Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 1024-1034.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.05.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Association of miR-499 rs3746444, miR-149 rs2292832 polymorphisms and their expression levels with helicobacter pylori-related gastric diseases and Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes
LIU Qi1, YU Chang1, YE Jintong1, ZHANG Ling1, LI Danyan1, DAI Yunkai1, ZHANG Yunzhan1, LUO Qi2, CHEN Weijing1, PAN Huaigeng1, LI Ruliu1, HU Ling1( )
)
- 1 Institute of Gastroenterology, Science and Technology Innovation Center, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, China
2 First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, China
-
Received:2023-06-22Accepted:2023-09-15Online:2024-10-15Published:2024-09-11 -
Contact:HU Ling, Institute of Gastroenterology, Science and Technology Innovation Center, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, China. drhuling@163.com -
Supported by:Exploration of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Characteristics During Benign and Malignant Pathological Evolution in Hp-Related Gastric Diseases from Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway based on the Theory of "Evil Poison Lead to Change"(81774238);Exploration of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Characteristics During Benign and Malignant Pathological Evolution in Hp-Related Gastric Diseases based on the Theory of "Latent Toxin" and the Polymorphism and Expression of Mucosal Barrier Related Genes(82174298)
Cite this article
LIU Qi, YU Chang, YE Jintong, ZHANG Ling, LI Danyan, DAI Yunkai, ZHANG Yunzhan, LUO Qi, CHEN Weijing, PAN Huaigeng, LI Ruliu, HU Ling. Association of miR-499 rs3746444, miR-149 rs2292832 polymorphisms and their expression levels with helicobacter pylori-related gastric diseases and Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 1024-1034.
share this article
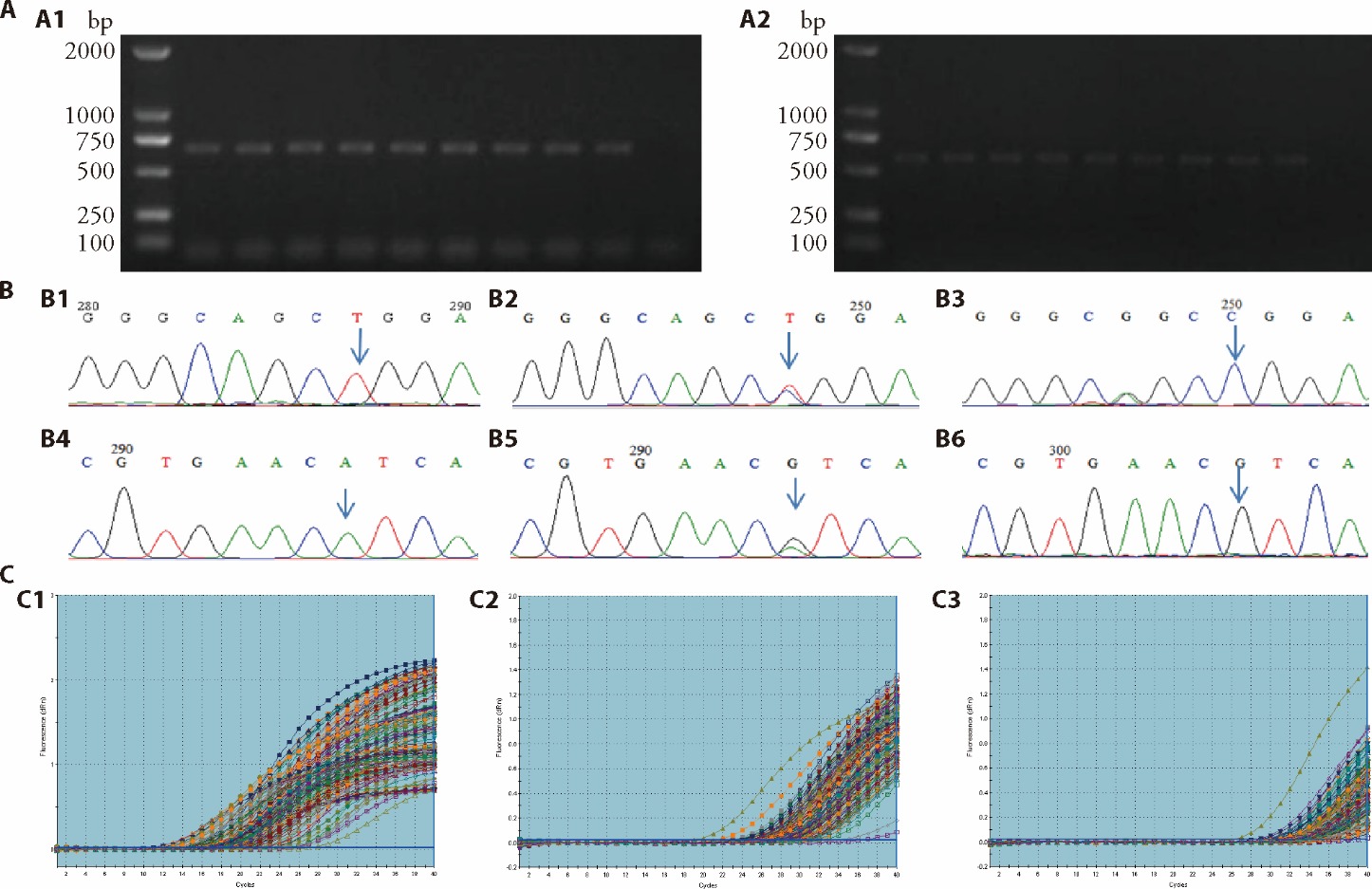
Figure 1 Genotying results of miR-499 rs3746444/miR-149 rs2292832 and detection of the relative expression of miR-499/miR-149 A: 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis for quality identification of PCR amplification products. A1: amplification of miR-149 rs2292832 locus; A2: amplification of miR-499 rs3746444 locus. 1 and 10 are positive control and negative control, respectively; Lane 2 to 9 represent 8 different individuals. B: Genotyping for miR-149 rs2292832 and miR-499 rs3746444. B1: TT homozygous wild type at miR-149 rs2292832; B2: CT heterozygous mutant type at miR-149 rs2292832; B3: CC homozygous mutant type at miR-149 rs2292832; B4: AA homozygous wild type at miR-499 rs3746444; B5: AG heterozygous mutant type at miR-499 rs3746444; B6: GG homozygous mutant type at miR-499 rs3746444. C: amplification curves of target gene and internal reference gene. C1: internal reference gene U6; C2: miR-149; C3: miR-499. PCR: polymerase chain reaction; bp: base pair; M: Maker; miR: microRNA.
