacy rates of the TCM symptoms in the two groups
| TCM Symptom | Group | Treatment time | Total number | Effective number | Ineffective number | Effective rate (%) | Ineffective rate (%) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Treatment | 1 week | 80 | 48 | 32 | 60.00 | 40.00 | 0.174 |
| Control | 83 | 41 | 42 | 49.40 | 50.60 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 80 | 70 | 10 | 87.50 | 12.50 | 0.006a | |
| Control | 83 | 58 | 25 | 69.88 | 30.12 | |||
| Poor appetite | Treatment | 1 week | 75 | 48 | 27 | 64.00 | 36.00 | 0.408 |
| Control | 80 | 46 | 34 | 57.50 | 42.50 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 75 | 72 | 3 | 96.00 | 4.00 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 80 | 62 | 18 | 77.50 | 22.50 | |||
| Abdominal distension | Treatment | 1 week | 90 | 61 | 29 | 67.78 | 32.22 | 0.016a |
| Control | 88 | 44 | 44 | 50.00 | 50.00 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 90 | 81 | 9 | 90.00 | 10.00 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 88 | 52 | 36 | 59.09 | 40.91 | |||
| Loose stools | Treatment | 1 week | 40 | 29 | 11 | 72.50 | 27.50 | 0.001a |
| Control | 52 | 20 | 32 | 38.46 | 61.54 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 40 | 37 | 3 | 92.50 | 7.50 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 52 | 25 | 27 | 48.08 | 51.92 |
| TCM Symptom | Group | Treatment time | Total number | Symptom disappear number | Symptom exist number | Symptom disappear rate (%) | Symptom exist rate (%) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Treatment | 1 week | 80 | 6 | 74 | 7.50 | 92.50 | 0.047a |
| Control | 83 | 1 | 82 | 1.20 | 98.80 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 80 | 26 | 54 | 32.50 | 67.50 | 0.867 | |
| Control | 83 | 28 | 55 | 33.73 | 66.27 | |||
| Poor appetite | Treatment | 1 week | 75 | 4 | 71 | 5.33 | 94.67 | 0.150 |
| Control | 80 | 1 | 79 | 1.25 | 98.75 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 75 | 32 | 43 | 42.67 | 57.33 | 0.736 | |
| Control | 80 | 32 | 48 | 40.00 | 60.00 | |||
| Abdominal distension | Treatment | 1 week | 90 | 8 | 82 | 8.89 | 91.11 | 0.761 |
| Control | 88 | 9 | 79 | 10.23 | 89.77 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 90 | 34 | 56 | 37.78 | 62.22 | 0.608 | |
| Control | 88 | 30 | 58 | 34.09 | 65.91 | |||
| Loose stools | Treatment | 1 week | 40 | 10 | 30 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 0.835 |
| Control | 52 | 14 | 38 | 26.92 | 73.08 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 40 | 25 | 15 | 62.50 | 37.50 | 0.022a | |
| Control | 52 | 20 | 32 | 38.46 | 61.54 |
Table 3 Comparison of the disappearance rates of the TCM symptoms in the two groups
| TCM Symptom | Group | Treatment time | Total number | Symptom disappear number | Symptom exist number | Symptom disappear rate (%) | Symptom exist rate (%) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Treatment | 1 week | 80 | 6 | 74 | 7.50 | 92.50 | 0.047a |
| Control | 83 | 1 | 82 | 1.20 | 98.80 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 80 | 26 | 54 | 32.50 | 67.50 | 0.867 | |
| Control | 83 | 28 | 55 | 33.73 | 66.27 | |||
| Poor appetite | Treatment | 1 week | 75 | 4 | 71 | 5.33 | 94.67 | 0.150 |
| Control | 80 | 1 | 79 | 1.25 | 98.75 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 75 | 32 | 43 | 42.67 | 57.33 | 0.736 | |
| Control | 80 | 32 | 48 | 40.00 | 60.00 | |||
| Abdominal distension | Treatment | 1 week | 90 | 8 | 82 | 8.89 | 91.11 | 0.761 |
| Control | 88 | 9 | 79 | 10.23 | 89.77 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 90 | 34 | 56 | 37.78 | 62.22 | 0.608 | |
| Control | 88 | 30 | 58 | 34.09 | 65.91 | |||
| Loose stools | Treatment | 1 week | 40 | 10 | 30 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 0.835 |
| Control | 52 | 14 | 38 | 26.92 | 73.08 | |||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 40 | 25 | 15 | 62.50 | 37.50 | 0.022a | |
| Control | 52 | 20 | 32 | 38.46 | 61.54 |
| TCM Symptom | Group | Treatment time | Total number | Mean ± SD | F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Treatment | 1 week | 80 | 2.3±1.7 | 0.809 | 0.491 |
| Control | 83 | 2.4±1.5 | ||||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 80 | 1.3±1.4 | 8.235 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 83 | 1.5±1.7 | ||||
| Poor appetite | Treatment | 1 week | 75 | 2.2±1.4 | 1.361 | 0.257 |
| Control | 80 | 2.5±1.3 | ||||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 75 | 0.9±1.1 | 16.237 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 80 | 1.4±1.6 | ||||
| Abdominal distension | Treatment | 1 week | 90 | 2.6±1.5 | 12.486 | <0.001a |
