Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 35-43.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.01.004
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Identifying Qingkailing (清开灵) ingredients-dependent mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor-axiation “π” structuring module with angiogenesis and neurogenesis effects
CHENG Kunming1, YUAN Jianan1, LIU Jun2, ZHANG Shengpeng1, XU Qixiang1, XIE Yong3, ZHAO Jingfeng3, ZHANG Xiaoxu2, TANG Xudong4, ZHENG Yongqiu1( ), WANG Zhong2(
), WANG Zhong2( )
)
- 1 Provincial Engineering Laboratory for Screening and Re-evaluation of Active Compounds of Herbal Medicines in Southern Anhui, Teaching and Research Section of Traditional Chinese Medicine, School of Pharmacy, Wannan Medical College, Wuhu 241000, China
2 Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
3 Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substances and Resources Utilization of Chinese Herbal Medicine, Ministry of Education, Department of Medicinal Plant Development, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100193, China
4 Department of Gastroenterology, Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100091, China
-
Received:2023-02-19Accepted:2023-05-22Online:2024-02-15Published:2023-12-28 -
Contact:WANG Zhong, Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China. zhonw@vip.sina.com;ZHENG Yongqiu, Provincial Engineering Laboratory for Screening and Re-evaluation of Active Compounds of Herbal Medicines in Southern Anhui, Teaching and Research Section of Traditional Chinese Medicine, School of Pharmacy, Wannan Medical College, Wuhu 241000, China. yongqiuzheng@sina.com -
Supported by:National Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for “Significant New Drugs Development”: Clinical Value Prescription Discovery and Evaluation Technology Based on Modular Pharmacology(2017ZX09301059);Joint Innovation Project of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences: Study on the Mechanism of Action of Neuronal Regenerative Function Module Activated by Qingkailing Components(ZZ11-026);University Collaborative Innovation Project of Anhui: Creation of a Combined Animal Model of Coronary Heart Disease Based on the Theory of Xin'an Medicine(GXXT-2020-024);University Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Province :Molecular Mechanism of the Anti-hepatic Fibrosis Effect of Wickerwork Amide Based on the Regulation of Intercellular Communication by PTRF(2023AH051752)
Cite this article
CHENG Kunming, YUAN Jianan, LIU Jun, ZHANG Shengpeng, XU Qixiang, XIE Yong, ZHAO Jingfeng, ZHANG Xiaoxu, TANG Xudong, ZHENG Yongqiu, WANG Zhong. Identifying Qingkailing (清开灵) ingredients-dependent mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor-axiation “π” structuring module with angiogenesis and neurogenesis effects[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 35-43.
