Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 676-685.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2023.04.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of Heshouwu (Radix Polygoni Multiflori) on gut mircobiota in mice with autoimmune encephalomyelitis
ZHOU Jun1, WANG Junhua2, LI Xiaobing2, WAN Chenyi2, LI Fangjun2, Lü Yanni3, CHEN Hao2( ), SUN Meiying2(
), SUN Meiying2( )
)
- 1 Department of Chinese Medicine, Gaoxin Branch of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330000, China
2 Department of Neurology, Gaoxin branch of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330000, China
3 Department of Pharmacy, Gaoxin branch of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330000, China
-
Received:2022-10-22Accepted:2023-03-04Online:2023-08-15Published:2023-07-03 -
Contact:CHEN Hao, Department of Neurology, Gaoxin branch of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330000, China. 15179132576@163.com. Telephone: +86-15113826448
SUN Meiying, Department of Neurology, Gaoxin branch of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330000, China. smy19871227@163.com. -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Role and Mechanism of Akkermansia-Mediated Activation of Microglia NLRP3 Inflammasome in Multiple Sclerosis(82101419);Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation: the Role and Mechanism of p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway Induced by Intestinal Flora Change in EAE Mice(20212BAB216024);Jiangxi Science and Technology Project of Chinese Medicine: Study on the Role and Mechanism of CGAS-STING Signaling Pathway in Microglia Mediated by Rhodiola Sachalinensis in Multiple Sclerosis(2021B660);Jiangxi Science and Technology Project of Chinese Medicine: Study on the Role and Mechanism of CGAS-STING Signaling Pathway in Microglia Mediated by Rhodiola Sachalinensis in Multiple Sclerosis(2022B1007);Jiangxi Science and Technology Program of Health Commission: the Role and Mechanism of Intestinal Flora Changes in Mediating the Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Microglia in Multiple Sclerosis(202210392);Science and Technology Research Project of Jiangxi Education: Study on the Role and Mechanism of p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway Induced by Intestinal Flora Changes in EAE Mice(GJJ200215);Scientific Research and Development Project of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University: Effects of Exercise Training on Intestinal Flora of Multiple Sclerosis Model Rats and Its Mechanism(YFYPY202021)
