Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1135-1143.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20241231.001
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical observation of white eye distribution in patients with hyperlipidemia: an artificial intelligence digital visual examination technique
SONG Tianli1, LI Haixia1( ), LIU Li'an2(
), LIU Li'an2( )
)
- 1 Department of Cardiology, the Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing100053, China
2 National College, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2024-07-12Accepted:2024-12-11Online:2025-10-15Published:2024-12-31 -
Contact:Prof. LI Haixia, Department of Cardiology, the Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing100053, China. 2272236055@qq.com;
Assoc. Prof. LIU Li'an, National College, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China. lianlau@126.com, Telephone: +86-15234839197 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China:Study on the Mechanism of Improving Cardiac Remodelling in Post-infarction Ischaemic Cardiomyopathy through lncRNA-Maternally Expressed Gene3/miR-223/ Stromal Interaction Molecule 1 Calcium Signalling Axis by Activate Blood and Reassure Formula(81973682);National Social Science Fund: Study on the Verification and Construction of the Theory System of Sanjiao Phase Fire and Yang Support Under the View of Civilisation Traceability(21VJXG037);First Published: a Randomised Controlled Study of Fuyang Qiangxin Tang in the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Heart Failure(2024-1-4151);Project for Enhancing Clinical Research and Achievement Transformation Capabilities of High-Level Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospitals: Evaluation of the Efficacy and Preclinical Study of Fuyang Qiangxin Granules, a Traditional Chinese Medicine for Heart Failure(HLCMHPP2023045)
Cite this article