share this article
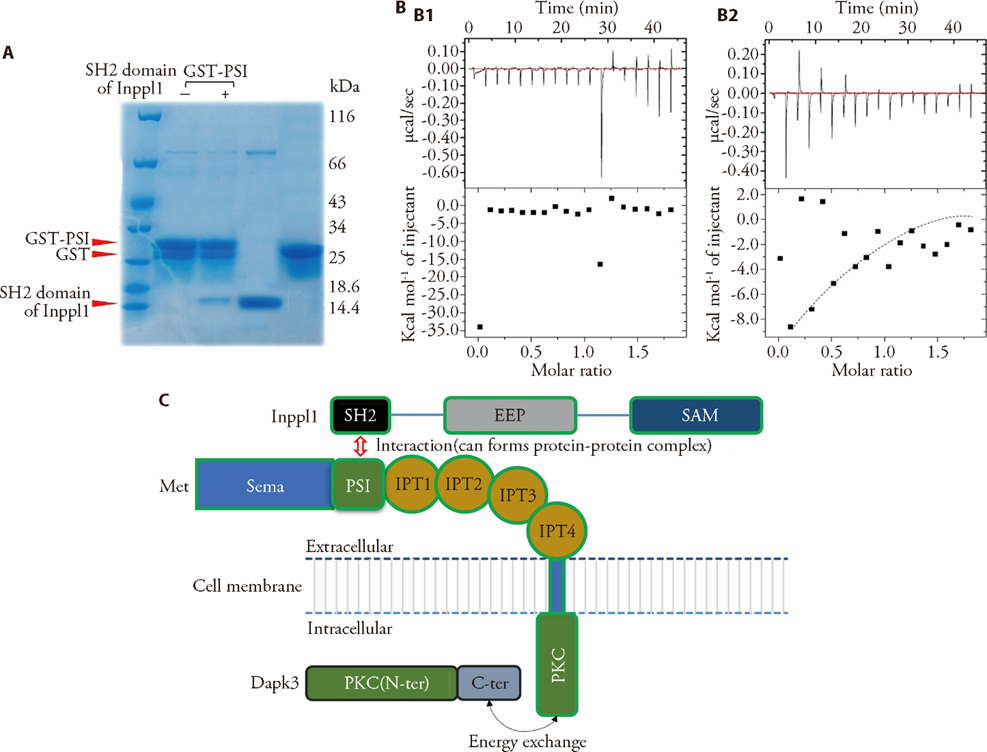
Figure 1 Effects of Met, Inppl1 and Dapk3 interaction models A: results of GST-pull down assays for GST-PSI domain of Met binding to the SH2 domain of Inppl1. The eluted and input proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB); B: ITC experiments with met and Dapk3; B1: results of ITC experiments of PKC domain of Dapk3 were titrated into PKC domain of Met; B2: C-terminal domain of Dapk3 was titrated into PKC domain of Met; Top panel: raw data obtained for a representative experiment from 19 injections. Bottom panel: the integrated data with a best-fit curve for the representative experiment generated using the Origin software package for a single-site binding model; C: interaction model among Met, Inppl1, and Dapk3. Inppl1: inositol polyphosphate phosphatase like 1; SH2: src homology; EEP: endonuclease-exonuclease-phosphatase; SAM: sterile alpha motif; Met: mesenchymal-epithelial transition; SEMA: semaphorins; PSI: plexin-semaphorin-integrindomain; IPT: immunoglobulin-plexins-transcription; Dapk3: death associated protein kinase 3; PKC: protein kinase c; Met: mesenchymal-epithelial transition; N-ter: N-terminus; C-ter: C-terminus; GST: glutathione-s-transferase; SDS-PAGE: sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; ITC: isothermal titration calorimetry.
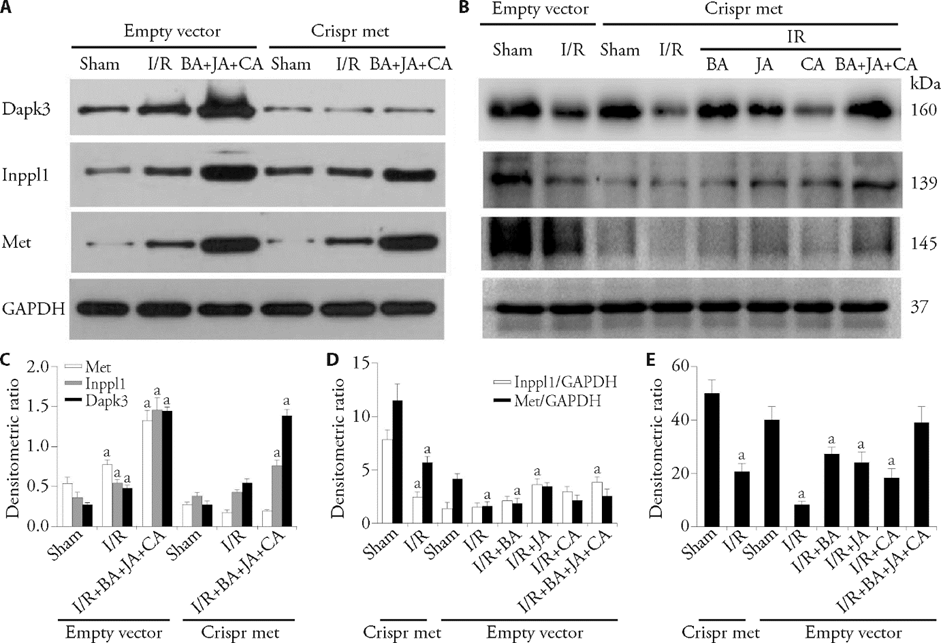
Figure 2 Crispr/cas9 Met inhibits Dapk3, Inppl1 and Met expression in brain homogenates A: immunoblots of Dapk3, Inppl1, and Met expressions in cerebral homogenates showed that treatments of Crispr Met can sufficiently block the effects of BA + JA + CA on Inppl1, but not Dapk3; B: immunoblots of Dapk3, Inppl1, and Met expressions showed that BA + JA + CA could increase Dapk3 and Inppl1 expressions blocked by Met crispr, while BA, JA, CA had no effects; C: bar graphs showed quantitative evaluation of A; D: bar graphs showed quantitative evaluation of B; E: bar graphs showed quantitative evaluation of B. BA: 750 mg JA/kg body weight, 210 mg CA/kg body weight, or 50 mg BA + 250 mg JA + 70 mg CA /kg body weight (BA+JA+CA group) during treatment. AS1949490 was used at a 300 mg/kg dose. BA: baicalin; CA: cholic acid; JA: jasminoidin; I/R: ischemia-reperfusion; Crispr: crispr/cas9; Met: mesenchymal-epithelial transition; Inppl1: inositol polyphosphate phosphatase like 1 ; Dapk3: death associated protein kinase 3. All data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Statistical significance between multiple groups was determined in this study primarily using one-way or two-way analysis of variance. aP < 0.05, compared to the Sham group.

