Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 389-399.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.03.006
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Acupotomy inhibits aberrant formation of subchondral bone through regulating osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand pathway in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis induced by modified Videman method
QIN Luxue1, GUO Changqing1( ), ZHAO Ruili2, WANG Tong1, WANG Junmei1, GUO Yan3, ZHANG Wei4, HU Tingyao1, CHEN Xilin1, ZHANG Qian1, ZHANG Dian1, XU Yue1
), ZHAO Ruili2, WANG Tong1, WANG Junmei1, GUO Yan3, ZHANG Wei4, HU Tingyao1, CHEN Xilin1, ZHANG Qian1, ZHANG Dian1, XU Yue1
- 1 School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
2 the First People's Hospital of Dongcheng District, Beijing 100050, China
3 Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100010, China
4 the Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing Universality of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2021-10-22Accepted:2022-12-01Online:2022-06-15Published:2022-05-20 -
Contact:GUO Changqing -
About author:Prof. GUO Changqing, School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China. Guochangqing66@163.com,Telephone: +86-10-64286687
-
Supported by:Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation: To Explore the Effect of Acupotomy on Subchondral Bone Remodeling in Early and Middle KOA Based on OPG/RANKL/RANK pathway(7192110)
Cite this article
QIN Luxue, GUO Changqing, ZHAO Ruili, WANG Tong, WANG Junmei, GUO Yan, ZHANG Wei, HU Tingyao, CHEN Xilin, ZHANG Qian, ZHANG Dian, XU Yue. Acupotomy inhibits aberrant formation of subchondral bone through regulating osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand pathway in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis induced by modified Videman method[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 389-399.
share this article
| Gene | Primer sequences |
|---|---|
| OPG | Forward:CGTGAAGAAGGAACTAGCATCTC |
| Reverse: ACTGCAAGCAGTAATAAGGGAAA | |
| RANKL | Forward: ACTTTGCGGTACAGGGTCAG |
| Reverse: GGCCACGCCTCTTAGTAGTC | |
| beta actin | Forward: TTGTCCCCCAACTTGAGATGTA |
| Reverse: GCACTTTTATTGAACTGGTCTCGT |
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| Gene | Primer sequences |
|---|---|
| OPG | Forward:CGTGAAGAAGGAACTAGCATCTC |
| Reverse: ACTGCAAGCAGTAATAAGGGAAA | |
| RANKL | Forward: ACTTTGCGGTACAGGGTCAG |
| Reverse: GGCCACGCCTCTTAGTAGTC | |
| beta actin | Forward: TTGTCCCCCAACTTGAGATGTA |
| Reverse: GCACTTTTATTGAACTGGTCTCGT |
| Group | n | Before treatment | After treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.0±0.00 |
| Model | 6 | 7.00±0.89a | 6.83±0.75a |
| Acupotomy | 6 | 7.33±0.82a | 4.57±0.78ab |
| EA | 6 | 7.33±0.82a | 4.57±0.78ab |
Table 2 Comparison of the improvement in the Lequesne index in different group ($\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | n | Before treatment | After treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.0±0.00 |
| Model | 6 | 7.00±0.89a | 6.83±0.75a |
| Acupotomy | 6 | 7.33±0.82a | 4.57±0.78ab |
| EA | 6 | 7.33±0.82a | 4.57±0.78ab |

Figure 1 Representative images from the hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of the Cartilage from various groups A-D: hematoxylin and eosin-staining (×100); A: control group; B: model group; C: EA group; D: acupotomy group; E: Mankin score of the control, model, EA and acupotomy groups. F, G: quantitative analysis for TAC thickness and the ratio of ACC/TAC. Control group: without any treatments and model establishment; model group: treated without acupotomy or electroacupuncture but joined model establishment; Apo (acupotomy group: treated only with acupotomy and joined model establishment; EA (electroacupuncture group): treated only with electroacupuncture and joined model establishment. Data represents mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). Compared with the control group, aP < 0.01, eP < 0.05; compared with the model group, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.05; compared with the EA group, cP < 0.05. Hematoxylin-eosin staining cartilage calcified cartilage (ACC) and total articular cartilage (TAC) thickness are marked by double-headed arrows.