| Control | 88 | 2.8±1.7 | ||||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 90 | 1.3±1.5 | 43.933 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 88 | 2.2±2.1 | ||||
| Loose stools | Treatment | 1 week | 40 | 2.1±1.9 | 12.655 | <0.001a |
| Control | 52 | 3.2±2.6 | ||||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 40 | 0.8±1.5 | 21.750 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 52 | 2.8±2.7 |
Table 4 Comparison of the TCM symptoms scores after treatment in the two groups
| TCM Symptom | Group | Treatment time | Total number | Mean ± SD | F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Treatment | 1 week | 80 | 2.3±1.7 | 0.809 | 0.491 |
| Control | 83 | 2.4±1.5 | ||||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 80 | 1.3±1.4 | 8.235 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 83 | 1.5±1.7 | ||||
| Poor appetite | Treatment | 1 week | 75 | 2.2±1.4 | 1.361 | 0.257 |
| Control | 80 | 2.5±1.3 | ||||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 75 | 0.9±1.1 | 16.237 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 80 | 1.4±1.6 | ||||
| Abdominal distension | Treatment | 1 week | 90 | 2.6±1.5 | 12.486 | <0.001a |
| Control | 88 | 2.8±1.7 | ||||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 90 | 1.3±1.5 | 43.933 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 88 | 2.2±2.1 | ||||
| Loose stools | Treatment | 1 week | 40 | 2.1±1.9 | 12.655 | <0.001a |
| Control | 52 | 3.2±2.6 | ||||
| Treatment | 2 weeks | 40 | 0.8±1.5 | 21.750 | <0.001a | |
| Control | 52 | 2.8±2.7 |
| Treatment time | Group | Total number | Number of systolic pressure abnormalities | Number of diastolic pressure abnormalities | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 weeks | Treatment | 100 | 3 | 5 | 1.000 |
| Control | 100 | 3 | 5 | 1.000 |
Table 5 Comparison of emerging abnormalities in heart rate and blood pressure during the trial
| Treatment time | Group | Total number | Number of systolic pressure abnormalities | Number of diastolic pressure abnormalities | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 weeks | Treatment | 100 | 3 | 5 | 1.000 |
| Control | 100 | 3 | 5 | 1.000 |
| [1] |
Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020; 323: 1061-9.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020; 579: 270-3.
DOI |
| [3] | Johns Hopkins University and Medicine. Johns Hopkins Corona Virus Resource Center (2021) maps and trends. 2020-01-22, Cited 2022-08-09; 1(1): 1 screen. Available from URL: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html. |
| [4] |
Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med 2020; 382: 1708-20.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Yang J, Zheng Y, Gou X, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis 2020; 94: 91-5.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Pan L, Mu M, Yang P, et al. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol 2020; 115: 766-73.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Han CQ, Duan CH, Zhang SY, et al. Digestive symptoms in COVID-19 patients with mild disease severity: clinical presentation, stool viral RNA testing, and outcomes. Am J Gastroenterol 2020; 115: 916-23.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Jin X, Lian JS, Hu JH, et al. Epidemiological, clinical and virological characteristics of 74 cases of coronavirus-infected disease 2019 (COVID-19) with gastrointestinal symptoms. Gut 2020; 69: 1002-9.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Sultan S, Altayar O, Siddique S M, et al. AGA institute rapid review of the gastrointestinal and liver manifestations of COVID-19, Meta-analysis of international data, and recommendations for the consultative management of patients with COVID-19. Gastroenterology 2020; 159: 320-34.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Cheung KS, Hung IFN, Chan PPY, et al. Gastrointestinal manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection and virus load in fecal samples from a Hongkong cohort: systematic review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2020; 159: 81-95.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Hajifathalian K, Krisko T, Mehta A, et al. Gastrointestinal and hepatic manifestations of 2019 novel coronavirus disease in a large cohort of infected patients from New York: clinical implications. Gastroenterology 2020; 159: 1137-40. |
| [12] |
Zhang Y, Chen C, Song Y, et al. Excretion of SARS-CoV-2 through faecal specimens. Emerg Microbes Infect 2020; 9: 2501-8.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Chu L, Huang F, Zhang MD, Huang B, Wang YG. Current status of Traditional Chinese Medicine for the treatment of COVID-19 in China. Chin Med 2021; 16: 63.
