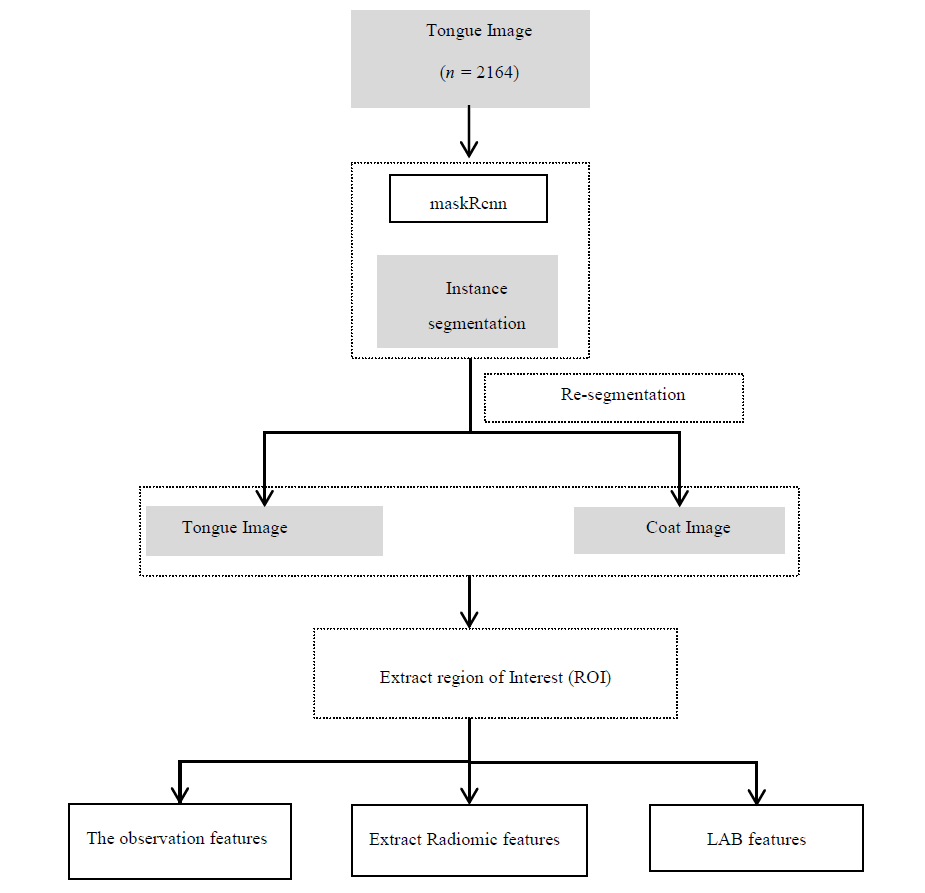
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 279-288.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220225.001
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mining intrinsic information of convalescent patients after suffering coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan
YAN Shixing1, Lü Yi2, LIU Ziqing3, REN Meng2, HE Haiyang1, XIAO Li5, GUO Feng1, PENG Miao2, LI Xiaoxia1, WANG Yong4, XU Xi2, YANG Tao6, SHAO Zuoyu2, HUANG Jingjing2, XIAO Mingzhong2( )
)
- 1 Department of TCM Data Intelligence, Shanghai Daosh Medical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai 201200, China
2 Hepatic Disease Institute, Hubei Key Laboratory of Theoretical and Applied Research of Liver and Kidney in Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, China; Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, China; Hubei Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430074, China
3 Electronical Medical Records and Information Management Center, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China
4 Chinese Medicine Development research Center, Shanghai Literature Institute of TCM, Shanghai 200025, China
5 College of Acupuncture and Massage, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
6 College of Artificial Intelligence and Information Technology, Institute of Information and Technology Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China
-
Received:2021-07-07Accepted:2021-10-29Online:2022-02-25Published:2022-02-25 -
Contact:XIAO Mingzhong -
About author:Dr. XIAO Mingzhong, Hepatic Disease Institute, Hubei Key Laboratory of Theoretical and Applied Research of Liver and Kidney in Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, China; Affifiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, China; Hubei Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430074, China. xmz0001@sohu.com, Telephone: +86-18908640865
-
Supported by:National key research and development plan-Clinical Evaluation of TCM Intervention in COVID-19 Recovery(2020YFC0845000);Clinical study on the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 with integrated Chinese and Western Medicine(2020YFC0841600);National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine-TCM Emergency Response Project for COVID-19(2020ZYLCYJ04)
Cite this article
YAN Shixing, Lü Yi, LIU Ziqing, REN Meng, HE Haiyang, XIAO Li, GUO Feng, PENG Miao, LI Xiaoxia, WANG Yong, XU Xi, YANG Tao, SHAO Zuoyu, HUANG Jingjing, XIAO Mingzhong. Mining intrinsic information of convalescent patients after suffering coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 279-288.
