Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 274-285.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230201.001
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Liver metabolomic characteristics in three different rat models of Yin deficiency based on ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry
HU Xingyao, LIU Hongning, YAN Xiaojun, CHEN Zhong, FU Liu, LIU Ge, CHEN Xuan, SHANG Guangbin( )
)
- Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Research Center for Differention and Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Basic Theory, Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of TCM Etiopathogenisis, Nanchang 330004, China
-
Received:2022-07-10Accepted:2022-12-16Online:2023-04-15Published:2023-03-14 -
Contact:Prof. SHANG Guangbin, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Research Center for Differention and Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine Basic Theory, Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of TCM Etiopathogenisis, Nanchang 330004, China. shanggb@jxutcm.edu.cn. Telephone: +86-113732901725 -
Supported by:Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jiangxi Province Double First-Class Discipline of Traditional Chinese Medicine Construction Project(JXSYLXK-ZHYI026);Supported by Science and Technology Program of Jiangxi Provincial Health and Health Commission(SKJP220210415);Exploring the Formation Mechanism of Liver and Kidney Yin Deficiency Based on Animal Model and Metabolomics; Supported by National TCM Leading Talent Support Program of the State Administration of TCM-Qi Huang Scholar(284, China TCM people's teaching letter [2018])
Cite this article
HU Xingyao, LIU Hongning, YAN Xiaojun, CHEN Zhong, FU Liu, LIU Ge, CHEN Xuan, SHANG Guangbin. Liver metabolomic characteristics in three different rat models of Yin deficiency based on ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 274-285.
share this article
| Observation index | Index score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Skin hair | Wither and easy to fall off 2 | Not shiny or fluffy 1 | Supple and shiny 0 |
| Behavioral activity | Active and frighten 2 | Hyperactivity 1 | Moderate activity 0 |
| Urinary status | Yellow and frequent urine 2 | Light yellow urine 1 | Normal urine 0 |
| Stool state | Dry stool 2 | Hard stool 1 | Normal stool 0 |
Table 1 Scoring criteria for appearance behavior of rats
| Observation index | Index score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Skin hair | Wither and easy to fall off 2 | Not shiny or fluffy 1 | Supple and shiny 0 |
| Behavioral activity | Active and frighten 2 | Hyperactivity 1 | Moderate activity 0 |
| Urinary status | Yellow and frequent urine 2 | Light yellow urine 1 | Normal urine 0 |
| Stool state | Dry stool 2 | Hard stool 1 | Normal stool 0 |
| Group | n | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 12 | 0.0±0.0 | 0.1±0.3 | 0.2±0.4 | 0.3±0.5 | 0.2±0.4 | 0.3±0.5 |
| Irritation induced model | 12 | 0.4±0.5 | 0.4±0.8 | 0.8±1.0 | 1.5±1.7a | 2.5±1.7b | 3.8±1.6b |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 12 | 0.5±0.7 | 0.7±0.8 | 1.2±1.5 | 1.2±1.3 | 1.8±1.3b | 3.3±1.0b |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 12 | 0.3±0.5 | 0.4±1.0 | 1.0±1.4 | 1.3±1.3a | 2.7±1.1b | 2.5±1.1b |
Table 2 Comparison of physical sign scores of rats in each group ($\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | n | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 12 | 0.0±0.0 | 0.1±0.3 | 0.2±0.4 | 0.3±0.5 | 0.2±0.4 | 0.3±0.5 |
| Irritation induced model | 12 | 0.4±0.5 | 0.4±0.8 | 0.8±1.0 | 1.5±1.7a | 2.5±1.7b | 3.8±1.6b |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 12 | 0.5±0.7 | 0.7±0.8 | 1.2±1.5 | 1.2±1.3 | 1.8±1.3b | 3.3±1.0b |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 12 | 0.3±0.5 | 0.4±1.0 | 1.0±1.4 | 1.3±1.3a | 2.7±1.1b | 2.5±1.1b |
| Group | n | Week 0 | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 12 | 36.4±0.6 | 35.8±0.7 | 36.4±0.8 | 36.4±0.5 | 36.4±0.5 | 36.0±0.6 | 36.1±0.5 |
| Irritation induced model | 12 | 36.2±1.0 | 36.2±0.8 | 36.5±0.8 | 36.7±0.6 | 37.0±0.5a | 36.7±0.7a | 36.5±0.6 |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 12 | 36.8±1.1 | 36.2±0.6 | 35.8±0.7 | 36.4±0.6 | 36.5±0.4 | 36.7±0.5a | 36.4±0.5 |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 12 | 35.7±1.2 | 36.3±0.6 | 36.2±0.7 | 37.0±0.6a | 36.8±0.5 | 36.5±0.5b | 36.3±0.4 |
Table 3 Comparison of changes in body temperature in rats of each group (℃, $\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | n | Week 0 | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 12 | 36.4±0.6 | 35.8±0.7 | 36.4±0.8 | 36.4±0.5 | 36.4±0.5 | 36.0±0.6 | 36.1±0.5 |
| Irritation induced model | 12 | 36.2±1.0 | 36.2±0.8 | 36.5±0.8 | 36.7±0.6 | 37.0±0.5a | 36.7±0.7a | 36.5±0.6 |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 12 | 36.8±1.1 | 36.2±0.6 | 35.8±0.7 | 36.4±0.6 | 36.5±0.4 | 36.7±0.5a | 36.4±0.5 |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 12 | 35.7±1.2 | 36.3±0.6 | 36.2±0.7 | 37.0±0.6a | 36.8±0.5 | 36.5±0.5b | 36.3±0.4 |
| Group | n | Week 0 | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 12 | 33.2±3.7 | 48.1±7.7 | 54.2±4.9 | 54.2±4.9 | 61.9±9.1 | 59.2±3.1 | 61.2±7.0 |
| Irritation induced model | 12 | 33.3±4.5 | 39.7±4.6b | 49.9±5.8b | 41.3±2.9a | 56.7±8.2 | 47.2±3.2a | 53.1±6.1b |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 12 | 31.5±4.2 | 45.6±3.0 | 49.0±3.5b | 50.0±2.0 | 59.2±4.0 | 56.5±7.5 | 52.2±4.1a |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 12 | 28.6±1.7a | 42.8±7.1 | 50.4±4.5 | 56.3±7.5 | 66.4±8.4 | 64.0±8.1 | 50.6±7.0a |