| Variable | HC (n = 35) | CI (n = 23) | GA (n = 11) | PGL (n = 79) | APL (n = 10) | GC (n = 45) | χ2 value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 2.46 | 0.782a | ||||||
| ≤40 | 11 | 8 | 3 | 21 | 1 | 12 | ||
| >40 | 24 | 15 | 8 | 58 | 9 | 33 | ||
| Gender | 5.93 | 0.313a | ||||||
| Male | 18 | 11 | 6 | 52 | 6 | 32 | ||
| Female | 17 | 12 | 5 | 27 | 4 | 13 | ||
| H. pylori | 29.52 | <0.001b | ||||||
| Positive | 19 | 15 | 11 | 73 | 10 | 39 | ||
| Negative | 16 | 8 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 |
Table 1 The baseline characteristics of participants (n)
| Variable | HC (n = 35) | CI (n = 23) | GA (n = 11) | PGL (n = 79) | APL (n = 10) | GC (n = 45) | χ2 value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 2.46 | 0.782a | ||||||
| ≤40 | 11 | 8 | 3 | 21 | 1 | 12 | ||
| >40 | 24 | 15 | 8 | 58 | 9 | 33 | ||
| Gender | 5.93 | 0.313a | ||||||
| Male | 18 | 11 | 6 | 52 | 6 | 32 | ||
| Female | 17 | 12 | 5 | 27 | 4 | 13 | ||
| H. pylori | 29.52 | <0.001b | ||||||
| Positive | 19 | 15 | 11 | 73 | 10 | 39 | ||
| Negative | 16 | 8 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 |
| Group | Genotype [n (%)] | Adjusteda OR (95% CI), P value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | AG | GG | AG vs AA | AG+GG vs AA | G vs A | ||
| Pathological groups | HC | 28 (80.0) | 7 (20.0) | 0 (0.0) | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| CI | 19 (82.6) | 4 (17.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0.814 (0.207-3.201), 0.768 | 0.815 (0.208-3.200), 0.770 | 0.834 (0.229-3.041), 0.783 | |
| GA | 9 (81.8) | 2 (18.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0.871 (0.143-5.304), 0.881 | 0.862 (0.142-5.238), 0.872 | 0.865 (0.158-4.733), 0.867 | |
| PGL | 61 (77.2) | 17 (21.5) | 1 (1.3) | 1.157 (0.400-3.343), 0.788 | 1.186 (0.414-3.398), 0.751 | 1.189 (0.447-3.162), 0.729 | |
| APL | 9 (90.0) | 1 (10.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.481 (0.049-4.757), 0.531 | 0.492 (0.050-4.861), 0.544 | 0.531 (0.058-4.839), 0.575 | |
| GC | 35 (77.8) | 9 (20.0) | 1 (2.2) | 1.125 (0.349-3.633), 0.843 | 1.266 (0.401-3.998), 0.688 | 1.379 (0.479-3.969), 0.551 | |
| TCM syndromes | NON | 9 (81.8) | 2 (18.2) | 0 (0.0) | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| SSDHS | 69 (77.5) | 19 (21.4) | 1 (1.1) | 1.312 (0.240-7.186), 0.754 | 1.314 (0.242-7.141), 0.752 | 1.275 (0.259-6.282), 0.765 | |
| LSDS | 52 (78.8) | 14 (21.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1.192 (0.203-6.997), 0.846 | 1.098 (0.188-6.400), 0.917 | 1.002 (0.190-5.279), 0.998 | |
| SQDS | 27 (84.4) | 4 (12.5) | 1 (3.1) | 0.649 (0.095-4.413), 0.658 | 0.807 (0.125-5.196), 0.807 | 0.986 (0.175-5.545), 0.987 | |
| IBSBS | 4 (80.0) | 1 (20.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1.052 (0.065-17.030), 0.971 | 1.022 (0.063-16.471), 0.988 | 0.991 (0.073-13.520), 0.994 | |
Table 2 Association of miR-499 rs3746444 (A > G) with gastric pathological features and TCM syndromes
| Group | Genotype [n (%)] | Adjusteda OR (95% CI), P value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | AG | GG | AG vs AA | AG+GG vs AA | G vs A | ||
| Pathological groups | HC | 28 (80.0) | 7 (20.0) | 0 (0.0) | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| CI | 19 (82.6) | 4 (17.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0.814 (0.207-3.201), 0.768 | 0.815 (0.208-3.200), 0.770 | 0.834 (0.229-3.041), 0.783 | |
| GA | 9 (81.8) | 2 (18.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0.871 (0.143-5.304), 0.881 | 0.862 (0.142-5.238), 0.872 | 0.865 (0.158-4.733), 0.867 | |
| PGL | 61 (77.2) | 17 (21.5) | 1 (1.3) | 1.157 (0.400-3.343), 0.788 | 1.186 (0.414-3.398), 0.751 | 1.189 (0.447-3.162), 0.729 | |
| APL | 9 (90.0) | 1 (10.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.481 (0.049-4.757), 0.531 | 0.492 (0.050-4.861), 0.544 | 0.531 (0.058-4.839), 0.575 | |
| GC | 35 (77.8) | 9 (20.0) | 1 (2.2) | 1.125 (0.349-3.633), 0.843 | 1.266 (0.401-3.998), 0.688 | 1.379 (0.479-3.969), 0.551 | |