share this article
| Item | Radiomic feature |
|---|---|
| First order | 10 percentile |
| Energy feature | |
| Interquartile range | |
| Maximum feature | |
| Mean absolute deviation | |
| Mean feature | |
| Median feature | |
| Minimum feature | |
| Range feature V | |
| Robust mean absolute deviation | |
| Standard deviation feature | |
| Total energy feature | |
| GLCM | Autocorrelation |
| Contrast | |
| Entropy | |
| Idn | |
| Cluster prominence | |
| Dissimilarity | |
| Joint energy | |
| GLRM | Gray-level non uniformity |
| Long-run emphasis | |
| Low gray-level run | |
| Short-run emphasis | |
| GLSZM | Small area emphasis |
| Small area low gray | |
| Zone percent | |
| NGTDM | Busyness |
| Coarseness | |
| Complexity | |
| Contrast | |
| Strength |
Table 1 Tongue radiomic features analyzed in this study
| Item | Radiomic feature |
|---|---|
| First order | 10 percentile |
| Energy feature | |
| Interquartile range | |
| Maximum feature | |
| Mean absolute deviation | |
| Mean feature | |
| Median feature | |
| Minimum feature | |
| Range feature V | |
| Robust mean absolute deviation | |
| Standard deviation feature | |
| Total energy feature | |
| GLCM | Autocorrelation |
| Contrast | |
| Entropy | |
| Idn | |
| Cluster prominence | |
| Dissimilarity | |
| Joint energy | |
| GLRM | Gray-level non uniformity |
| Long-run emphasis | |
| Low gray-level run | |
| Short-run emphasis | |
| GLSZM | Small area emphasis |
| Small area low gray | |
| Zone percent | |
| NGTDM | Busyness |
| Coarseness | |
| Complexity | |
| Contrast | |
| Strength |
| Tongue feature | Feature | Day 0 (n = 737) | Day 14 (n = 768) | Day 28 (n = 659) | P value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numbers | Rate (%) | Numbers | Rate (%) | Numbers | Rate (%) | ||||||
| Greasy fur | YES | 355 | 48.17 | 384 | 50.00 | 243 | 36.87 | < 0.01 | |||
| NO | 382 | 51.83 | 384 | 50.00 | 416 | 63.13 | |||||
| putrid fur | YES | 50 | 6.78 | 48 | 6.25 | 17 | 2.58 | < 0.01 | |||
| NO | 687 | 93.22 | 720 | 93.75 | 642 | 97.42 | |||||
| Peeling | YES | 114 | 15.47 | 148 | 19.27 | 130 | 19.73 | 0.070 | |||
| NO | 623 | 84.53 | 620 | 80.73 | 529 | 80.27 | |||||
| Teeth-mark | YES | 187 | 25.37 | 241 | 32.70 | 91 | 13.81 | < 0.01 | |||
| NO | 550 | 74.63 | 527 | 71.51 | 568 | 86.19 | |||||
| Crack | YES | 173 | 23.47 | 182 | 23.70 | 145 | 22.00 | 0.6517 | |||
| NO | 564 | 76.53 | 586 | 76.30 | 514 | 78.00 | |||||
| Thick-thin | Thick | 570 | 77.34 | 624 | 81.25 | 471 | 71.47 | < 0.01 | |||
| Thin | 167 | 22.66 | 144 | 18.75 | 188 | 28.53 | |||||
| Fat-lean | Fat | 268 | 36.36 | 255 | 33.20 | 229 | 34.75 | 0.33 | |||
| Lean | 2 | 0.27 | 2 | 0.26 | 2 | 0.30 | |||||
| Moderate | 467 | 63.37 | 511 | 66.54 | 428 | 64.95 | |||||
Table 2 Univariate clinical tongue features analysis of patients with COVID-19
| Tongue feature | Feature | Day 0 (n = 737) | Day 14 (n = 768) | Day 28 (n = 659) | P value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numbers | Rate (%) | Numbers | Rate (%) | Numbers | Rate (%) | ||||||
| Greasy fur | YES | 355 | 48.17 | 384 | 50.00 | 243 | 36.87 | < 0.01 | |||
| NO | 382 | 51.83 | 384 | 50.00 | 416 | 63.13 | |||||
| putrid fur | YES | 50 | 6.78 | 48 | 6.25 | 17 | 2.58 | < 0.01 | |||
| NO | 687 | 93.22 | 720 | 93.75 | 642 | 97.42 | |||||
