Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 1150-1159.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230904.002
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Dangua Fang (丹瓜方) regulating tricarboxylic acid cycle and respiratory chain and its mechanism in diabetic rats
HENG Xianpei1, WANG Zhita1, YANG Liuqing1, LI Liang1, HUANG Suping2( )
)
- 1 Department of Endocrinology, People's Hospital Affiliated to Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350004, China
2 Academy of Integrative Medicine Fujian, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, China
-
Received:2022-06-03Accepted:2022-09-21Online:2023-10-25Published:2023-09-04 -
Contact:Prof. HENG Xianpei, Department of Endocrinology, People's Hospital Affiliated to Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350004, China. hengxianpei@hotmail.com. Telephone: +86-13067366157 -
Supported by:Based on the "miR34a/Nampt-NAD+-TAC" Pathway to Study the Mechanism of Simultaneously Treating the Phlegm and Blood Stasis in the Regulation of Glycolipid(81873213);Study on the Mechanism of Simultaneously Treating the Phlegm and Blood Stasis on Glycolipid Metabolism Based on Intestinal Fat Absorption Regulated by miR-34a/Stat3-Nfil3 Pathway(82074308);Based on the tricarboxylic acid Cycle-Mediated Transformation of "α-KG→Glutamate"(8227150196);Preparation of Monomeric Traditional Chinese Medicine Complexes Based on Nampt's Activation of Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle and Respiratory Chain to Interfere with Glycolipid Metabolism(2022Y41010015)
Cite this article
HENG Xianpei, WANG Zhita, YANG Liuqing, LI Liang, HUANG Suping. Dangua Fang (丹瓜方) regulating tricarboxylic acid cycle and respiratory chain and its mechanism in diabetic rats[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1150-1159.
share this article
| Group | n | Base | Week 2 | Week 4 | Week 6 | Week 8 | Week10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7 | 487±30 | 554±39 | 572±36 | 579±35 | 591±34 | 585±33 |
| Model | 7 | 486±28 | 465±36a | 464±25a | 473±28a | 477±28a | 497±29a |
| Dangua | 7 | 489±23 | 447±27 | 472±25 | 491±27 | 483±22 | 509±24 |
| DanInhibit | 7 | 493±34 | 453±21 | 458±33 | 467±30 | 474±25 | 499±27 |
| Inhibitor | 7 | 492±34 | 498±38b | 499±35c | 506±23c | 514±34c | 525±34c |
Table 1 Tendency chart of weight change among groups ($\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | n | Base | Week 2 | Week 4 | Week 6 | Week 8 | Week10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7 | 487±30 | 554±39 | 572±36 | 579±35 | 591±34 | 585±33 |
| Model | 7 | 486±28 | 465±36a | 464±25a | 473±28a | 477±28a | 497±29a |
| Dangua | 7 | 489±23 | 447±27 | 472±25 | 491±27 | 483±22 | 509±24 |
| DanInhibit | 7 | 493±34 | 453±21 | 458±33 | 467±30 | 474±25 | 499±27 |
| Inhibitor | 7 | 492±34 | 498±38b | 499±35c | 506±23c | 514±34c | 525±34c |
| Group | n | Liver weight (g) | Liver index (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contol | 7 | 14.13±1.46 | 2.41±0.15 | |
