Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1238-1253.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20250929.002
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Four-dimensional data independent acquisition proteomics and metabolomics reveal mechanisms of hydrogen-rich water at Zusanli (ST36) point against triple-negative breast cancer in mice
LIU Jingxuan1, MO Qian1, LEI Guowu1, JIA Yejuan1, LI Aiying2, JIA Chunsheng1( ), PAN Lijia1(
), PAN Lijia1( )
)
- 1 College of Acupuncture and moxibustion and Massage, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China
2 College of Basic Medicine, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China
-
Received:2025-06-03Accepted:2025-09-09Online:2025-12-15Published:2025-09-29 -
Contact:Prof. PAN Lijia, College of Acupuncture and moxibustion and Massage, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China. panlijia369@126.com, Telephone: +86-13373013018; +86-18032003570;
Prof. JIA Chunsheng, College of Acupuncture and moxibustion and Massage, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China. jia7158@163.com -
Supported by:Exploring the Advantages of Micro-needle System Therapy for Specific Diseases and the Patterns of Acupoint Selection through Data Mining Techniques(81473773);Exploring the Molecular Mechanism behind How Hydrogen Mitigates the Aging of Vascular Endothelial Cells Induced by Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia, Utilizing the Keap1-Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 Signaling Pathway(ZD2020142);Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Hydrogen-rich Water Acupoint Injection on Tumors in Mice with Triple-negative Breast Cancer(CXZZBS2024154)
Cite this article
LIU Jingxuan, MO Qian, LEI Guowu, JIA Yejuan, LI Aiying, JIA Chunsheng, PAN Lijia. Four-dimensional data independent acquisition proteomics and metabolomics reveal mechanisms of hydrogen-rich water at Zusanli (ST36) point against triple-negative breast cancer in mice[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1238-1253.
share this article

Figure 1 Impact of injecting hydrogen-rich water into the Zusanli (ST36) acupoint on the growth of triple-negative breast cancer in mice A: variations in body mass, n = 8; B: tumor volumes of mice on day 1 of intervention, n = 8; C: tumor volume of mice on day 21 of intervention, n = 8. D: tumor weights of mice on day 21 of intervention, n = 8. E: tumor HE staining: Black stars, necrotic areas; black arrows, inflammatory cells; red arrows, mitotic figures; E1: Model group; E2: H2ST36 group; E3: AcST36 group; E4: NaST36 group; 200 ×; n = 3; F: statistical graph of TUNEL (TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling) fluorescence intensity, n = 3; G: TUNEL fluorescence intensity (scale bar =75 μm; 200 ×); G1: Model group-DAPI; G2: Model group-TUNEL; G3:Model group-Merge; G4: H2ST36 group-DAPI; G5: H2ST36 group-TUNEL; G6: H2ST36 group-Merge; G7: AcST36 group-DAPI; G8: AcST36 group-TUNEL; G9: AcST36 group-Merge; G10: NaST36 group-DAPI; G11: NaST36 group-TUNEL; G12: NaST36 group-Merge. Control and Model groups: no treatment + 21 d; H2ST36 group: hydrogen-rich water + 0.05 mL into each acupoint every other day + 21 d; AcST36 group: acupuncture + 15 min every other day + 21 d; NaST36 group: saline solution + 0.05 mL into each acupoint every other day + 21 d. HE: hematoxylin and eosin; H2ST36: hydrogen-rich water injection into the Zusanli (ST36) acupoint; AcST36: acupuncture; NaST36: sodium chloride injection Zusanli (ST36); TUNEL: TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling; DAPI: ?4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. One-way analysis of variance was used to compare more than two groups, followed by the least significant difference test to detect differences between groups. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. Comparison with the Model group, aP < 0.05; comparison with the H2ST36 group, bP < 0.05; comparison with the AcST36 group; cP < 0.05, comparison with the NaST36 group; dP < 0.05, comparison with the Control group, eP < 0.05.