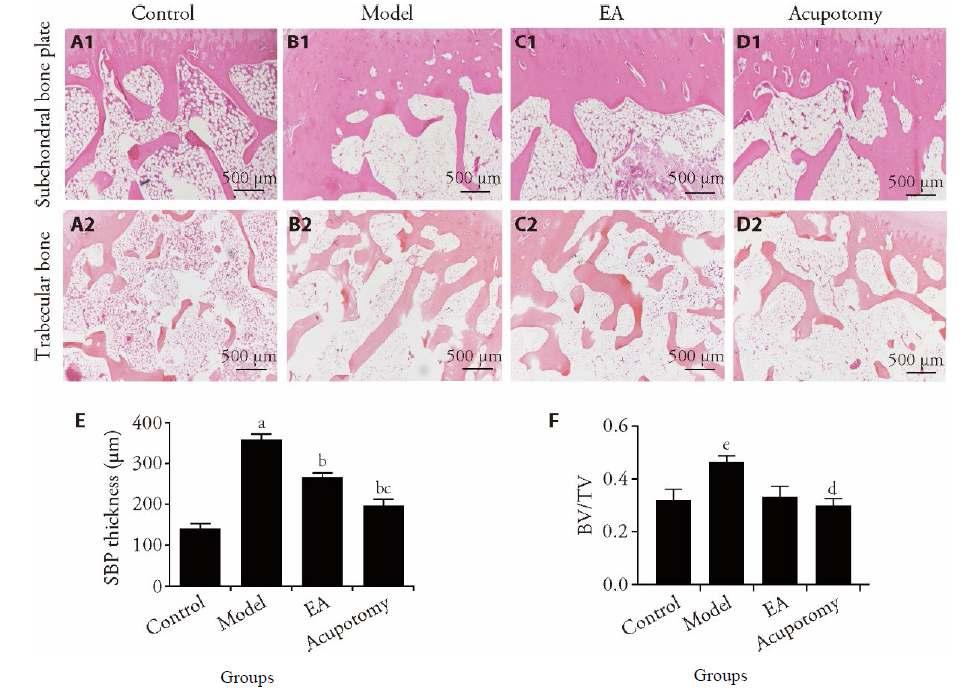
Figure 2 Histomorphometric analysis of subchondral bone A1-D1: subchondral bone plate (HE staining, × 40); A2-D2: trabecular bone (HE staining, ×40); A1, A2: control group; B1, B2: model group; C1, C2: EA group; D1, D2: acupotomy group. E and F: bone volume/tissue volume (BV/TV) and SBP thickness. Control group: without any treatments and model establishment; model group: treated without acupotomy or electroacupuncture but joined model establishment; Apo (acupotomy group: treated only with acupotomy and joined model establishment; EA (electroacupuncture group): treated only with electroacupuncture and joined model establishment. Data represents mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). Compared with the control group, aP < 0.01, eP < 0.05; compared with the model group, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.05; compared with the EA group, cP < 0.05.

Figure 3 Subchondral bone collagen fiber ultrastructure by scanning electron microscopy in different groups (magnification: ×5000, ×10000) A1-D1: trabecular bone collagen fiber (magnification: ×5000); A2-D2: trabecular bone collagen fiber (magnification: ×10000); A1, A2: control group; B1, B2: model group; C1, C2: acupotomy group; D1, D2: EA group. Control group: without any treatments and model establishment; model group: treated without acupotomy or electroacupuncture but joined model establishment; Apo (acupotomy group: treated only with acupotomy and joined model establishment; EA (electroacupuncture group): treated only with electroacupuncture and joined model establishment.

Figure 4 Effects of acupotomy and EA intervention on OPG/RANKL signaling pathway-related genes and proteins expression in subchondral bone A: protein expression of OPG and RANKL in different groups. B: OPG gene expression; C: RANKL gene expression; D: ratio of OPG mRNA/RANKL mRNA; E: OPG protein relative abundances; F: RANKL protein relative abundances; G: ratio of OPG protein/RANKL protein; Data represents mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). Compared with the control group, aP < 0.01, cP < 0.05; compared with the model group, dP < 0.01, bP < 0.05.