| Model | 7 | 31.71±4.84a | 6.44±1.22a | |
| Dangua | 7 | 25.18±4.84b | 4.95±0.90b | |
| DanInhib | 7 | 33.48±4.97c | 6.88±1.69c | |
| Inhibitor | 7 | 34.86±6.92d | 6.64±1.26c |
Table 2 Liver weight and liver index among groups ($\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | n | Liver weight (g) | Liver index (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contol | 7 | 14.13±1.46 | 2.41±0.15 | |
| Model | 7 | 31.71±4.84a | 6.44±1.22a | |
| Dangua | 7 | 25.18±4.84b | 4.95±0.90b | |
| DanInhib | 7 | 33.48±4.97c | 6.88±1.69c | |
| Inhibitor | 7 | 34.86±6.92d | 6.64±1.26c |
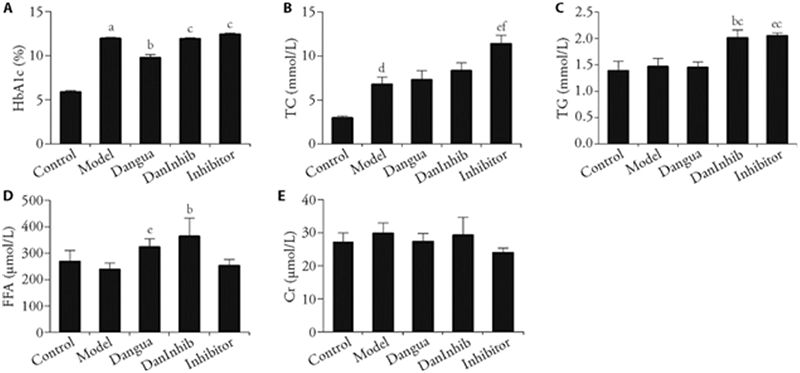
Figure 1 Comparison of HbA1c, TC, TG, FFA, and Cr A: percent of HbA1c; B: total cholesterol content; C: triglycerides content; D: free fatty acids content; E: serum creatinine content. Rats with normal blood glucose were fed with high-fat and high-sugar chow for 4 weeks, then injected with STZ 25 mg/kg for 2 consecutive days to selected the diabetic model. Control: fed a conventional diet without modelling; model: given sterile water by gastric perfusion once a day and injected aquae pro injection intraperitoneally every Monday at 3:00 pm; Dangua: Dangua liquor 20.5 g·kg-1·d-1 by perfusion and aquae pro injection intraperitoneally just like that in the model group; Inhibitor: sterile water by perfusion and GEN-617 intraperitoneally, 1.25 mg/kg; DanInhit: Dangua liquor and GEN-617 synchronously. STZ: streptozotocin; Cr: serum creatinine; TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglycerides; FFA: free fatty acids; HbA1c: glycosylated hemoglobin A1c. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 7). Compared with control group, aP < 0.01, dP < 0.01; compared with model group, bP < 0.01, eP < 0.05; compared with Dangua group, cP < 0.01, fP < 0.05.

Figure 2 HE staining, Masson staining, and Oil red O staining of hepatic tissue (×100) A, D, G, J, M: HE staining (×100); B, E, H, K, N: Masson staining (×100); C, F, T, L, O: Oil red O staining (×100). A-C: Control group; D-F: model group; G-I: Dangua group: J-L: DanInhibit group: M-O: inhibitor group. Rats with normal blood glucose were fed with high-fat and high-sugar chow for 4 weeks, then injected with STZ 25 mg/kg for 2 consecutive days to selected the diabetic model. Control: fed a conventional diet without modelling (n = 7); model: given sterile water by gastric perfusion once a day and injected aquae pro injection intraperitoneally every Monday at 3:00 pm (n = 7); Dangua: Dangua liquor 20.5 g·kg-1·d-1 by perfusion and aquae pro injection intraperitoneally just like that in the model group (n = 7); Inhibitor: sterile water by perfusion and GEN-617 intraperitoneally, 1.25 mg/kg (n = 7); DanInhit: Dangua liquor and GEN-617 synchronously. Morphological samples were taken from the distal end of the hepatic right lobe (n = 7). HE: hematoxylin-eosin; STZ: streptozotocin.