| Peeling | YES | 114 | 15.47 | 148 | 19.27 | 130 | 19.73 | 0.070 | |||
| NO | 623 | 84.53 | 620 | 80.73 | 529 | 80.27 | |||||
| Teeth-mark | YES | 187 | 25.37 | 241 | 32.70 | 91 | 13.81 | < 0.01 | |||
| NO | 550 | 74.63 | 527 | 71.51 | 568 | 86.19 | |||||
| Crack | YES | 173 | 23.47 | 182 | 23.70 | 145 | 22.00 | 0.6517 | |||
| NO | 564 | 76.53 | 586 | 76.30 | 514 | 78.00 | |||||
| Thick-thin | Thick | 570 | 77.34 | 624 | 81.25 | 471 | 71.47 | < 0.01 | |||
| Thin | 167 | 22.66 | 144 | 18.75 | 188 | 28.53 | |||||
| Fat-lean | Fat | 268 | 36.36 | 255 | 33.20 | 229 | 34.75 | 0.33 | |||
| Lean | 2 | 0.27 | 2 | 0.26 | 2 | 0.30 | |||||
| Moderate | 467 | 63.37 | 511 | 66.54 | 428 | 64.95 | |||||
| Recovery day | Mean | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tongue | Coat | ||||||||
| L | A | B | L | A | B | ||||
| 0 | 60.21 | 12.24 | 6.4 | 60.06 | 13.92 | 6.59 | |||
| 14 | 59.48 | 13.69 | 8.29 | 59.78 | 15.22 | 8.39 | |||
| 28 | 57.18 | 11.83 | 3.53 | 57.03 | 13.89 | 3.84 | |||
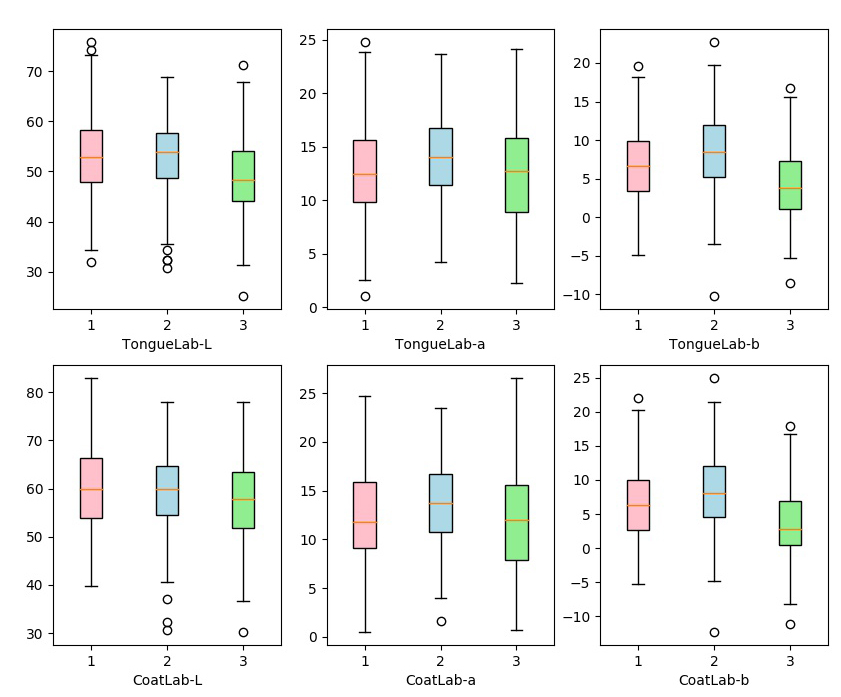
Table 3 Clinical tongue lab mean-value features of patients with coronavirus disease 2019
| Recovery day | Mean | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tongue | Coat | ||||||||
| L | A | B | L | A | B | ||||
| 0 | 60.21 | 12.24 | 6.4 | 60.06 | 13.92 | 6.59 | |||
| 14 | 59.48 | 13.69 | 8.29 | 59.78 | 15.22 | 8.39 | |||
| 28 | 57.18 | 11.83 | 3.53 | 57.03 | 13.89 | 3.84 | |||
| Recovery day | Mann-Whitney | Wilcoxon |
|---|---|---|
| 0 vs 14 | 0.67 | 0.47 |
| 14 vs 28 | 0.01 | < 0.01 |
| 0 vs 28 | < 0.01 | < 0.01 |
Table 4 Clinical tongue color features a P-value analysis of patients with coronavirus disease 2019
| Recovery day | Mann-Whitney | Wilcoxon |
|---|---|---|
| 0 vs 14 | 0.67 | 0.47 |
| 14 vs 28 | 0.01 | < 0.01 |
| 0 vs 28 | < 0.01 | < 0.01 |
| Radiomics feature | Recovery day | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 14 d | 28 d | |
| CoatGLCMAutocorrelation | 30.910 | 28.230 | 30.960 |
| CoatGLCMContrast | 0.173 | 0.174 | 0.194 |
| CoatGLCMEntropy | 0.606 | 0.600 | 0.665 |
| CoatGLCMIdn | 0.981 | 0.980 | 0.979 |
| CoatGLCMClusterProminence | 117.570 | 90.660 | 100.910 |
| CoatGLCMDissimilarity | 0.158 | 0.159 | 0.183 |
| CoatGLCMJointEnergy | 0.316 | 0.356 | 0.262 |
| CoatGLRMGrayLevelNonUniformity | 1913 | 2895 | 1130 |
| CoatGLRMLongRunEmphasis | 346.100 | 371.410 | 129.580 |
| CoatGLRMLowGrayLevelRun | 0.069 | 0.081 | 0.063 |
| CoatGLRMShortRunEmphasis | 0.289 | 0.293 | 0.312 |
| CoatGLSZMSmallAreaEmphasis | 0.315 | 0.310 | 0.331 |
| CoatGLSZMSmallAreaLowGray | 0.024 | 0.028 | 0.024 |
| CoatGLSZMZonePercent | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.017 |
| CoatNGTDMBusyness | 54.000 | 86.000 | 25.000 |
| CoatNGTDMCoarseness | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| CoatNGTDMComplexity | 4.291 | 3.706 | 4.901 |
| CoatNGTDMContrast | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.007 |
| CoatNGTDMStrength | 0.041 | 0.045 | 0.043 |
| CoatFirstOrder10Percentile | 148.730 | 145.950 | 143.300 |
| CoatFirstOrderEnergyFeature | 1.599 | 1.470 | 1.789 |
| CoatFirstOrderInterquartileRange | 10.276 | 8.998 | 12.194 |
| CoatFirstOrderMaximumFeature | 151.220 | 147.880 | 146.410 |
| CoatFirstOrderMeanAbsoluteDeviation | 20.820 | 18.690 | 22.900 |
| CoatFirstOrderMeanFeature | 24.150 | 21.180 | 28.880 |