Figure 3 Inhibition of biological effects of the modules of neurons generation composed of Met, Inppl1, and Dapk3 impaired BA + JA + CA-induced angiogenesis and neurogenesis A: co-treatment with SHIP2 inhibitors AS1949490 and/or Crispr-Met impaired BA + JA + CA-induced angiogenesis as demonstrated by CD31 and BrdU immunostaining (× 40 magnification, each sample was repeated three times, use of immunofluorescence staining). A1: Sham Group; A2: I/R group; A3: I/R + BA + JA + CA group; A4: I/R + BA + JA + CA + AS group; A5: I/R + BA + JA + CA + CrisprMet group; A6: I/R + BA + JA + CA + CrisprMet + AS group; Arrows point to co-localisation of CD31 and BrdU indicate angiogenesis. B: co-treatment with SHIP2 inhibitors AS1949490 and/or Crispr-Met impaired BA + JA + CA-induced neurogenesis as demonstrated by NeuN and BrdU immunostaining (× 40 magnification, each sample was repeated three times, use of immunofluorescence staining); B1: Sham Group; B2: I/R group; B3: I/R + BA + JA + CA group; B4: I/R + BA + JA + CA + AS group; B5: I/R + BA + JA + CA + CrisprMet group; B6: I/R + BA + JA + CA + CrisprMet + AS group. The arrows point to the co-localisation of NeuN and BrdU, suggesting that neuronal biogenesis. C: contents of BDNF in brain tissues; D: contents of VEGF in brain tissues; E: bar graphs showed quantitative evaluation of A; F: bar graphs showed quantitative evaluation of B. 750 mg JA/kg body weight, 210 mg CA/kg body weight, or 50 mg BA + 250 mg JA + 70 mg CA /kg body weight (BA + JA + CA group) during treatment. AS1949490 was used at a 300 mg/kg dose. BA: baicalin; CA: cholic acid; JA: jasminoidin; I/R: ischemia-reperfusion; Crispr: Crispr/cas9; Met: mesenchymal-epithelial transition; Inppl1: inositol polyphosphate phosphatase like 1; Dapk3: death associated protein kinase 3; SHIP2: src homology 2 domain-containing inositol 5'-phosphatase 2; BrdU: bromodeoxyuridine; AS: Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor. Statistical significance between multiple groups was determined in this study primarily using one-way or two-way analysis of variance. All data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). aP < 0.05, compared with sham + empty vector group; bP < 0.05, compared with I/R group; cP < 0.05, compared with I/R + BA + JA + CA group; dP < 0.05, compared with sham + I/R + BA + JA + CA + Crispr Met + AS group.