SONG Tianli, LI Haixia, LIU Li'an. Clinical observation of white eye distribution in patients with hyperlipidemia: an artificial intelligence digital visual examination technique[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1135-1143.
share this article
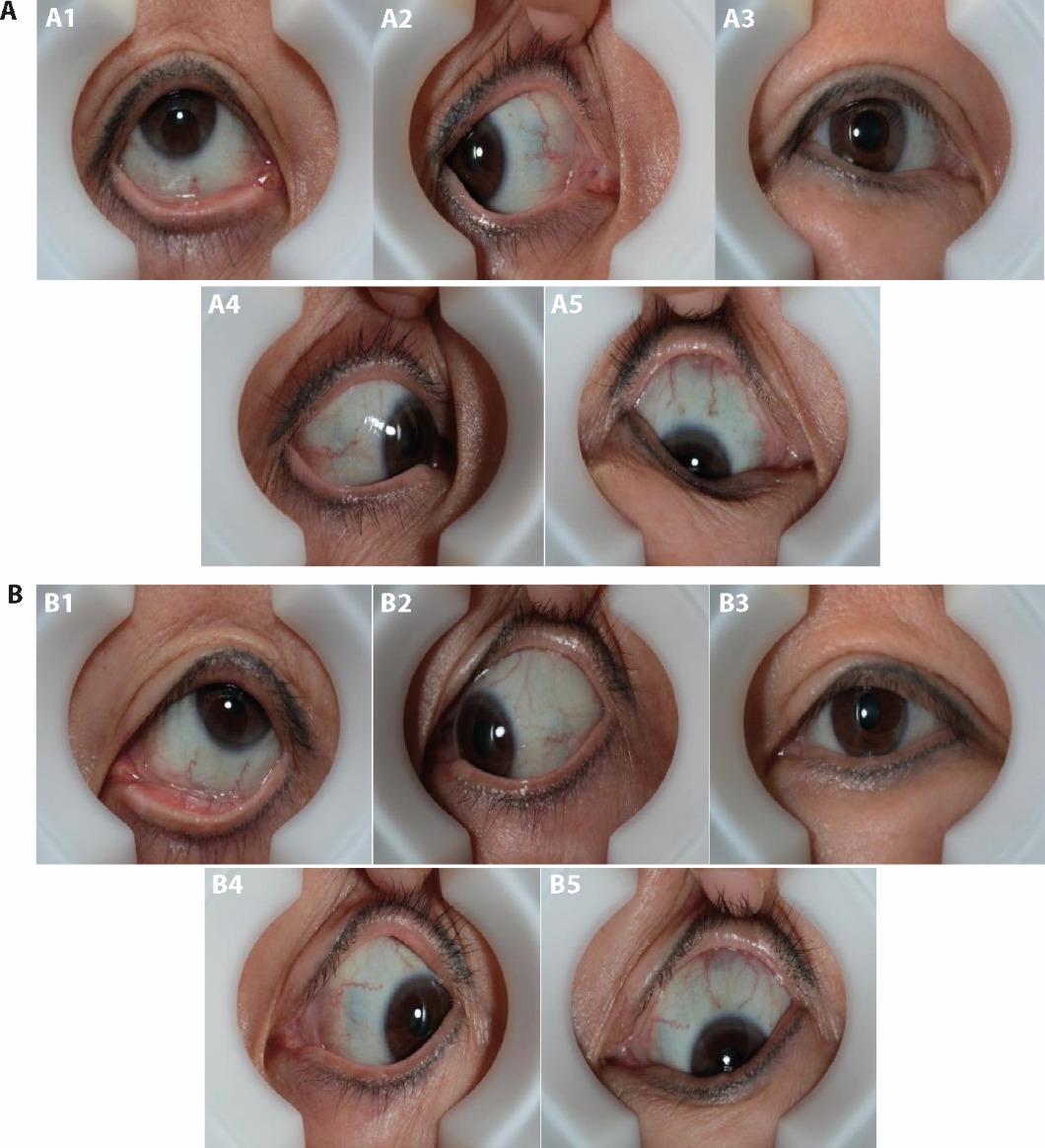
Figure 1 White Eye Elephant Real Picture Collection A: left eye. A1: left eye up vision; A2: left eye right vision; A3: left eye front view; A4: left eye left vision; A5: left eye down vision; B: right eye. B1: right eye up vision; B2: right eye right vision ; B3: right eye front view; B4: right eye left vision; B5: right eye down vision.
| Group | Population | Phlegm turbid internal obstruction | Phlegm and blood stasis intermingled | Spleen deficiency and excessive dampness | Qi deficiency and blood stasis | Qi stagnation and blood stasis | Deficiency of liver and kidney Yin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLP | 80 | 32 (40)a | 19 (23.75) | 11 (13.75) | 9 (11.25) | 6 (7.5) | 3 (3.75) |
| NC | 70 | 13 (18.57) | 6 (8.57) | 10 (14.29) | 8 (11.43) | 18 (28.71) | 15 (21.43) |
| P value | 0.026 | 0.277 | 0.923 | 0.958 | 0.312 | 0.305 |
Table 1 Group comparison of the frequency of Chinese medicine evidence in hyperlipidemia patients [n (%)]
| Group | Population | Phlegm turbid internal obstruction | Phlegm and blood stasis intermingled | Spleen deficiency and excessive dampness | Qi deficiency and blood stasis | Qi stagnation and blood stasis | Deficiency of liver and kidney Yin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLP | 80 | 32 (40)a | 19 (23.75) | 11 (13.75) | 9 (11.25) | 6 (7.5) | 3 (3.75) |
| NC | 70 | 13 (18.57) | 6 (8.57) | 10 (14.29) | 8 (11.43) | 18 (28.71) | 15 (21.43) |
| P value | 0.026 | 0.277 | 0.923 | 0.958 | 0.312 | 0.305 |
| Morphological characteristics of choroid veins | HLP group (n = 80) | NC group (n = 70) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spot | 11.1±3.2 | 7.5±4.1 | 0.0071a |
