Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 794-803.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240515.001
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Sanhua Tang (三化汤) protects against ischemic stroke by preventing blood-brain barrier injury: a network pharmacology and in vivo experiments
LUO Shan1, YANG Fan2, CHEN Yuanchun2, ZHAO Ruoxi2, LIU Haiye1, GAO Fei3, MA Wencan3, GAO Weijuan1,4( ), YU Wentao3,4,5(
), YU Wentao3,4,5( )
)
- 1 College of Basic Medicine, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China
2 Graduate School, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050091, China
3 College of Acupuncture and Massage, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China
4 Hebei Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Research on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases, Shijiazhuang 050091, China
5 Hebei International Joint Research Centre for Acupuncture and Moxibustion of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050091, China
-
Received:2023-01-11Accepted:2023-07-16Online:2024-08-15Published:2024-05-15 -
Contact:Prof. YU Wentao, College of Acupuncture and Massage, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China,yuwentao@hebcm.edu.cn ; Prof. GAO Weijuan, College of the Basic Medicine, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China.gwj6088@163.com Telephone: +86-311-89926400 -
Supported by:Hebei Province Natural Science Foundation Project: Based on The Xuan Fu Theory to Explore Sanhua Tang on Ischemic Stroke Blood-brain Barrier Protection Mechanism Research(H2022423327);Science and Technology Program of Hebei Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine: based on The Changes in Gut Microbiota, Explore Sanhua Tang From The Perspective of "Opening the Xuan Fu" Protective Phlegm Heat Relieving Excess Syndrome of Ischemic Stroke Mechanism of Action of the Blood-brain Barrier(2022090);Hebei Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Research on Cardio- cerebrovascular Disease in 2021 Project:Based on the Gut-brain Axis, Explore Sanhua Tang's Treatment of Ischemic Stroke Syndrome (Phlegm Heat Relieving Empirical Model)(2021201);Innovation Funding Program for Doctoral Students in Hebei Province: the Mechanism Research of Sanhua Tang Regulating Gut Microbiota, Improving the Blood-brain Barrier Damage of Ischemic Stroke(CXZZBS2022095);National College Students' Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program: Based on the Xuan Fu Theory to Explore Sanhua Tang on Ischemic stroke Blood-brain Barrier Protection Mechanism Research(202114432005);Special Project on the Cultivation of Scientific and Technological Innovation Ability of College and Middle School Students in Hebei Province: Mechanism Research of Bushen Huoxue Fang on Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampal Nerve After Vascular Dementia through Phosphatidylinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase b/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Pathways(22E50142D)
Cite this article
LUO Shan, YANG Fan, CHEN Yuanchun, ZHAO Ruoxi, LIU Haiye, GAO Fei, MA Wencan, GAO Weijuan, YU Wentao. Sanhua Tang (三化汤) protects against ischemic stroke by preventing blood-brain barrier injury: a network pharmacology and in vivo experiments[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 794-803.
share this article

Figure 1 Compound-targets network and Herb-pathway-targets network A: the network had 121 nodes representing the potential active components of SHT and 353 edges, describing the relationship between them. The triangle represents IS, and the square represents the four herbs of SHT. DH (Dahuang), ZS (Zhishi), QH (Qianghuo), and HP (Houpu) stand for herbs' abbreviation. The hexagon represents effective chemical compounds, and the diamond represents targets. B: circles represent compounds, arrows represent pathways, squares represent the top 10 core targets, and triangles represent IS. SHT: Sanhua Tang; IS: ischemic stroke.