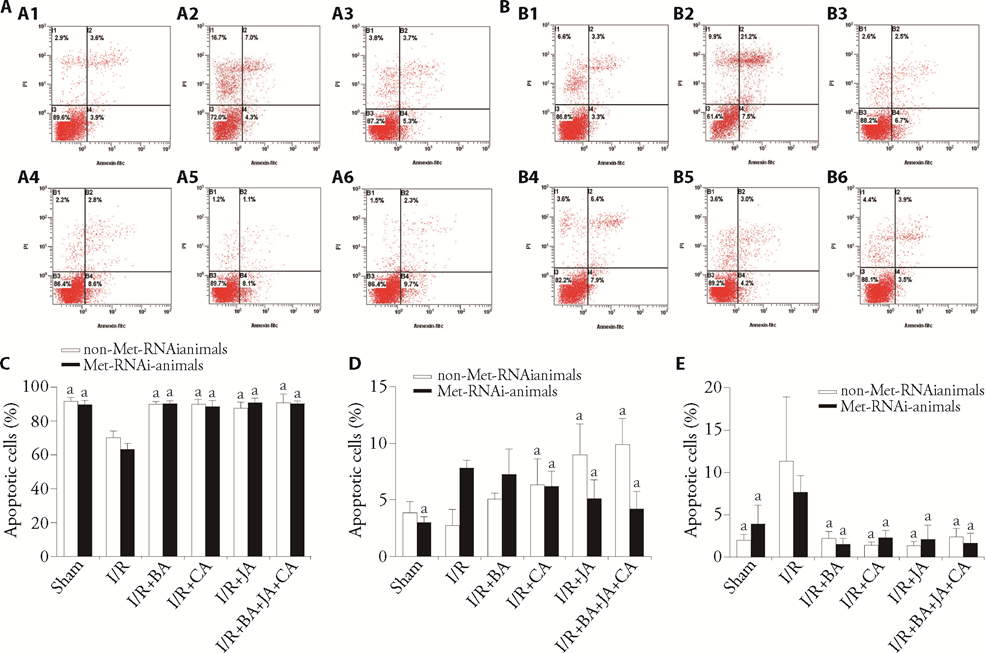
Figure 4 Effects of Crispr-Met on BA + JA + CA-induced apoptosis of neurons as demonstrated by PI and Annexin-FITC V staining A: neuronal apoptosis in Met Crispr animals; A1: Sham group; A2: I/R group; A3: I/R + BA group; A4: I/R + CA group; A5: I/R + JA group; A6: I/R + BA + CA + JA group; B: neuroapoptosis in non-Met Crispr animals; B1: Sham group; B2: I/R group; B3: I/R + BA group; B4: I/R + CA group; B5: I/R + JA group; B6: I/R + BA + CA + JA group; C: percentages of apoptotic cells are indicated; D: percentages of apoptotic cells are indicated; E: percentages of apoptotic cells are indicated. 750 mg JA/kg body weight, 210 mg CA/kg body weight, or 50 mg BA + 250 mg JA + 70 mg CA /kg body weight (BA + JA + CA group) during treatment. AS1949490 was used at a 300 mg/kg dose; Met: mesenchymal-epithelial transition; PI: propidine iodide; FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate; BA: baicalin; CA: cholic acid; JA: jasminoidin; I/R: ischemia-reperfusion. All data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Statistical significance between multiple groups was determined in this study primarily using one-way or two-way analysis of variance. aP < 0.05, compared with I/R.
| 1. |
Beltrao P, Cagney G, Krogan NJ. Quantitative genetic interactions reveal biological modularity. Cell 2010; 141: 739-45.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Suthram S, Dudley JT, Chiang AP, Chen R, Hastie TJ, Butte AJ. Network-based elucidation of human disease similarities reveals common functional modules enriched for pluripotent drug targets. PLoS Comput Biol 2010; 6: e1000662.
DOI URL |
| 3. |
Lorenz DM, Jeng A, Deem MW. The emergence of modularity in biological systems. Phys Life Rev 2011; 8: 129-60.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Wang Z, Wang YY. Modular pharmacology: deciphering the interacting structural organization of the targeted networks. Drug Discov Today 2013; 18: 560-6.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Ravasz E, Somera AL, Mongru DA, Oltvai ZN, Barabási AL. Hierarchical organization of modularity in metabolic networks. Science 2002; 297: 1551-5.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Wang Z, Liu J, Yu Y, Chen Y, Wang Y. Modular pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov 2012; 7: 667-77.
DOI URL |
| 7. |
Horvath S, Dong J. Geometric interpretation of gene coexpression network analysis. PLoS Comput Biol 2008; 4: e1000117.
DOI URL |
| 8. |
Wang W, Jiang B, Sun H, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and mortality of stroke in china: results from a nationwide population-based survey of 480 687 adults. Circulation 2017; 135: 759-71.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Meng X, Chu G, Yang Z, et al. Metformin protects neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury by down-regulating mad2b. Cell Physiol Biochem 2016; 40: 477-85.
DOI URL |
| 10. |
Chelluboina B, Nalamolu KR, Mendez GG, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell treatment prevents post-stroke dysregulation of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Cell Physiol Biochem 2017; 44: 1360-69.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Liu J, Zhang ZJ, Zhou CX, et al. Outcome-dependent global similarity analysis of imbalanced core signaling pathways in ischemic mouse hippocampus. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2012; 11: 1070-82.