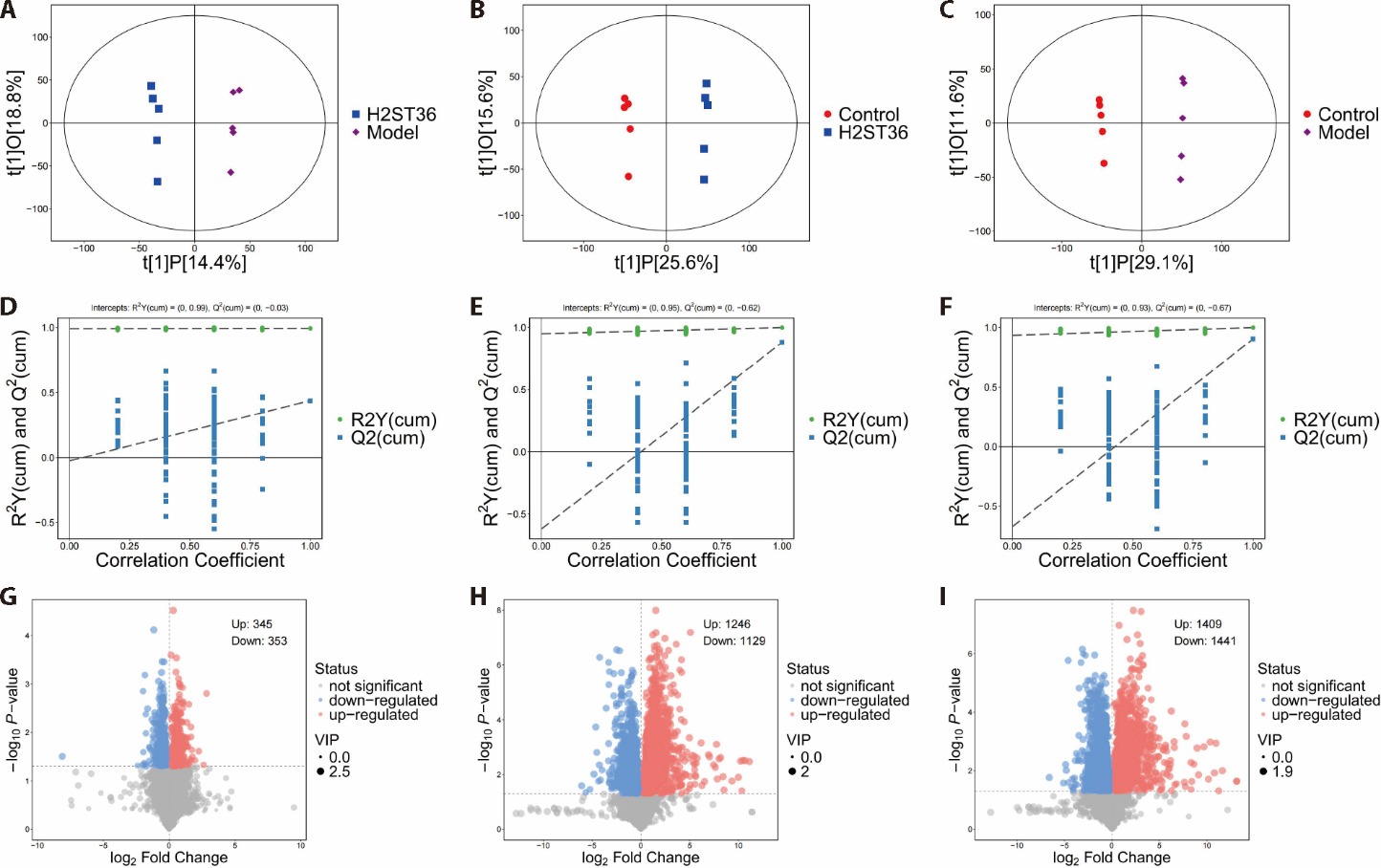
Figure 2 OPLS-DA models and volcano plots of differential metabolites for different comparison groups (n = 5) A: OPLS-DA score plot of Model group vs H2ST36 group; B: OPLS-DA score plot of Control group vs H2ST36 group; C: OPLS-DA score plot of Control group vs Model group; D: OPLS-DA permutation plot of Model group vs H2ST36 group; E: OPLS-DA permutation plot of Control group vs H2ST36 group; F: OPLS-DA permutation plot of Control group vs Model group; G: volcano plot of Model group vs H2ST36 group; H: volcano plot of Control group vs H2ST36 group; I: volcano plot of Control group vs Model group. Control group: no treatment was administered to the mice following the sham surgery procedure; Model group: the mice received no post-modeling treatment, 21 d; H2ST36 group: inject hydrogen-rich water into the Zusanli (ST36) acupoint, inject 0.05 mL into each acupoint every other day, for a total of 21 d. H2ST36: hydrogen-rich water injection into the Zusanli (ST36) acupoint; VIP: variable importance in projection; OPLS-DA: Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis.
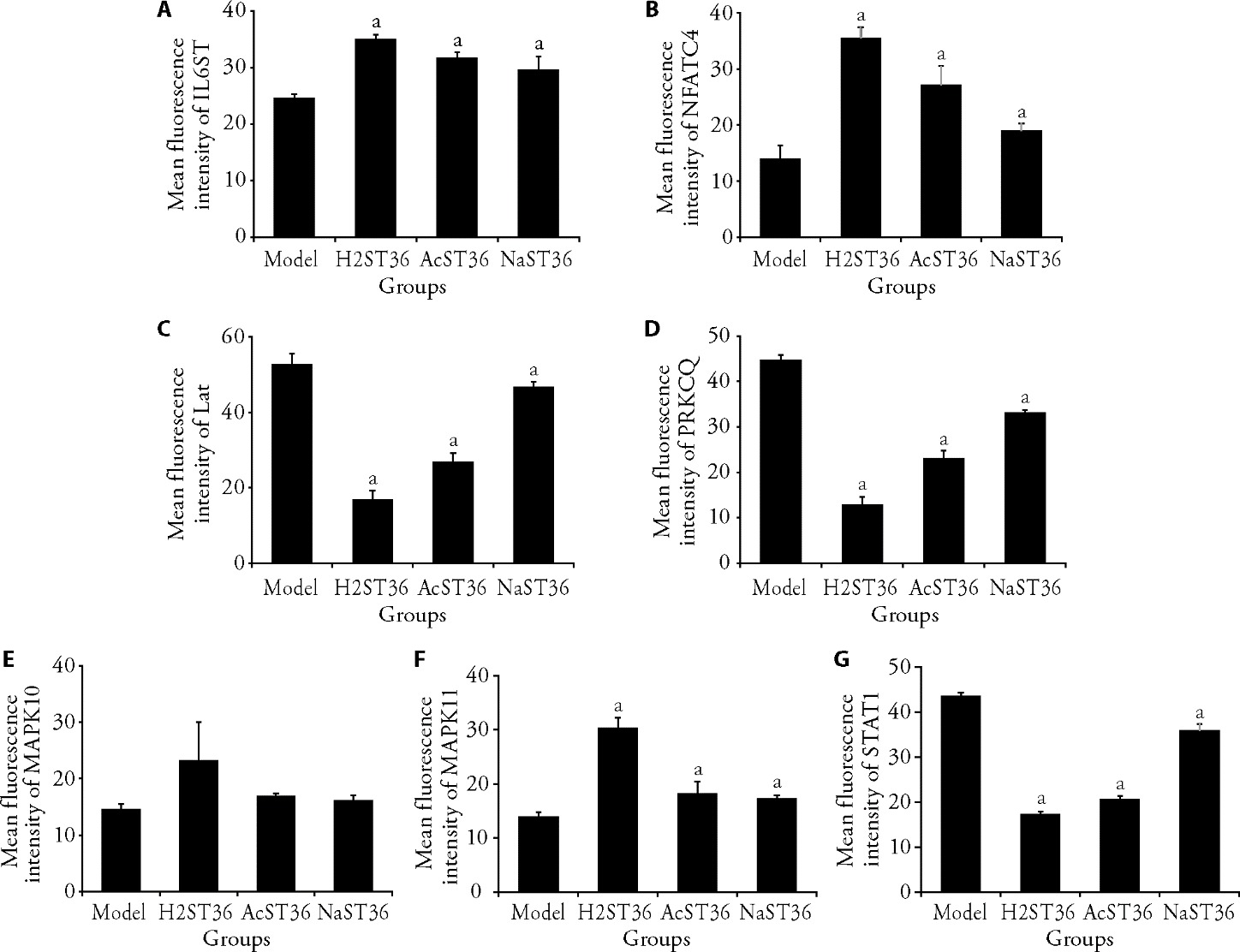
Figure 3 Immunofluorescence assay for differentially expressed proteins A: analysis results of differential immunofluorescence staining for IL6ST; B: analysis results of differential immunofluorescence staining for NFATC4; C: analysis results of differential immunofluorescence staining for Lat; D: analysis results of differential immunofluorescence staining for STAT1; E: analysis results of differential immunofluorescence staining for MAPK10; F: analysis results of differential immunofluorescence staining for MAPK11; G: analysis results of differential immunofluorescence staining for PRKCQ. Model group: no post-modeling treatment + 21 d; H2ST36 group: inject hydrogen-rich water + 0.05 mL into each acupoint every