Table 4 Comparison of changes in water consumption in rats of each group (mL, $\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | n | Week 0 | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 12 | 33.2±3.7 | 48.1±7.7 | 54.2±4.9 | 54.2±4.9 | 61.9±9.1 | 59.2±3.1 | 61.2±7.0 |
| Irritation induced model | 12 | 33.3±4.5 | 39.7±4.6b | 49.9±5.8b | 41.3±2.9a | 56.7±8.2 | 47.2±3.2a | 53.1±6.1b |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 12 | 31.5±4.2 | 45.6±3.0 | 49.0±3.5b | 50.0±2.0 | 59.2±4.0 | 56.5±7.5 | 52.2±4.1a |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 12 | 28.6±1.7a | 42.8±7.1 | 50.4±4.5 | 56.3±7.5 | 66.4±8.4 | 64.0±8.1 | 50.6±7.0a |
| Group | n | Week 0 | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 12 | 16.0±0.6 | 26.7±1.9 | 34.7±8.9 | 31.2±1.3 | 32.3±3.9 | 32.5±1.7 | 28.6±0.9 |
| Irritation induced model | 12 | 16.5±0.5 | 25.6±1.9 | 29.1±1.3 | 26.6±3.7 | 30.5±1.6 | 28.8±2.3b | 25.4±2.2b |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 12 | 15.3±1.2 | 24.7±1.7a | 30.2±1.5 | 30.2±2.1 | 32.2±2.4 | 30.1±0.7b | 25.9±2.2b |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 12 | 13.8±1.3a | 24.8±3.3a | 34.2±2.7 | 37.3±4.7b | 41.5±1.9b | 33.5±5.1 | 31.0±1.7b |
Table 5 Comparison of changes in diet in rats of each group (g, $\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | n | Week 0 | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 12 | 16.0±0.6 | 26.7±1.9 | 34.7±8.9 | 31.2±1.3 | 32.3±3.9 | 32.5±1.7 | 28.6±0.9 |
| Irritation induced model | 12 | 16.5±0.5 | 25.6±1.9 | 29.1±1.3 | 26.6±3.7 | 30.5±1.6 | 28.8±2.3b | 25.4±2.2b |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 12 | 15.3±1.2 | 24.7±1.7a | 30.2±1.5 | 30.2±2.1 | 32.2±2.4 | 30.1±0.7b | 25.9±2.2b |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 12 | 13.8±1.3a | 24.8±3.3a | 34.2±2.7 | 37.3±4.7b | 41.5±1.9b | 33.5±5.1 | 31.0±1.7b |
| Group | n | cAMP (nmol/L) | cGMP (nmol/L) | cAMP /cGMP (nmol/L) | E2 (ng/mL) | T (ng/mL) | E2/T (ng/mL) | ALT (μ/L) | AST (μ/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 12 | 39.5±8.1 | 38.7±11.4 | 0.9±0.4 | 89.2±16.3 | 9.0±5.0 | 13.6±8.8 | 32.4±8.0 | 133.7±36.3 |
| Irritation induced Model | 12 | 32.7±12.1 | 37.3±14.8 | 1.2±0.4 | 91.2±19.4 | 7.6±3.8 | 17.2±12.3 | 53.1±8.5b | 184.6±52.3b |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 12 | 53.8±14.5a | 18.8±4.0a | 3.1±1.3a | 114.3±26.0b | 8.2±5.2 | 19.7±13.0 | 61.4±15.6a | 196.6±61.3a |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 12 | 52.1±8.8a | 15.3±3.2a | 3.5±0.8a | 127.6±30.1a | 6.7±1.5 | 26.9±18.0 | 76.0±39.0a | 209.8±54.3a |
Table 6 Comparison of Serum cAMP, cGMP, cAMP/cGMP, E2, T, E2/T, ALT, AST Levels in Rats of Each Group ($\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | n | cAMP (nmol/L) | cGMP (nmol/L) | cAMP /cGMP (nmol/L) | E2 (ng/mL) | T (ng/mL) | E2/T (ng/mL) | ALT (μ/L) | AST (μ/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 12 | 39.5±8.1 | 38.7±11.4 | 0.9±0.4 | 89.2±16.3 | 9.0±5.0 | 13.6±8.8 | 32.4±8.0 | 133.7±36.3 |
| Irritation induced Model | 12 | 32.7±12.1 | 37.3±14.8 | 1.2±0.4 | 91.2±19.4 | 7.6±3.8 | 17.2±12.3 | 53.1±8.5b | 184.6±52.3b |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 12 | 53.8±14.5a | 18.8±4.0a | 3.1±1.3a | 114.3±26.0b | 8.2±5.2 | 19.7±13.0 | 61.4±15.6a | 196.6±61.3a |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 12 | 52.1±8.8a | 15.3±3.2a | 3.5±0.8a | 127.6±30.1a | 6.7±1.5 | 26.9±18.0 | 76.0±39.0a | 209.8±54.3a |
| Group | Liver index | Kidney index |
|---|---|---|
| Blank | 2.58±0.09 | 0.65±0.04 |
| Irritation induced model | 2.58±0.13 | 0.66±0.03 |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 2.89±0.37a | 0.70±0.07 |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 3.03±0.23a | 0.82±0.07a |
Table 7 Comparison of liver index and kidney index of rats in each group (%, $\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | Liver index | Kidney index |
|---|---|---|
| Blank | 2.58±0.09 | 0.65±0.04 |
| Irritation induced model | 2.58±0.13 | 0.66±0.03 |
| Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model | 2.89±0.37a | 0.70±0.07 |
| Thyroxine-reserpine induced model | 3.03±0.23a | 0.82±0.07a |

Figure 1 Histopathological changes of rat liver and kidney in each group (HE staining) A: blank group of liver tissue (× 100); B: blank group of liver tissue (× 400); C: irritation induced model group of liver tissue (× 100); D: irritation induced model group of liver tissue (× 400); E: Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model group of liver tissue (× 100); F: Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model group of liver tissue (× 400); G: thyroxine-reserpine induced model group of liver tissue (× 100); H: thyroxine-reserpine induced model group of liver tissue (× 400); I: blank group of kidney tissue (× 100); J: blank group of kidney tissue (× 400); K: Irritation induced model group of kidney tissue (× 100); L: irritation induced model group of kidney tissue (× 400); M: Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model group of kidney tissue (× 100); N: Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model group of kidney tissue (× 400); O: thyroxine-reserpine induced model group of kidney tissue (× 100); P: thyroxine-reserpine induced model group of kidney tissue (× 400); (Scale bar indicates 100 μm, × 100; scale bar indicates 50 μm, × 400). HE: hematoxylin-eosin.

Figure 2 PCA scores of liver tissue samples of each group of animals A: positive ion mode; B: negative ion mode; 1: blank group; 2: irritation induced model group; 3: Fuzi-Ganjiang induced model group; 4: thyroxine-reserpine induced model group.