| CoatFirstOrderMedianFeature | 15.260 | 13.450 | 17.520 |
| CoatFirstOrderMinimumFeature | 204.250 | 199.160 | 202.150 |
| CoatFirstOrderRangeFeatureV | 150.450 | 147.340 | 145.330 |
| CoatFirstOrder RobustMeanAbsoluteDeviation | 502.160 | 396.940 | 576.670 |
| CoatFirstOrderStandardDeviationFeature | 0.406 | 0.440 | 0.351 |
| CoatFirstOrderTotalEnergyFeature | 32.400 | 37.390 | 28.680 |
Table 5 Clinical tongue coat radiomics features analysis of patients with coronavirus disease 2019
| Radiomics feature | Recovery day | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 14 d | 28 d | |
| CoatGLCMAutocorrelation | 30.910 | 28.230 | 30.960 |
| CoatGLCMContrast | 0.173 | 0.174 | 0.194 |
| CoatGLCMEntropy | 0.606 | 0.600 | 0.665 |
| CoatGLCMIdn | 0.981 | 0.980 | 0.979 |
| CoatGLCMClusterProminence | 117.570 | 90.660 | 100.910 |
| CoatGLCMDissimilarity | 0.158 | 0.159 | 0.183 |
| CoatGLCMJointEnergy | 0.316 | 0.356 | 0.262 |
| CoatGLRMGrayLevelNonUniformity | 1913 | 2895 | 1130 |
| CoatGLRMLongRunEmphasis | 346.100 | 371.410 | 129.580 |
| CoatGLRMLowGrayLevelRun | 0.069 | 0.081 | 0.063 |
| CoatGLRMShortRunEmphasis | 0.289 | 0.293 | 0.312 |
| CoatGLSZMSmallAreaEmphasis | 0.315 | 0.310 | 0.331 |
| CoatGLSZMSmallAreaLowGray | 0.024 | 0.028 | 0.024 |
| CoatGLSZMZonePercent | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.017 |
| CoatNGTDMBusyness | 54.000 | 86.000 | 25.000 |
| CoatNGTDMCoarseness | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| CoatNGTDMComplexity | 4.291 | 3.706 | 4.901 |
| CoatNGTDMContrast | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.007 |
| CoatNGTDMStrength | 0.041 | 0.045 | 0.043 |
| CoatFirstOrder10Percentile | 148.730 | 145.950 | 143.300 |
| CoatFirstOrderEnergyFeature | 1.599 | 1.470 | 1.789 |
| CoatFirstOrderInterquartileRange | 10.276 | 8.998 | 12.194 |
| CoatFirstOrderMaximumFeature | 151.220 | 147.880 | 146.410 |
| CoatFirstOrderMeanAbsoluteDeviation | 20.820 | 18.690 | 22.900 |
| CoatFirstOrderMeanFeature | 24.150 | 21.180 | 28.880 |
| CoatFirstOrderMedianFeature | 15.260 | 13.450 | 17.520 |
| CoatFirstOrderMinimumFeature | 204.250 | 199.160 | 202.150 |
| CoatFirstOrderRangeFeatureV | 150.450 | 147.340 | 145.330 |
| CoatFirstOrder RobustMeanAbsoluteDeviation | 502.160 | 396.940 | 576.670 |
| CoatFirstOrderStandardDeviationFeature | 0.406 | 0.440 | 0.351 |
| CoatFirstOrderTotalEnergyFeature | 32.400 | 37.390 | 28.680 |
| Radiomics feature | P-value (Wilcoxon Test) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 vs 14 | 14 vs 28 | 0 vs 28 | |
| CoatGLCMAutocorrelation | 0.010 | 0.005 | 0.882 |
| CoatGLCMContrast | 0.962 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLCMEntropy | 0.820 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLCMIdn | 0.176 | 0.048 | 0.001 |
| CoatGLCMClusterProminence | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLCMDissimilarity | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.401 |
| CoatGLCMJointEnergy | 0.864 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLRMGrayLevelNonUniformity | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLRMLongRunEmphasis | 0.644 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLRMLowGrayLevelRun | 0.029 | 0.009 | 0.258 |
| CoatGLRMShortRunEmphasis | 0.727 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| CoatGLSZMSmallAreaEmphasis | 0.109 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLSZMSmallAreaLowGray | 0.038 | 0.241 | 0.678 |