other day + 21 d; AcST36 group: acupuncture stimulation + 15 min every other day + 21 d; NaST36 group: saline solution injection + 0.05 mL into each acupoint every other day + 21 d. H2ST36: hydrogen-rich water injection into the Zusanli (ST36) acupoint; AcST36: acupuncture; NaST36: sodium chloride injection Zusanli (ST36); IL6ST: interleukin 6 signal transducer; NFATC4: nuclear factor of activated T cells 4; Lat: linker for activation of T cells; PRKCQ: protein kinase C, theta; MAPK10: recombinant mitogen activated protein kinase 10; MAPK11: recombinant mitogen activated protein kinase 11; STAT1: signal transducer and activator of transcription 1. One-way analysis of variance was used to compare more than two groups, followed by the least significant difference test to detect differences between groups. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Comparison with the Model group, aP < 0.05.
| Protein | Model (n = 6) | H2ST36 (n = 6) | AcST36 (n = 6) | NaST36 (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL6ST | 1.00±0.16 | 2.67±0.25a | 1.99±0.10a | 1.45±0.18b |
| Lat | 1.00±0.15 | 0.34±0.04a | 0.62±0.10a | 0.83±0.10c |
| MAPK10 | 1.00±0.29 | 2.98±0.46a | 2.38±0.47a | 1.64±0.35d |
| STAT1 | 1.01±0.06 | 0.29±0.11a | 0.49±0.13a | 0.79±0.07b |
| MAPK11 | 0.99±0.16 | 2.93±0.38a | 2.26±0.30a | 1.66±0.22b |
| NFATC4 | 1.01±0.36 | 2.79±0.29a | 2.15±0.27a | 1.74±0.36b |
| PRKCQ | 1.00±0.08 | 0.36±0.14a | 0.54±0.11a | 0.78±0.06b |
Table 1 Western blotting analysis results ( $\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Protein | Model (n = 6) | H2ST36 (n = 6) | AcST36 (n = 6) | NaST36 (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL6ST | 1.00±0.16 | 2.67±0.25a | 1.99±0.10a | 1.45±0.18b |
| Lat | 1.00±0.15 | 0.34±0.04a | 0.62±0.10a | 0.83±0.10c |
| MAPK10 | 1.00±0.29 | 2.98±0.46a | 2.38±0.47a | 1.64±0.35d |
| STAT1 | 1.01±0.06 | 0.29±0.11a | 0.49±0.13a | 0.79±0.07b |