| Point | 5.7±2.5 | 6.8±3.3 | 0.870 |
| Blood vein | 17.2±1.3 | 15.7±3.8 | 0.536 |
| Mound | 6.3±4.4 | 4.9±3.2 | 0.619 |
| Foggy | 8.4±2.2 | 5.7±1.2 | 0.032b |
| Lunar halo | 5.0±1.7 | 4.2±2.1 | 0.718 |
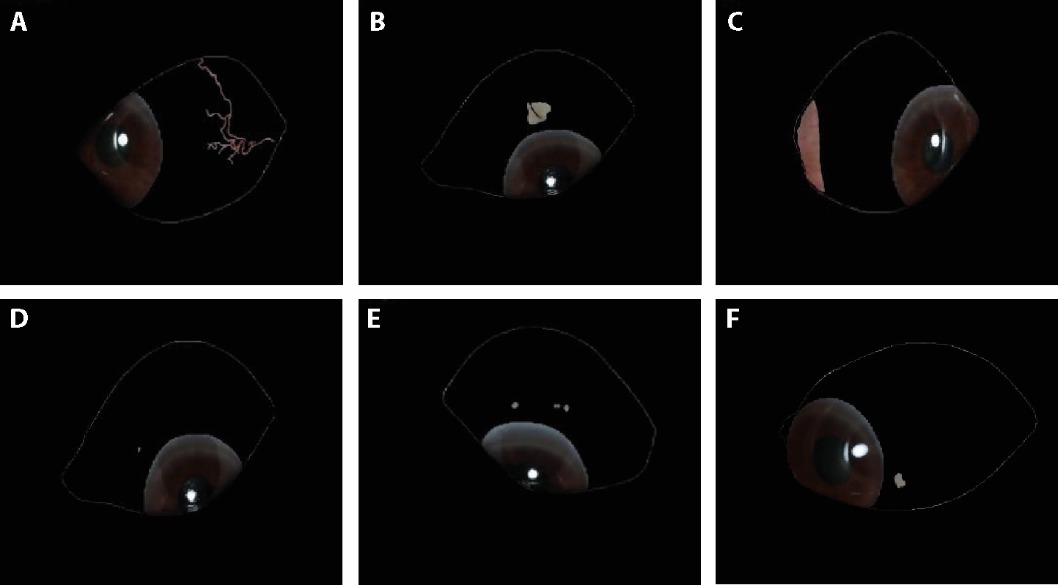
Table 2 Group comparison of the scores of the morphological characteristics of the white eye chakra ( x - ± s)
| Morphological characteristics of choroid veins | HLP group (n = 80) | NC group (n = 70) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spot | 11.1±3.2 | 7.5±4.1 | 0.0071a |
| Point | 5.7±2.5 | 6.8±3.3 | 0.870 |
| Blood vein | 17.2±1.3 | 15.7±3.8 | 0.536 |
| Mound | 6.3±4.4 | 4.9±3.2 | 0.619 |
| Foggy | 8.4±2.2 | 5.7±1.2 | 0.032b |
| Lunar halo | 5.0±1.7 | 4.2±2.1 | 0.718 |
| Subzone | HLP group (n = 80) | NC group (n = 70) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 17.72±1.66 | 6.57±1.41 | 0.003a |
| B | 12.32±3.71 | 3.78±4.74 | 0.005 a |
| C | 9.25±1.03 | 8.72±1.75 | 0.58 |
| D | 4.55±2.76 | 3.26±1.82 | 0.503 |
| E | 11.27±3.14 | 9.65±4.21 | 0.472 |
| F | 7.53±1.82 | 6.25±1.29 | 0.49 |
| G | 1.77±3.62 | 2.87±3.50 | 0.51 |
| H | 9.65±1.47 | 5.22±4.31 | 0.09 |
| I | 6.42±2.72 | 6.01±1.76 | 0.92 |
| J | 5.88±0.26 | 7.93±1.15 | 0.67 |
| K | 7.21±1.23 | 6.72±2.27 | 0.593 |
| L | 1.66±2.31 | 2.96±3.07 | 0.66 |
| M | 8.79±1.25 | 5.03±1.26 | 0.03b |
| N | 6.72±3.56 | 3.06±2.99 | 0.08 |
| O | 11.05±3.51 | 2.73±4.77 | 0.005a |
Table 3 Group comparison of the scores of the zonal characteristics of the white eye chakra ( x - ± s)
| Subzone | HLP group (n = 80) | NC group (n = 70) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 17.72±1.66 | 6.57±1.41 | 0.003a |
| B | 12.32±3.71 | 3.78±4.74 | 0.005 a |
| C | 9.25±1.03 | 8.72±1.75 | 0.58 |
| D | 4.55±2.76 | 3.26±1.82 | 0.503 |
| E | 11.27±3.14 | 9.65±4.21 | 0.472 |
| F | 7.53±1.82 | 6.25±1.29 | 0.49 |
| G | 1.77±3.62 | 2.87±3.50 | 0.51 |
| H | 9.65±1.47 | 5.22±4.31 | 0.09 |
| I | 6.42±2.72 | 6.01±1.76 | 0.92 |
