Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1111-1117.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.06.002
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Multi-omics analysis reveals the neuroprotective effect of Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba extract against Parkinson’s disease in mouse
KANG Sohi1,2, LEE Sueun3, MOON Byeong Cheol3, SONG Jun Ho3,4, KIM Sung-Ho2, MOON Changjong2, LEE Soong-In5, KIM Chul6( ), KIM Joong Sun2(
), KIM Joong Sun2( )
)
- 1 Department of Anatomy and Convergence Medical Science, College of Medicine, Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju 52727, Republic of Korea
2 College of Veterinary Medicine and BK21 FOUR Program, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 61186, Republic of Korea
3 Herbal Medicine Resources Research Center, Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine, 111, Geonjae-ro, Naju-si, Jeollanam-do 58245, Republic of Korea
4 Department of Biology, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 28644, Republic of Korea
5 Department of Oriental Medicine Prescription, College of Oriental Medicine, Dong-Shin University, Naju-si, Jeollanam-do 58245, Republic of Korea
6 KM Data Division, Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine, 1672 Yuseong-daero, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 34054, Republic of Korea
-
Received:2020-11-22Accepted:2023-12-06Online:2024-12-15Published:2024-11-12 -
Contact:KIM Joong Sun, College of Veterinary Medicine and BK21 FOUR Program, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 61186, Republic of Korea. centraline@jnu.ac.kr Telephone: +82-428689582; +82-625302815
KIM Chul, KM Data Division, Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine, 1672 Yuseong-daero, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 34054, Republic of Korea. chulnice@kiom.re.kr -
Supported by:Development of Sustainable Application for Standard Herbal Resource by the Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine(KSN2012320)
Cite this article
KANG Sohi, LEE Sueun, MOON Byeong Cheol, SONG Jun Ho, KIM Sung-Ho, MOON Changjong, LEE Soong-In, KIM Chul, KIM Joong Sun. Multi-omics analysis reveals the neuroprotective effect of Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba extract against Parkinson’s disease in mouse[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1111-1117.
share this article
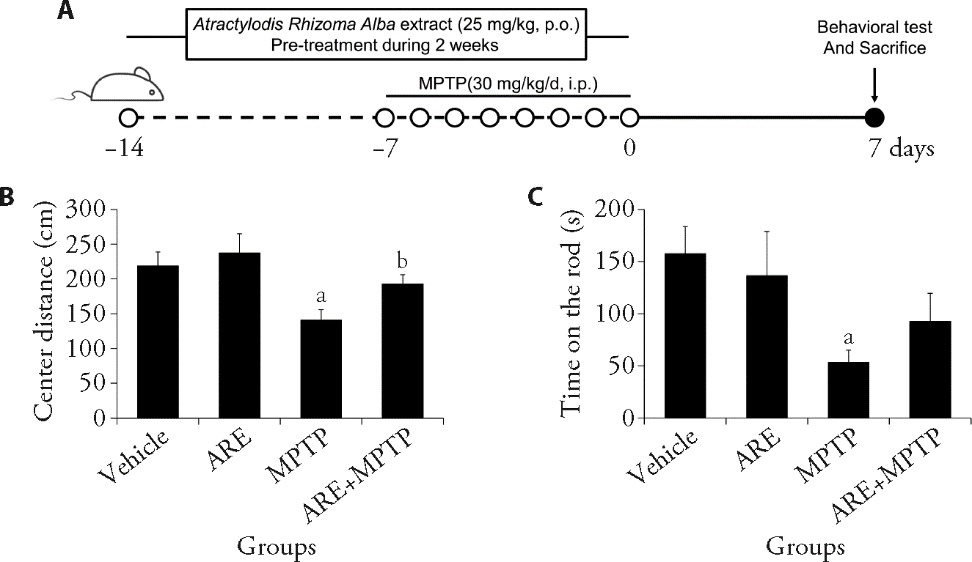
Figure 1 Therapeutic effect of Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba extracts in a Parkinson’s disease murine model A: schematic diagram of drug treatment, behavioral test, and tissue preparation; B: MPTP treatment decreases the total distance in the center of the OFT. ARE increases the distance in the center area of OFT; C: motor skill learning of the MPTP-induced mice in the rotarod test provides evidence of the therapeutic effect of ARE. Vehicle group: saline p.o. + saline i.p. ARE group: ARE 20 mg·kg-1·d-1 p.o. + saline i.p. MPTP group: saline p.o. + MPTP 30 mg·kg-1·d-1 i.p. ARE + MPTP group: ARE 20 mg·kg-1·d-1 p.o. + MPTP 30 mg·kg-1·d-1 i.p. ARE: Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba extract; p.o., per oral; MPTP: 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; OFT: open field test. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 7). aP < 0.01 vs the vehicle-treated control group; bP < 0.05 vs the vehicle-treated MPTP-induced PD mice group.