PMID |
| 12. |
Li KN, Zhang YY, Yu YN, Wu HL, Wang Z. Met-controlled allosteric module of neural generation as a new therapeutic target in rodent brain ischemia. Chin J Integr Med 2021; 27: 896-904.
DOI |
| 13. |
Lü C, Maharjan S, Wang Q, et al. A-lipoic acid promotes neurological recovery after ischemic stroke by activating the nrf2/ho-1 pathway to attenuate oxidative damage. Cell Physiol Biochem 2017; 43: 1273-87.
DOI URL |
| 14. |
Yang K, Bai H, Ouyang Q, Lai L, Tang C. Finding multiple target optimal intervention in disease-related molecular network. Mol Syst Biol 2008; 4: 228.
DOI PMID |
| 15. |
Rognan D. Chemogenomic approaches to rational drug design. Br J Pharmacol 2007; 152: 38-52.
DOI URL |
| 16. |
Hellerstein MK. Exploiting complexity and the robustness of network architecture for drug discovery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2008; 325: 1-9.
DOI PMID |
| 17. |
Tegner J, Yeung MK, Hasty J, Collins JJ. Reverse engineering gene networks: integrating genetic perturbations with dynamical modeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003; 100: 5944-9.
DOI URL |
| 18. |
Kam TI, Park H, Gwon Y, et al. Fcγriib-ship2 axis links aβ to tau pathology by disrupting phosphoinositide metabolism in alzheimer's disease model. Elife 2016; 5: e18691.
DOI URL |
| 19. |
Bottaro DP, Rubin JS, Faletto DL, et al. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science 1991; 251: 802-4.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Koch A, Mancini A, El Bounkari O, Tamura T. The sh2-domian-containing inositol 5-phosphatase (ship)-2 binds to c-mett directly via tyrosine residue 1356 and involves hepatocyte growth factor (hgf)-induced lamellipodium formation, cell scattering and cell spreading. Oncogene 2005; 24: 3436-47.
DOI |
| 21. |
Usui T, Okada M, Hara Y, Yamawaki H. Death-associated protein kinase 3 mediates vascular inflammation and development of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 2012; 60: 1031-9.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Rivas S, Marín A, Samtani S, González-Feliú E, Armisén R. Met signaling pathways, resistance mechanisms, and opportunities for target therapies. Int J Mol Sci 2022; 23: 13898.
DOI URL |
| 23. |
Eagleson KL, Lane CJ, McFadyen-Ketchum L, Solak S, Wu HH, Levitt P. Distinct intracellular signaling mediates c-met regulation of dendritic growth and synaptogenesis. Dev Neurobiol 2016; 76: 1160-81.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Salian-Mehta S, Xu M, Wierman ME. Axl and met crosstalk to promote gonadotropin releasing hormone (gnrh) neuronal cell migration and survival. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2013; 374: 92-100.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Chen YY, Yu YN, Zhang YY, et al. Quantitative determination of flexible pharmacological mechanisms based on topological variation in mice anti-ischemic modular networks. PLoS One 2016; 11: e0158379.
DOI URL |
| 26. |
Li B, Wang Y, Gu H, et al. Modular screening reveals driver induced additive mechanisms of baicalin and jasminoidin on cerebral ischemia therapy. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022; 9: 813983.