Figure 2 Conformations of some key compounds and core targets A: AKT1 with luteolin; B: IL-6 with luteolin; C: TNF with luteolin; D: CASP3 with luteolin; E: AKT1 with naringenin; F: CASP3 with beta-sitosterol. GLN: glutamine; ASN: asparagine; LYS: lysine; ALA: alanine; MET: methionine; LEU: leucine; ARG: arginine; PHE: phenylalanine; TRP: tryptophan; AKT1: v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; CASP3: cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 3.
| Neurological dysfunction | ANOVA | Treatment (between columns) | Residual (within columns) | F (DFn, DFd) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurological score | SS | 924.4 | 447.4 | F (5, 102) = 42.15 | < 0.0001 |
| DF | 5 | 102 | |||
| MS | 184.9 | 4.387 | |||
| Infarct area | SS | 3.165 | 0.6348 | F (5, 23) = 22.93 | < 0.0001 |
| DF | 5 | 23 | |||
| MS | 0.6329 | 0.02760 | |||
| Number of positive cells | SS | 19256 | 5910 | F (5, 30) = 19.55 | < 0.0001 |
| DF | 5 | 30 | |||
| MS | 3851 | 197.0 |
Table 1 Statistical results of neurological score, infarct area and the number of positive cells between each group after ANOVA
| Neurological dysfunction | ANOVA | Treatment (between columns) | Residual (within columns) | F (DFn, DFd) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurological score | SS | 924.4 | 447.4 | F (5, 102) = 42.15 | < 0.0001 |
| DF | 5 | 102 | |||
| MS | 184.9 | 4.387 | |||
| Infarct area | SS | 3.165 | 0.6348 | F (5, 23) = 22.93 | < 0.0001 |
| DF | 5 | 23 | |||
| MS | 0.6329 | 0.02760 | |||
| Number of positive cells | SS | 19256 | 5910 | F (5, 30) = 19.55 | < 0.0001 |
| DF | 5 | 30 | |||
| MS | 3851 | 197.0 |

Figure 3 Effect of SHT on neurological dysfunction A: TTC staining of cerebral slices of each group; B: Nissl staining observation of ischemic penumbra of rats in each group under × 400 magnification. B1: the sham group; B2: the M group; B3: the SL group; B4: the SM group; B5: the SH group; B6: the AE group. Microscopic observation showed that the green arrows were normal neurons, the neurons were regularly arranged, the whole blue staining and the Nissl corpuscles were dark blue, thick, and dense granules. The red arrows were degenerative and necrotic neurons, the arrangement of neurons was disordered, Nissl corpuscles decreased or even disappeared, and the whole was in a lightly stained state. M: middle cerebral artery occlusion; AE: aloeemodin; SL: Sanhua Tang at low dosage; SM: medium dosage; SH: high dosage; SHT: Sanhua Tang; TTC: triphenyltetrazolium chloride; MCAO: middle cerebral artery occlusion. M: model group were orally administered with saline 1 mL/100 g per day for 5 d; SL: this group were orally administered Sanhua Tang 0.18 g/mL before stroke induction once daily for 4 d, and continued administration for one day after MCAO surgery. As the same goes SM 0.36 g/mL, SH group 0.72 g/mL, and AE 5 mg/mL.
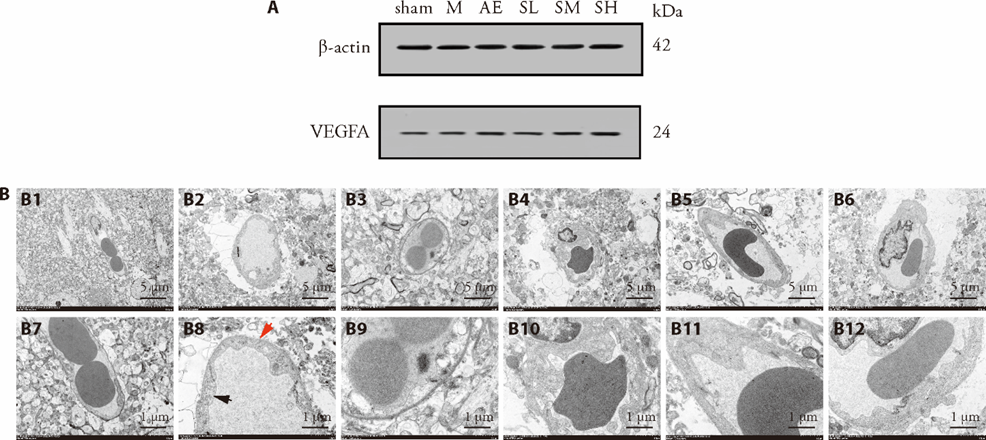
Figure 4 Effect of SHT on inflammatory damage of BBB A: comparison of the protein expression levels of VEGFA in rats. [Mean (SD), n = 4]. B: comparison of BBB ultrastructure under TEM in each group. Each group had two views, B1-6 at low power (× 3000) and B7-12 at high power (× 8000); B1, B7: the sham group; B2, B8: the M group; B3, B9: the AE group; B4, B10: the SL group; B5, B11: the SM group; B6, B12: the SH group. M: middle cerebral artery occlusion; AE: aloeemodin; SL: Sanhua Tang at low dosage; SM: medium dosage; SH: high dosage; SHT: Sanhua Tang; MCAO: middle cerebral artery occlusion; BBB: blood-brain barrier; TEM: transmission electron microscope. M: model group were orally administered with saline 1 mL/100 g per day for 5 d; SL: this group were orally administered Sanhua Tang 0.18 g/mL before stroke induction once daily for 4 d, and continued administration for one day after MCAO surgery. As the same goes SM 0.36 g/mL, SH group 0.72 g/mL, and AE 5 mg/mL.