| TCM syndromes | NON | 9 (81.8) | 2 (18.2) | 0 (0.0) | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| SSDHS | 69 (77.5) | 19 (21.4) | 1 (1.1) | 1.312 (0.240-7.186), 0.754 | 1.314 (0.242-7.141), 0.752 | 1.275 (0.259-6.282), 0.765 | |
| LSDS | 52 (78.8) | 14 (21.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1.192 (0.203-6.997), 0.846 | 1.098 (0.188-6.400), 0.917 | 1.002 (0.190-5.279), 0.998 | |
| SQDS | 27 (84.4) | 4 (12.5) | 1 (3.1) | 0.649 (0.095-4.413), 0.658 | 0.807 (0.125-5.196), 0.807 | 0.986 (0.175-5.545), 0.987 | |
| IBSBS | 4 (80.0) | 1 (20.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1.052 (0.065-17.030), 0.971 | 1.022 (0.063-16.471), 0.988 | 0.991 (0.073-13.520), 0.994 | |
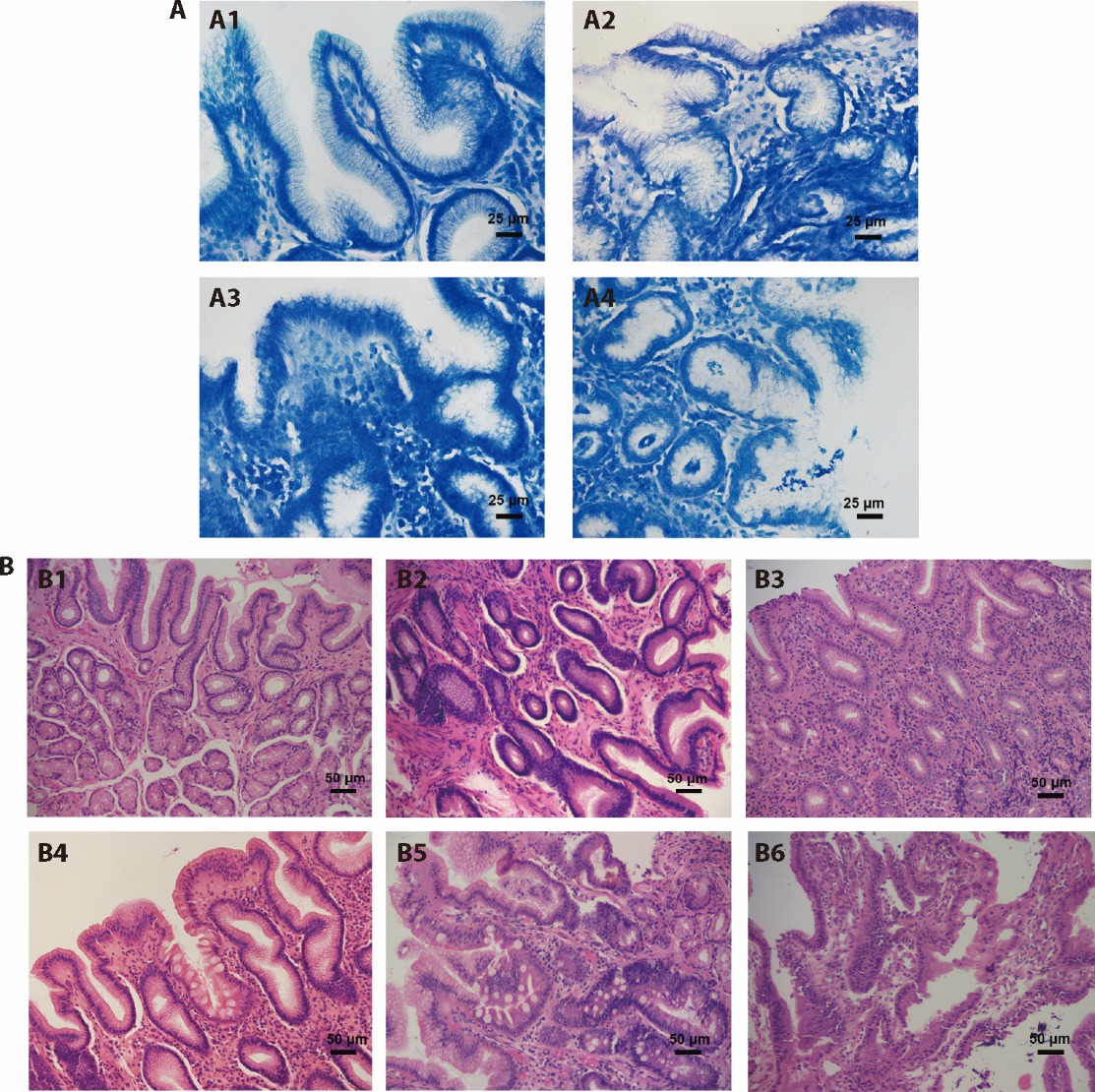
Figure 2 representative images of H. pylori infection and different gastric mucosal pathological changes A: H. pylori infection in gastric mucosa (methylene blue staining, ×400). A1: H. pylori negative; A2: mild H. pylori infection; A3: moderate H. pylori infection; A4: severe H. pylori infection. B: histopathological changes of gastric mucosa (hematoxylin-eosin staining, ×200). B1: normal gastric mucosa; B2: gastric mucosa with moderate inflammation; B3: moderate atrophic gastric mucosa with severe inflammation; B4: moderate dysplasia of gastric mucosa with mild atrophy, intestinal metaplasia, inflammation; B5: severe dysplasia of gastric mucosa with moderate intestinal metaplasia; B6: gastric mucosal carcinogenesis. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
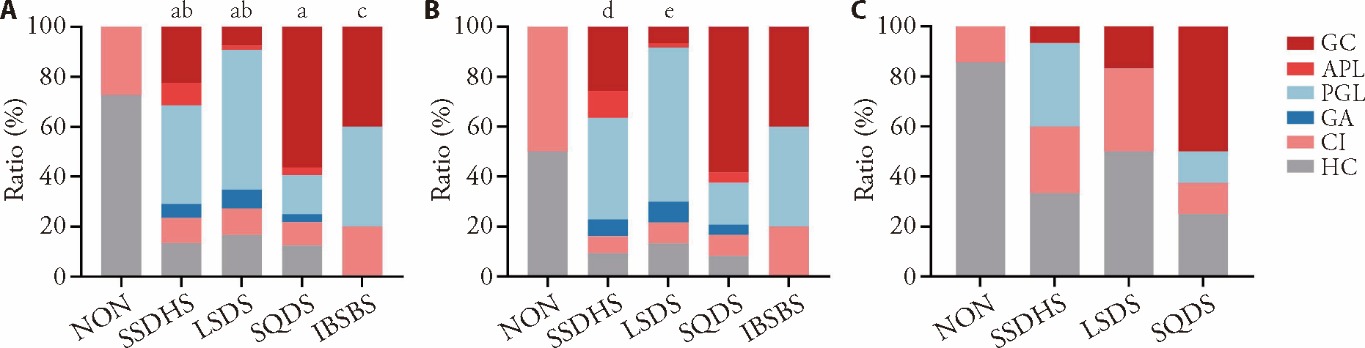
Figure 3 Comparison between different TCM syndrome groups A: comparison among all subjects (n = 203); B: comparison among H. pylori-positive subjects (n = 167); C: comparison among H. pylori-negative subjects (n = 36). NON group: subjects without obvious symptoms; SSDHS group: subjects diagnosed with SSDHS; LSDS group: subjects diagnosed with LSDS; SQDS group: subjects diagnosed with SQDS; IBSBS group: subjects diagnosed with IBSBS. TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; HC: healthy control; CI: chronic inflammation; GA: gastric atrophy; PGL: precancerous gastric lesions; APL: advanced precancerous lesions; GC: gastric cancer; SSDHS: spleen-stomach damp-heat syndrome; LSDS: liver-stomach disharmony syndrome; SQDS: spleen Qi deficiency syndrome; IBSBS: internal block of static blood syndrome; NON: non-symptomatic. The count data was compared by χ2 test and Fisher’s exact test. aP ﹤0.001 and cP ﹤0.01, compared with the NON group. bP ﹤0.001 and eP ﹤0.001, compared with the SQDS group. dP ﹤0.01, compared with the SQDS group.
| Group | Genotype [n (%)] | Adjusteda OR (95% CI), P value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TT | CT | CC | CT vs TT | CT + CC vs TT | C vs T | |
| Pathological | ||||||
| HC | 15 (42.8) | 17 (48.6) | 3 (8.6) | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| CI | 10 (43.5) | 10 (43.5) | 3 (13.0) | 0.920 (0.296-2.854), 0.885 | 1.012 (0.346-2.957), 0.983 | 1.105 (0.502-2.436), 0.804 |
| GA | 9 (81.8) | 2 (18.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0.245 (0.043-1.386), 0.112 | 0.192 (0.035-1.063), 0.059 | 0.207 (0.043-0.989), 0.048 |
| PGL | 32 (40.5) | 42 (53.2) | 5 (6.3) | 1.472 (0.593-3.651), 0.405 | 1.266 (0.531-3.019), 0.595 | 1.001 (0.524-1.912), 0.997 |
| APL | 4 (40.0) | 6 (60.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1.665 (0.364-7.605), 0.511 | 1.294 (0.290-5.778), 0.735 | 0.890 (0.288-2.744), 0.839 |
| GC | 21 (46.7) | 17 (37.8) | 7 (15.5) | 0.871 (0.319-2.378), 0.787 | 0.982 (0.381-2.533), 0.970 | 1.102 (0.543-2.235), 0.789 |
| TCM syndromes | ||||||
| NON | 3 (27.3) | 8 (72.7) | 0 (0.0) | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| SSDHS | 38 (42.7) | 39 (43.8) | 12 (13.5) | 0.376 (0.087-1.632), 0.192 | 0.467 (0.108-2.019), 0.308 | 0.878 (0.333-2.320), 0.794 |
| LSDS | 31 (47.0) | 30 (45.4) | 5 (7.6) | 0.351 (0.077-1.601), 0.176 | 0.387 (0.085-1.762), 0.220 | 0.694 (0.251-1.915), 0.480 |