Cite this article
ZHOU Jun, WANG Junhua, LI Xiaobing, WAN Chenyi, LI Fangjun, Lü Yanni, CHEN Hao, SUN Meiying. Efficacy of Heshouwu (Radix Polygoni Multiflori) on gut mircobiota in mice with autoimmune encephalomyelitis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 676-685.
share this article
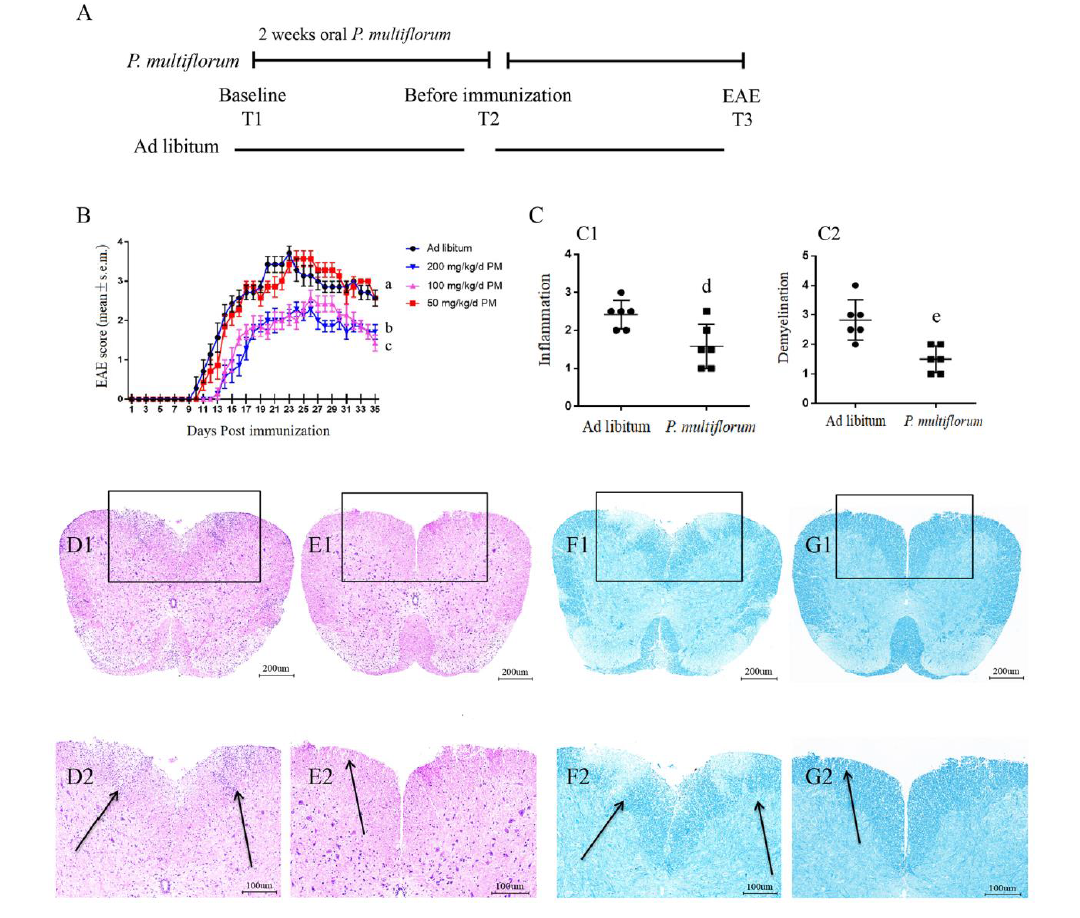
Figure 1 Heshouwu (Radix Polygoni Multiflori) ameliorated the severity of EAE mice A: schematic timeline for the experimental procedures, at baseline (T1) mice in P. multiflorum group were administered orally with Heshouwu (Radix Polygoni Multiflori, 100 mg·kg-1·d-1) and Ad libitum group were treated with vehicle buffer for 2 weeks. (T2) Thereafter, all mice were injected intraperitoneally with PTX (300 mg, resuspended in 100 μL phosphate-buffered saline) and MOG35-55 peptide in CFA for immunization 7 d additionally, (T3) clinical EAE. B: EAE clinical score was assessed in mice treated with either vehicle buffer (ad libitum) or different concentration of P. multiforum (50, 100 and 200 mg·kg-1·d-1) daily and shown (n = 7). Three independent experiments were performed. Data represent mean ± standard error of mean. a: ns: no significance, compared with the ad libitum group. bP < 0.01, compared with the ad libitum group. cP < 0.01, compared with the ad libitum group. C1: quantification of inflammation in the lumbosacral spinal cords in the groups of mice treated with either vehicle buffer (ad libitum) or P. multiforum (100 mg·kg-1·d-1) (n = 6) on day 21 post-immunization. C2: quantification of demyelination in the lumbosacral spinal cords in the groups of mice treated with either vehicle buffer (ad libitum) or P. multiforum (100 mg·kg-1·d-1) (n = 6) on day 21 post-immunization. Data represent mean ± standard deviation. eP < 0.05, compared with the ad libitum group. dP < 0.01, compared with the Ad libitum group. D1-E1: hematoxylin-eosin staining of lumbar spinal cord sections in groups of mice treated with either vehicle buffer (ad libitum) or 100 mg·kg-1·d-1 P. multiforum (scale bar 200 μm, magnification: ×100). D2-E2: scale bar 100 μm, magnification: ×200. F1-G1: luxol fast blue staining of lumbar spinal cord sections in groups of mice treated with either vehicle buffer (ad libitum) or 100 mg·kg-1·d-1 P. multiforum (scale bar 200 μm, magnification: ×100). F2-G2: scale bar 100 μm, magnification: ×200. EAE: experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; PTX: pertussis toxin; CFA: complete Freund’s adjuvant; P. multiforum: Heshouwu (Radix Polygoni Multiflori).
