Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 250-255.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.02.005
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
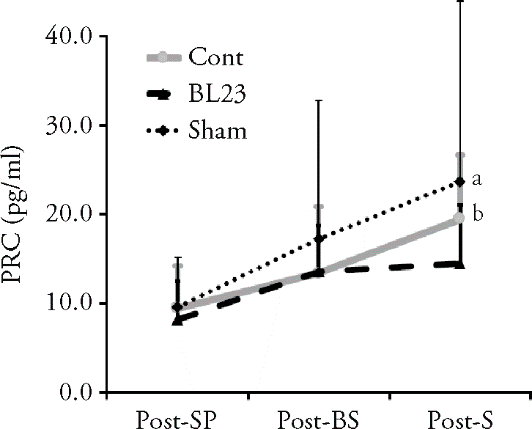
Specific acupuncture stimulation of Shenshu (BL23) affects sympathetic nervous activity-associated plasma renin concentration changes
Kanae Umemoto1( ), Tomoya Hayashi2, Kaori Fukushige3, Shuichi Hirai4, Hayato Terayama5, Kou Sakabe5, Munekazu Naito3
), Tomoya Hayashi2, Kaori Fukushige3, Shuichi Hirai4, Hayato Terayama5, Kou Sakabe5, Munekazu Naito3
- 1 Graduate School of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Meiji University of Integrative Medicine, Nantan, Kyoto 629-0392, Japan; Department of Anatomy, Division of Basic Medical Sc+ience, Tokai University School of Medicine, Isehara, Kanagawa 259-1193, Japan; Department of Anatomy, Aichi Medical University School of Medicine, Nagakute, Aichi 480-1195, Japan
2 Graduate School of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Meiji University of Integrative Medicine, Nantan, Kyoto, 629-0392, Japan; Department of Physiology, Meiji University of Integrative Medicine, Nantan, Kyoto 629-0392, Japan
3 Department of Anatomy, Aichi Medical University School of Medicine, Nagakute, Aichi 480-1195, Japan
4 Department of Anatomy, Aichi Medical University School of Medicine, Nagakute, Aichi 480-1195, Japan; Division of Anatomical Science, Department of Functional Morphology, Nihon University School of Medicine, Itabashi-ku, Tokyo 173-0032, Japan
5 Department of Anatomy, Division of Basic Medical Science, Tokai University School of Medicine, Isehara, Kanagawa 259-1193, Japan
Kanae Umemoto, Tomoya Hayashi, Kaori Fukushige, Shuichi Hirai, Hayato Terayama, Kou Sakabe, Munekazu Naito. Specific acupuncture stimulation of Shenshu (BL23) affects sympathetic nervous activity-associated plasma renin concentration changes[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 250-255.