Figure 5 Immunohistochemical detection of RANKL and OPG in rabbits subchondral bone of different groups, and staining densities were quantified by IPP analysis. A1-D1: OPG; A2-D2: RANKL; A1, A2: control group; B1, B2: model group; C1, C2: EA group; D1, D2: acupotomy group. E, F: The mean ± SE staining density for RANKL (E) or OPG (F) protein expression. G: The mean RANKL/OPG ratio for protein expression. Data represents mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). Compared with the control group, aP < 0.05; compared with the model group, bP < 0.05. The red arrows represent cells positive for OPG and RANKL. OPG: Osteoprotegerin; RANKL: receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand.
| 1 |
Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012; 380:2163-96.
DOI URL |
| 2 |
Lane NE, Shidara K, Wise BL. Osteoarthritis year in review 2016: clinical. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2017; 25:209-15.
DOI URL |
| 3 |
Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, Goode AP, Jordan JM. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: the chronic osteoarthritis management initiative of the U.S. bone and joint initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2014; 43:701-12.
DOI URL |
| 4 | Hugle T, Geurts J. What drives osteoarthritis-synovial versus subchondral bone pathology. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2017; 56:1461-71. |
| 5 |
Iijima H, Aoyama T, Ito A, et al. Immature articular cartilage and subchondral bone covered by menisci are potentially susceptive to mechanical load. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2014; 15:101.
DOI URL |
| 6 |
Chen X, Wang ZQ, Duan N, Zhu GY, Schwarz EM, Xie C. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res 2018; 59:99-107.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
Zhen G, Wen C, Jia XF, et al. Inhibition of TGF-beta signaling in mesenchymal stem cells of subchondral bone attenuates osteoarthritis. Nat Med 2013; 19:704-12.
DOI URL |
| 8 |
Holzer LA, Kraiger M, Talakic E, et al. Microstructural analysis of subchondral bone in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoporos Int 2020; 31:2037-45.
DOI PMID |
| 9 |
Findlay DM, Atkins GJ. Osteoblast-chondrocyte interactions in osteoarthritis. Curr Osteoporos Rep 2014; 12:127-34.
DOI PMID |
| 10 |
Bellido M, Lugo L, Roman-Blas JA, et al. Subchondral bone microstructural damage by increased remodelling aggravates experimental osteoarthritis preceded by osteoporosis. Arthritis Res Ther 2010; 12:R152.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Schaffler MB, Kennedy OD. Osteocyte signaling in bone. Curr Osteoporos Rep 2012; 10:118-25.
DOI PMID |
| 12 | Zhou XC, Cao H, Yuan Y, Wu W. Biochemical Signals Mediate the Crosstalk between Cartilage and Bone in Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int 2020; 2020:5720360. |
| 13 |
Felson DT. Osteoarthritis as a disease of mechanics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013; 21:10-5.
DOI URL |
| 14 |
Lin M, Li X, Liang WN, et al. Needle-knife therapy improves the clinical symptoms of knee osteoarthritis by inhibiting the expression of inflammatory cytokines. Exp Ther Med 2014; 7:835-42.
DOI URL |
| 15 | Ma SN, Xie ZG, Guo Y, et al. Effect of acupotomy on FAK-PI3K signaling pathways in KOA rabbit articular cartilages. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017; 2017:4535326. |
| 16 | Liang CX, Guo Y, Tao L, et al. Effects of acupotomy intervention on regional pathological changes and expression of cartilage-mechanics related proteins in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2015; 40:119-24, 140. |
| 17 | Langenskiold A, Michelsson JE, Videman T. Osteoarthritis of the knee in the rabbit produced by immobilization. Attempts to achieve a reproducible model for studies on pathogenesis and therapy. Acta Orthop Scand 1979; 50:1-14. |
| 18 |
Nagira K, Ikuta Y, Shinohara M, et al. Histological scoring system for subchondral bone changes in murine models of joint aging and osteoarthritis. Sci Rep 2020; 10:10077.
DOI PMID |
| 19 |
Mitchell RE, Huitema LF, Skinner RE, et al. New tools for studying osteoarthritis genetics in zebrafish. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013; 21:269-78.
DOI URL |
| 20 |
Samvelyan HJ, Hughes D, Stevens C, Staines KA. Models of osteoarthritis: relevance and new insights. Calcif Tissue Int 2021; 109:243-56.