| Item | T1 | T3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ad libitum (n = 7) | P. multiforum (n = 7) | ad libitum (n = 7) | P. multiforum (n = 7) | ||
| GM-CSF | 1.70±0.17 | 1.72±0.23 | 3.31±0.23 | 2.20±0.27a | |
| IL-10 | 3.39±0.23 | 3.65±0.21 | 2.14±0.14 | 2.85±0.25b | |
| IL-21 | 7.11±0.32 | 7.24±0.29 | 4.51±0.36 | 6.28±0.29a | |
| IL-17A | 4.39±0.20 | 4.79±0.46 | 12.71±0.78 | 8.85±0.74a | |
| IL-17F | 3.41±0.21 | 3.29±0.23 | 7.88±0.36 | 5.77±0.32a | |
| IL-22 | 48.40±2.19 | 50.95±1.64 | 125.37±3.90 | 102.00±4.83a | |
Table 1 Changes in serum levels of cytokines at T1 and T3
| Item | T1 | T3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ad libitum (n = 7) | P. multiforum (n = 7) | ad libitum (n = 7) | P. multiforum (n = 7) | ||
| GM-CSF | 1.70±0.17 | 1.72±0.23 | 3.31±0.23 | 2.20±0.27a | |
| IL-10 | 3.39±0.23 | 3.65±0.21 | 2.14±0.14 | 2.85±0.25b | |
| IL-21 | 7.11±0.32 | 7.24±0.29 | 4.51±0.36 | 6.28±0.29a | |
| IL-17A | 4.39±0.20 | 4.79±0.46 | 12.71±0.78 | 8.85±0.74a | |
| IL-17F | 3.41±0.21 | 3.29±0.23 | 7.88±0.36 | 5.77±0.32a | |
| IL-22 | 48.40±2.19 | 50.95±1.64 | 125.37±3.90 | 102.00±4.83a | |

Figure 2 Heshouwu (Radix Polygoni Multiflori) alleviated Th17/Treg imbalance in inguinal LN of EAE mice A: representative flow cytometric analysis (A1) and the percentage (right) of CD4+ T cells producing IL-17A (A2), GM-CSF (A3), IFN-γ (A4) in the CNS 21 d after immunization was shown (n = 6). aP < 0.01, frequency of IL-17A+ CD4+ T cells were compared with the ad libitum group. bP < 0.05, frequency of GM-CSF+ CD4+ T cells were compared with the ad libitum group. c: ns, frequency of IFN-γ+ CD4+ T cells were compared with the ad libitum group. B: representative flow cytometric analysis (B1) and the percentage (right) of CD4+ T cells producing IL-17A (B2), GM-CSF (B3), IFN-γ (B4) in the inguinal LN 21 d after immunization was shown (n = 6). dP < 0.01, frequency of IL-17A+ CD4+ T cells were compared with the ad libitum group. e: ns, frequency of GM-CSF+ CD4+ T cells were compared with the ad libitum group. f: ns, frequency of IFN-γ+ CD4+ T cells were compared with the ad libitum group. C: representative flow cytometric analysis (C1) and the percentage (C2) of CD4+ T cells producing Foxp3 in the CNS 21 d after immunization was shown (n = 6). g: ns, frequency of Foxp3+ CD4+ T cells were compared with the ad libitum group. D: representative flow cytometric analysis (D1) and the percentage (D2) of CD4+ T cells producing Foxp3 in the inguinal LN 21 d after immunization was shown (n = 6). hP < 0.01, frequency of Foxp3+ CD4+ T cells were compared with the ad libitum group. CNS: central nervous system; ns: no significance; LN: lymph node. IL-17: interleukin 17; IFN-γ: interferon-γ; GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor.