| J | 5.88±0.26 | 7.93±1.15 | 0.67 |
| K | 7.21±1.23 | 6.72±2.27 | 0.593 |
| L | 1.66±2.31 | 2.96±3.07 | 0.66 |
| M | 8.79±1.25 | 5.03±1.26 | 0.03b |
| N | 6.72±3.56 | 3.06±2.99 | 0.08 |
| O | 11.05±3.51 | 2.73±4.77 | 0.005a |
| Morphological characteristics of choroid veins | HLP group (n = 80) | NC group (n = 70) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red | 9.5±0.7 | 7.3±2.1 | 0.529 |
| Pink | 7.7±1.7 | 6.2±1.6 | 0.63 |
| Dark red | 12.2±5.3 | 5.1±4.3 | 0.007a |
| Dull colour | 10.7±3.2 | 8.9±2.5 | 0.406 |
| Dull pink | 9.0±0.3 | 8.3±1.9 | 0.891 |
| Yellow | 10.8±1.4 | 4.0±1.3 | 0.003 a |
| Dark yellow | 6.6±3.3 | 4.4±2.1 | 0.472 |
| Pale yellow | 5.8±2.1 | 4.1±2.6 | 0.864 |
| Cyan and purple | 7.4±1.8 | 6.0±2.8 | 0.512 |
| Brown | 5.2±3.2 | 5.3±1.1 | 0.91 |
Table 4 Group comparison of color characteristic scores of white eye chakra ( x - ± s)
| Morphological characteristics of choroid veins | HLP group (n = 80) | NC group (n = 70) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red | 9.5±0.7 | 7.3±2.1 | 0.529 |
| Pink | 7.7±1.7 | 6.2±1.6 | 0.63 |
| Dark red | 12.2±5.3 | 5.1±4.3 | 0.007a |
| Dull colour | 10.7±3.2 | 8.9±2.5 | 0.406 |
| Dull pink | 9.0±0.3 | 8.3±1.9 | 0.891 |
| Yellow | 10.8±1.4 | 4.0±1.3 | 0.003 a |
| Dark yellow | 6.6±3.3 | 4.4±2.1 | 0.472 |
| Pale yellow | 5.8±2.1 | 4.1±2.6 | 0.864 |
| Cyan and purple | 7.4±1.8 | 6.0±2.8 | 0.512 |
| Brown | 5.2±3.2 | 5.3±1.1 | 0.91 |
| 1. |
Karr S. Epidemiology and management of hyperlipidemia. Am J Manag Care 2017; 23: S139-48.
PMID |
| 2. | Xu CX, Pan RL, Dong MC, et al. Based on intestinal flora, to investigate the mechanism of lipid-lowering effect of total glucosides of robust ligustrum on golden hamsters with hyperlipidemia. Chin Pharmacol Bull 2024; 40: 476-83. |
| 3. |
Lee S, Kim H, Kim C, et al. Effect of methanol extract of Schisandrae Fructus on high fat diet induced hyperlipidemic mice. J Tradit Chin Med 2019; 39: 818-25.