| CoatGLSZMZonePercent | 0.410 | 0.003 | 0.000 |
| CoatNGTDMBusyness | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatNGTDMCoarseness | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatNGTDMComplexity | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.005 |
| CoatNGTDMContrast | 0.084 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatNGTDMStrength | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrder10Percentile | 0.133 | 0.060 | 0.003 |
| CoatFirstOrderEnergyFeature | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderInterquartileRange | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderMaximumFeature | 0.081 | 0.283 | 0.013 |
| CoatFirstOrderMeanAbsoluteDeviation | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderMeanFeature | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderMedianFeature | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderMinimumFeature | 0.000 | 0.030 | 0.063 |
| CoatFirstOrderRangeFeatureV | 0.084 | 0.146 | 0.004 |
| CoatFirstOrder RobustMeanAbsoluteDeviation | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderStandardDeviationFeature | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderTotalEnergyFeature | 0.400 | 0.000 | 0.007 |
Table 6 P-value of Wilcoxon test of recovery period patients between 0 and 14 d, 14 and 28 d, and 0 and 28 d
| Radiomics feature | P-value (Wilcoxon Test) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 vs 14 | 14 vs 28 | 0 vs 28 | |
| CoatGLCMAutocorrelation | 0.010 | 0.005 | 0.882 |
| CoatGLCMContrast | 0.962 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLCMEntropy | 0.820 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLCMIdn | 0.176 | 0.048 | 0.001 |
| CoatGLCMClusterProminence | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLCMDissimilarity | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.401 |
| CoatGLCMJointEnergy | 0.864 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLRMGrayLevelNonUniformity | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLRMLongRunEmphasis | 0.644 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLRMLowGrayLevelRun | 0.029 | 0.009 | 0.258 |
| CoatGLRMShortRunEmphasis | 0.727 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| CoatGLSZMSmallAreaEmphasis | 0.109 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatGLSZMSmallAreaLowGray | 0.038 | 0.241 | 0.678 |
| CoatGLSZMZonePercent | 0.410 | 0.003 | 0.000 |
| CoatNGTDMBusyness | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatNGTDMCoarseness | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatNGTDMComplexity | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.005 |
| CoatNGTDMContrast | 0.084 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatNGTDMStrength | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrder10Percentile | 0.133 | 0.060 | 0.003 |
| CoatFirstOrderEnergyFeature | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderInterquartileRange | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderMaximumFeature | 0.081 | 0.283 | 0.013 |
| CoatFirstOrderMeanAbsoluteDeviation | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderMeanFeature | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderMedianFeature | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderMinimumFeature | 0.000 | 0.030 | 0.063 |