Figure 3 Heshouwu (Radix Polygoni Multiflori) reconstituted the composition and diversity of gut microbiota in mice The clearance of intestinal flora by cocktail antibiotics was verified by 16s rRNA sequencing analysis. A: genus species phylogeny tree. B: PCoA plot shows the gut microbiota composition in group of mice treated with vehicle buffer (ad libitum) or 100 mg·kg-1·d-1 P. multiforum. C: relative abundances of the gastric microbiota at phylum (C1) and genus (C2) level in group of mice treated with vehicle buffer (ad libitum) or 100 mg·kg-1·d-1 P. multiforum. D: relative abundances of Bacteroidetes phylum (D1) and Firmicutes phylum (D2) in group of mice treated with vehicle buffer (ad libitum) or 100 mg·kg-1·d-1 P. multiforum. aP < 0.01, relative abundances of Bacteroidetes phylum were compared with the ad libitum group. bP < 0.01, relative abundances of Firmicutes phylum were compared with the ad libitum group. E: cladogram representation of the genus species in gastric microbiota in group of mice treated with vehicle buffer (ad libitum) or 100 mg·kg-1·d-1 P. multiforum. F: identify the specific microbiota taxa that significantly associated with 100 mg·kg-1·d-1 P. multiforum treatment by LEfSe. EAE: experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; P. multiforum: Heshouwu (Radix Polygoni Multiflori); PCoA: principal coordinate analysis; FMT: fecal microbiota transplantation; LDA: linear discriminant analysis; LEfSe: LDA effect size.
| 1. | Correale J, Gaitan MI, Ysrraelit MC, Fiol MP. Progressive multiple sclerosis: from pathogenic mechanisms to treatment. Brain 2017; 140: 527-46. |
| 2. |
Olek MJ. Multiple sclerosis. Ann Intern Med 2021; 174: Itc81-96.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Lecuyer E, Rakotobe S, Lengline-Garnier H, et al. Segmented filamentous bacterium uses secondary and tertiary lymphoid tissues to induce gut IgA and specific T helper 17 cell responses. Immunity 2014; 40: 608-20.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Yang Y, Torchinsky MB, Gobert M, et al. Focused specificity of intestinal T(H)17 cells towards commensal bacterial antigens. Nature 2014; 510: 152-6.
DOI |
| 5. |
Chen H, Ma X, Si L, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine in multiple sclerosis: theory and practice. Curr Pharmacol Rep 2018; 4: 436-46.
DOI |
| 6. |
Peng Y, Zhang S, Liu Z, et al. Gut microbiota and Chinese medicine syndrome: altered fecal microbiotas in spleen (Pi)-deficient patients. J Tradit Chin Med 2020; 40: 137-43.
PMID |
| 7. |
Lyu M, Wang YF, Fan GW, Wang XY, Xu SY, Zhu Y. Balancing herbal medicine and functional food for prevention and treatment of cardiometabolic diseases through modulating gut microbiota. Front Microbiol 2017; 8: 2146.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Wu J, Wei Z, Cheng P, et al. Rhein modulates host purine metabolism in intestine through gut microbiota and ameliorates experimental colitis. Theranostics 2020; 10: 10665-79.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Lin L, Ni B, Lin H, et al. Traditional usages, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb.: a review. J Ethnopharmacol 2015; 159: 158-83.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Bounda GA, Feng YU. Review of clinical studies of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. and its isolated bioactive compounds. Pharmacognosy Res 2015; 7: 225-36.
DOI URL |
| 11. | Sun Y, Mei L, Seon Y, et al. Novel compound from Polygonum multiflorum inhibits inflammatory response in LPS-stimulated microglia by upregulating AMPK/Nrf2 pathways. Neurochem Int 2016; 100: 21-9. |
| 12. | Zhou X, Yang Q, Xie Y, et al. Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside extends mouse life span via upregulating neural klotho and downregulating neural insulin or insulin-like growth factor 1. Neurobiol Aging 2015; 36: 1462-70. |
| 13. |
Chen H, Ma X, Liu Y, et al. Gut microbiota interventions with clostridium butyricum and norfloxacin modulate immune response in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice. Front Immunol 2019; 10: 1662.