| Group | n | OAA (ng/μL) | ICA (ng/μL) | α-KG (ng/μL) | SDH (U/mg) | COX (ng/mL) | ATPs (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contol | 6 | 18.8±3.6 | 36.2±2.6 | 5.3±0.8 | 47.3±47.9 | 17.7±0.7 | 1406.9±108.6 |
| Model | 6 | 16.2±3.9 | 32.0±2.6a | 3.8±0.6a | 219.9±52.4d | 17.4±2.2 | 1563.6±126.4a |
| Dangua | 6 | 15.2±1.2 | 47.1±3.3b | 3.8±1.1 | 126.6±102.3e | 17.1±3.0 | 1506.3±125.7 |
| Daninhib | 6 | 17.3±3.2 | 32.3±3.9c | 4.4±1.6 | 116.2±94.8e | 18.1±2.3 | 1557.6±195.2 |
| Inhibitor | 6 | 15.8±3.6 | 30.4±4.2c | 4.1±1.7 | 54.4±46.7b | 18.3±1.5 | 1658.9±135.1f |
Table 3 Comparison of OAA, ICA, α-KG, SDH, COX, and ATPs ($\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | n | OAA (ng/μL) | ICA (ng/μL) | α-KG (ng/μL) | SDH (U/mg) | COX (ng/mL) | ATPs (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contol | 6 | 18.8±3.6 | 36.2±2.6 | 5.3±0.8 | 47.3±47.9 | 17.7±0.7 | 1406.9±108.6 |
| Model | 6 | 16.2±3.9 | 32.0±2.6a | 3.8±0.6a | 219.9±52.4d | 17.4±2.2 | 1563.6±126.4a |
| Dangua | 6 | 15.2±1.2 | 47.1±3.3b | 3.8±1.1 | 126.6±102.3e | 17.1±3.0 | 1506.3±125.7 |
| Daninhib | 6 | 17.3±3.2 | 32.3±3.9c | 4.4±1.6 | 116.2±94.8e | 18.1±2.3 | 1557.6±195.2 |
| Inhibitor | 6 | 15.8±3.6 | 30.4±4.2c | 4.1±1.7 | 54.4±46.7b | 18.3±1.5 | 1658.9±135.1f |
Figure 3 Melt curve plot and amplification plot of mt-ND1-mRNA and Nampt-mRNA A-C: amplification plot (n = 6). A: mt-ND1-mRNA; B: Nampt-mRNA; C: NADPH-mRNA. D-F: melt curve plot (n = 6). D: mt-ND1-mRNA; E: Nampt-mRNA; F: NADPH-mRNA. Rats with normal blood glucose were fed with high-fat and high-sugar chow for 4 weeks, then injected with STZ 25 mg/kg for 2 consecutive days to selected the diabetic model. Control: fed a conventional diet without modelling; model: given sterile water by gastric perfusion once a day and injected aquae pro injection intraperitoneally every Monday at 3:00 pm; Dangua: Dangua liquor 20.5 g·kg-1·d-1 by perfusion and aquae pro injection intraperitoneally just like that in the model group; Inhibitor: sterile water by perfusion and GEN-617 intraperitoneally,1.25 mg/kg; DanInhit: Dangua liquor and GEN-617 synchronously. NADPH as internal reference. It demonstrated that The Melt Curve Plot and Amplification Plot of mt-ND1-mRNA and Nampt-mRNA were comparable. mt-ND1: mitochondrial nadhdehydrogenase-1; Nampt: nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; NADH: reduced NAD+; NAD+: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; STZ: streptozotocin.
| Group | n | mt-ND1-mRNA | Nampt-mRNA | n | Nampt (ng/mL) | NAD+ (pg/mL) | NADH (pg/mL) | NAD/NADH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contol | 6 | 14.27±3.45 | 6.47±1.89 | 7 | 30.03±10.54 | 1158.26±239.45 | 395.72±53.84 | 2.93±0.49 |
| Model | 6 | 21.70±7.09 a | 4.56±1.71a | 7 | 58.13±10.93d | 1256.68±217.25 | 429.53±81.82 | 2.99±0.62 |
| Dangua | 6 | 21.10±6.07 | 6.86±1.26b | 7 | 76.69±9.87e | 1284.05±259.42 | 405.87±52.72 | 3.23±0.79 |
| DanInhib | 6 | 18.82±4.31 | 4.60±1.21c | 7 | 72.57±13.39b | 1341.55±258.08 | 442.88±86.21 | 3.08±0.55 |
| Inhibitor | 6 | 18.80±5.75 | 5.40±1.70 | 7 | 62.46±4.10c | 1273.06±261.77 | 421.98±110.10 | 3.12±0.70 |
Table 4 Comparison of mt-ND1-mRNA, Nampt-mRNA, Nampt, NAD+, NAD and NAD/NADH ($\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | n | mt-ND1-mRNA | Nampt-mRNA | n | Nampt (ng/mL) | NAD+ (pg/mL) | NADH (pg/mL) | NAD/NADH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contol | 6 | 14.27±3.45 | 6.47±1.89 | 7 | 30.03±10.54 | 1158.26±239.45 | 395.72±53.84 | 2.93±0.49 |
| Model | 6 | 21.70±7.09 a | 4.56±1.71a | 7 | 58.13±10.93d | 1256.68±217.25 | 429.53±81.82 | 2.99±0.62 |
| Dangua | 6 | 21.10±6.07 | 6.86±1.26b | 7 | 76.69±9.87e | 1284.05±259.42 | 405.87±52.72 | 3.23±0.79 |
| DanInhib | 6 | 18.82±4.31 | 4.60±1.21c | 7 | 72.57±13.39b | 1341.55±258.08 | 442.88±86.21 | 3.08±0.55 |
| Inhibitor | 6 | 18.80±5.75 | 5.40±1.70 | 7 | 62.46±4.10c | 1273.06±261.77 | 421.98±110.10 | 3.12±0.70 |
| 1. | Heng XP. Problems and challenges in drug treatment of glycolipid metabolism disorders. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2021; 41: 9-12. |
| 2. |
Heng XP, Li XJ, Li L, Yang LQ, Wang ZT, Huang SP. Therapy to obese type 2 diabetes mellitus: how har will we go down the wrong road? Chin J Integr Med 2020; 26: 62-71.