DOI URL |
| [1] | SHI Xiao, WANG Lina, HU Jianpeng, ZHANG Limiao, WANG Jin. Effect of Naoluoxintong formula (脑络欣通方) and its split prescriptions on cerebral vascular regeneration in rats with the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1140-1149. |
| [2] | DAI Zeqi, LIAO Xing, GUAN Yueyue, ZENG Zixiu, TANG Jun, HU Jing. Bloodletting puncture in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: protocol for a mixed-method study of a multi-center randomized controlled trial and focus group [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1259-1267. |
| [3] | LI Menghan, YAN Yan, DENG Shizhe, WANG Yu, FU Yu, SHI Lei, YANG Jin, ZHANG Chunhong. Contralateral needling at the foot of unaffected side combining with rehabilitation treatment for motor dysfunction of hand after ischemic stroke: study protocol for a randomized controlled pilot trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 1034-1039. |
| [4] | JIANG Jianzhen, ZHANG Xin, LUO Zhenguo, SU Chengguo, ZHOU Haiyan, JIANG Yuqing, XIAO Xianjun, CHEN Yunfei, ZHU Jun. Efficacy of electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36) and Xuanzhong (GB39) on synovial angiogenesis in rats with adjuvant arthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 955-962. |
| [5] | MENG Xiangran, CAO Xue, SUN Minglin, AI Yanke, HE Liyun, LIU Jia. Effectiveness and safety of Angong Niuhuang pill (安宫牛黄丸) in treatment of acute stroke: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 650-660. |
| [6] | LI He, SU Wenquan, LI Shanshan, JI Hanrui, CHENG Jiangyan, CUI Fangyuan, TANG Lu, ZHOU Li, GAO Ying, DONG Xinglu. Supplementing Qi and activating blood circulation method to treat vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia with posterior circulatory watershed infarction: a case report of two patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 824-828. |
| [7] | XIE Le, MAO Guo, XIE Yao, CAO Sijia, ZHOU Shen, JIANG Junlin, YAO Ting, FAN Jianhu, LIU Dong, KANG Fuliang, WU Dahua, GE Jinwen. Efficacy of Baishao Luoshi decoction (白芍络石方) on synaptic plasticity in rats with post stroke spasticity [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 295-302. |
| [8] | Minh Duc Nguyen, Thanh Van Tran, Quoc Vinh Nguyen, Ninh Khac Nguyen, Son Truong Vu, Luu Trong Nguyen, Linh Vu Phuong Dang. Effectiveness on post-stroke hemiplegia in patients: electroacupuncture plus cycling vs electroacupuncture alone [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 352-358. |
| [9] | YOU Jianyu, LI Haiyan, XIE Dingyi, CHEN Mingren, CHEN Rixin. Efficacy of acupuncture therapy for post-stroke fatigue: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 27-33. |
| [10] | LI Miao, ZHENG Jialu, WANG Shuangshuang, CHEN Lei, PENG Xiao, CHEN Jinfang, AN Hongmei, HU Bing. Tenglong Buzhong granules (藤龙补中颗粒) inhibits the growth of SW620 human colon cancer in vivo [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 701-706. |
| [11] | ZHOU Ziyi, WAN Can, ZHAO Yuanqi, LIU Xiangzhe, GAO Ying, AN Hongwei, LI Lejun, ZHANG Huili, YU Xiaofei, ZHANG Xinchun, WANG Huijuan, SHI Qing, WEI Chunhua, CHEN Jie, HUANG Wenguo, CHEN Junbin, GAO Ying, HU Mingzhe, CAI Yefeng. Efficacy and safety of a sequential treatment with clearing heat and eliminating phlegm and tonifying Qi and activating blood circulation in treating acute ischemic stroke: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 604-610. |
| [12] | XIE Yunhui, GU Hao, ZHAO Qing, LI Dejie, GONG Ying, XIE Junxing, SHI Guofeng. Efficacy of meridian massage for motor function after a stroke: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 321-331. |
| [13] | LI Zhiyong, ZHU Na, LI Jianliang, FENG Liang, JIANG Yanyan, LI Caifeng, LIN Ling, HUANG Xiulan. Effcacy-oriented compatibility for Tianma (Rhizoma Gastrodiae), Yanlingcao (Trillium tschonoskii Maxim) and Bingpian (Borneolum Syntheticum) on improving cerebral ischemia stroke by network pharmacology and serum pharmacological methods [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 408-416. |
| [14] | Jingjing WEI, Rongjuan GUO, Guojing FU, Xiao LIANG, Zhenmin XU, Min JIA, Zixiu ZENG, Wanqing DU, Weiwei JIAO, Linjuan SUN, Hongmei LIU, Chunli GUO, Chenguang TONG, Yunling ZHANG, Xing LIAO. Registration of intervention trials of Traditional Chinese Medicine for four neurological diseases on Chinese Clinical Trial Registry and ClinicalTrials.gov: a narrative review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 148-153. |
| [15] | LI Yuanqi, LI Weili, YU Xinhui, WU Hua, WANG Yuanzhong, JIN Ya, HAO Lele, LIU Mingmin, SONG Xiaoge. Mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine Bushenantai granules (补肾安胎颗粒) in promoting angiogenesis at the maternal-fetal interface of recurrent spontaneous abortion mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 556-563. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