| CoatFirstOrderRangeFeatureV | 0.084 | 0.146 | 0.004 |
| CoatFirstOrder RobustMeanAbsoluteDeviation | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderStandardDeviationFeature | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CoatFirstOrderTotalEnergyFeature | 0.400 | 0.000 | 0.007 |
| 1. | World Health Organization. Pneumonia of unknown cause-China. WHO online, 2020-01-05, cited 2020-01-05; 1: 1 screen. Available from URL: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2020-DON229. |
| 2. |
Zhang BC, Zhou XY, Qiu YR, et al. Clinical characteristics of 82 cases of death from COVID-19. PLoS One 2020; 15: e0235458.
DOI URL |
| 3. |
Liang KJ, Huang XD, Chen H, et al. Tongue diagnosis and treatment in Traditional Chinese Medicine for severe COVID-19: a case report. Ann Palliat Med 2020; 9: 2400-7.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H. Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016; 278: 563-77.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Aerts HJWL, Velazquez ER, Leijenaar RTH, et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat Commun 2014; 5: 4006.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Zhang B, Tian J, Dong D, et al. Radiomics features of multiparametric MRI as novel prognostic factors in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2017; 23: 4259-69.
DOI PMID |
| 7. |
Tang Q, Yang T, Yoshimura Y, et al. Learning-based tongue detection for automatic tongue color diagnosis system. Artif Life Robot 2020; 25: 363-9.
DOI URL |
| 8. | He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, et al. Mask r-cnn. Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis 2017: 2961-9. |
| 9. | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition. Proc IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 2016: 770-8. |
| 10. | Girshick R. Fast r-cnn. Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis 2015: 1440-8. |
| 11. | Bai L Y, Shi Y, Wu J, et al. A novel automatic tongue coating extraction method in tongue diagnose of Traditional Chinese Medicine. World Congr Medi Phys Biomed Eng 2006. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2007: 2624-7. |
| 12. | Otsu N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 1979; 9: 62-6. |
| 13. | Liu M, Zhao J, Li G, Zhang HM, Wu TX. Tongue coat information extraction of the Traditional Chinese Medicine with hyperspectral image. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi 2017; 37: 162-5. |
| 14. |
Lu HF, Ren ZQ, Li A, et al. Deep sequencing reveals microbiota dysbiosis of tongue coat in patients with liver carcinoma. Sci Rep 2016; 6: 1-11.
DOI URL |
| 15. | Takahashi M. Relationship between dental pathogenic bacteria in tongue coat and clinical oral status. Koku Eisei Gakkai Zasshi 2006; 56: 137-47. |
| 16. |
Perumal V, Narayanan V, Rajasekar S J S. Detection of COVID-19 using CXR and CT images using transfer learning and Haralick features. Appl Intell 2021; 51: 341-58.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Fave X, Zhang L, Yang J, et al. Impact of image preprocessing on the volume dependence and prognostic potential of radiomics features in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Cancer Res 2016; 5: 349-63.