| Inflammatory damage of BBB | ANOVA | Treatment (between columns) | Residual (within columns) | F (DFn, DFd) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levels of IL-6 | SS | 966.0 | 954.9 | F (5, 30) = 6.070 | 0.0005 |
| DF | 5 | 30 | |||
| MS | 193.2 | 31.83 | |||
| Levels of IL-10 | SS | 109.4 | 172.7 | F (5, 30) = 3.802 | 0.0087 |
| DF | 5 | 30 | |||
| MS | 21.89 | 5.757 | |||
| Levels of TNF-α | SS | 99.52 | 171.7 | F (5, 30) = 3.478 | 0.0135 |
| DF | 5 | 30 | |||
| MS | 19.90 | 5.723 | |||
| Levels of VEGFA | SS | 3.438 | 0.6922 | F (5, 18) = 17.88 | < 0.0001 |
| DF | 5 | 18 | |||
| MS | 0.6876 | 0.03846 |
Table 2 Statistical results of inflammatory factors and VEGFA protein expression levels between each group after ANOVA
| Inflammatory damage of BBB | ANOVA | Treatment (between columns) | Residual (within columns) | F (DFn, DFd) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levels of IL-6 | SS | 966.0 | 954.9 | F (5, 30) = 6.070 | 0.0005 |
| DF | 5 | 30 | |||
| MS | 193.2 | 31.83 | |||
| Levels of IL-10 | SS | 109.4 | 172.7 | F (5, 30) = 3.802 | 0.0087 |
| DF | 5 | 30 | |||
| MS | 21.89 | 5.757 | |||
| Levels of TNF-α | SS | 99.52 | 171.7 | F (5, 30) = 3.478 | 0.0135 |
| DF | 5 | 30 | |||
| MS | 19.90 | 5.723 | |||
| Levels of VEGFA | SS | 3.438 | 0.6922 | F (5, 18) = 17.88 | < 0.0001 |
| DF | 5 | 18 | |||
| MS | 0.6876 | 0.03846 |
| 1. |
Campbell B, De Silva D, Macleod M, et al. Ischaemic stroke. Nature reviews Disease primers 2019; 5: 70.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Boot E, Ekker MS. Ischaemic stroke in young adults: a global perspective. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2020; 91: 411-7.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Zhou M, Wang H, Zeng X, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019; 394: 1145-58.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Wang L, Zhang X, Xiong X, Zhu H. Nrf2 regulates oxidative stress and its role in cerebral ischemic stroke. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022; 11: 2377. |
| 5. | Kim SY, Buckwalter M, Soreq H, Vezzani A, Kaufer D. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction-induced inflammatory signaling in brain pathology and epileptogenesis. Epilepsia 2012 Suppl 6: 37-44. |
| 6. | Li S. Possible associations between TCM syndromes and molecular network regulatory mechanisms. In: Hangzhou Li S, editors. Zhong Guo Ke Xue Ji Shu Xie Hui Xue Hui Xue Shu Bu. Zhejiang 1999: the First Annual Conference of China Association for Science and Technology; 1999: 519. |
| 7. |
Hopkins AL. Network pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat Chem Biol 2008; 4: 682-90.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Dong R, Huang R, Shi X, Xu Z, Mang J. Exploration of the mechanism of luteolin against ischemic stroke based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental verification. Bioengineered 2021; 12: 12274-93.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Zhang W, Zhang L, Wang WJ, et al. Network pharmacology and in vitro experimental verification to explore the mechanism of Sanhua decoction in the treatment of ischaemic stroke. Pharm Biol 2022; 60: 119-30.