| SQDS | 14 (43.8) | 17 (53.1) | 1 (3.1) | 0.436 (0.092-2.069), 0.296 | 0.447 (0.094-2.119), 0.310 | 0.693 (0.241-1.998), 0.498 |
| IBSBS | 5 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | - | - |
Table 3 Association of miR-149 rs2292832 (T > C) with gastric pathological features and TCM syndromes
| Group | Genotype [n (%)] | Adjusteda OR (95% CI), P value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TT | CT | CC | CT vs TT | CT + CC vs TT | C vs T | |
| Pathological | ||||||
| HC | 15 (42.8) | 17 (48.6) | 3 (8.6) | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| CI | 10 (43.5) | 10 (43.5) | 3 (13.0) | 0.920 (0.296-2.854), 0.885 | 1.012 (0.346-2.957), 0.983 | 1.105 (0.502-2.436), 0.804 |
| GA | 9 (81.8) | 2 (18.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0.245 (0.043-1.386), 0.112 | 0.192 (0.035-1.063), 0.059 | 0.207 (0.043-0.989), 0.048 |
| PGL | 32 (40.5) | 42 (53.2) | 5 (6.3) | 1.472 (0.593-3.651), 0.405 | 1.266 (0.531-3.019), 0.595 | 1.001 (0.524-1.912), 0.997 |
| APL | 4 (40.0) | 6 (60.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1.665 (0.364-7.605), 0.511 | 1.294 (0.290-5.778), 0.735 | 0.890 (0.288-2.744), 0.839 |
| GC | 21 (46.7) | 17 (37.8) | 7 (15.5) | 0.871 (0.319-2.378), 0.787 | 0.982 (0.381-2.533), 0.970 | 1.102 (0.543-2.235), 0.789 |
| TCM syndromes | ||||||
| NON | 3 (27.3) | 8 (72.7) | 0 (0.0) | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| SSDHS | 38 (42.7) | 39 (43.8) | 12 (13.5) | 0.376 (0.087-1.632), 0.192 | 0.467 (0.108-2.019), 0.308 | 0.878 (0.333-2.320), 0.794 |
| LSDS | 31 (47.0) | 30 (45.4) | 5 (7.6) | 0.351 (0.077-1.601), 0.176 | 0.387 (0.085-1.762), 0.220 | 0.694 (0.251-1.915), 0.480 |
| SQDS | 14 (43.8) | 17 (53.1) | 1 (3.1) | 0.436 (0.092-2.069), 0.296 | 0.447 (0.094-2.119), 0.310 | 0.693 (0.241-1.998), 0.498 |
| IBSBS | 5 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | - | - |
| Genotype | HC (n = 35) | CI (n = 23) | P, OR (95% CI) | GA (n = 11) | P, OR (95% CI) | PGL (n = 79) | P, OR (95% CI) | APL (n = 10) | P, OR (95% CI) | GC (n = 45) | P, OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA/TT | 13 (37.1) | 8 (34.8) | 0.855, 1.108 (0.369-3.323) | 7 (63.6) | 0.169, 0.338 (0.083-1.379) | 26 (32.9) | 0.660, 1.205 (0.525-2.765) | 3 (30.0) | 1.000, 1.379 (0.303-6.281) | 18 (40.0) | 0.795, 0.886 (0.357-2.199) |
| AA/CT | 13 (37.1) | 8 (34.8) | 0.855, 1.108 (0.369-3.323) | 2 (18.2) | 0.296, 2.659 (0.496-14.247) | 31 (39.2) | 0.832, 0.915 (0.403-2.080) | 6 (60.0) | 0.281, 0.394 (0.093-1.661) | 11 (24.4) | 0.219, 1.826 (0.695-4.797) |
| AA/CC | 2 (5.7) | 3 (13.0) | 0.376, 0.404 (0.062-2.631) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000, - | 4 (5.1) | 1.000, 1.136 (0.198-6.514) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000, - | 6 (13.4) | 0.455, 0.394 (0.074-2.085) |
| AG/TT | 2 (5.7) | 2 (8.7) | 1.000, 0.636 (0.083-4.896) | 2 (18.2) | 0.238, 0.273 (0.034-2.214) | 5 (6.3) | 1.000, 0.897 (0.165-4.863) | 1 (10.0) | 0.539, 0.545 (0.044-6.719) | 3 (6.7) | 1.000, 0.848 (0.134-5.377) |
| AG/CT | 4 (11.4) | 2 (8.7) | 1.000, 1.355 (0.227-8.078) | 0 (0.0) | 0.559, - | 11 (13.9) | 1.000, 0.798 (0.235-2.704) | 0 (0.0) | 0.561, - | 5 (11.1) | 1.000, 1.032 (0.256-4.169) |
| AG/CC | 1 (3.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | 1.000, - | 1 (1.3) | 0.522, 2.294 (0.139-37.761) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000, - | 1 (2.2) | 1.000, 1.294 (0.078-21.446) |
| GG/TT | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 1 (1.3) | 1.000, - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - |
| GG/CT | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 1 (2.2) | 1.000, - |
| GG/CC | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - |
Table 4 Distribution of combined genotypes of miR-499 and miR-149 among pathological groups [n (%)]