DOI |
| 4. |
Yao YS, Li TD, Zeng ZH. Mechanisms underlying direct actions of hyperlipidemia on myocardium: an updated review. Lipids Health Dis 2020; 19: 23.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Tummala R, Gupta M, Devanabanda RA, et al. Bempedoic acid and its role in contemporary management of hyperlipidemia in atherosclerosis. Ann Med 2022; 54: 1287-96. |
| 6. | Zhang NQ, Feng YM. Huang Di Nei Jing. Wuhan: Hubei Science and Technology Press, 2022: 89-90. |
| 7. | Xing RW. Huang Di Nei Jing Lingshu. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 2017: 52-5. |
| 8. | Wei GN, Zhang K. Tu Jie Huang Di Nei Jing Lingshu. Beijing: Ancient Books of Traditional Chinese Medicine Publishing House, 2018: 33-6. |
| 9. | Yang SY. Ren Zhai Zhi Zhi. Beijing: Ancient Books of Traditional Chinese Medicine Publishing House, 2016: 77-8. |
| 10. | Wang ZW, Liu J, Li JJ, et al. Guidelines for lipid management in China (2023). Zhong Guo Xun Huan Za Zhi 2023; 38: 237-71. |
| 11. | National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Dietary guidelines for adults with hyperlipidemia (2023 Edition). Quan Ke Yi Xue Lin Chuang Yu Jiao Yu 2023; 21: 581-3. |
| 12. | Liang Y. Diagnostic value of intelligent analysis system of White Eye imaging for diabetic microvascular disease. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023: 65-8. |
| 13. | Wei XQ. A study on the distribution of TCM syndromes of diabetic retinopathy based on "eye Diagnostic Instrument" and analysis of related factors. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023: 26-7. |
| 14. | Liu X, Zhang QY, Quan HH, et al. Analyzed the visual features of hypertension and its correlation with the syndrome elements based on digital visual diagnosis technology. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2024; 30: 413-7. |
| 15. | Song TL, Ma J, Li HX, Sun YZ. A correlation study on the characteristics and pathogenesis of the ocular network in hypertensive patients based on the theory of eye diagnosis in Traditional Chinese Medicine and the analysis of white eye imaging AI and optical technology. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2024; 42: 15-9+285-7. |
| 16. | National Health Commission Disease Control and Prevention Bureau. Report on nutrition and chronic diseases in China 2020. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2021: 21-5. |
| 17. | Yang SY. Ren Zhai Zhi Zhi Fang ed. Shanghai: Ancient Books of Traditional Chinese Medicine Publishing House, 1991: 52-3. |
| 18. | Gong Z. Literature study of the Huang Di Nei Jing Su Wen Jie Zhu. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2009: 52. |
| 19. | Asiedu K, Krishnan AV, Kwai N, Poynten A, Markoulli M. Conjunctival microcirculation in ocular and systemic microvascular disease. Clin Exp Optom 2023; 106: 694-702. |
| 20. |
Baykal C, Polat AE, Yazganoglu KD, Buyukbabani N. The clinical spectrum of xanthomatous lesions of the eyelids. Int J Dermatol 2017; 56: 981-92.
DOI PMID |
| 21. | Fliesler SJ. Introduction to the thematic review series: seeing 2020: lipids and lipid-soluble molecules in the eye. J Lipid Res 2010; 51: 13. |
| 22. |
El-Sayyad HI, Elmansi AA, Bakr EH. Hypercholesterolemia-induced ocular disorder: ameliorating role of phytotherapy. Nutrition 2015; 31: 1307-16.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
Frank RN. Diabetic retinopathy and systemic factors. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol 2015; 22: 151-6.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Chou YY, Ma J, Su X, Zhong Y. Emerging insights into the relationship between hyperlipidemia and the risk of diabetic retinopathy. Lipids Health Dis 2020; 19: 241.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Huo J, Duan JG, Liu LS, et al. Evaluation of individualized treatment of nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: a multicenter, randomized, parallel-controlled study. J Tradit Chin Med 2022; 42: 90-5.