| No. | HMDB ID | Retention time(min) | m/z | Formula | Biomarkers name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HMDB0000254 | 1.047 | 117.0192 | C4H6O4 | Succinic acid |
| 2 | HMDB0006355 | 0.662 | 175.024 | C6H8O6 | D-Glucurono-6,3-lactone |
| 3 | HMDB0032387 | 4.722 | 187.0973 | C9H16O4 | (+/-)-Methyl 5-acetoxyhexanoate |
| 4 | HMDB0012204 | 1.931 | 218.1037 | C10H13N5O | Cis-zeatin |
| 5 | HMDB0000767 | 0.628 | 243.062 | C9H12N2O6 | Pseudouridine |
| 6 | HMDB0002186 | 16.312 | 253.2176 | C16H30O2 | Hypogeic acid |
| 7 | HMDB0003040 | 0.662 | 267.0727 | C10H12N4O5 | Arabinosylhypoxanthine |
| 8 | HMDB0031067 | 11.668 | 269.2483 | C17H3402 | (S)-14-Methylhexadecanoic acid |
| 9 | HMDB0010734 | 11.971 | 271.2283 | C16H32O3 | (R)-3-Hydroxy-hexadecanoic acid |
| 10 | HMDB0003426 | 2.666 | 277.1223 | C11H22N2O4S | Pantetheine |
| 11 | HMDB0001388 | 9.348 | 277.2179 | C18H30O2 | Alpha-Linolenic acid |
| 12 | HMDB0030430 | 9.916 | 279.2334 | C18H32O2 | Linalylcaprylate |
| 13 | HMDB0000207 | 17.749 | 281.2483 | C18H34O2 | Oleic acid |
| 14 | HMDB0000299 | 1.564 | 283.0683 | C10H12N4O6 | Xanthosine |
| 15 | HMDB0000827 | 19.001 | 283.2642 | C18H36O2 | Stearic acid |
| 16 | HMDB0000594 | 2.766 | 293.1146 | C14H18N2O5 | gamma-Glutamylphenylalanine |
| 17 | HMDB0037396 | 17.614 | 299.2581 | C18H36O3 | xi-10-Hydroxyoctadecanoic acid |
| 18 | HMDB0001999 | 9.234 | 301.219 | C20H30O2 | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| 19 | HMDB0006036 | 17.614 | 303.2323 | C20H32O2 | Mesterolone |
| 20 | HMDB0002925 | 10.885 | 305.2479 | C20H34O2 | 8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid |
| 21 | HMDB0061650 | 12.355 | 313.2386 | C18H34O4 | 9,10-Epoxystearic acid |
| 22 | HMDB0006048 | 16.146 | 315.2337 | C21H32O2 | Bolasterone |
| 23 | HMDB0005998 | 11.318 | 319.2279 | C20H32O3 | 20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid |
| 24 | HMDB0032143 | 17.597 | 331.2637 | C22H36O2 | Palaudine |
| 25 | HMDB0035676 | 9.816 | 337.2388 | C20H34O4 | 1-Hydroxy-1-phenyl-3-hexadecanone |
| 26 | HMDB0002995 | 17.598 | 340.2854 | C20H39NO3 | 12-Keto-tetrahydro-leukotriene B4 |
| 27 | HMDB0013308 | 0.946 | 346.0556 | C10H14N5O7P | Stearoylglycine |
| 28 | HMDB0014096 | 0.678 | 350.1076 | C13H21NO10 | 5'-Hydroxypiroxicam |
| 29 | HMDB0000785 | 7.026 | 351.218 | C20H32O5 | N-Acetyl-7-O-acetylneuraminic acid |
| 30 | HMDB0035338 | 1.948 | 357.0895 | C11H23N2O7PS | Sterebin B |
| 31 | HMDB0001416 | 4.687 | 359.1258 | C18H20N2O6 | Pantetheine 4'-phosphate |
| 32 | HMDB0006045 | 14.225 | 360.2553 | C22H35NO3 | Dityrosine |
| 33 | HMDB0005096 | 16.495 | 403.1591 | C25H24O5 | N-Arachidonoyl glycine |
| 34 | HMDB0030785 | 6.676 | 423.2748 | C24H40O6 | Mammeigin |
| 35 | HMDB0013192 | 16.697 | 429.1753 | C20H30O10 | 3a,7b,21-Trihydroxy-5b-cholanoic acid |
| 36 | HMDB0032622 | 8.48 | 435.2774 | C25H40O6 | Phenethylrutinoside |
| 37 | HMDB0029949 | 18.985 | 437.2665 | C21H43O7P | Pangamic acid |
| 38 | HMDB0007850 | 6.559 | 448.3074 | C26H43NO5 | LysoPA(0:0/18:0) |
| 39 | HMDB0000708 | 9.883 | 452.2795 | C28H39NO4 | Glycoursodeoxycholic acid |
| 40 | HMDB0011473 | 5.64 | 514.285 | C26H45NO7S | LysoPE(0:0/16:0) |
| 41 | HMDB0000036 | 1.046 | 611.1452 | C20H32N6O12S2 | Taurocholic acid |
| 42 | HMDB0003337 | 19.252 | 766.5397 | C43H78NO8P | Oxidized glutathione |
| 43 | HMDB0007949 | 17.597 | 331.2637 | C22H36O2 | PC(15:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) |
| 44 | HMDB0004226 | 0.527 | 130.0854 | C6H11NO2 | N4-Acetylaminobutanal |
| 45 | HMDB0031160 | 0.749 | 137.0453 | C5H12S2 | 1-Pentanesulfenothioic acid |
| 46 | HMDB0031210 | 3.397 | 159.0284 | C6H6O5 | Zymonic acid |
| 47 | HMDB0002052 | 5.121 | 201.0392 | C8H8O6 | Maleylacetoacetic acid |
| 48 | HMDB0011175 | 1.928 | 220.117 | C10H13N5O | Leucylproline |
| 49 | HMDB0032318 | 2.119 | 229.1538 | C11H20N2O3 | Hexanal octane-1,3-diol acetal |
| 50 | HMDB0028932 | 15.964 | 229.216 | C14H28O2 | Leucyl-Isoleucine |
| 51 | HMDB0035358 | 3.588 | 245.1858 | C12H24N2O3 | Ketosantalic acid |
| 52 | HMDB0000086 | 7.902 | 251.1637 | C15H22O3 | Glycerophosphocholine |
| 53 | HMDB0011171 | 10.05 | 258.1094 | C8H20NO6P | gamma-Glutamylleucine |
| 54 | HMDB0034495 | 2.484 | 261.1438 | C11H20N2O6 | 6,10,14-Trimethyl-5,9,13-pentadecatrien-2-one |
| 55 | HMDB0030964 | 9.916 | 263.2365 | C18H30O | Linolenelaidic acid |
| 56 | HMDB0062656 | 15.697 | 279.232 | C18H30O2 | Linoleamide |
| 57 | HMDB0061864 | 15.038 | 280.2632 | C18H33NO | Dihomolinoleic acid |
| 58 | HMDB0002117 | 16.69 | 281.2472 | C18H32O2 | Oleamide |
| 59 | HMDB0006221 | 16.478 | 282.2789 | C18H35NO | 13-cis Retinol |
| 60 | HMDB0002100 | 1.549 | 285.082 | C10H12N4O6 | Palmitoylethanolamide |
| 61 | HMDB0000269 | 19.11 | 285.2783 | C18H36O2 | Sphinganine |
| 62 | HMDB0002177 | 10.267 | 287.2366 | C20H30O | Cis-8,11,14,17-Eicosatetraenoic acid |
| 63 | HMDB0029826 | 7.425 | 300.2892 | C18H37NO2 | Hallacridone |
| 64 | HMDB0004610 | 7.225 | 318.2999 | C18H39NO3 | Phytosphingosine |
| 65 | HMDB0012252 | 7.731 | 324.2892 | C20H37NO2 | Linoleoylethanolamide |