Figure 2 Histological examination evaluating the effect of ARE in a Parkinson’s disease murine model A: immunostaining for TH-positive dopaminergic neurons in the SN of vehicle group (A1), MPTP group (A2), and ARE + MPTP group (A3); B: immunostaining for TH-positive dopaminergic neurons in the striatum of vehicle group (B1), MPTP group (B2), and ARE + MPTP group (B3); C: bar graph representing TH-positive cells in the SN; D: bar graph representing TH-positive intensity in the striatum. Vehicle group: saline p.o. + saline i.p. ARE group: ARE 20 mg·kg-1·d-1 p.o. + saline i.p. MPTP group: saline p.o. + MPTP 30 mg/kg/day i.p. ARE + MPTP group: ARE 20 mg·kg-1·d-1 p.o. + MPTP 30 mg·kg-1·d-1 i.p. ARE: Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba extract; TH: tyrosine hydroxylase; SN: substantia nigra; MPTP: 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 3). aP < 0.05 vs the control group; bP < 0.05 vs the vehicle-treated MPTP-induced PD mice group.
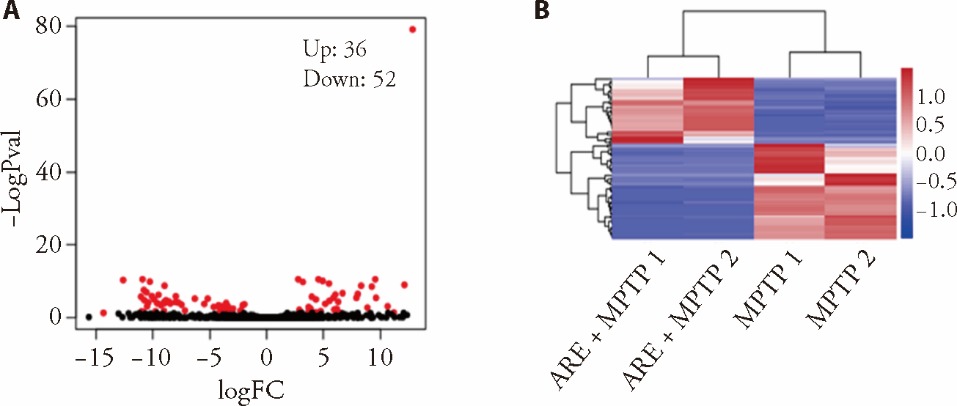
Figure 3 RNA-seq correlation analysis A: scatter plot; B: heatmap of differentially expressed genes between the MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease group and ARE-treated MPTP groups (n = 2 mice per group). MPTP group: saline p.o. + MPTP 30 mg·kg-1·d-1 i.p. ARE + MPTP group: ARE 20 mg·kg-1·d-1 p.o. + MPTP 30 mg·kg-1·d-1 i.p. MPTP: 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; ARE: Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba extract.

Figure 4 Methyl-seq correlation analysis A: the stacking bar graph shows the percentage of hypermethylated and hypomethylated CpGs for each chromosome; B: heamap of differentially methylated DNA between the MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease group and ARE-treated MPTP groups (n = 2 mice per group). MPTP group: saline p.o. + MPTP 30 mg·kg-1·d-1 i.p. ARE + MPTP group: ARE 20 mg·kg-1·d-1 p.o. + MPTP 30 mg·kg-1·d-1 i.p. MPTP: 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; ARE: Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba extract.