| Genotype | HC (n = 35) | CI (n = 23) | P, OR (95% CI) | GA (n = 11) | P, OR (95% CI) | PGL (n = 79) | P, OR (95% CI) | APL (n = 10) | P, OR (95% CI) | GC (n = 45) | P, OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA/TT | 13 (37.1) | 8 (34.8) | 0.855, 1.108 (0.369-3.323) | 7 (63.6) | 0.169, 0.338 (0.083-1.379) | 26 (32.9) | 0.660, 1.205 (0.525-2.765) | 3 (30.0) | 1.000, 1.379 (0.303-6.281) | 18 (40.0) | 0.795, 0.886 (0.357-2.199) |
| AA/CT | 13 (37.1) | 8 (34.8) | 0.855, 1.108 (0.369-3.323) | 2 (18.2) | 0.296, 2.659 (0.496-14.247) | 31 (39.2) | 0.832, 0.915 (0.403-2.080) | 6 (60.0) | 0.281, 0.394 (0.093-1.661) | 11 (24.4) | 0.219, 1.826 (0.695-4.797) |
| AA/CC | 2 (5.7) | 3 (13.0) | 0.376, 0.404 (0.062-2.631) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000, - | 4 (5.1) | 1.000, 1.136 (0.198-6.514) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000, - | 6 (13.4) | 0.455, 0.394 (0.074-2.085) |
| AG/TT | 2 (5.7) | 2 (8.7) | 1.000, 0.636 (0.083-4.896) | 2 (18.2) | 0.238, 0.273 (0.034-2.214) | 5 (6.3) | 1.000, 0.897 (0.165-4.863) | 1 (10.0) | 0.539, 0.545 (0.044-6.719) | 3 (6.7) | 1.000, 0.848 (0.134-5.377) |
| AG/CT | 4 (11.4) | 2 (8.7) | 1.000, 1.355 (0.227-8.078) | 0 (0.0) | 0.559, - | 11 (13.9) | 1.000, 0.798 (0.235-2.704) | 0 (0.0) | 0.561, - | 5 (11.1) | 1.000, 1.032 (0.256-4.169) |
| AG/CC | 1 (3.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | 1.000, - | 1 (1.3) | 0.522, 2.294 (0.139-37.761) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000, - | 1 (2.2) | 1.000, 1.294 (0.078-21.446) |
| GG/TT | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 1 (1.3) | 1.000, - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - |
| GG/CT | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 1 (2.2) | 1.000, - |
| GG/CC | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - | 0 (0.0) | - |

Figure 4 Comparison of miR-499 and miR-149 expression levels between different pathological groups and TCM syndromes A: comparison of miR-499 expression level between pathological groups among all subjects (n = 203); B: comparison of miR-499 expression level between pathological groups among H. pylori positive subjects (n = 167); C: comparison of miR-499 expression level between pathological groups among negative subjects (n = 36); D: comparison of miR-149 expression level between pathological groups among all subjects (n = 203); E: comparison of miR-149 expression level between pathological groups among H. pylori positive subjects (n = 167); F: comparison of miR-149 expression level between pathological groups among negative subjects (n = 36); G: comparison of miR-499 expression level between different TCM syndromes among all subjects (n = 203); H: comparison of miR-499 expression level between different TCM syndromes among H. pylori positive subjects (n = 167); I: comparison of miR-499 expression level between different TCM syndromes among negative subjects (n = 36); J: comparison of miR-149 expression level between different TCM syndromes among all subjects (n = 203); K: comparison of miR-149 expression level between different TCM syndromes among H. pylori positive subjects (n = 167); L: comparison of miR-149 expression level between different TCM syndromes among negative subjects (n = 36). The column height represents the median expression levels of miRNAs and the error bars represent the interquartile range. HC group includes healthy individuals subjected to routine physical examination; CI group includes patients with moderate to severe gastric mucosal inflammation; GA group contains patients only suffering from gastric mucosal atrophy; PGL group involves patients with gastric atrophy accompanied by intestinal metaplasia or dysplasia. APL group comprises patients with severe dysplasia; GC group includes patients diagnosed with gastric cancer. NON group: subjects without obvious symptoms; SSDHS group: subjects diagnosed with SSDHS; LSDS group: subjects diagnosed with LSDS; SQDS group: subjects diagnosed with SQDS; IBSBS group: subjects diagnosed with IBSBS. HC: healthy control; CI: chronic inflammation; GA: gastric atrophy; PGL: precancerous gastric lesions; APL: advanced precancerous lesions; GC: gastric cancer. SSDHS: spleen-stomach damp-heat syndrome; LSDS: liver-stomach disharmony syndrome; SQDS: spleen Qi deficiency syndrome; IBSBS: internal block of static blood syndrome; NON: non-symptomatic; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori. The measurement data was compared by Kruskal-Wallis test. aP ﹤0.01 and cP ﹤0.05, compared with the GC group. bP ﹤0.05 and dP ﹤0.01, compared with the HC group.