| 66 | HMDB0002183 | 7.093 | 329.2471 | C22H32O2 | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| 67 | HMDB0032476 | 19.304 | 341.3041 | C21H40O3 | Polyoxyethylene (600) monoricinoleate |
| No. | HMDB ID | Retention time(min) | m/z | Formula | Biomarkers Name |
| 68 | HMDB0002007 | 9.795 | 357.2784 | C24H36O2 | Tetracosahexaenoic acid |
| 69 | HMDB0034031 | 16.595 | 357.3002 | C21H40O4 | 3-(2-Heptenyloxy)-2-hydroxypropyl undecanoate |
| 70 | HMDB0000476 | 14.22 | 362.2687 | C22H35NO3 | 3-Oxo-4,6-choladienoic acid |
| 71 | HMDB0013627 | 6.838 | 371.2574 | C24H34O3 | Cervonoylethanolamide |
| 72 | HMDB0012866 | 8.513 | 373.2734 | C24H36O3 | 9'-Carboxy-alpha-chromanol |
| 73 | HMDB0006898 | 8.494 | 391.2835 | C24H38O4 | Chenodeoxyglycocholic acid |
| 74 | HMDB0000331 | 8.265 | 450.3206 | C26H43NO5 | 3a,7b,12a-Trihydroxyoxocholanyl-Glycine |
| 75 | HMDB0011475 | 5.672 | 466.3154 | C26H43NO6 | LysoPE (0:0/18:1(11Z)) |
| 76 | HMDB0011129 | 11.104 | 480.3083 | C23H46NO7P | LysoPE (0:0/18:0) |
| 77 | HMDB0010395 | 9.73 | 482.3234 | C23H48NO7P | LysoPC (20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) |
| 78 | HMDB0008177 | 6.612 | 516.2981 | C26H45NO7P | PC (18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) |
Table 8 Different endogenous compounds in rat liver
| No. | HMDB ID | Retention time(min) | m/z | Formula | Biomarkers name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HMDB0000254 | 1.047 | 117.0192 | C4H6O4 | Succinic acid |
| 2 | HMDB0006355 | 0.662 | 175.024 | C6H8O6 | D-Glucurono-6,3-lactone |
| 3 | HMDB0032387 | 4.722 | 187.0973 | C9H16O4 | (+/-)-Methyl 5-acetoxyhexanoate |
| 4 | HMDB0012204 | 1.931 | 218.1037 | C10H13N5O | Cis-zeatin |
| 5 | HMDB0000767 | 0.628 | 243.062 | C9H12N2O6 | Pseudouridine |
| 6 | HMDB0002186 | 16.312 | 253.2176 | C16H30O2 | Hypogeic acid |
| 7 | HMDB0003040 | 0.662 | 267.0727 | C10H12N4O5 | Arabinosylhypoxanthine |
| 8 | HMDB0031067 | 11.668 | 269.2483 | C17H3402 | (S)-14-Methylhexadecanoic acid |
| 9 | HMDB0010734 | 11.971 | 271.2283 | C16H32O3 | (R)-3-Hydroxy-hexadecanoic acid |
| 10 | HMDB0003426 | 2.666 | 277.1223 | C11H22N2O4S | Pantetheine |
| 11 | HMDB0001388 | 9.348 | 277.2179 | C18H30O2 | Alpha-Linolenic acid |
| 12 | HMDB0030430 | 9.916 | 279.2334 | C18H32O2 | Linalylcaprylate |
| 13 | HMDB0000207 | 17.749 | 281.2483 | C18H34O2 | Oleic acid |
| 14 | HMDB0000299 | 1.564 | 283.0683 | C10H12N4O6 | Xanthosine |
| 15 | HMDB0000827 | 19.001 | 283.2642 | C18H36O2 | Stearic acid |
| 16 | HMDB0000594 | 2.766 | 293.1146 | C14H18N2O5 | gamma-Glutamylphenylalanine |
| 17 | HMDB0037396 | 17.614 | 299.2581 | C18H36O3 | xi-10-Hydroxyoctadecanoic acid |
| 18 | HMDB0001999 | 9.234 | 301.219 | C20H30O2 | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| 19 | HMDB0006036 | 17.614 | 303.2323 | C20H32O2 | Mesterolone |
| 20 | HMDB0002925 | 10.885 | 305.2479 | C20H34O2 | 8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid |
| 21 | HMDB0061650 | 12.355 | 313.2386 | C18H34O4 | 9,10-Epoxystearic acid |
| 22 | HMDB0006048 | 16.146 | 315.2337 | C21H32O2 | Bolasterone |
| 23 | HMDB0005998 | 11.318 | 319.2279 | C20H32O3 | 20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid |
| 24 | HMDB0032143 | 17.597 | 331.2637 | C22H36O2 | Palaudine |
| 25 | HMDB0035676 | 9.816 | 337.2388 | C20H34O4 | 1-Hydroxy-1-phenyl-3-hexadecanone |
| 26 | HMDB0002995 | 17.598 | 340.2854 | C20H39NO3 | 12-Keto-tetrahydro-leukotriene B4 |
| 27 | HMDB0013308 | 0.946 | 346.0556 | C10H14N5O7P | Stearoylglycine |
| 28 | HMDB0014096 | 0.678 | 350.1076 | C13H21NO10 | 5'-Hydroxypiroxicam |
| 29 | HMDB0000785 | 7.026 | 351.218 | C20H32O5 | N-Acetyl-7-O-acetylneuraminic acid |
| 30 | HMDB0035338 | 1.948 | 357.0895 | C11H23N2O7PS | Sterebin B |
| 31 | HMDB0001416 | 4.687 | 359.1258 | C18H20N2O6 | Pantetheine 4'-phosphate |
| 32 | HMDB0006045 | 14.225 | 360.2553 | C22H35NO3 | Dityrosine |
| 33 | HMDB0005096 | 16.495 | 403.1591 | C25H24O5 | N-Arachidonoyl glycine |
| 34 | HMDB0030785 | 6.676 | 423.2748 | C24H40O6 | Mammeigin |
| 35 | HMDB0013192 | 16.697 | 429.1753 | C20H30O10 | 3a,7b,21-Trihydroxy-5b-cholanoic acid |
| 36 | HMDB0032622 | 8.48 | 435.2774 | C25H40O6 | Phenethylrutinoside |
| 37 | HMDB0029949 | 18.985 | 437.2665 | C21H43O7P | Pangamic acid |
| 38 | HMDB0007850 | 6.559 | 448.3074 | C26H43NO5 | LysoPA(0:0/18:0) |
| 39 | HMDB0000708 | 9.883 | 452.2795 | C28H39NO4 | Glycoursodeoxycholic acid |
| 40 | HMDB0011473 | 5.64 | 514.285 | C26H45NO7S | LysoPE(0:0/16:0) |
| 41 | HMDB0000036 | 1.046 | 611.1452 | C20H32N6O12S2 | Taurocholic acid |
| 42 | HMDB0003337 | 19.252 | 766.5397 | C43H78NO8P | Oxidized glutathione |
| 43 | HMDB0007949 | 17.597 | 331.2637 | C22H36O2 | PC(15:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) |
| 44 | HMDB0004226 | 0.527 | 130.0854 | C6H11NO2 | N4-Acetylaminobutanal |
| 45 | HMDB0031160 | 0.749 | 137.0453 | C5H12S2 | 1-Pentanesulfenothioic acid |
| 46 | HMDB0031210 | 3.397 | 159.0284 | C6H6O5 | Zymonic acid |
| 47 | HMDB0002052 | 5.121 | 201.0392 | C8H8O6 | Maleylacetoacetic acid |
| 48 | HMDB0011175 | 1.928 | 220.117 | C10H13N5O | Leucylproline |