| MAPK11 | 0.99±0.16 | 2.93±0.38a | 2.26±0.30a | 1.66±0.22b |
| NFATC4 | 1.01±0.36 | 2.79±0.29a | 2.15±0.27a | 1.74±0.36b |
| PRKCQ | 1.00±0.08 | 0.36±0.14a | 0.54±0.11a | 0.78±0.06b |
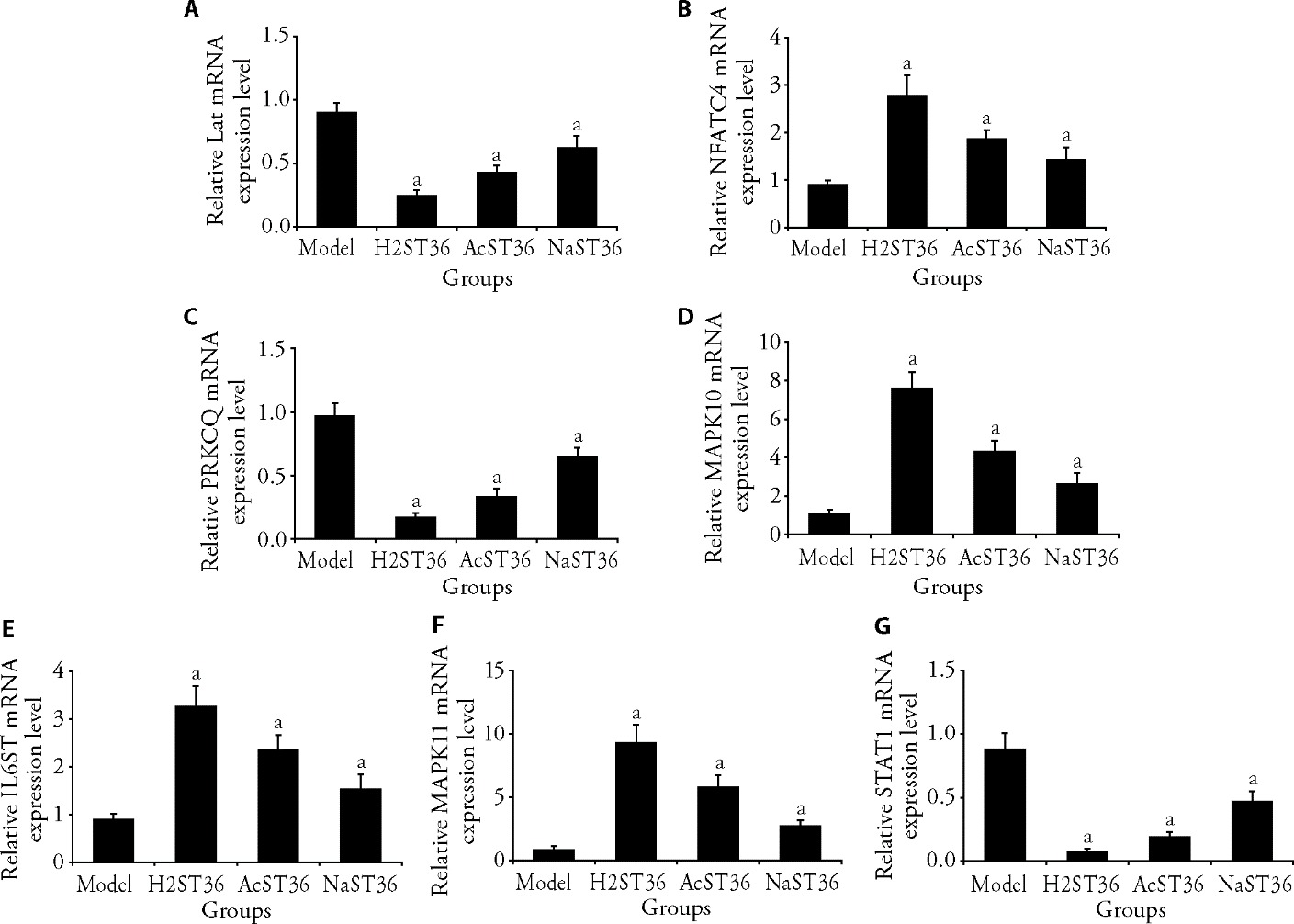
Figure 4 qRT-PCR results A: relative Lat mRNA expression level; B: relative NFATC4 mRNA expression level; C: relative PRKCQ mRNA expression level; D: relative MAPK10 mRNA expression level; E: relative IL6ST mRNA expression level; F: relative MAPK11 mRNA expression level; G: relative STAT1 mRNA expression level. Model group: no post-modeling treatment + 21 d; H2ST36 group: inject hydrogen-rich water + 0.05 mL into each acupoint every other day + 21 d; AcST36 group: acupuncture stimulation + 15 min every other day + 21 d; NaST36 group: saline solution injection + 0.05 mL into each acupoint every other day + 21 d. qRT-PCR: quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; H2ST36: hydrogen-rich water injection into the Zusanli (ST36) acupoint; AcST36: acupuncture; NaST36: sodium chloride injection Zusanli (ST36); IL6ST: interleukin 6 signal transducer; NFATC4: nuclear factor of activated T cells 4; Lat: Linker for activation of T cells; PRKCQ: protein kinase C, theta; MAPK10: recombinant mitogen activated protein kinase 10; MAPK11: recombinant mitogen activated protein kinase 11; STAT1: signal transducer and activator of transcription 1. One-way analysis of variance was used to compare more than two groups, followed by the least significant difference test to detect differences between groups. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). Comparison with the Model group, aP < 0.05.
| 1. | Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA 2024; 74: 229-63. |
| 2. |
Katsika L, Boureka E, Kalogiannidis I, et al. Screening for breast cancer: a comparative review of guidelines. Life 2024; 14: 777.