| Relative expression level | Median | GC | HC | Crude OR (95% CI) | Adjustedb OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-499 | |||||
| Q1 (≤0.38) | 0.15 | 7 | 13 | 1.000 (reference) | 1.000 (reference) |
| Q2 (0.39-1.02) | 0.67 | 11 | 9 | 2.270 (0.636-8.106) | 1.816 (0.414-7.962) |
| Q3 (1.03-2.18) | 1.48 | 12 | 8 | 2.786 (0.773-10.043) | 3.230 (0.728-14.327) |
| Q4 (≥2.19) | 6.23 | 15 | 5 | 5.571 (1.420-21.860) | 6.482 (1.283-32.752) |
| P for trend | - | - | - | 0.032 | 0.035 |
| miR-149 | |||||
| Q1 (≤0.21) | 0.10 | 17 | 3 | 1.000 (reference) | 1.000 (reference) |
| Q2 (0.22-0.64) | 0.34 | 10 | 11 | 0.160 (0.036-0.717) | 0.166 (0.031-0.881) |
| Q3 (0.65-1.35) | 1.01 | 13 | 6 | 0.382 (0.080-1.825) | 0.467 (0.083-2.607) |
| Q4 (≥1.36) | 2.39 | 5 | 15 | 0.059 (0.012-0.289) | 0.075 (0.012-0.463) |
| P for trend | - | - | - | 0.002 | 0.028 |
Table 5 ORsa of GC by quartiles of expression levels of miR-499/miR-149
| Relative expression level | Median | GC | HC | Crude OR (95% CI) | Adjustedb OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-499 | |||||
| Q1 (≤0.38) | 0.15 | 7 | 13 | 1.000 (reference) | 1.000 (reference) |
| Q2 (0.39-1.02) | 0.67 | 11 | 9 | 2.270 (0.636-8.106) | 1.816 (0.414-7.962) |
| Q3 (1.03-2.18) | 1.48 | 12 | 8 | 2.786 (0.773-10.043) | 3.230 (0.728-14.327) |
| Q4 (≥2.19) | 6.23 | 15 | 5 | 5.571 (1.420-21.860) | 6.482 (1.283-32.752) |
| P for trend | - | - | - | 0.032 | 0.035 |
| miR-149 | |||||
| Q1 (≤0.21) | 0.10 | 17 | 3 | 1.000 (reference) | 1.000 (reference) |
| Q2 (0.22-0.64) | 0.34 | 10 | 11 | 0.160 (0.036-0.717) | 0.166 (0.031-0.881) |
| Q3 (0.65-1.35) | 1.01 | 13 | 6 | 0.382 (0.080-1.825) | 0.467 (0.083-2.607) |
| Q4 (≥1.36) | 2.39 | 5 | 15 | 0.059 (0.012-0.289) | 0.075 (0.012-0.463) |
| P for trend | - | - | - | 0.002 | 0.028 |
| 1. | Wroblewski LE, Peek RM, Jr. Helicobacter pylori, cancer, and the gastric microbiota. In: Jansen M, Wright NA, eds. Stem cells, pre-neoplasia, and early cancer of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Adv Exp Med Biol 2016; 903: 393-408. |
| 2. |
Eed EM, Hawash YA, Khalifa AS, et al. Molecular diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance in the Taif region, Saudi Arabia. Microbiol Immunol 2019; 63: 199-205.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Correa P. Gastric cancer: overview. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2013; 42: 211-7. |
| 4. |
Yamaoka Y, Kikuchi S, El-Zimaity HMT, Gutierrez O, Osato MS, Graham DY. Importance of Helicobacter pylori oipA in clinical presentation, gastric inflammation, and mucosal interleukin 8 production. Gastroenterology 2002; 123: 414-24.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009; 136: 215-33.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Ling H, Fabbri M, Calin GA. MicroRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2013; 12: 847-65.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Yang YL, Liu P, Li D, Yang Q, Li B, Jiang XJ. Stat-3 signaling promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer through PDCD4 downregulation. Gaoxiong Yi Xue Ke Xue Za Zhi 2020; 36: 244-49. |
| 8. | Jin D, Huang K, Peng L, et al. Circular RNA circDNA2 upregulates CCDC6 expression to promote the progression of gastric cancer via miR-149-5p suppression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2021; 26: 360-73. |
| 9. |
Nicoloso MS, Sun H, Spizzo R, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms inside microRNA target sites influence tumor susceptibility. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 2789-98.