DOI |
| [14] | National Health Commission & State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Diagnosis and treatment protocol for novel coronavirus pneumonia. Jiangsu Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2020; 52: 1-6. |
| [15] |
Xiao MZ, Tian JX, Zhou YN, et al. Efficacy of Huoxiang Zhengqi dropping pills and Lianhua Qingwen granules in treatment of COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial. Pharmacol Res 2020; 161: 105126.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Chen SF, Li YQ, He FY, Pan LL. Effect of Saussurea on lappa on gastric function. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 1994; 14: 406-8. |
| [17] | Zhou XM, Zhang LM, Cao YL, Song QL, Li N. Effect of muxiang dynamics capsules inclusion (MDCI) on gastric emptying in mice. Shenyang Yao Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2003; 20: 207-9. |
| [18] | Hou Y, Zhang X. Effects of radix aucklandiae on small intestine movement in normal rats. Zhong Yi Xue Bao 2019; 34: 1921-5. |
| [19] | Yang E, Zhong YM, Feng YF. Advance on the chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. Guangdong Yao Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2012; 28: 218-21. |
| [20] | Yan WL, Wang SS, Ren X. Experimental study of atractylodes on intestinal microflora in mice. Shandong Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2011; 30: 417-9. |
| [21] | Li W, Wen HM, Cui XB, et al. Effective components of rhizoma atractylodis macrocephalae in invigorating spleen. Nanjing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2006; 22: 366-7. |
| [22] | Ma XS, Fan XP, Chen Z, Li CW, Xing YS. Effects of rhizoma atractylodis macrocephalae on the contraction of isolated ileum of guinea pig. Xin Xiao Hua Bing Xue Za Zhi 1996; 11: 603-4. |
| [23] | Ma L, Yin L, Wang B, Zhao X, Fu XY. Research progress of Poria ocos. Ya Tai Chuan Tong Yi Yao 2015; 11: 55-9. |
| [24] | Peng C. Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Beijing: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press, 2012: 183. |
| [25] | Li X, Li Y. The research progress of the pharmacological function of active components extracted from Gancao. Jiangsu Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2019; 51: 81-6. |
| [26] | Lü GY, Yu LX. Effects of processed liquorice products on the activity of isolated intestine in rabbits. Zhong Yao Tong Bao 1986; 11: 21-3. |
| [27] | Li QY, Liang SL, Chu HB, Yang YJ, Yan FG. Study on the active parts of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium in increasing gastrointestinal motility. Zhong Cheng Yao 2012; 34: 941-3. |
| [28] | Fu MQ, Xiao GS, Wu JJ, Chen YL, Wen J, Xu YJ. Studies on chemical basis of digestion promoting function of pericarpium citri reticulatae (Citrus reticulate ‘Chachi’). Zhong Guo Shi Pin Xue Bao 2018; 18: 56-64. |
| [1] | FAN Rong, HE Haoyu, TANG Tao, CUI Hanjin. Long-term effects of Qingfei Paidu decoction (清肺排毒汤) in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 acute pneumonia after treatment: a protocol for systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1068-1071. |
| [2] | ZHANG Meizhen, HAO Xiaohui, TANG Yiting, CHEN Yupeng, HE Puyu, ZHAO Liming, PANG Bing, NI Qing. Efficacy and safety of Buyang Huanwu decoction (补阳还五汤) for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 841-850. |
| [3] | SUN Wu, ZHAO Yuwei, LIAO Liang, ZHAO Zhonghui, CHEN Shiqi, YAN Xiaoling, WANG Xueyao, CHAO Guojun, ZHOU Jian. Effectiveness and safety of Xuebijing injection for patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 631-639. |
| [4] | LUO Xin, XIE Jing, HUANG Li, GAN Wenfan, CHEN Ming. Efficacy and safety of activating blood circulation and removing blood stasis of Traditional Chinese Medicine for managing renal fibrosis in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 429-440. |