| 49 | HMDB0032318 | 2.119 | 229.1538 | C11H20N2O3 | Hexanal octane-1,3-diol acetal |
| 50 | HMDB0028932 | 15.964 | 229.216 | C14H28O2 | Leucyl-Isoleucine |
| 51 | HMDB0035358 | 3.588 | 245.1858 | C12H24N2O3 | Ketosantalic acid |
| 52 | HMDB0000086 | 7.902 | 251.1637 | C15H22O3 | Glycerophosphocholine |
| 53 | HMDB0011171 | 10.05 | 258.1094 | C8H20NO6P | gamma-Glutamylleucine |
| 54 | HMDB0034495 | 2.484 | 261.1438 | C11H20N2O6 | 6,10,14-Trimethyl-5,9,13-pentadecatrien-2-one |
| 55 | HMDB0030964 | 9.916 | 263.2365 | C18H30O | Linolenelaidic acid |
| 56 | HMDB0062656 | 15.697 | 279.232 | C18H30O2 | Linoleamide |
| 57 | HMDB0061864 | 15.038 | 280.2632 | C18H33NO | Dihomolinoleic acid |
| 58 | HMDB0002117 | 16.69 | 281.2472 | C18H32O2 | Oleamide |
| 59 | HMDB0006221 | 16.478 | 282.2789 | C18H35NO | 13-cis Retinol |
| 60 | HMDB0002100 | 1.549 | 285.082 | C10H12N4O6 | Palmitoylethanolamide |
| 61 | HMDB0000269 | 19.11 | 285.2783 | C18H36O2 | Sphinganine |
| 62 | HMDB0002177 | 10.267 | 287.2366 | C20H30O | Cis-8,11,14,17-Eicosatetraenoic acid |
| 63 | HMDB0029826 | 7.425 | 300.2892 | C18H37NO2 | Hallacridone |
| 64 | HMDB0004610 | 7.225 | 318.2999 | C18H39NO3 | Phytosphingosine |
| 65 | HMDB0012252 | 7.731 | 324.2892 | C20H37NO2 | Linoleoylethanolamide |
| 66 | HMDB0002183 | 7.093 | 329.2471 | C22H32O2 | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| 67 | HMDB0032476 | 19.304 | 341.3041 | C21H40O3 | Polyoxyethylene (600) monoricinoleate |
| No. | HMDB ID | Retention time(min) | m/z | Formula | Biomarkers Name |
| 68 | HMDB0002007 | 9.795 | 357.2784 | C24H36O2 | Tetracosahexaenoic acid |
| 69 | HMDB0034031 | 16.595 | 357.3002 | C21H40O4 | 3-(2-Heptenyloxy)-2-hydroxypropyl undecanoate |
| 70 | HMDB0000476 | 14.22 | 362.2687 | C22H35NO3 | 3-Oxo-4,6-choladienoic acid |
| 71 | HMDB0013627 | 6.838 | 371.2574 | C24H34O3 | Cervonoylethanolamide |
| 72 | HMDB0012866 | 8.513 | 373.2734 | C24H36O3 | 9'-Carboxy-alpha-chromanol |
| 73 | HMDB0006898 | 8.494 | 391.2835 | C24H38O4 | Chenodeoxyglycocholic acid |
| 74 | HMDB0000331 | 8.265 | 450.3206 | C26H43NO5 | 3a,7b,12a-Trihydroxyoxocholanyl-Glycine |
| 75 | HMDB0011475 | 5.672 | 466.3154 | C26H43NO6 | LysoPE (0:0/18:1(11Z)) |
| 76 | HMDB0011129 | 11.104 | 480.3083 | C23H46NO7P | LysoPE (0:0/18:0) |
| 77 | HMDB0010395 | 9.73 | 482.3234 | C23H48NO7P | LysoPC (20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) |
| 78 | HMDB0008177 | 6.612 | 516.2981 | C26H45NO7P | PC (18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) |
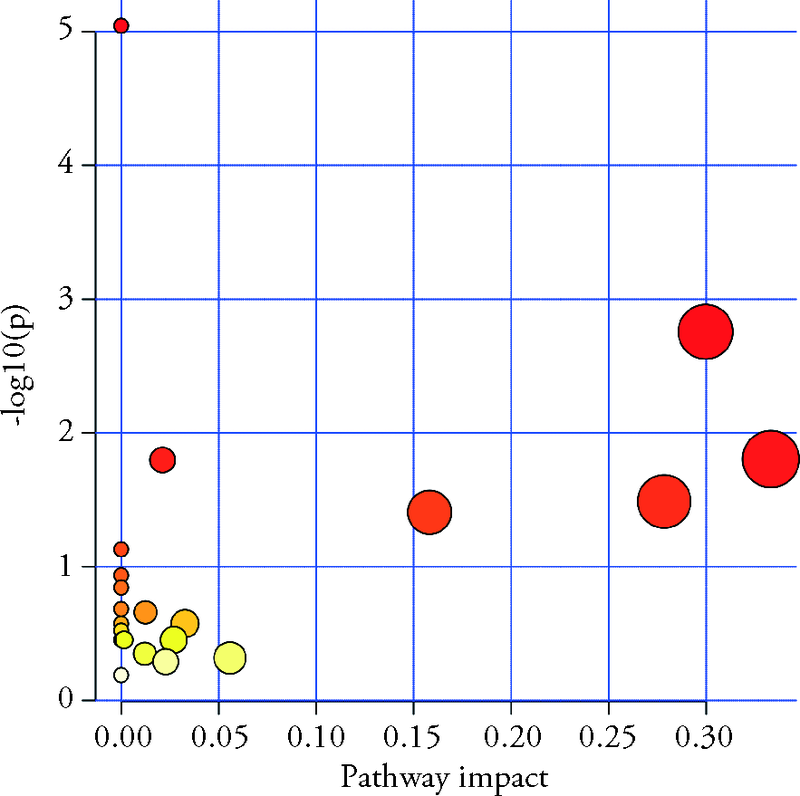
| No. | Pathway Name | Total | Hits | Raw p | Holm adjust | FDR p | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | 36 | 6 | 0.000099 | 0.008348 | 0.008348 | 0 |
| 2 | Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 36 | 4 | 0.0076 | 0.63076 | 0.31918 | 0.29983 |
| 3 | alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism | 13 | 2 | 0.032911 | 1 | 0.92151 | 0.33333 |
| 4 | Arachidonic acid metabolism | 36 | 3 | 0.044951 | 1 | 0.94396 | 0.0212 |
| 5 | Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis | 19 | 2 | 0.06634 | 1 | 1 | 0.27857 |
| 6 | Sphingolipid metabolism | 21 | 2 | 0.079235 | 1 | 1 | 0.15822 |
| 7 | Linoleic acid metabolism | 5 | 1 | 0.10783 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 8 | Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | 8 | 1 | 0.16702 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 9 | Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 10 | 1 | 0.20434 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 10 | Butanoate metabolism | 15 | 1 | 0.29068 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 11 | Glycerolipid metabolism | 16 | 1 | 0.30683 | 1 | 1 | 0.01246 |
| 12 | Ether lipid metabolism | 20 | 1 | 0.3679 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 13 | Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) | 20 | 1 | 0.3679 | 1 | 1 | 0.03273 |
| 14 | Propanoate metabolism | 23 | 1 | 0.41025 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 15 | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 28 | 1 | 0.47478 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 16 | Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | 28 | 1 | 0.47478 | 1 | 1 | 0.00152 |
| 17 | Glutathione metabolism | 28 | 1 | 0.47478 | 1 | 1 | 0.02698 |
| 18 | Arginine and proline metabolism | 38 | 1 | 0.58393 | 1 | 1 | 0.01212 |
| 19 | Tyrosine metabolism | 42 | 1 | 0.62112 | 1 | 1 | 0.05581 |
| 20 | Primary bile acid biosynthesis | 46 | 1 | 0.65508 | 1 | 1 | 0.02285 |
| 21 | Purine metabolism | 66 | 1 | 0.78516 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Table 9 Analysis of key metabolic pathways in rat liver tissue metabolism
| No. | Pathway Name | Total | Hits | Raw p | Holm adjust | FDR p | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | 36 | 6 | 0.000099 | 0.008348 | 0.008348 | 0 |
| 2 | Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 36 | 4 | 0.0076 | 0.63076 | 0.31918 | 0.29983 |
| 3 | alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism | 13 | 2 | 0.032911 | 1 | 0.92151 | 0.33333 |