DOI |
| 3. | Yang LQ, Li L, Heng XP, Huang SP, Pan XD. Effects of Dangua recipe on inflammatory markers and endothelial cell function in diabetic rats with arteriosclerosis. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2017; 37: 692-8. |
| 4. | Xu RX, Wang ZT, Cheng YC, et al. Effects of Dangua recipe on myocardial ATP, PPARα, GLUT-4, and morphology in diabetic rats. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2018; 38: 1363-8. |
| 5. | Chen YC, Li L, Heng XP, et al. Effects of Dangua recipe on expression levels of caspase-3 protein, Bcl-2 and Bax mRNA in brain tissue of Apo E-/- diabetes model mice. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2017; 37: 1476-81. |
| 6. | Heng XP, Yang LQ, Huang SP, et al. A clinical study of Danggua Humai oral liquid on cardiovascular risk factors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2019; 39: 275-81. |
| 7. |
Lan YL, Huang XP, Heng XP, et al. Dangua fang improves glycolipid metabolic disorders by promoting hepatic adenosine 5’-monophosphate activated protein kinase expression in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Chin J Integr Med 2015; 21: 188-95.
DOI URL |
| 8. |
Heng XP, Wang ZT, Li L, Yang LQ, Huang SP. Mechanisms of Dangua Fang in improving glycolipid metabolic disorders based on transcriptomics. Chin J Integr Med 2022; 28: 130-7.
DOI |
| 9. |
Grolla AA, Miggiano R, Marino DD, et al. A nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase-GAPDH interaction sustains the stress-induced NMN/NAD+ salvage pathway in the nucleus. J Biol Chem 2020; 295: 3635-51.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Lundt S, Zhang N, Wang X, Polo-Parada L, Ding S. The effect of NAMPT deletion in projection neurons on the function and structure of neuromuscular junction (NMJ) in mice. Sci Rep 2020; 10: 99.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Yoshida M, Satoh A, Lin JB, et al. Extracellular vesicle-contained eNAMPT delays aging and extends lifespan in mice. Cell Metab 2019; 30: 329-42.e5.
DOI PMID |
| 12. |
Vorobieva VV, Shabanov PD. Tissue-specific peculiarities of vibration-induced hypoxia in rabbit liver and kidney. Bull Exp Biol Med 2019; 167: 621-3.
DOI |
| 13. |
Zhang J, Wang YT, Miller JH, Day MM, Munger JC, Brookes PS. Accumulation of succinate in cardiac ischemia primarily occurs via canonical krebs cycle activity. Cell Rep 2018; 23: 2617-28.
DOI URL |
| 14. |
Alshahrani A, AlDubayee M, Zahra M, et al. Differential expression of human N-alpha-acetyltransferase 40 (hNAA40), nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) and sirtuin-1 (SIRT-1) pathway in obesity and T2DM: modulation by metformin and macronutrient intake. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2019; 12: 2765-74.