DOI URL |
| 3. | Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Sun KX, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2016. Zhong Hua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2023; 45: 212-20. |
| 4. | Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA 2023; 73: 17-48. |
| 5. | Park JH, Ahn JH, Kim SB. How shall we treat early triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC): from the current standard to upcoming immuno-molecular strategies. Esmo open 2018; 3: e000357. |
| 6. |
Stevens KN, Vachon CM, Couch FJ. Genetic susceptibility to triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 2025-30.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Xie S, Sun Y, Zhao X, et al. An update of the molecular mechanisms underlying anthracycline induced cardiotoxicity. Front Pharmacol 2024; 15: 1406247. |
| 8. |
Aghili M, Taherioun M, Jafari F, et al. Duloxetine to prevent neuropathy in breast cancer patients under paclitaxel chemotherapy (a double-blind randomized trial). Support Care Cancer 2024; 32: 493.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Ma W, Wang X, Zhang D, Mu X. Research progress of disulfide bond based tumor microenvironment targeted drug delivery system. Int J Nanomed 2024; 19: 7547-66. |
| 10. |
Zhao D, Li Z, Ji DK, Xia Q. Recent progress of multifunctional molecular probes for triple-negative breast cancer theranostics. Pharmaceutics 2024; 16: 803.
DOI URL |
| 11. | Greenlee H, DuPont-Reyes MJ, Balneaves LG, et al. Clinical practice guidelines on the evidence-based use of integrative therapies during and after breast cancer treatment. CA Cancer J Clin 2017; 67: 194-232. |
| 12. |
Zhang J, Qin Z, So TH, et al. Acupuncture for chemotherapy-associated insomnia in breast cancer patients: an assessor-participant blinded, randomized, sham-controlled trial. Breast Cancer Res 2023; 25: 49.
DOI PMID |
| 13. | Xu Y, Yu J, Shen R, Shan X, Zhou W, Wang J. Comparison efficacy and safety of acupuncture and moxibustion therapies in breast cancer-related lymphedema: a systematic review and network Meta-analysis. PLoS One 2024; 19: e0303513. |
| 14. | Hershman DL, Unger JM, Greenlee H, et al. Comparison of acupuncture vs sham acupuncture or waiting list control in the treatment of aromatase inhibitor-related joint pain: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open 2022; 5: e2241720. |
| 15. |
Gosain R, Gage-Bouchard E, Ambrosone C, Repasky E, Gandhi S. Stress reduction strategies in breast cancer: review of pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic based strategies. Semin Immunopathol 2020; 42: 719-34.
DOI |
| 16. | Tran S, Hickey M, Saunders C, Ramage L, Cohen PA. Nonpharmacological therapies for the management of menopausal vasomotor symptoms in breast cancer survivors. Support Care Cancer 2021; 29: 1183-93. |
| 17. |
Zhang ZJ, Man SC, Yam LL, et al. Electroacupuncture trigeminal nerve stimulation plus body acupuncture for chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment in breast cancer patients: an assessor-participant blinded, randomized controlled trial. Brain Behav Immun 2020; 88: 88-96.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Höxtermann MD, Haller H, Aboudamaah S, et al. Safety of acupuncture in oncology: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cancer 2022; 128: 2159-73.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | Epstein AS, Liou KT, Romero SAD, et al. Acupuncture vs massage for pain in patients living with advanced cancer: the IMPACT randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open 2023; 6: e2342482. |
| 20. | Li A, Cao T, Feng L, Hu Y, Zhou Y, Yang P. Recent advances in metal-hydride-based disease treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2024; 16: 5355-67. |
| 21. |
Hirano SI, Ichikawa Y, Sato B, Yamamoto H, Takefuji Y, Satoh F. Molecular hydrogen as a potential clinically applicable radioprotective agent. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 4566.
DOI URL |
| 22. |
Li Y, Li G, Suo L, Zhang J. Recent advances in studies of molecular hydrogen in the treatment of pancreatitis. Life Sci 2021; 264: 118641.
DOI URL |
| 23. |
Qiu P, Liu Y, Zhang J. Recent advances in studies of molecular hydrogen against sepsis. Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15: 1261-75.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Ji P, Yang K, Xu Q, et al. Mechanisms and application of gas-based anticancer therapies. Pharmaceuticals 2023; 16: 1394.
DOI URL |
| 25. |
Zhou W, Zhang J, Chen W, Miao C. Prospects of molecular hydrogen in cancer prevention and treatment. J Cancer Res Clin 2024; 150: 170.
DOI |
| 26. |
Hirano SI, Yamamoto H, Ichikawa Y, Sato B, Takefuji Y, Satoh F. Molecular hydrogen as a novel antitumor agent: possible mechanisms underlying gene expression. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 8724.
DOI URL |
| 27. |
Chen JB, Kong XF, Qian W, et al. Two weeks of hydrogen inhalation can significantly reverse adaptive and innate immune system senescence patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a self-controlled study. Med Gas Res 2020; 10: 149-54.
DOI URL |
| 28. |
Li S, Liao R, Sheng X, et al. Hydrogen gas in cancer treatment. Front Oncol 2019; 9: 696.