| 1. | Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. The Korean Pharmacopoeial Forum. 18th ed. North Chungcheong: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, 2021: 116-23. |
| 2. | Zhang WJ, Zhao ZY, Chang LK, et al. Atractylodis Rhizoma: a review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and quality control. J Ethnopharmacol 2021; 266: 113415. |
| 3. |
Zhu B, Zhang QL, Hua JW, Cheng WL, Qin LP. The traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.: a review. J Ethnopharmacol 2018; 226: 143-67.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Park ST, Lee MS, Jeon BH, Park KI, Oh JM. Effect of Atractylodis Rhizoma alba on osteoclast formation. J Physiol Pathol Kor Med 2011; 25: 109-14. |
| 5. | Choi S. Pharmacological and molecular studies of Atracylodes japonica Koidzumi on anti-oxidant activity. Seoul: KyungHee University, 2011: 1-29. |
| 6. | Han YK, Park YK. Effect of Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba water extract on streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Korea J Herbol 2011; 26: 23-30. |
| 7. | Park CS, Kim DH. Biological activities of extracts from Scutellaria baicalensis, Zizyphus jujuba and Atractylodes macrocephala. Korea J Herbol 2008; 23: 41-51. |
| 8. | Lim SY, Kim HR, Choi YS, Lee I. Review of current clinical studies for herbal medicine of Parkinson’s disease in Traditional Chinese Medicine. J Physiol Pathol Kor Med 2016; 30: 327-37. |
| 9. | Jang JH, Jung K, Kim JS, Jung I, Yoo H, Moon C. Potential application of Yokukansan as a remedy for Parkinson’s disease. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018; 2018. |
| 10. | Kim YE, Kim IW, Lee JH, Lee SG, Lee KS. Case report of Parkinson's disease diagnosed as deficiency of Qi and blood. J Intern Kor Med 2009; 30: 901-8. |
| 11. | Jeong HS, Kim HR, Kim SY, et al. Effects of Korean medicine on pain in patients with Parkinson's disease: a retrospective study. J Intern Kor Med 2020; 41: 947-58. |
| 12. | Kim SW, Yang JY, Lee YJ, et al. A case of Parkinson's disease patient with nausea and vomiting induced by taking levodopa. J Intern Kor Med 2019; 40: 246-53. |
| 13. | Lee SJ, Ha JB, Lew JH. A case study of parkinson's disease patient with anorexia and nausea treated with korean-medicine treatment including Hyangsayukgunja-tang. J Intern Kor Med 2020; 41: 717-23. |
| 14. | More S, Choi DK. Neuroprotective role of atractylenolide-I in an in vitro and in vivo model of Parkinson’s disease. Nutrients 2017; 9: 451. |
| 15. | Kang S, Lee SE, Lee A, et al. Protective effects of Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba Extract on seizures mice model. Korea J Herbol 2021; 36: 1-8. |
| 16. |
Zuzuárregui JRP, During EH. Sleep issues in Parkinson’s disease and their management. Neurotherapeutics 2020; 17: 1480-94.
DOI PMID |
| 17. |
Lee E, Hwang I, Park S, et al. MPTP-driven NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia plays a central role in dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Cell Death Differ 2019; 26: 213-28.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Latif S, Jahangeer M, Razia DM, et al. Dopamine in Parkinson's disease. Clin Chim Acta 2021; 522: 114-26.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Wada M, Ang MJ, Weerasinghe-Mudiyanselage PD, et al. Behavioral characterization in MPTP/p mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Integr Neurosci 2021; 20: 307-20.
DOI PMID |
| 20. | Bossers K, Meerhoff G, Balesar R, et al. Analysis of gene expression in Parkinson's disease: possible involvement of neurotrophic support and axon guidance in dopaminergic cell death. Brain Pathol 2009; 19: 91-107. |
| 21. | Simunovic F, Yi M, Wang Y, et al. Gene expression profiling of substantia nigra dopamine neurons: further insights into Parkinson's disease pathology. Brain 2009; 132: 1795-809. |
| 22. |
Duke D, Moran L, Kalaitzakis M, et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals link between proteasomal and mitochondrial pathways in Parkinson’s disease. Neurogenetics 2006; 7: 139-48.
DOI PMID |
| 23. | Moran LB, Graeber MB. Towards a pathway definition of Parkinson’s disease: a complex disorder with links to cancer, diabetes and inflammation. Neurogenetics 2008; 9: 1-13. |
| 24. | Han HY, Yang YS, Kim SN, et al. Two-week repeated dose toxicity of Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba in F344 rats. Nat Prod Sci 2016; 22: 180-6. |
| 25. |
Kim JS, Lim HS, Moon BC, et al. Epigenetic mechanisms involved in the neuroprotective effect of scorpion extract in a Parkinson's disease murine model based on multi-omics approach. J Tradit Chin Med 2021; 41: 390.
DOI |
| 26. | Meredith GE, Rademacher DJ. MPTP mouse models of Parkinson's disease: an update. J Parkinsons Dis 2011; 1: 19-33. |
| 27. | Rozas G, Guerra M, Labandeira-Garcıa J. An automated rotarod method for quantitative drug-free evaluation of overall motor deficits in rat models of parkinsonism. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 1997; 2: 75-84. |
| 28. |
Sedelis M, Schwarting RK, Huston JP. Behavioral phenotyping of the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Behav Brain Res 2001; 125: 109-25.