DOI PMID |
| 14. |
Chen H, Shen L, Liu Y, et al. Strength exercise confers protection in central nervous system autoimmunity by altering the gut microbiota. Front Immunol 2021; 12: 628629.
DOI URL |
| 15. |
Rao T, Liu YT, Zeng XC, Li CP, Ouyang DS. The hepatotoxicity of Polygonum multiflorum: the emerging role of the immune-mediated liver injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2021; 42: 27-35.
DOI |
| 16. |
O'Neill EJ, Day MJ, Wraith DC. IL-10 is essential for disease protection following intranasal peptide administration in the C57BL/6 model of EAE. J Neuroimmunol 2006; 178: 1-8.
PMID |
| 17. |
Zeinali H, Baluchnejadmojarad T, Fallah S, Sedighi M, Moradi N, Roghani M. S-allyl cysteine improves clinical and neuropathological features of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57BL/6 mice. Biomed Pharmacother 2018; 97: 557-63.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Chen H, Chen Z, Shen L, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation from patients with autoimmune encephalitis modulates Th 17 response and relevant behaviors in mice. Cell Death Discov 2020; 6: 75.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Bellemore SM, Nikoopour E, Schwartz JA, Krougly O, Lee-Chan E, Singh B. Preventative role of interleukin-17 producing regulatory T helper type 17 (T(reg)17) cells in type 1 diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice. Clin Exp Immunol 2015; 182: 261-9.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
McGeachy MJ, Bak-Jensen KS, Chen Y, et al. TGF-beta and IL-6 drive the production of IL-17 and IL-10 by T cells and restrain TH-17 cell-mediated pathology. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 1390-7.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Goverman J. Autoimmune T cell responses in the central nervous system. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 393-407.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Gaboriau-Routhiau V, Rakotobe S, Lecuyer E, et al. The key role of segmented filamentous bacteria in the coordinated maturation of gut helper T cell responses. Immunity 2009; 31: 677-89.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
Jarrell JT, Gao L, Cohen DS, Huang X. Network medicine for alzheimer's disease and Traditional Chinese Medicine. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2018; 23: 1143.
DOI URL |
| 24. |
Wang ZY, Liu J, Zhu Z, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine compounds regulate autophagy for treating neurodegenerative disease: a mechanism review. Biomed Pharmacother 2021; 133: 110968.
DOI URL |
| 25. | Qi MZ, Su XH, Lin N, Kong XY. Effect of neutrophil extracellular traps on ischemic stroke and intervention of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2021; 46: 1-5. |
| 26. |
Zhang Y, Lou Y, Wang J, Yu C, Shen W. Research status and molecular mechanism of the Traditional Chinese Medicine and antitumor therapy combined strategy based on tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol 2020; 11: 609705.
DOI URL |
| 27. |
Lin X, Liu Y, Ma L, et al. Amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by Rhodiola rosea, a natural adaptogen. Biomed Pharmacother 2020; 125: 109960.
DOI PMID |
| 28. |
Levy M, Kolodziejczyk AA, Thaiss CA, Elinav E. Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2017; 17: 219-32.
DOI PMID |
| 29. |
Chang CJ, Lin CS, Lu CC, et al. Ganoderma lucidum reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Nat Commun 2015; 6: 7489.
DOI |
| 30. |
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006; 444: 1022-3.
DOI |
| 31. |
Julia V, Macia L, Dombrowicz D. The impact of diet on asthma and allergic diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 2015; 15: 308-22.
DOI PMID |
| 32. |
Tolhurst G, Heffron H, Lam YS, et al. Short-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion via the G-protein-coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes 2012; 61: 364-71.