DOI PMID |
| 29. |
Shih YW, Yang SF, Chien MH, Chang CW, Chang VHS, Tsai HT. Significant effect of acupressure in elevating blood stem cell factor during chemotherapy in patients with gynecologic cancer. J Nurs Res 2018; 26: 411-19.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Zhang B, Xu F, Hu P, et al. Needleless transcutaneous electrical acustimulation: a pilot study evaluating improvement in post-operative recovery. Am J Gastroenterol 2018; 113: 1026-35.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Mao H, Mao JJ, Guo M, et al. Effects of infrared laser moxibustion on cancer-related fatigue: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Cancer 2016; 122: 3667-72.
DOI PMID |
| 32. |
Hsiung WT, Chang YC, Yeh ML, Chang YH. Acupressure improves the postoperative comfort of gastric cancer patients: a randomised controlled trial. Complement Ther Med 2015; 23: 339-46.
DOI URL |
| 33. | Zhang FC, Gao TY, Zhang CX, et al. Effect of moxibustion combined with chemotherapy on immune checkpoints in tumor tissue of breast cancer-bearing mice. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2025; 50: 319-26. |
| 34. |
Liu S, Wang Z, Su Y, et al. A neuroanatomical basis for electroacupuncture to drive the vagal-adrenal axis. Nature 2021; 598: 641-45.
DOI |
| 35. |
Liu F, Wang Y, Lyu K, et al. Acupuncture and its ability to restore and maintain immune homeostasis. QJM 2024; 117: 167-76.
DOI URL |
| 36. |
Wang N, Zhao L, Zhang D, Kong F. Research progress on the immunomodulatory mechanism of acupuncture in tumor immune microenvironment. Front Immunol 2023; 14: 1092402.
DOI URL |
| 37. |
Gao S, Hsu TW, Li MO. Immunity beyond cancer cells: perspective from tumor tissue. Trends cancer 2021; 7: 1010-19.
DOI PMID |
| 38. | Basu A, Ramamoorthi G, Albert G, et al. Differentiation and regulation of TH Cells: a balancing act for cancer immunotherapy. Front immunol 2021; 12: 669474. |
| 39. |
Martínez-Pérez C, Leung J, Kay C, et al. The signal transducer IL6ST (gp130) as a predictive and prognostic biomarker in breast cancer. J Pers medicine 2021; 11: 618.
DOI URL |
| 40. |
Martínez-Pérez C, Kay C, Meehan J, Gray M, Dixon JM, Turnbull AK. The IL6-like cytokine family: role and biomarker potential in breast cancer. J Pers Med 2021; 11: 1073.
DOI URL |
| 41. |
Mathe A, Wong-Brown M, Morten B, et al. Novel genes associated with lymph node metastasis in triple negative breast cancer. Sci Rep 2015; 5: 15832.
DOI PMID |
| 42. |
Zhong QH, Zha SW, Lau ATY, Xu YM. Recent knowledge of NFATc4 in oncogenesis and cancer prognosis. Cancer Cell Int 2022; 22: 212.
DOI |
| 43. |
Fougère M, Gaudineau B, Barbier J, et al. NFAT 3 transcription factor inhibits breast cancer cell motility by targeting the lipocalin 2 gene. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2292-301.
DOI PMID |
| 44. |
Guaddachi F, Bergerat D, et al. Extracellular vesicles produced by NFAT3-expressing cells hinder tumor growth and metastatic dissemination. Sci Rep 2020; 10: 8964.
DOI PMID |
| 45. | Barollo S, Bertazza L, Watutantrige-Fernando S, et al. Overexpression of L-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1) and 2 (LAT2): novel markers of neuroendocrine tumors. PLoS One 2016; 11: e0156044. |
| 46. |
Furuya M, Horiguchi J, Nakajima H, Kanai Y, Oyama T. Correlation of L-type amino acid transporter 1 and CD98 expression with triple negative breast cancer prognosis. Cancer Sci 2012; 103: 382-9.
DOI URL |
| 47. |
Du D, Liu C, Qin M, et al. Metabolic dysregulation and emerging therapeutical targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Pharm Sin B 2022; 12: 558-80.
DOI PMID |
| 48. |
Zhang C, Xu J, Xue S, Ye J. Prognostic value of L-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1) in various cancers: a Meta-analysis. Mol Diagn Ther 2020; 24: 523-36.
DOI PMID |
| 49. |
Häfliger P, Charles RP. The L-Type Amino Acid Transporter LAT1-an emerging target in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 2428.
DOI URL |
| 50. |
Cormerais Y, Giuliano S, LeFloch R, et al. Genetic disruption of the multifunctional CD98/LAT1 complex demonstrates the key role of essential amino acid transport in the control of mTORC1 and tumor growth. Cancer Res 2016; 76: 4481-92.
DOI PMID |
| 51. |
Kurozumi S, Kaira K, Matsumoto H, et al. Association of L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) with the immune system and prognosis in invasive breast cancer. Sci Rep 2022; 12: 2742.
DOI PMID |
| 52. |
Li YJ, Zhang C, Martincuks A, Herrmann A, Yu H. STAT proteins in cancer: orchestration of metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 2023; 23: 115-34.
DOI |
| 53. |
Erdogan F, Radu TB, Orlova A, et al. JAK-STAT core cancer pathway: an integrative cancer interactome analysis. J Cell Mol Med 2022; 26: 2049-62.