| 4 | Arachidonic acid metabolism | 36 | 3 | 0.044951 | 1 | 0.94396 | 0.0212 |
| 5 | Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis | 19 | 2 | 0.06634 | 1 | 1 | 0.27857 |
| 6 | Sphingolipid metabolism | 21 | 2 | 0.079235 | 1 | 1 | 0.15822 |
| 7 | Linoleic acid metabolism | 5 | 1 | 0.10783 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 8 | Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | 8 | 1 | 0.16702 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 9 | Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 10 | 1 | 0.20434 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 10 | Butanoate metabolism | 15 | 1 | 0.29068 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 11 | Glycerolipid metabolism | 16 | 1 | 0.30683 | 1 | 1 | 0.01246 |
| 12 | Ether lipid metabolism | 20 | 1 | 0.3679 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 13 | Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) | 20 | 1 | 0.3679 | 1 | 1 | 0.03273 |
| 14 | Propanoate metabolism | 23 | 1 | 0.41025 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 15 | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 28 | 1 | 0.47478 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 16 | Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | 28 | 1 | 0.47478 | 1 | 1 | 0.00152 |
| 17 | Glutathione metabolism | 28 | 1 | 0.47478 | 1 | 1 | 0.02698 |
| 18 | Arginine and proline metabolism | 38 | 1 | 0.58393 | 1 | 1 | 0.01212 |
| 19 | Tyrosine metabolism | 42 | 1 | 0.62112 | 1 | 1 | 0.05581 |
| 20 | Primary bile acid biosynthesis | 46 | 1 | 0.65508 | 1 | 1 | 0.02285 |
| 21 | Purine metabolism | 66 | 1 | 0.78516 | 1 | 1 | 0 |

Figure 4 Metabolism diagram of liver tissues in rats with Yin deficiency A: biosynthesis of pantothenic acid and CoA; B: α-linolenic acid metabolism; C: glycero-phospholipid metabolism; D: sphingolipid metabolism.
| 1. | Liu K, Liu N. Discussion on the theory of Yin and Yang in Traditional Chinese Medicine and health preservation. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2010; 12: 89-91. |
| 2. | Shan S, Yan XJ, Liu HN. Modern research progress on Yin deficiency. Shi Jie Ke Xue Ji Shu-Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Hua 2018; 20: 1501-5. |
| 3. | Zhang ZG. Animal experimental study on modified Yiguanjian on prevention and treatment of rats with alcohalic hepatitis liver kidney Yin deficiency syndrome. Shanxi: Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2014: 2-3. |
| 4. | Shang BX, Zhang HX, Lu YT, et al. Insights from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine to elucidate association of Lily disease and Yin deficiency and internal heat of depression. Evid-Based Compl Alt 2020: 8899079. |
| 5. | Qiao TY, Wang AM, Liu WL. Establishment and evaluation of TCM deficiency syndrome animal model. Zhejiang Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2017; 41: 923-7+940. |
| 6. | Jiang LF, He WP, Li SH, Liao PD. Comment on the modeling methods and thinking of animal models of Yin deficiency syndrome. Shandong Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2009; 33: 15-8. |
| 7. | Yang B, Yang Q, Zhang AH, Wang XJ. Research progress of Traditional Chinese Medicine based on metabolomics technology. Zhong Guo Yi Xue Dao Bao 2019; 16: 24-8. |
| 8. |
Chen RY, Li ZY, Yuan YL, et al. A comprehensive analysis of metabolomics and transcriptomics in non-small cell lung cancer. Plos One, 2020; 15: e0232272.
DOI URL |
| 9. |
Weckwerth W. Metabolomics in systems biology. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2003; 54: 669-89.
PMID |
| 10. |
Raamsdonk LM, Teusink B, Broadhurst D, et al. A functional genomics strategy that uses matabolome data to reveal the phenotype of silent mutations. Nat Biotechnol 2001; 19: 45-50.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Zhang AH, Sun H, Wang P, Han Y, Wang XJ. Modern analytical techniques in metabolomics analysis. Analyst 2012; 137: 293.
DOI PMID |
| 12. |
Nybo SE, Lamberts JT. Integrated use of LC/MS/MS and LC/Q-TOF/MS targeted metabolomics with automated label-free microscopy for quantification of purine metabolites in cultured mammalian cells. Purinerg Signal 2019; 15: 17-25.
DOI |
| 13. |
Kawai T, Ota N, Okada K, et al. Ultrasensitive single cell metabolomics by capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry with a thin-walled tapered emitter and large-volume dual sample preconcentration. Anal Chem 2019; 91: 10564-72.
DOI PMID |
| 14. |
Ahamad SR, Alhaider AQ, Raish M, Shakeel F. Metabolomic and elemental analysis of camel and bovine urine by GC-MS and ICP-MS. Saudi J Biol Sci 2017; 24: 23-9.
DOI PMID |
| 15. |
Bouatra S, Aziat F, Mandal R, et al. The human urine metabolome. Plos One 2013; 8:e73076.
DOI URL |
| 16. |
Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, et al. HMDB: a knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37: D603-10.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Psychogios N, Hau DD, Peng J, et al. The human serum metabolome. PLoS One 2011; 6: e16957.