DOI URL |
| 15. | Heng XP, Li L, Wang ZT, et al. Research the genes nature about Gan disease transferring to Pi in metabolic diseases. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2021; 41: 56-64. |
| 16. |
Heng XP, Li L, Yang LQ, Wang ZT. Efficacy of Dangua Fang on endothelial cells damaged by oxidative stress. J Tradit Chin Med 2022; 42: 900-7.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | JIN Shenyi, LIU Yahua, HAN Xu, CAI Mengjie, XU Jiatuo, LU Hao, CHEN Qingguang. Dark red tongue color formation caused by hyperglycemia is attributed to decreased blood flow of tongue tissue partially due to nuclear factor-kappa B pathway activation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1118-1125. |
| [2] | QIN Xihui, PANG Jianli, XIONG Guan, FENG Jie. Bo′s abdominal acupuncture improves disordered metabolism in obese type 2 diabetic rats through regulating fibroblast growth factor 21 and its related adipokines [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1200-1208. |
| [3] | JIANG Li, FU Qiang, WANG Shidong, ZHAO Jinxi, CHEN Yu, LI Jiayue, XIAO Yonghua, HUANG Weijun, SUN Ruixi, XIAO Yao, SHEN Aijia, WANG Junheng, LIU Jiangteng, FU Xiaozhe, LI Yuanyuan, ZHAO Yu, XUE Taiqi. Effects of Shenlian formula (参连方) on microbiota and inflammatory cytokines in adults with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomized clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 760-769. |
| [4] | QU Yilun, CHENG Haimei, WANG Qian, LI Shuang, DUAN Shuwei, FENG Zhe, LI Weizhen, JIANG Shuangshuang, YANG Hongtao, MAO Yonghui, GENG Yanqiu, LI Jijun, LIU Yuning, TIAN Jinzhou, LIU Hongfang, DONG Zheyi, CHEN Xiangmei. Noninvasive identificational diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy and non-diabetic renal disease based on clinical characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine symptom pattern and conventional medicine [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 588-593. |
| [5] | HENG Xianpei, LI Liang, YANG Liuqin, WANG Zhita. Efficacy of Dangua Fang (丹瓜方) on endothelial cells damaged by oxidative stress [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 900-907. |
| [6] | You WU, Yuli HU, Wei LIU, Boju SUN, Chengfei ZHANG, Lili WU, Tonghua LIU. Flavonoids from traditional Chinese herbs for diabetes in rats: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 1-8. |
| [7] | XIA Xichao, LI Bin, QIU Ju, TIAN Gang, CHEN Changdong, LA Ming, ZHANG Ke, QI Jinxu, LI Yanyan, GAO Huashan, SHAO Xiangyang, SU Congying, WANG Mengqi, OUYANG Jingfeng. Antioxidative and immunological effects of Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharides on the spleen injury of diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 739-746. |
| [8] | YIN Yundong, FANG Zhaohui, WU Yuanyuan, YOU Liangzhen. Effect of Shenzhu Tiaopi granule(参术调脾颗粒) on hepatic insulin resistance in diabetic Goto-Kakizakirats via liver kinase B1/adenosine 5'-monophosphate/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(1): 107-116. |
| [9] | Cui Xiaobing, Huang Zhiyong, Lou Linjie, Cheng Saibo, Zhang Yu, Zhang Yaxin, Jia Yuhua, Zhou Fenghua. Dingxin recipe alleviates atherosclerosis injury in Apo E-knockout mice via downregulation of visfatin expression and inhibition of the visfatin-induced inflammatory response [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(6): 938-946. |
| [10] | Wang Jianxing, Yu Xiaohan, Jiang Yan, Wang Yan, Li Ying, Han Shuying. Effects of a fermented buckwheat flower and leaf extract on the blood glucose and lipid profile of type 2 diabetic db/db mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(2): 197-203. |
| [11] | Rangachari Balamurugan, Jeong Hwa Kim, Mi-na Jo, Chenglian Xue, Jin kyu Park, Jae Kwon Lee. Bee wax coated water-soluble fraction of bee venom improved altered glucose homeostasis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(06): 842-852. |
| [12] | Zhang Zexi, Zhang Lei, Xu Hansong. Effect of Astragalus polysaccharide in treatment of diabetes mellitus: a narrative review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(01): 133-138. |
| [13] | Zhang Yi, Mo Fangfang, Zhang Dongwei, Gao Sihua, Zhao Dandan, Yu Na, Mu Qianqian, Zuo Jiacheng, Ma Yue. Jiangtang Xiaoke granule attenuates glucose metabolism disorder via regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress in the liver of type 2 diabetes mellitus mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(04): 570-578. |
| [14] | Dai Guohua, Gao Wulin, Bi Dongxue, Liu Chunhua, Liu Yuhan, Wang Ning, Zhao Chen. Efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine in patients with acute myocardial infarction suffering from diabetes mellitus [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(03): 412-418. |
| [15] | Yang Hongchang, Wu Xueping, Wang Min. Effect of conventional medical treatment plus Qigong exercise on type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese patients:A Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(02): 167-174. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