DOI PMID |
| 10. | Xu Z, Zhang E, Duan W, Sun C, Bai S, Tan X. The association between miR-499 polymorphism and cancer susceptibility: a Meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther 2015; 8: 2179-86. |
| 11. |
Zhang L, Liu Q, Wang F. Association Between miR-149 gene rs2292832 polymorphism and risk of gastric cancer. Arch Med Res 2018; 49: 270-7.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Tang JL, Liu BY, Ma KW. Traditional Chinese medicine. Lancet 2008; 372: 1938-40. |
| 13. | Bian Y, Chen X, Cao H, et al. A correlational study of Weifuchun and its clinical effect on intestinal flora in precancerous lesions of gastric cancer. Chin Med 2021; 16: 120. |
| 14. | Wen J, Wu S, Ma X, Zhao Y. Zuojin pill attenuates Helicobacter pylori-induced chronic atrophic gastritis in rats and improves gastric epithelial cells function in GES-1cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2021; 285: 114855. |
| 15. | Hu Y, Pan X, Nie M, et al. A clinical study of Yiqi Huayu Jiedu decoction reducing the risk of postoperative gastric cancer recurrence and metastasis Study protocol for a randomized controlled trail. Medicine 2020; 99: e21775. |
| 16. |
Jiang M, Lu C, Zhang C, et al. Syndrome differentiation in modern research of Traditional Chinese Medicine. J Ethnopharmacol 2012; 140: 634-42.
DOI PMID |
| 17. | Yang Y, Qu XH, Yang M, Wang X, Meng M, Wei W. Correlation between Traditional Chinese medicine syndromes and cancer risk of patients with chronic atrophic gastritis. J Tradit Chin Med 2020; 61: 319-24. |
| 18. | Wan ZX, Hu JR, Ma LF, Zhou J, Li QW. Clinical study of tongue manifestation and TCM syndromes before and after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018; 24: 1558-61. |
| 19. |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T) (-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 2001; 25: 402-8.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH, et al. Classification and grading of gastritis - the updated Sydney system. Am J Surg Pathol 1996; 20: 1161-81.
DOI PMID |
| 21. | Zheng XY. Guiding principle of clinical research on new drugs of traditional Chinese medicine trial edition. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2002: 126. |
| 22. | Zhang SS, Hu L, Li RL. Expert consensus on TCM diagnosis and treatment of spleen deficiency syndrome (2017). J Tradit Chin Med 2017; 58: 1525-30. |
| 23. | Zhang SS, Huang HQ, Fang WY, Li SQ. Expert consensus on TCM diagnosis and treatment of spleen-stomach damp-heat syndrome ( 2017 ). J Tradit Chin Med 2017; 58: 987-90. |
| 24. | Moss SF. The clinical evidence linking Helicobacter pylori to gastric cancer. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017; 3: 183-91. |
| 25. | Dos Santos MP, Pereira JN, De Labio RW, et al. Decrease of miR-125a-5p in gastritis and gastric cancer and its possible association with H. pylori. J Gastrointest Cancer 2021; 52: 569-74. |
| 26. | Schaalan M, Mohamed W, Fathy S. MiRNA-200c, MiRNA-139 and ln RNA H19; new predictors of treatment response in H-pylori- induced gastric ulcer or progression to gastric cancer. Microb Pathog 2020; 149: 104442. |
| 27. | Song MY, Su HJ, Zhang L, et al. Genetic plymorphisms of miR-146a and miR-27a, H. pylori infection, and risk of gastric lesions in a Chinese population. PLoS One 2013; 8: e61250. |
| 28. |
Cai M, Zhang YT, Ma YY, et al. Association between microRNA-499 polymorphism and gastric cancer risk in Chinese population. Bull Cancer 2015; 102: 973-8.
DOI PMID |
| 29. | Cimpeanu RA, Popescu DM, Burada F, et al. miR-149 rs2292832 C > T polymorphism and risk of gastric cancer. Rom J Morphol Embryol 2017; 58: 125-9. |
| 30. | Wu XJ, Mi YY, Yang H, et al. Association of the hsa-mir-499 (rs3746444) polymorphisms with gastric cancer risk in the Chinese population. Onkologie 2013; 36: 573-6. |
| 31. |
Schork NJ, Fallin D, Lanchbury JS. Single nucleotide polymorphisms and the future of genetic epidemiology. Clin Genet 2000; 58: 250-64.
PMID |
| 32. |
Fang J, Chen W, Meng X. Downregulating circRNA_0044516 inhibits cell proliferation in gastric cancer through miR-149/Wnt1/β-catenin pathway. J Gastrointest Surg 2021; 25: 1696-705.