DOI PMID |
| 10. | Cai W, Wang L, Guo L, et al. Correlation analysis between post-stroke constipation and brain injury. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2013; 33: 117-20. |
| 11. | Lu L. Clinical observation of modified Sanhua decoction in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke (phlegm-heat and fu-organ excess syndrome). Changchun: Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, 2022: 1-54. |
| 12. |
Guo W, Huang J, Wang N, et al. Integrating network pharmacology and pharmacological evaluation for deciphering the action mechanism of herbal formula Zuojin pill in suppressing hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Pharmacol 2019; 10: 1185.
DOI PMID |
| 13. |
UniProt Consortium. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic acids research 2021; 49: D480-9.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Barshir R, Fishilevich S, Iny-Stein T, et al. GeneCaRNA: a comprehensive gene-centric database of human non-coding rnas in the genecards suite. J Mol Biol 2021; 433: 166913. |
| 15. |
Amberger JS, Bocchini CA, Scott AF, Hamosh A. OMIM.org: leveraging knowledge across phenotype-gene relationships. Nucleic acids research 2019; 47: D1038-43.
DOI |
| 16. | Guillen J. The use of performance standards by AAALAC International to evaluate ethical review in European institutions. Lab Anim (NY) 2010; 39: 49-53. |
| 17. | Tsan MF, Grabenbauer M, Nguyen Y. Lapse in institutional animal care and use committee continuing reviews. PLoS One 2016; 11: e0162141. |
| 18. |
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989; 20: 84-91.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | Socala K, Doboszewska U, Szopa A, et al. The role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders. Pharmacol Res 2021; 172: 105840. |
| 20. |
Bieber M, Gronewold J, Scharf AC, et al. Validity and reliability of neurological scores in mice exposed to middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 2019; 50: 2875-82.
DOI PMID |
| 21. | Luo S, Chen Y, Zhao R, et al. Application of omics technology to investigate the mechanism underlying the role of San Hua Tang in regulating microglia polarization and blood-brain barrier protection following ischemic stroke. J Ethnopharmacol 2023; 314: 116640. |
| 22. | Ding T, Tang L, Hu B, Yuan J, Li X, Wen J. Effects of arteriovenous thrombolysis combined with mechanical throm-bectomy on efficacy and neurological function of acute cerebral infarct patients. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int 2024; 2024: 987282. |
| 23. |
Xiao S, Lina W, Jianpeng HU, Limiao Z, Jin W. Effect of Naoluoxintong formula and its split prescriptions on cerebral vascular regeneration in rats with the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. J Tradit Chin Med 2023; 43: 1140-49.