DOI URL |
| 18. | Zinn PO, Singh SK, Kotrotsou A, et al. 139 Clinically applicable and biologically validated MRI radiomic test method predicts glioblastoma genomic landscape and survival. Neurosurgery 2016; 63: 156-7. |
| 19. | R Core Team. R: Language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2020-04-24, cited 2020-07-01. Available from URL: http://www.R-project.org. |
| 20. |
Ndako JA, Olisa JA, Ifeanyichukwu IC, et al. Evaluation of diagnostic assay of patients with enteric fever by the box-plot distribution method. New Microbes New Infect 2020; 38: 100795.
DOI URL |
| 21. |
Ansorena D, De Peña M P Astiasarán I, et al. Colour evaluation of chorizo de Pamplona, a Spanish dry fermented sausage: Comparison between the CIE L∗ a∗ b∗ and the Hunter lab systems with illuminants D65 and C. Meat Sci 1997; 46: 313-8.
PMID |
| 22. | Recky M, Leberl F. Windows detection using k-means in cie-lab color space. Proc IEEE Int Conf Pattern Recognit. 2010: 356-9. |
| 23. |
Larrauri García JA, Saura Calixto F. Evaluation of CIE-lab colour parameters during the clarification of a sugar syrup from Mesquite pods (Prosopis Pallida L.). Int J Food Sci 2000; 35: 385-9.
DOI URL |
| 24. |
Malela-Majika JC. New distribution-free memory-type control charts based on the Wilcoxon rank-sum statistic. Qual Technol Quant Manag 2021; 18: 135-55.
DOI URL |
| 25. |
Hsu PC, Wu HK, Huang YC, et al. Gender-and age-dependent tongue features in a community-based population. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98: e18350.
DOI URL |
| 26. | Alsini AY, Sayed S, Alkaf HH, et al. Tongue reconstruction post partial glossectomy during the COVID-19 pandemic. A case report. Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2020, 59: 53-6. |
| 27. |
Wu D, Wu T, Liu Q, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 outbreak: what we know. Int J Infect Dis 2020, 94: 44-8.
DOI PMID |
| 28. |
Pástor Ľ, Vorsatz M B. Mutual fund performance and flows during the COVID-19 crisis. Rev Asset Pricing Stud 2020; 10: 791-833.
DOI URL |
| 29. | Guo WT, Li H, Zhu YT, et al. Prediction of clinical phenotypes in invasive breast carcinomas from the integration of radiomics and genomics data. J Med Imaging (Bellingham) 2015, 2: 041007. |
| 30. |
Li H, Zhu YT, Burnside ES, et al. MR imaging radiomics signatures for predicting the risk of breast cancer recurrence as given by research versions of MammaPrint, Oncotype DX, and PAM50 gene assays. Radiology 2016, 281: 382-91.
DOI URL |
| 31. | Shu ZX, Zhou YN, Chang K, et al. Clinical features and the Traditional Chinese Medicine therapeutic characteristics of 293 COVID-19 inpatient cases. Front Med 2020: 760-75. |
| 32. | Shu ZX, Chang K, Zhou YN, et al. Add-on Chinese medicine for coronavirus disease 2019 (ACCORD): a retrospective cohort study of hospital registries. Am J Chin Med 2021: 1-33. |
| [1] | FAN Rong, HE Haoyu, TANG Tao, CUI Hanjin. Long-term effects of Qingfei Paidu decoction (清肺排毒汤) in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 acute pneumonia after treatment: a protocol for systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1068-1071. |
| [2] | SUN Wu, ZHAO Yuwei, LIAO Liang, ZHAO Zhonghui, CHEN Shiqi, YAN Xiaoling, WANG Xueyao, CHAO Guojun, ZHOU Jian. Effectiveness and safety of Xuebijing injection for patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 631-639. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yuehong, SHAO Xianzhi, ZHAO Qianlong, ZHAN Hualong, ZHANG Jianhua, DU Sisi, CHEN Jing, LIU Yingfang, ZHOU Haiwang, CHEN Xinsheng, HONG Ying, LIAN Fengmei, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Effectiveness of Xiangsha Liujun pills (香砂六君丸) on decreased digestive function in convalescent patients of coronavirus disease 2019: a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 552-558. |
| [4] | XU Guihua, CHEN Feifei, ZHANG Wei, WU Yingen, CHEN Xiaorong, SHI Kehua, WANG Zhenwei, SHI Miaoyan, ZHANG Xing, LU Yunfei, YUAN Weian, LYU Hua, CHEN Xuan. Effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine on coronavirus disease 2019 in 92 patients: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 582-587. |