DOI URL |
| 21 |
Li W, Lin JJ, Wang ZW, et al. Bevacizumab tested for treatment of knee osteoarthritis via inhibition of synovial vascular hyperplasia in rabbits. J Orthop Translat 2019; 19:38-46.
DOI URL |
| 22 |
Matsui H, Shimizu M, Tsuji H. Cartilage and subchondral bone interaction in osteoarthrosis of human knee joint: a histological and histomorphometric study. Microsc Res Tech 1997; 37:333-42.
DOI URL |
| 23 |
Finnila M, Thevenot J, Aho OM, et al. Association between subchondral bone structure and osteoarthritis histopathological grade. J Orthop Res 2017; 35:785-92.
DOI URL |
| 24 |
Boyd SK, Muller R, Zernicke RF. Mechanical and architectural bone adaptation in early stage experimental osteoarthritis. J Bone Miner Res 2002; 17:687-94.
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Frost HM. From Wolff's law to the Utah paradigm: insights about bone physiology and its clinical applications. Anat Rec 2001; 262:398-419.
PMID |
| 26 |
Matsui H, Shimizu M, Tsuji H. Cartilage and subchondral bone interaction in osteoarthrosis of human knee joint: a histological and histomorphometric study. Microsc Res Tech 1997; 37:333-42.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Nakasa T, Ishikawa M, Takada T, Miyaki S, Ochi M. Attenuation of cartilage degeneration by calcitonin gene-related paptide receptor antagonist via inhibition of subchondral bone sclerosis in osteoarthritis mice. J Orthop Res 2016; 34:1177-84.
DOI URL |
| 28 |
Zhu XB, Chan YT, Yung PSH, Tuan RS, Jiang Y. Subchondral bone remodeling: a therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020; 8:607764.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Xu B, Xing RL, Huang ZQ, et al. Excessive mechanical stress induces chondrocyte apoptosis through TRPV4 in an anterior cruciate ligament-transected rat osteoarthritis model. Life Sci 2019; 228:158-66.
DOI URL |
| 30 |
He ZN, Nie PF, Lu JL, et al. Less mechanical loading attenuates osteoarthritis by reducing cartilage degeneration, subchondral bone remodelling, secondary inflammation, and activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Bone Joint Res 2020; 9:731-41.
DOI URL |
| 31 |
Wu L, Guo HH, Sun KN, Zhao X, Ma T, Jin CH. Sclerostin expression in the subchondral bone of patients with knee osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med 2016; 38:1395-402.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Cui Z, Crane J, Xie H, et al. Halofuginone attenuates osteoarthritis by inhibition of TGF-beta activity and H-type vessel formation in subchondral bone. Ann Rheum Dis 2016; 75:1714-21.
DOI URL |
| 33 |
Bannuru RR, Osani MC, Vaysbrot EE, et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2019; 27:1578-89.
DOI URL |
| 34 |
Arden NK, Perry TA, Bannuru RR, et al. Non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis: comparison of ESCEO and OARSI 2019 guidelines. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2021; 17:59-66.
DOI URL |
| 35 |
Greif DN, Emerson CP, Jose J, Toumi H, Best TM. Enthesopathy-an underappreciated role in osteoarthritis? Curr Sports Med Rep 2020; 19:495-7.
DOI URL |
| 36 |
Resorlu M, Doner D, Karatag O, Toprak CA. The Relationship between chondromalacia patella, medial meniscal tear and medial periarticular bursitis in patients with osteoarthritis. Radiol Oncol 2017; 51:401-6.
DOI URL |
| 37 | Zhong WQ, Lao JX, Li SC, et al. Observation on the difference of curative effect between Neixiyan and Waixiyan on degenerative knee osteoarthritis. Guang Ming Zhong Yi 2011; 26:108-9. |
| 38 | Que Q H, He F, Wang J, et al. Application of five points behind the knee combined with electroacupuncture in the treatment of early knee osteoarthritis. Rehabilitation Medicine 2014; 24:55-6. |
| 39 | Zhang TM, Zhang Q, Zeng CX, et al. The tool and effect principle of acupotomology. Zhong Guo Yi Yao Dao Bao 2016; 13:163-6. |
| 40 | Liu BZ. Study on the etiology and pathology of chronic soft tissue injury and the mechanism of acupotomy. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Yuan Chen Jiao Yu 2012; 10:58-60. |
| 41 | Lin WC, Liu CY, Tang CL, Hsu CH. Acupuncture and small needle scalpel therapy in the treatment of calcifying tendonitis of the gluteus medius: a case report. Acupunct Med 2012; 30. |
| 42 |
Mills K, Hunt MA, Leigh R, Ferber R. A systematic review and Meta-analysis of lower limb neuromuscular alterations associated with knee osteoarthritis during level walking. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2013; 28:713-24.