DOI PMID |
| 54. |
Wong GL, Manore SG, Doheny DL, Lo HW. STAT family of transcription factors in breast cancer: pathogenesis and therapeutic opportunities and challenges. Semin Cancer Biol 2022; 86: 84-106.
DOI PMID |
| 55. |
Banik S, Rakshit S, Sarkar K. The role of STAT1 in T Helper Cell Differentiation during breast cancer progression. J Breast Cancer 2021; 24: 253-65.
DOI PMID |
| 56. | Serrano López J, Jiménez-Jiménez C, Chutipongtanate S, et al. High-throughput RNA sequencing transcriptome analysis of ABC-DLBCL reveals several tumor evasion strategies. Leukemia Lymphoma 2022; 63: 1861-70. |
| 57. |
Li H, Li Y, Zhang Y, et al. MAPK 10 expression as a prognostic marker of the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol 2021; 11: 687371.
DOI URL |
| 58. |
Atyah M, Zhou C, Zhou Q, et al. The age-specific features and clinical significance of NRF2 and MAPK10 expression in HCC patients. Int J Gen Med 2022; 15: 737-48.
DOI PMID |
| 59. |
Sun R, Xiang T, Tang J, et al. 19q13 KRAB zinc-finger protein ZNF471 activates MAPK10/JNK3 signaling but is frequently silenced by promoter CpG methylation in esophageal cancer. Theranostics 2020; 10: 2243-59.
DOI PMID |
| 60. |
Tsai YC, Huang CY, Hsueh YM, et al. Genetic variants in MAPK 10 modify renal cell carcinoma susceptibility and clinical outcomes. Life Sci 2021; 275: 119396.
DOI URL |
| 61. |
Rachwał K, Niedźwiedź I, Waśko A, et al. Red Kale (Brassica oleracea L. ssp. acephala L. var. sabellica) induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells in vitro. Molecules 2023; 28: 6938.
DOI URL |
| 62. |
Wang Z, Liu W, Chen C, Yang X, Luo Y, Zhang B. Low mutation and neoantigen burden and fewer effector tumor infiltrating lymphocytes correlate with breast cancer metastasization to lymph nodes. Sci Rep 2019; 9: 253.
DOI PMID |
| 63. |
Roche O, Fernández-Aroca DM, Arconada-Luque E, et al. p38β and cancer: the beginning of the road. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 7524.
DOI URL |
| 64. |
Katopodis P, Kerslake R, Zikopoulos A, Beri N, Anikin V. p38β-MAPK11 and its role in female cancers. J Ovarian Res 2021; 14: 84.
DOI PMID |
| 65. | Gao Y, Hu S, Li R, et al. Hyperprogression of cutaneous T cell lymphoma after anti-PD-1 treatment. JCI Insight insight 2023; 8: e164793. |
| 66. | Belguise K, Sonenshein GE. PKCtheta promotes c-Rel-driven mammary tumorigenesis in mice and humans by repressing estrogen receptor alpha synthesis. JCI Insight 2007; 117: 4009-21. |
| 67. |
Byerly JH, Port ER, Irie HY. PRKCQ inhibition enhances chemosensitivity of triple-negative breast cancer by regulating Bim. Breast Cancer Res 2020; 22: 72.
DOI PMID |
| 68. |
Byerly J, Halstead-Nussloch G, Ito K, Katsyv I, Irie HY. PRKCQ promotes oncogenic growth and anoikis resistance of a subset of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 2016; 18: 95.
DOI PMID |
| 69. |
Nicolle A, Zhang Y, Belguise K. The emerging function of PKCtheta in cancer. Biomolecules 2021; 11: 221.
DOI URL |
| 70. |
Zhu J, Thompson CB. Metabolic regulation of cell growth and proliferation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2019; 20: 436.
DOI |
| 71. | Xu J, Zhao Y, Tyler Mertens R, Ding Y, Xiao P. Sweet regulation-the emerging immunoregulatory roles of hexoses. J Adv Res 2025; 69: 361-79. |
| 72. |
Dougan J, Hawsawi O, Burton LJ, et al. Proteomics-metabolomics combined approach identifies peroxidasin as a protector against metabolic and oxidative stress in prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 3046.
DOI URL |
| 73. |
Alwehaibi MA, Al-Ansari MM, Alfadda AA, et al. Proteomics investigation of the impact of the enterococcus faecalis secretome on MCF-7 tumor cells. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24: 14937.
DOI URL |
| 74. |
Majtan T, Olsen T, Sokolova J, et al. Deciphering pathophysiological mechanisms underlying cystathionine beta-synthase-deficient homocystinuria using targeted metabolomics, liver proteomics, sphingolipidomics and analysis of mitochondrial function. Redox Biol 2024; 73: 103222.
DOI URL |
| 75. |
Lu L, Kotowska AM, Kern S, et al. Metabolomic and proteomic analysis of ApoE4-carrying H4 neuroglioma cells in Alzheimer's disease using OrbiSIMS and LC-MS/MS. Anal Chem 2024; 96: 11760-70.
DOI PMID |
| 76. |
Wettersten HI, Hakimi AA, Morin D, et al. Grade-dependent metabolic reprogramming in kidney cancer revealed by combined proteomics and metabolomics analysis. Cancer Res 2015; 75: 2541-52.
DOI PMID |
| 77. |
Bai T, Wan Q, Yue C, et al. Combined spatial metabolomics and 4D-DIA quantitative proteomics approaches to explore the relationship between lung cancer and the heart. Sci Rep 2025; 15: 14878.