DOI PMID |
| 33. |
Link A, Schirrmeister W, Langner C, et al. Differential expression of microRNAs in preneoplastic gastric mucosa. Sci Rep 2015; 5: 8270.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Caren Cortes-Marquez A, Mendoza-Elizalde S, Arenas-Huertero F, et al. Differential expression of miRNA-146a and miRNA-155 in gastritis induced by Helicobacter pylori infection in paediatric patients, adults, and an animal model. BMC Infect Dis 2018; 18: 463. |
| 35. | Correa P. Human gastric carcinogenesis: a multistep and multifactorial process--first american cancer society award Lecture on cancer epidemiology and prevention. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 6735-40. |
| 36. | Meng JY, Tan J, Guo YT, Zhang TF, Meng LJ. Analysis on the characteristics of microcosmic differentiation of gastric mucosa and precancerous lesionsin patients with chronic atrophic gastritis. J Tradit Chin Med 2015; 56: 1307-10. |
| 37. | Liu QS, Sang Y, Cai DL, Chen ZY, Lai LQ, Zhang J. Study on relationship between TCM syndrome of chronic atrophic gastritis and c-mycDNA. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2016; 34: 132-5. |
| 38. | Liu LS, Liu WJ, Xu XZ, et al. Expressions of mitophagy-related proteins in gastric mucosal cells of rats in spleen Qi deficiency. Shi Jie Ke Xue Ji Shu-Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Hua 2020; 22: 3089-93. |
| [1] | GAO Changjiu, DING Song, Shadi A.D. Mohammed, LU Fang, LIU Changfeng, TENG Zhan, XU Peng, LIU Shumin. Cardioprotective mechanism of Qixuan Yijianing (芪玄抑甲宁) formula in Graves’ disease mice using miRNA sequencing approach [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1127-1136. |
| [2] | GUO Yuxi, LI Ze, CHENG Nan, JIA Xuemei, WANG Jie, MA Hongyu, ZHAO Runyuan, LI Bolin, XUE Yucong, CAI Yanru, YANG Qian. High-throughput sequencing analysis of differential microRNA expression in the process of blocking the progression of chronic atrophic gastritis to gastric cancer by Xianglian Huazhuo formula (香连化浊方) [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 703-712. |
| [3] | SHEN Jie, YIN Yaoli, LI Hongxiao, LU Ge, ZHU Yaoyao, QIN Yantong, JIN Xun, CHENG Jie, SHEN Meihong. Effect of moxibustion on expression profile of miRNAs in Tripterygium glycoside-induced decreased ovarian reserve [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 745-752. |
| [4] | DING Luobin, WANG Huajun, LI Yao, LI Jia, LI Ling, GAO Yangping, GUAN Jian, GENG Weiqiang. Electroacupuncture stimulating Neixiyan (EX-LE5) and Dubi (ST35) alleviates osteoarthritis in rats induced by anterior cruciate ligament transaction via affecting DNA methylation regulated transcription of miR-146a and miR-140-5p [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 983-990. |
| [5] | TANG Yanping, LI Peicai, LIU Xi, LIU Lei, GONG Yanxia, WEI Xiaodong, LIU Lina, YANG Li. A single-center retrospective study on epidemiological and Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome characteristics of 21010 patients with reflux/heartburn symptoms [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 574-581. |
| [6] | QU Yilun, CHENG Haimei, WANG Qian, LI Shuang, DUAN Shuwei, FENG Zhe, LI Weizhen, JIANG Shuangshuang, YANG Hongtao, MAO Yonghui, GENG Yanqiu, LI Jijun, LIU Yuning, TIAN Jinzhou, LIU Hongfang, DONG Zheyi, CHEN Xiangmei. Noninvasive identificational diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy and non-diabetic renal disease based on clinical characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine symptom pattern and conventional medicine [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 588-593. |
| [7] | HU Xingyao, LIU Hongning, YAN Xiaojun, CHEN Zhong, FU Liu, LIU Ge, CHEN Xuan, SHANG Guangbin. Liver metabolomic characteristics in three different rat models of Yin deficiency based on ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 274-285. |
| [8] | HUANG Qiuyue, YE Hui, SHI Zongming, JIA Xiaofen, LIN Miaomiao, CHU Yingming, YU Jing, ZHANG Xuezhi. Efficacy of Qingre Huashi decoction (清热化湿方) on infection of Helicobacter pylori: inhibiting adhesion, antioxidant, and anti-inflammation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 915-921. |
| [9] | DING Jiamin, XING Yifeng, CHEN Zuoliang, CHEN Wanlu, MA Zhongxiong, XIE Yunde, ZHOU Lin. Qilan preparation (芪蓝颗粒) inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by down-regulating microRNA-21 in human Tca8113 tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 693-700. |
| [10] | WANG Jin, WANG Huijie, XIAO Ying, GUO Jiaxuan, ZHAO Yubin. Microecology-turbidity toxin theory: correlation between helicobacter pylori infection and manifestation of tongue and gastroscopy [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 458-462. |
| [11] | GU Xiaoli, CHEN Menglei, LIU Minghui, ZHANG Zhe, ZHAO Weiwei, CHENG Wenwu. Value of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome differentiation in predicting the survival time of patients with advanced cancer [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 636-641. |
| [12] | Shi Xiaoshuang, Wu Haomeng, Ma Xiangxue, Yin Xiaolan, Li Xia, Ma Jinxin, Wang Fengyun, Tang Xudong. Effect of Chinese Herbal Medicines on Helicobacter pylori-associated gastroduodenal ulcers: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(04): 459-465. |
| [13] | Wang Weijie, Tang Xiaopo, Wang Xinchang, Jiang Quan, Fan Yongsheng. Classifying rheumatoid arthritis by Traditional Chinese Medicine Zheng: a multi-center cross-sectional study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(03): 425-432. |
| [14] | Cao Yunxiang, Guo Yunke, Zong Ruikai, Huang Chuanbing, Wang Yue, Liu Jian. Drug-containing serum of Xinfeng capsules protect against H9C2 from death by enhancing miRNA-21 and inhibiting toll-like receptor 4/phosphorylated p-38(p-p38)/p-p65 signaling pathway and proinflammatory cytokines expression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(03): 359-365. |
| [15] | Shi Zongming, Ye Hui, Yu Jing, Cheng Hong, Li Jiang, Zhang Xuezhi. Jinghua Weikang capsule protects against Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammatory responses via the nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(03): 366-372. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 54
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 39
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