DOI URL |
| 43 | Fu D E L, Guo CQ, Jin XF, et al. Effect of acupotomy treatment on tensile mechanical properties of medial collateral ligaments in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis. Shi Jie Zhong Yi Yao 2014; 9:912-5. |
| 44 | Wang LJ, Shi XW, Zhang W, Wang T, Zhou S, Guo CQ. Effect of needle knife intervention on tensile mechanics of femoral quadriceps tendon in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis. Zhong Guo Gu Shang 2019; 32:462-8. |
| 45 | Hu B, Yu JN, Zhang HF, Liu NG, Guo CQ. Effect of acupotomy intervention on contractility of quadriceps femoris and pathological changes of articular cartilage in KOA rabbits. Zhen Jiu Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2018; 34:50-4. |
| 46 | Gao Y, Wang T, Zhang W, et al. Effect of acupotomy on chondrocyte proliferation and expression of CyclinD1, CDK4 and CDK6 in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis. J Tradit Chin Med Sci 2019; 6:277-91. |
| 47 |
Schaffler MB, Kennedy OD. Osteocyte signaling in bone. Curr Osteoporos Rep 2012; 10:118-25.
DOI PMID |
| 48 |
Zheng WW, Li XL, Liu DQ, et al. Mechanical loading mitigates osteoarthritis symptoms by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy. Faseb J 2019; 33:4077-88.
DOI URL |
| 49 |
Zhen G, Wen C, Jia X, et al. Inhibition of TGF-beta signaling in mesenchymal stem cells of subchondral bone attenuates osteoarthritis. Nat Med 2013; 19:704-12.
DOI URL |
| 50 |
Lin CX, Liu LL, Zeng C, et al. Activation of mTORC1 in subchondral bone preosteoblasts promotes osteoarthritis by stimulating bone sclerosis and secretion of CXCL12. Bone Res 2019; 7:5.
DOI URL |
| 51 |
Yang PF, Nie XT, Zhao DD, et al. Deformation regimes of collagen fibrils in cortical bone revealed by in situ morphology and elastic modulus observations under mechanical loading. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 2018; 79:115-21.
DOI URL |
| 52 |
Garnero P. The role of collagen organization on the properties of bone. Calcif Tissue Int 2015; 97:229-40.
DOI URL |
| 53 |
Bailey AJ, Sims TJ, Knott L. Phenotypic expression of osteoblast collagen in osteoarthritic bone: production of type I homotrimer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2002; 34:176-82.
DOI URL |
| 54 |
Zhang Y, Paul EM, Sathyendra V, et al. Enhanced osteoclastic resorption and responsiveness to mechanical load in gap junction deficient bone. PLoS One 2011; 6:e23516.
DOI URL |
| 55 |
Sanchez C, Pesesse L, Gabay O, et al. Regulation of subchondral bone osteoblast metabolism by cyclic compression. Arthritis Rheum 2012; 64:1193-203.
DOI URL |
| 56 |
Chatmahamongkol C, Pravitharangul A, Suttapreyasri S, Leethanakul C. The effect of compressive force combined with mechanical vibration on human alveolar bone osteoblasts. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res 2019; 9:81-5.
DOI PMID |
| 57 |
Wu YQ, Zhang P, Dai QG, et al. Osteoclastogenesis accom-panying early osteoblastic differentiation of BMSCs promoted by mechanical stretch. Biomed Rep 2013; 1:474-8.
DOI URL |
| 58 | Vaysbrot EE, Osani MC, Musetti MC, McAlindon TE, Bannuru RR. Are bisphosphonates efficacious in knee osteoarthritis? A Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2018; 26:154-64. |
| 59 |
Martel-Pelletier J, Barr AJ, Cicuttini FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2016; 2:16072.