DOI PMID |
| 33. | Smith PM, Howitt MR, Panikov N, et al. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science (New York, NY) 2013; 341: 569-73. |
| 34. |
Anhê FF, Roy D, Pilon G, et al. A polyphenol-rich cranberry extract protects from diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance and intestinal inflammation in association with increased Akkermansia spp. population in the gut microbiota of mice. Gut 2015; 64: 872-83.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Logsdon AF, Erickson MA, Rhea EM, Salameh TS, Banks WA. Gut reactions: how the blood-brain barrier connects the microbiome and the brain. Exp Biol Med (Maywood, NJ) 2018; 243: 159-65.
DOI URL |
| 36. |
Dendrou CA, Fugger L, Friese MA. Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Immunol 2015; 15: 545-58.
DOI PMID |
| 37. |
Uyttenhove C, Gaignage M, Donckers D, et al. Prophylactic treatment against GM-CSF, but not IL-17, abolishes relapses in a chronic murine model of multiple sclerosis. Eur J Immunol 2018; 48: 1883-91.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Vendrik KEW, Ooijevaar RE, de Jong PRC, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation in neurological disorders. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020; 10: 98.
DOI URL |
| 39. |
Kong G, Ellul S, Narayana VK, et al. An integrated metagenomics and metabolomics approach implicates the microbiota-gut-brain axis in the pathogenesis of Huntington's disease. Neurobiol Dis 2021; 148: 105199.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LI Chaoran, YANG Yan, FENG Chuwen, LI Heng, QU Yuanyuan, WANG Yulin, WANG Delong, WANG Qingyong, GUO Jing, SHI Tianyu, SUN Xiaowei, WANG Xue, HOU Yunlong, SUN Zhongren, YANG Tiansong. Integrated 'omics analysis for the gut microbiota response to moxibustion in a rat model of chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1176-1189. |
| [2] | JIANG Yiqian, ZHOU Xibin, PU Wenyuan, ZHOU Chunxiang. Sanwu Baisan decoction (三物白散) inhibits colorectal cancer progression in mice by remodeling gut microbiota and tumorigenesis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 466-473. |
| [3] | YANG Yang, YUAN Haining, JIA Hongxiao, NING Yanzhe, WANG Di, ZHANG Lei, YAN Kaijuan, GUO Yumeng, WANG Fei, SUN Weishuang, CHEN Pei. Therapy of replenishing Yin and regulating Yang for manic episode in bipolar disorder: study protocol for a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 594-601. |
| [4] | SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, ZHAO Tingting, WANG Yuhang, PEI Lixia, SUN Jianhua. Electroacupuncture at Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) alleviates stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by modulating gut microbiota and corticotropin-releasing factor [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 732-740. |
| [5] | YU Zeyue, HAO Liyu, LI Zongyuan, SUN Jianhui, CHEN Hongying, HUO Hairu, LI Xiaoqin, SHAN Zhongchao, LI Hongmei. Correlation between slow transit constipation and spleen Qi deficiency, and gut microbiota: a pilot study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 353-363. |
| [6] | Huixiang ZHANG, Limei WANG, Jipeng GUO, Jiai WANG, Qianqian ZHANG, Yutao WANG, Xun LIU, Lihuan ZHANG, Lanlan SHI, Hongxiang WU, Xue CAO. Gut microbiota and differential genes-maintained homeostasis is key to maintaining health of individuals with Yang-deficiency constitution [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 96-101. |
| [7] | PAN Lijia, MA Shuya, WEN Jing, ZHANG Xiaoqi, XING Haijiao, JIA Chunsheng. Direct contact moxibustion promotes apoptosis of gastric cancer cells in rats by regulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 943-952. |
| [8] | Sun Zhigao, Hu Yazhuo, Wang Yuguo, Feng Jian, Dou Yongqi. Bupi Hewei decoction ameliorates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal dysbiosis in rats through T helper 17/T regulatory cell signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(1): 38-48. |
| [9] | Peng Ying, Zhang Shuoying, Liu Zhiwei, Ji Jia, Wu Chunfu, Yang Jingyu, Li Xiaobo. Gut microbiota and Chinese medicine syndrome: altered fecal microbiotas in spleen(Pi)-deficient patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(1): 137-143. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