DOI URL |
| 18. | Wishart DS, Lewis MJ, Morrissey JA, et al. The human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome. J Chromatogr A 2008; 871: 164-73. |
| 19. | Zhang L. Study of the Essence of the spleen Qi deficiency based on metabolomics of urine. Dalian: Dalian Medical University, 2009: 7-8. |
| 20. | Bai H, Ren XQ. Research progress on material basis of TCM syndrome based on metabonomics. Zhong Guo Yi Yao Ke Xue 2016; 6: 52-5. |
| 21. | Cui Y, Guo H, Kuang HX, Wang QH. Overview on application of metabonomics in study on Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2017; 32: 672-5. |
| 22. | Wang L, Zhang XP, Wang WS, Zeng YC, Zhang H, Mu sha jiang ASYM. Experimental study on the establishment of a rat model of ED caused by liver-Qi stagnation syndrome. Zhong Yi Yao Xue Bao 2017; 45: 9-13. |
| 23. | Yang CP, Xue CM. Establishment of a model of Yin deficiency in mice caused by warming drugs and its effect on antioxidant effect in mice. Sichuan Zhong Yi 2004; 22: 14-5. |
| 24. | Fan WH, Yue GX, Ren XQ, Lu YQ, Tang S. Change Which a rat model with Yin-diffiency of liver and kidney induced by slow irritation on hypothalamus-pituitary-thypoid gland and regulatory effect of herbs. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Xin Xi Za Zhi 2001; 8: 21-3. |
| 25. | Shang JJ, Sun C, Liu HY. Establishment and evaluation of hyperuricemia rat model with spleen deficiency syndrome. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2020; 26: 1076-9. |
| 26. | Zhang CZ, Wang TF. Research progress on the relationship between cAMP and cGMP antagonistic metabolic regulation and TCM syndromes. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 1999; 22: 3-5. |
| 27. | Luo Y. Reserch of making kidney-Yin deficiency model in SD rat with thyroid. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2006: 8-9. |
| 28. | Xie XY, Wang HJ. Relationship between red blood cell distribution width, serum ALT, AST, ALB levels and chronic hepatitis B hepatocyte inflammation. Jian Yan Yi Xue Yu Lin Chuang 2020; 17: 1684-7. |
| 29. | Feng DR, Wei B, Huang ZT. Experimental study on liver-kidney Yin deficiency syndrome model in rat with hyperlipidemia. Guangxi Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2010; 13: 4-5+16. |
| 30. | Chen W, Guo XJ, Wang SC, Zou YH, Zhang YL, Xie LL. Laboratory animal model studies and analysis of literature statistics on core journal of Chinese medicine from 2005 to 2009. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Yuan Cheng Jiao Yu 2011; 9: 107-8. |
| 31. | Fan WH, Yue GX, Li SX, et al. A rat model with Yin-diffiency of the liver and kidney induced by slow irritation. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2001; 8: 67-9. |
| 32. | Jia L, Wang LL, Meng L, et al. Literature research on characteristics of liver Yin deficiency syndrome and the medication rule of syndrome differentiation. Shi Jie Zhong Yi Yao 2020; 15: 2704-8. |
| 33. | Wang SM, Xu XY. Effect of Ziyinqingre agents on plasma cyclic nucleotide. Zhong Guo Yao Ye 2003; 12: 26-7. |
| 34. | Wang P, Wang XJ. Overview of animal models of kidney-Yin deficiency syndrome. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Xin Xi Za Zhi 2013; 30: 123-5. |
| 35. | Peng Y, Zhang YD. Research status of kidney deficiency and sex hormones. Heilongjiang Zhong Yi Yao 2003; 6: 50-2. |
| 36. | Liu WL, Zhang HY, Mu Y, et al. To construct and evaluate the animal model of Yin-deficiency syndrome of liver and kidney in the acute hepatic injury. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2010; 12: 41-3. |
| 37. | Jia L, Wang LL, Meng L, et al. Effect and mechanism of total glucosides of Paeoniae Radix Alba on combined model of chemical liver injury and liver Yin deficiency syndrome in rats. Zhong Cao Yao 2020; 51: 1885-92. |
| 38. |
Abou DA, El Jalkh T, Eid AA, Fornoni A, Marples B, Zeidan YH. Translational aspects of sphingolipid metabolism in renal disorders. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18: 2528.
DOI URL |
| 39. |
Qureshi AA, Sami SA, Salser WA, Khan FA. Dose-dependent suppression of serum cholesterol by tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF 25) of rice bran in hypercholesterolemic humans. Atherosclerosis 2002; 161: 199-207.
PMID |
| 40. |
Huang SM, Bisogno T, Petros TJ, et al. Identification of a new class of molecules, the arachidonyl aminoacids, and characterization of one member that inhibits pain. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 42639-44.
DOI PMID |
| 41. |
Zaccagnino P, Saltarella M, D'Oria S, Corcelli A, Saponetti MS, Lorusso M. N-arachidonylglycine causes ROS production and cytochrome c release in liver mitochondria. Free Radical Bio Med 2009; 47: 585-92.
DOI PMID |
| 42. |
Siegmund SV, Qian T, de Minicis S, et al. The endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoyl glycerol induces death of hepatic stellate cells via mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. FASEB Journal 2007; 21: 2798-806.
PMID |
| 43. |
Xue LJ, Han JQ, Zhou YC, et al. Untargeted metabolomics characteristics of nonobese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high-temperature-processed feed in Sprague-Dawley rats. World J Gastroenterolo 2020; 26: 7299-311.
DOI URL |
| 44. |
Zhang L, Wu GY, Wu YJ, Liu SY. The serum metabolic profiles of different Barcelona stages hepatocellular carcinoma associated with hepatitis B virus. Oncol Lett 2018; 15: 956-62.
DOI PMID |
| 45. | Chen H, Tan XF. Identification of α-linolenic acid metabolism pathway based on transcriptome data of verniciafordii kernels during tung oil synthesis stage. Lin Ye Ke Xue 2015; 51: 41-8. |
| 46. |
Aliza HS, Michael AC. Update on alpha-linolenic acid. Nutr Rev 2008; 66: 326-32.
DOI PMID |
| 47. |
Pal M, Ghosh M. Studies on comparative efficacy of α-linolenic acid and α-eleostearic acid on prevention of organic mercury-induced oxidative stress in kidney and liver of rat. Food Chem Toxicol 2012; 50: 1066-72.
DOI PMID |
| 48. | Chen FL. Effect of α-linolenic acid on bone metabolism in male SD rats fed on high-fat-diet and its mechanism. Shandong: Shandong University, 2019: 58-9. |
| 49. | Abbiss H, Maker GL, Gummer JPA, et al. Untargeted gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolomics analysis of kidney and liver tissue from the Lewis polycystic kidney rat. J Chromatogr B 2019; 1118-1119: 25-32. |
| 50. | Lu X. LC-MS based serum and tissue metabolomics studies on hepatocellular carcinoma. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016: 113-14. |
| 51. |
Yuan ZW, Yang LH, Zhang XS, Ji P, Hua YL, Wei YM. Mechanism of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du decoction and its effective fraction in alleviating acute ulcerative colitis in mice: Regulating arachidonic acid metabolism and glycerophospholipid metabolism. J Ethnopharmacol 2020; 259: 112872.
DOI URL |
| 52. | Zhang D, Zhao ZJ, Fan J, Yao J, Wei C, Guo YC. Screening of serum metabolic biomarkers of HBV-related liver fibrosis based on high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry technology. ChongqingYi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2022; 47: 733-9. |
| 53. | Zhao DP, Zhang JJ, He C, et al. Study on mechanism of nourishing blood and smoothing liver effects of Paeoniae Radix Alba based on metabolomics information. Zhong Cao Yao 2017; 48: 3412-8. |
| 54. | Zhang J. The study on lipid-lowering effect of aromatized wet drug on nutritional obese rats and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells adipogenic. Nanchang: Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2019: 23-24. |
| 55. | Sun JL, Lin HZ, Gou P. Research progress of sphingolipid metabolism and related diseases. Biotechnology 2011; 21: 93-7. |
| 56. |
Nojima H, Freeman CM, Gulbins E, Lentsch AB. Sphingolipids in liver injury, repair and regeneration. Biol Chem 2015; 396: 633-43.