DOI PMID |
| 29. |
Fernandez-Espejo E. Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 2004; 29: 15-30.
PMID |
| 30. |
Dauer W, Przedborski S. Parkinson's disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 2003; 39: 889-909.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Zhang T, Chen T, Chen P, Zhang B, Hong J, Chen L. MPTP-induced dopamine depletion in basolateral amygdala via decrease of D2R activation suppresses GABAA receptors expression and LTD induction leading to anxiety-like behaviors. Front Mol Neurosci 2017; 10: 247. |
| 32. | Jayaraj RL, Elangovan N, Manigandan K, Singh S, Shukla S. CNB-001 a novel curcumin derivative, guards dopamine neurons in MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. BioMed research international 2014; 2014: 236182. |
| 33. |
Bos JL, Rehmann H, Wittinghofer A. GEFs and GAPs: critical elements in the control of small G proteins. Cell 2007; 129: 865-77.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Xiong Y, Coombes CE, Kilaru A, et al. GTPase activity plays a key role in the pathobiology of LRRK2. PLoS Genet 2010; 6: e1000902. |
| 35. | Kang S, Kim JS, Lee J, Moon C, Kim C. Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression changes in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s diseases mouse model. Kor Herb Med Inform 2021; 9: 209-20. |
| 36. |
Gogia N, Chimata AV, Deshpande P, Singh A, Singh A. Hippo signaling: bridging the gap between cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Neural Regen Res 2021; 16: 643.
DOI PMID |
| 37. | Caricasole A, Bakker A, Copani A, Nicoletti F, Gaviraghi G, Terstappen G. Two sides of the same coin: Wnt signaling in neurodegeneration and neuro-oncology. Biosci Rep 2005; 25: 309-27. |
| 38. |
Inestrosa NC, Arenas E. Emerging roles of Wnts in the adult nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 2010; 11: 77-86.
DOI PMID |
| 39. | Rawal N, Corti O, Sacchetti P, et al. Parkin protects dopaminergic neurons from excessive Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 388: 473-8. |
| [1] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [2] | WU Haiyang, WANG Ying, HAN Wei, LI Huihui, JI Haisheng, LIU Xiuxiu. Protective effect of Tongdu Tiaoshen acupuncture combined with Xiaoxuming decoction (小续命汤) on dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 484-493. |
| [3] | ZHAO Lixia, SUN Wei, BAI Decheng. Protective effect of resveratrol on rat cardiomyocyte H9C2 cells injured by hypoxia/reoxygenation by regulating mitochondrial autophagy via PTEN-induced putative kinase protein 1/Parkinson disease protein 2 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 176-186. |
| [4] | XU Qian, QIN Wei, WU Fangzhen, LIN Yao, HONG Liting, CHEN Dan, HU Xuefeng, CAI Jing. Effect of Roucongrong(Herba Cistanches Deserticolae) decoction on the substantia nigra through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in rats with Parkinson's disease induced by 6-hydroxydopamine hydrochloride [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 762-770. |
| [5] | Joong Sun Kim, Hye-Sun Lim, Byeong Cheol Moon, Mary Jasmin Ang, Sung-Ho Kim, Changjong Moon, Boseok Seong, Yunji Jang, Hyung-Yong Kim, Chul Kim. Epigenetic mechanisms involved in the neuroprotective effect of scorpion extract in a Parkinson's disease murine model based on multi-omics approach [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 390-396. |
| [6] | Liu Meijun, Hu Chongshan, Zhang Yaodan, Li Qizheng, Zhang Qi, Fang Yu, Sun Honghui, Hou Xiaolin, Jin Shuoguo, Tao Liangjing, Yang Dongdong. Effect of Huatan Jieyu granules in treatment of Parkinson's disease patients with sleep disorder identified as symptom pattern of phlegma-heat-stirring wind [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(3): 461-466. |
| [7] | Liu Quanfeng, Sang Heon Kim, Yung-Wei Sung, Sok Cheon Pak, Wonwoong Lee, Jongki Hong, Jaehwan Jang, Kyoung Sang Cho, Songhee Jeon, Byung-Soo Koo. Neuroprotective effects of Suhexiang Wan on the in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson's disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(06): 800-808. |
| [8] | Chen Hongzhi, He Jiancheng, Teng Long, Yuan Canxing, Zhang Zhe. Traditional Chinese Medicine symptom pattern analysis for Parkinson's disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(05): 688-694. |
| [9] | Xiao Danqing. Acupuncture for Parkinson's Disease: a review of clinical,animal,and functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging studies [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(06): 709-717. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