DOI |
| 24. | Zhao XH, Li QJ. To explore the clinical efficacy of Tongfu Qutan decoction in the treatment of phlegm-heat syndrome in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Shi Jie Zui Xin Yi Xue Xin Xi Wen Zhai 2019; 19: 260-1. |
| 25. | Zhang HL. Efficacy of Huatan Tongfu decoction in the treatment of apoplexy and its effect on serum inflammatory factors and neurological function score. Zhong Guo Min Jian Liao Fa 2019; 27: 48-51. |
| 26. | Wang F, Liu JX, Wang MM, Qiao Y. Improvement and mechanism of Dahuang (rhubarb) extract on blood-brain barrier permeability in rats with cerebral infarction. Shandong Zhong Yi Yao 2021; 61: 48-51. |
| 27. | Zhao X, Ji MY, Dong Q. Effects of magnolol on neuroinflammation and HPA axis in mice with post-stroke depression. Shen Jing Sun Shang Yu Gong Neng Chong Jian 2020; 15: 645-7. |
| 28. | Qiu S. Effect of Fructus Aurantii Immaturus on the structure and function of interstitial cells of Cajal in rats with cerebral infarction. Jinan: Shangdong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2014: 1-60. |
| 29. |
Li S, Zhang ZQ, Wu LJ, Zhang XG, Li YD, Wang YY. Understanding ZHENG in Traditional Chinese Medicine in the context of neuro-endocrine-immune network. IET Syst Biol 2007; 1: 51-60.
DOI PMID |
| 30. | Li S, Zhang B. Traditional Chinese Medicine network pharmacology: theory, methodology and application. Chin J Nat Med 2013; 11: 110-20. |
| 31. | YingHuang, Gao SS, Gong ZH, Li WJ, Xiao j. Mechanism of sanhua decoction in the treatment of ischemic stroke based on network pharmacology methods and experimental verification. Biomed Res Int 2022; 2022: 7759402. |
| 32. |
Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M. The blood-brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis 2004; 16: 1-13.
DOI PMID |
| 33. |
Kim JS. tPA Helpers in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: are they ready for clinical use? J Stroke 2019; 21: 160-74.
DOI PMID |
| 34. |
Qiao H, Dong L, Zhang X, et al. Protective effect of luteolin in experimental ischemic stroke: upregulated SOD1, CAT, Bcl-2 and claudin-5, down-regulated MDA and Bax expression. Neurochem Res 2012; 37: 2014-24.
DOI PMID |
| 35. | Reza Nazifi SM, Asgharshamsi MH, Dehkordi MM, Zborowski KK. Antioxidant properties of aloe vera components: a dft theoretical evaluation. Free Radic Res 2019; 53: 922-31. |
| 36. | Wu J, Ke X, Wang W, et al. Aloe-emodin suppresses hypoxia-induced retinal angiogenesis via inhibition of HIF-1α/VEGF pathway. Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12: 1363-71. |
| 37. |
Hu B, Zhang H, Meng X, Wang F, Wang P. Aloe-emodin from rhubarb (Rheum rhabarbarum) inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol 2014; 153: 846-53.
DOI PMID |
| 38. | Cheng JZ, Cha J, Xiang H. Naringenin alleviated the SH-SY5Y cells death and insulin resistance by activating mTOR/p70S6K signalling pathway in oxidative stress induced by H2O2. Chongqing Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2019, 44: 424-9. |
| 39. |
Lambertsen KL, Finsen B, Clausen BH. Post-stroke inflammation-target or tool for therapy? Acta Neuropathol 2019; 137: 693-714.
DOI PMID |
| 40. | Chen B, Li X, Li J. Relationship between TIA and IL6, IL8 and IL10. Nao Yu Shen Jing Ji Bing Za Zhi 2013; 21: 247-50. |
| 41. | Liu T, Han S, Dai Q, et al. IL-17A-mediated excessive autophagy aggravated neuronal ischemic injuries via src-pp2b-mtor pathway. Front Immunol 2019; 10: 2952. |
| 42. | Sabat R, Grütz G, Warszawska K, et al. Biology of interleukin-10. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2010; 21: 331-44. |
| 43. |
Lucitti JL, Mackey JK, Morrison JC, Haigh JJ, Adams RH, Faber JE. Formation of the collateral circulation is regulated by vascular endothelial growth factor-A and a disintegrin and metalloprotease family members 10 and 17. Circ Res 2012; 111: 1539-50.
DOI PMID |
| 44. |
You T, Bi Y, Li J, et al. IL-17 induces reactive astrocytes and up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) through JAK/STAT signaling. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 41779.
DOI PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