DOI PMID |
| 57. |
Sandy AL, Jennifer IO, Mariana N Nikolova-Karakashian. Activation of sphingolipid turnover and chronic generation of ceramide and sphingosine in liver during aging. Mech Ageing Dev 2000; 120: 111-25.
PMID |
| 58. | Norris GH, Blesso CN. Dietary and endogenous sphingolipid metabolism in chronic inflammation. Nutrients 2017; 9: 1180. |
| 59. | Braun F, Rinschen MM, Bartels V, et al. Altered lipid metabolism in the aging kidney identified by three layered omic analysis. Aging (Albany NY) 2016; 8: 441-57. |
| 60. | Yang YH, Xiao CL. The functions and biosynthesis of pantothenate. Sheng Ming De Hua Xue 2008; 28: 448-52. |
| 61. |
Duncan ES, Alessio C, Chris A. Coenzymebiosynthesis: enzymemechanism, structure and inhibition. Nat Prod Rep 2007; 24: 1009-26.
DOI PMID |
| 62. | Ping F, Guo Y, Cao YM, et al. Metabolomics analysis of the renal cortex in rats with acute kidney injury induced by sepsis. Front Mol BioSci 2019; 20: 152. |
| 63. | Liu L, Zhu MX, Li QW, Lan XJ, Sui YT, Liang H. Intervention effect of Sijunzi decoction to ageing changes of nephridial tissue based on metabonomics. Zhong Yi Yao Xue Bao 2017; 45: 48-53. |
| 64. |
Ma T, Liu TH, Xie PF, et al. UPLC-MS-based urine nontargeted metabolic profiling identifies dysregulation of pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis pathway in diabetic kidney disease. Life Sci 2020; 258: 118160.
DOI URL |
| 65. |
Wei X, Jiang S, Chen YY, et al. Cirrhosis related functionality characteristic of the fecal microbiotaas revealed by a metaproteomic approach. BMC Gastroenterol 2016; 16: 121.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WANG Jiabao, ZHANG Lishuang, NIU Baihan, YU Yajun, YANG Fengwen, MIAO Lin, CHAI Lijuan, DING Xinya, SUN Yingjie, WANG Yujing, WANG Lin, ZHANG Han, WANG Yi, LI Lin. Efficacy and safety of Weichang’ an pill (胃肠安丸) combined with Western Medicine on gastrointestinal diseases: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1057-1067. |
| [2] | LI He, SU Wenquan, LI Shanshan, JI Hanrui, CHENG Jiangyan, CUI Fangyuan, TANG Lu, ZHOU Li, GAO Ying, DONG Xinglu. Supplementing Qi and activating blood circulation method to treat vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia with posterior circulatory watershed infarction: a case report of two patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 824-828. |
| [3] | HOU Chao, ZHANG Yusen, YANG Die, LI Yifei, ZHANG Xiaochun, LIU Yanqing. Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine on the survival of patients with stage I gastric cancer and high-risk factors: a real-world retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 568-573. |
| [4] | TANG Yanping, LI Peicai, LIU Xi, LIU Lei, GONG Yanxia, WEI Xiaodong, LIU Lina, YANG Li. A single-center retrospective study on epidemiological and Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome characteristics of 21010 patients with reflux/heartburn symptoms [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 574-581. |
| [5] | QU Yilun, CHENG Haimei, WANG Qian, LI Shuang, DUAN Shuwei, FENG Zhe, LI Weizhen, JIANG Shuangshuang, YANG Hongtao, MAO Yonghui, GENG Yanqiu, LI Jijun, LIU Yuning, TIAN Jinzhou, LIU Hongfang, DONG Zheyi, CHEN Xiangmei. Noninvasive identificational diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy and non-diabetic renal disease based on clinical characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine symptom pattern and conventional medicine [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 588-593. |
| [6] | XU Qing, WANG Yang, LI Zhongyu, YAN Jiaxing, ZHAO Yingpan, WANG Ping, WEN Yandong. Therapeutic mechanisms of integrated traditional Chinese and conventional medicine underlying its treatment of precancerous lesions of gastric cancer [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 1023-1028. |
| [7] | XIA Wenguang, ZHENG Chanjuan, ZHANG Jixian, HUANG Min, LI Qinglin, DUAN Can, LI Zhengliang, FAN Cunyu, ZOU Yilong, XU Bo, YANG Fengwen, LIU Qingquan. Randomized controlled study of a diagnosis and treatment plan for moderate coronavirus disease 2019 that integrates Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 234-241. |
| [8] | LIU Wei, WU Yuanhao, XUE Bin, JIN Yue, ZHANG Shumin, LI Peihao, XIE Qing, WANG Aihua, GAO Jingyue, CAI Yue, ZHANG Bo, LIU Xiaoya, WANG Yi, DUAN Ran. Effect of integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine on Gout [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 806-816. |
| [9] | GU Xiaoli, CHEN Menglei, LIU Minghui, ZHANG Zhe, ZHAO Weiwei, CHENG Wenwu. Value of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome differentiation in predicting the survival time of patients with advanced cancer [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 636-641. |
| [10] | LIANG Qijun;TANG Xiaoling;YU Jiong;XIONG Monian;ZHU Huifang;XIONG Linkai;ZENG Ru;YU Peiwen;. Clinical observation of Yiqi Qingdu Prescription(益气清毒方)on the treatment of intermediate-stage and advanced non-small-cell lung cancer [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(2): 308-315. |
| [11] | GOU Xiaowen, GAO Zezheng, YANG Yingying, LI Qingwei, CHEN Keyu, LEI Ye, SONG Bin, ZHAO Linhua, TONG Xiaolin. State-target strategy:a bridge for the integration of Chinese and Western Medicine [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(1): 1-5. |
| [12] | WANG Xue, XIONG Jun, YANG Jun, YUAN Ting, JIANG Yunfeng, ZHOU Xiaohong, LIAO Kai, XU Lingling. Meta-analysis of the clinical effectiveness of combined acupuncture and Western Medicine to treat post-stroke depression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(1): 6-16. |
| [13] | Siu Wing Sum, Shiu Hoi Ting, Shum Wai Ting, Ko Chun Hay, Lau Clara Bik San, Hung Leung Kim, Leung Ping Chung. Chinese topical herbal medicine gives additive effect on pharmaceutical agent on fracture healing [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(06): 853-860. |
| [14] | Wang Weijie, Tang Xiaopo, Wang Xinchang, Jiang Quan, Fan Yongsheng. Classifying rheumatoid arthritis by Traditional Chinese Medicine Zheng: a multi-center cross-sectional study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(03): 425-432. |
| [15] | Liu Zhibin, Li Xia, Yang Jiping, Xu Liran, Guo Huijun. Differences in acquired immune deficiency syndrome treatment and evaluation strategies between Chinese and Western Medicine [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(06): 718-722. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||