| [5] | YANG Cunqing, LIAN Fengmei, YANG Guiping, HUANG Yufeng, ZHANG Shuangbin, WANG Jianghua, ZHOU Jing, GUO Dongqing, SHEN Chuanyun, YE Tiansong, FU Aojie, LI Xiaoli, CHEN Le, ZHANG Huifeng, TU Qiyin, WANG Ying, YANG Wenzhe, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Effectiveness of Xiaoyao capsule (逍遥丸) on sleep disorders and mood disturbance in patients in recovery from coronavirus disease 2019: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 343-351. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yuehong, DONG Dandan, YAN Youqin, ZHANG Hao, WANG Guangli, ZHOU Wei, LI Wei, QIU Li, LI Tingming, LIU Quan, XIA Ping, MAO Lina, YANG Danlin, YANG Lu, LIAN Fengmei, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Effectiveness and safety of Jinshuibao capsules (金水宝胶囊) in treatment of residual cardiopulmonary symptoms in convalescent patients of coronavirus disease 2019: a pilot randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 134-139. |
| [7] | AN Xuedong, MAO Lina, XIA Ping, SU Wen, WANG Beibei, KOU Leiya, ZHANG Zequan, QI Meng, HU Song, CHEN Jing, LI Xiujuan, LIU Jinwei, ZHOU Juan, QIAO Jie, LUO Dan, LUO Guangwei, YAN Youqin, YANG Guiping, DONG Dandan, ZHOU Wei, TAO Junxiu, JIN De, TONG Xiaolin, WEI Li. Effects of Shengmai Yin (生脉饮) on pulmonary and cardiac function in coronavirus disease 2019 convalescent patients with cardiopulmonary symptoms: a randomized, double blind, multicenter control trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 140-145. |
| [8] | LI Ximeng, KANG Yuan, LI Wenjing, LIU Zhuangzhuang, XU Zhenlu, ZHANG Xiaoyu, CAI Runlan, GAO Yuan, QI Yun. Comparing the effects of three decoctions for coronavirus disease 2019 on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-related toll-like receptors-mediated inflammations [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 51-59. |
| [9] | ZHU Qingguang, ZHANG Shuaipan, LI Jingxian, SUN Wuquan, CHENG Wei, ZHAN Chao, CHENG Yanbin, FANG Lei, FANG Min. Effectiveness of Liu-zi-jue exercise on coronavirus disease 2019 in the patients: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 997-10053. |
| [10] | AN Xuedong, ZHANG Qing, TAO Junxiu, LI Li, CHEN Yun, LI Kejian, HE Jing, LIU Ru, GUO Juan, ZHANG Jia, ZHU Hui, LIAN Fengmei, LI Xiaodong. Shugan Jieyu capsule (舒肝解郁胶囊) improve sleep and emotional disorder in coronavirus disease 2019 convalescence patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 803-809. |
| [11] | CHEN Huang, SHI Lushaobo, SHI Zengping, XIA Yi, WANG Dong. Factors influencing physician's behavioral intention to use Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat coronavirus disease 2019 based on the theory of planned behavior [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 633-6400. |
| [12] | ZHAO Yufeng, PANG Huaxin, Lü Lanting, ZHOU Pei, WANG Kaining, CAI Shengxing, ZHANG Huifeng, LI Kun. Risk assessment and analysis of Traditional Chinese Medicine intervention in coronavirus disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 472-478. |
| [13] | XIA Wenguang, ZHENG Chanjuan, ZHANG Jixian, HUANG Min, LI Qinglin, DUAN Can, LI Zhengliang, FAN Cunyu, ZOU Yilong, XU Bo, YANG Fengwen, LIU Qingquan. Randomized controlled study of a diagnosis and treatment plan for moderate coronavirus disease 2019 that integrates Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 234-241. |
| [14] | LI Li, AN Xuedong, ZHANG Qing, TAO Junxiu, HE Jing, CHEN Yun, LI Kejian, LIU Ru, GUO Juan, ZHANG Hao, TONG Xiaolin, BA Yuanming. Shumian capsule(舒眠胶囊) improves symptoms of sleep mood disorder in convalescent patients of Corona Virus Disease 2019 [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 974-981. |
| [15] | BAO Chunmiao, LI Binbin. Traditional Chinese Medicine enhances absorption of lung lesions in corona virus disease 2019 patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 982-984. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||