DOI PMID |
| 60 |
Sun YJ, Wu YC, Zhang FJ, Zhang P, Tang ZY. Effects of electroacupuncture on muscle state and electrophysiological changes in rabbits with lumbar nerve root compression. Chin J Integr Med 2013; 19:446-52.
DOI URL |
| [1] | YANG Yi, YE Huijun, ZHENG Huiling, JIN Lihua. Clinical observation on 90 cases of primary dysmenorrhea treated by buccal acupuncture therapy: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 172-181. |
| [2] | Chen Xilin, GUO Yan, LU Juan, QIN Luxue, HU Tingyao, ZENG Xin, WANG Xinyue, ZHANG Anran, ZHUANG Yuxin, ZHONG Honggang, GUO Changqing. Acupotomy ameliorates subchondral bone absorption and mechanical properties in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis by regulating bone morphogenetic protein 2-Smad1 pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 734-743. |
| [3] | CHEN Ying, SUN Jingqing, LYU Tianli, HONG Jiahui, LIU Yuhan, ZHU Liying, LI Bin, LIU Lu. Effect of acupuncture treatment on nonketotic hyperglycemic hemichorea-hemiballismus: a case report [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 829-833. |
| [4] | YIN Xiuping, ZHANG Xiaotong, ZHU Rongjia, SONG Ping. Effect of astragaloside IV on the immunoregulatory function of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from patients with psoriasis vulgaris [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 513-519. |
| [5] | HAO Fuliang, MEI Shuang, LIU Xiao, LIU Yang, ZHANG Xudong, DONG Fusheng. Icariin contributes to healing skull defects in rabbit models [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 470-477. |
| [6] | Fang Ting, Li Qi, Zhou Fanyuan, Liu Fushui, Liu Zhongyong, Zhao Meimei, Chen Mei, You Jianyu, Jin Yuli, Xie Jinmei. Effect and safety of acupotomy in treatment of knee osteoarthritis:a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(3): 355-364. |
| [7] | Siu Wing Sum, Shiu Hoi Ting, Shum Wai Ting, Ko Chun Hay, Lau Clara Bik San, Hung Leung Kim, Leung Ping Chung. Chinese topical herbal medicine gives additive effect on pharmaceutical agent on fracture healing [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(06): 853-860. |
| [8] | Zhang Wei, Gao Yang, Guo Changqing, Ibrahim Zeyad Ali Khattab, Farid Mokhtari. Effect of acupotomy versus electroacupuncture on ethology and morphology in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(02): 229-236. |
| [9] | Dai Yan, Chen Qingqing, Guan Ruodan, Xu Rui, Qiu Chang, Song Xue, Guo Qianqian, Wang Zhiyu, Chen Qianjun. Effect of Jianpi Bushen formula on aromatase-inhibitor-associated bone loss after menopause [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(06): 879-889. |
| [10] | Zheng Yu, Lu Luo, Yu Li, Qiaofeng Wu, Shufang Deng, Shouying Lian, Fanrong Liang. Different manual manipulations and electrical parameters exert different therapeutic effects of acupuncture [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014, 34(06): 754-758. |
| [11] | Tao Huang, Lijian Yang, Shuyong Jia, Xiang Mu, Mozheng Wu, Hang Ye, Weizhe Liu, Xinnong Cheng. Capillary blood flow in patients with dysmenorrhea treated with acupuncture [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(06): 757-760. |
| [12] | Wei He, Yuanyuan Tong, Yingkai Zhao, Li Zhang, Hui Ben, Qingguang Qin, Feng Huang, Peijing Rong. Review of controlled clinical trials on acupuncture versus sham acupuncture in Germany [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(03): 403-407. |
| [13] | Ji Chen, Yulan Ren, Yong Tang, Zhengjie Li, Fanrong Liang. Acupuncture therapy for angina pectoris:a systematic review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012, 32(04): 494-501. |
| [14] | Youzhi Sun, Steve An Xue, Zhengyun Zuo. Acupuncture therapy on apoplectic aphasia rehabilitation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012, 32(03): 314-321. |
| [15] | Xuming Yang, Lingyu Xu, Fei Zhong, Ying Zhu. Data mining-based detection of acupuncture treatment on juvenile myopia [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012, 32(03): 372-376. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