| [5] | XU Guihua, CHEN Feifei, ZHANG Wei, WU Yingen, CHEN Xiaorong, SHI Kehua, WANG Zhenwei, SHI Miaoyan, ZHANG Xing, LU Yunfei, YUAN Weian, LYU Hua, CHEN Xuan. Effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine on coronavirus disease 2019 in 92 patients: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 582-587. |
| [6] | YANG Cunqing, LIAN Fengmei, YANG Guiping, HUANG Yufeng, ZHANG Shuangbin, WANG Jianghua, ZHOU Jing, GUO Dongqing, SHEN Chuanyun, YE Tiansong, FU Aojie, LI Xiaoli, CHEN Le, ZHANG Huifeng, TU Qiyin, WANG Ying, YANG Wenzhe, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Effectiveness of Xiaoyao capsule (逍遥丸) on sleep disorders and mood disturbance in patients in recovery from coronavirus disease 2019: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 343-351. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yuehong, DONG Dandan, YAN Youqin, ZHANG Hao, WANG Guangli, ZHOU Wei, LI Wei, QIU Li, LI Tingming, LIU Quan, XIA Ping, MAO Lina, YANG Danlin, YANG Lu, LIAN Fengmei, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Effectiveness and safety of Jinshuibao capsules (金水宝胶囊) in treatment of residual cardiopulmonary symptoms in convalescent patients of coronavirus disease 2019: a pilot randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 134-139. |
| [8] | AN Xuedong, MAO Lina, XIA Ping, SU Wen, WANG Beibei, KOU Leiya, ZHANG Zequan, QI Meng, HU Song, CHEN Jing, LI Xiujuan, LIU Jinwei, ZHOU Juan, QIAO Jie, LUO Dan, LUO Guangwei, YAN Youqin, YANG Guiping, DONG Dandan, ZHOU Wei, TAO Junxiu, JIN De, TONG Xiaolin, WEI Li. Effects of Shengmai Yin (生脉饮) on pulmonary and cardiac function in coronavirus disease 2019 convalescent patients with cardiopulmonary symptoms: a randomized, double blind, multicenter control trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 140-145. |
| [9] | LI Ximeng, KANG Yuan, LI Wenjing, LIU Zhuangzhuang, XU Zhenlu, ZHANG Xiaoyu, CAI Runlan, GAO Yuan, QI Yun. Comparing the effects of three decoctions for coronavirus disease 2019 on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-related toll-like receptors-mediated inflammations [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 51-59. |
| [10] | ZHU Qingguang, ZHANG Shuaipan, LI Jingxian, SUN Wuquan, CHENG Wei, ZHAN Chao, CHENG Yanbin, FANG Lei, FANG Min. Effectiveness of Liu-zi-jue exercise on coronavirus disease 2019 in the patients: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 997-10053. |
| [11] | ZHOU Yingyan, LIANG Huasheng, YAN Jingyao, HE Xiaohong, PAN Lili, LI Xue, CHEN Xianghong, CHEN Xiumin, YANG Aicheng, HUANG Qingchun. Effectiveness and safety of tripterygium glycosides tablet (雷公藤多苷片) for lupus nephritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 671-680. |
| [12] | AN Xuedong, ZHANG Qing, TAO Junxiu, LI Li, CHEN Yun, LI Kejian, HE Jing, LIU Ru, GUO Juan, ZHANG Jia, ZHU Hui, LIAN Fengmei, LI Xiaodong. Shugan Jieyu capsule (舒肝解郁胶囊) improve sleep and emotional disorder in coronavirus disease 2019 convalescence patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 803-809. |
| [13] | LIN Yi, LI Xun, WANG Zi, ZHENG Xiaoran, HANG Haiyan, LI Lingling. Efficacy and safety of external application of Chinese herbal medicine for psoriasis vulgaris: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 493-504. |
| [14] | HUANG Yusi, YANG Jiju, LI Xinyi, HAO Huifeng, LI Chong, ZHANG Fan, LIN Haiming, XIE Xianfei, HE Ke, TIAN Guihua. Effectiveness and safety of electroacupuncture for the treatment of pain after laparoscopic surgery: a systematic review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 505-512. |
| [15] | CHEN Huang, SHI Lushaobo, SHI Zengping, XIA Yi, WANG Dong. Factors influencing physician's behavioral intention to use Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat coronavirus disease 2019 based on the theory of planned behavior [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 633-6400. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||