DOI |
| [1] | WANG Ci, CAO Yawen, WANG Jiaying, CHEN Jixin, MA Xue, WANG Xianliang, MAO Jingyuan. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture for arrythmias: an overview of systematic reviews and Meta-analyses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1178-1190. |
| [2] | SHOU Yin, JIANG Juntao, HU Jianlin, JI Wei, CHEN Chunyan, HU Li, MA Yuhang, ZHANG Bimeng. Electroacupuncture alleviates type 2 diabetes mellitus by promoting plasma-derived exosomal circular RNA of enhancer of zeste homolog 1 expression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1228-1237. |
| [3] | LYU Hequn, ZENG Chunli, ZHANG Hanrui, YANG Chen, SHEN Yan, PENG Yongjun. Effect of Xuanfei Tongqiao acupuncture on nasal inflammation in rats with allergic rhinitis: modulation of long non-coding RNA growth arrest-specific transcript 5 methylation modification [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1263-1272. |
| [4] | ZHANG Qiongshuai, LI Yi, CAO Fang, ZHI Mujun, WANG Le, LIU Ruyao, FENG Juanjuan. Effect of acupuncture on brain microenvironment in rats with post-stroke limb spasticity based on single-cell transcriptome sequencing technology [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1273-1282. |
| [5] | ZHANG Yuan, CHENG Shizan, HUA Yue, SHI Ji, SU Guoming, ZHANG Chao, LIAN Jing, LIU Pengpeng, JIA Tianzhu. Mechanisms of Suanzaoren (Ziziphi Spinosae Semen) and its processed products in treating insomnia: an integrated study based on network pharmacology and metabolomics [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [6] | CHENG Ziqi, DONG Xin, Temuribagen , XU Caimeng, HU Shaonan, CHEN Qianwen, WANG Yuewu, WANG Haibo, HE Xiaoyu, XUE Dan, XUE Peifeng. Exploration of the mechanism of the Mongolian medicine Tonglaga-5 (通拉嘎-5) for the treatment of n-methyl-n′-nitro-n-nitrosoguanidine-induced chronic atrophic gastritis based on network pharmacology and metabolomics [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1366-1375. |
| [7] | XU Yuqin, YUAN Jinjun, ZHU Yanxian, CHEN Chen, MA Xiaoming, JIANG Jiaona, HUANG Xingxian, LUO Wenshu, LIU Fan, YANG Zhuoxin, ZHOU Yumei. Observation of the efficacy and safety of acupuncture for postpartum depression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1405-1413. |
| [8] | PAN Tingyu, YAO Jing, GE Yue, YANG Shuang, SUN Zikai, WEI Yu, WU Jieyu, XU Yong, ZHOU Xianmei, HE Hailang. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolomics study of the protective mechanism of Shenji Guben decoction (参吉固本方) on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1009-1018. |
| [9] | WANG Yue, LIU Xingxing, GUO Yi, GUO Yongming, YUAN Gongming, ZHANG Yu, ZHENG Zhiyu, XU Yuan, LI Yuan. Characterization of acupuncture on central amino acid metabolism based on targeted neurotransmitter analysis in mice with inflammatory pain [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1019-1027. |
| [10] | GUO Jixing, JI Changchun, XIE Chaoju, RAO Xiang, SUN Zhangyin, XING Yu, ZHANG Rongni, QU Qiangqiang, DONG Youpeng, YANG Jinsheng. Various acupuncture therapies for managing nonspecific low back pain: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 954-962. |
| [11] | WANG Raoqiong, HAO Linyao, LU Ye, WANG Lingxue, LI Jianrong, PENG Yan, TANG Hongmei, LI Shuangyang, BAI Xue. Mechanism analysis of Tongqiao Yizhi decoction (通窍益智颗粒) in treating vascular dementia rats by brain tissue untargeted metabonomics and fecal 16S rRNA gene sequencing [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 759-769. |
| [12] | ZHAO Ping, HE Xingbo, HAN Xudong, CHEN Xinyue, LI Zhanglong, SONG Jike, XING Wenjia, WU Jiangfeng, GUO Bin, BI Hongsheng. Mechanism of electroacupuncture involve in lens-induced myopia guinea pigs by inhibiting wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 796-805. |
| [13] | ZHENG Ruwen, DONG Xu, WANG Tianyi, FENG Liyuan, ZHANG Hongyan, HUO Hong, ZHANG Ying, ZHANG Qianshi, ZHU Xingyan, WANG Dongyan. Electroacupuncture versus conventional acupuncture of scalp motor area for post-stroke wrist dyskinesia and its effect on muscle function: a randomized, controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 852-859. |
| [14] | SONG Jianfei, QIN Zhengyuan, GU Xinlu, ZHANG Yan, LI Xingrui. Efficacy of acupuncture combined with upper limb rehabilitation robot-assisted training for neuroplasticity and functional recovery of patients with stroke: a prospective cohort study based on functional near-infrared spectroscopy technology [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 860-866. |
| [15] | Kanae Umemoto, SHAN Xiyao, Takuro Ishikawa, Tadashi Watsuji, Yasuharu Watanabe, Munekazu Naito. Novel insight into the site-specificity of Hegu (LI4): morphological, biomechanical, and histological analyses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 867-872. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