DOI |
| 26. | Zhang MZ, Hao XH, Tanh YT, et al. Efficacy and safety of Buyang Huanwu decoction for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2023; 43: 841-50. |
| 27. | Heng XP, Wang ZT, Yang LQ, et al. Dangua Fang regulating tricarboxylic acid cycle and respiratory chain and its mechanism in diabetic rats. J Tradit Chin Med 2023; 43: 1150-9. |
| 28. | Zhang JM, Liang SL, Nie P, et al. Efficacy of Kushen decoction on high-fat-diet-induced hyperlipidemia in rats. J Tradit Chin Med 2022; 42: 364-71. |
| 29. | Chen BJ, Huang XD, Peng HT, et al. Effectiveness and safety of red yeast rice predominated by monacolin K β-hydroxy acid form for hyperlipidemia treatment and management. J Tradit Chin Med 2022; 42: 264-71. |
| [1] | FAN Mengyue, YAO Lin, ZHANG Guoqing, WANG Ruixue, CHEN Kexin, FAN Yujing, WANG Ziming, FU Jia, CHEN Yongjun, WANG Taiyi. Study on subtyping and Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment of depression based on machine learning and text mining [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1152-1163. |
| [2] | ZHANG Jiri Mutu, LIANG Shilong, NIE Peng, LIAO Yong’an, AI Qinying, YAN Xiaojun, LIU Hongning, JI Yanhua, ZENG Zhijun. Efficacy of Kushen decoction (苦参汤) on high-fat-diet-induced hyperlipidemia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 364-371. |
| [3] | CHEN Benjian, HUANG Xiaodan, PENG Huiting, LI Yishi, CAO Yongtao, WU Huanlin, XU Danping. Effectiveness and safety of red yeast rice predominated by monacolin K β-hydroxy acid form for hyperlipidemia treatment and management [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 264-271. |
| [4] | Sun Chen, Wang Li, Sun Jing, Wang Zheng, Tang Zhishu. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of rutin on hyperglycemic rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(4): 640-645. |
| [5] | Se-Eun Lee, Hyungwoo Kim, Chang-Hyun Kim, Chiyeon Lim, Suin Cho. Effect of methanol extract of Schisandrae Fructus on high fat diet induced hyperlipidemic mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(06): 818-825. |
| [6] | Wonseok Chung, Jimi Ryu, Seokhee Chung, Sungsoo Kim. Effect of Qingxue Dan on obesity and metabolic biomarker: a double-blind randomized-controlled pilot study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(03): 291-298. |
| [7] | Yao Haiqiang, Zhang Zengliang, Wang Ji, Zuo Jiacheng, Chen Yu, Zhu Libing, Li Xiaoke, Yang Zheng, Wang Zisong, Sun Ranran, Xu Xuanxuan, Li Changming, Wu Yanling, Li Lingru, Wang Qi. Efficacy and safety of Yinchenwuling powder for hyperlipidemia: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(02): 135-143. |
| [8] | Wang Yuanyuan, Jin Minghua, Zhang Lina, Li Suhua, Zhai Jiayu, Shen Yongzhi, Chen Chunyu, Qin Jian. Effect of a combination of calorie-restriction therapy and Lingguizhugan decoction on levels of fasting blood lipid and inflammatory cytokines in a high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia rat model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(02): 218-221. |
| [9] | Jiangquan Liao, Jiaxing Tian, Tengfei Li, Weijiang Song, Weihan Zhao, Jinhang Du. Xuefuzhuyu decoction for hyperlipidemia: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trails [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014, 34(04): 411-418. |
| [10] | Xianfeng Ye, Huifang Zhang. Influence of moxibustion temperatures on blood lipids, endothelin-1, and nitric oxide in hyperlipidemia patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(05): 592-596. |
| [11] | Xichao Xia, Yuhong Ma, Xiankun Xing, Chuanfeng Huang, Ling Li, Gaixia Gui, Qingchun Liu, Shipeng Xue. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect of different extracts of Guizhencao (Herba Bidentis Bipinnatae) against liver injury in hyperlipidemia rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(04): 518-523. |
| [12] | Minggang Wei, Peihua Xiong, Ling Zhang, Mei Fei, Aiping Chen, Fengling Li. Perilla oil and exercise decrease expressions of tumor necrosis factor-α,plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and highly sensitive C-reactive protein in patients with hyperlipidemia [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(02): 170-175. |
| [13] | Yubin Yang, Jian Qin, Bin Ke, Junjie Zhang, Lanying Shi, Qiong Li. Effect of Linguizhugan decoction on hyperlipidemia rats with intermittent fasting [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(02): 250-252. |
| [14] | Dong Bai, Jiannan Song. Plasma metabolic biomarkers for syndrome of phlegm and blood stasis in hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012, 32(04): 578-583. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||