Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 372-378.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.03.004
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated 2 contributes to electroacupuncture analgesia on lumbar disc herniation-induced radicular pain through activation of microglia in spinal dorsal horn
QIN Qingguang, CHEN Zujiang, FAN Weimin, LI Junhua, LIAO Liqing, LI Yikai( )
)
- School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China
-
Received:2021-11-23Accepted:2021-02-26Online:2022-06-15Published:2022-05-20 -
Contact:LI Yikai -
About author:LI Yikai, School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China. ortho@fimmu.com,Telephone: +86-20-61648455
-
Supported by:Inheritance and Innovation in TCM “Hundred-Thousand-Ten Thousand” Talent Project(Qinhuang Project)(F119090038);National Natural Science Foundation of China (Based on the Cascade Reaction of Microglia-Astrocyte research exosomal miRNA mechanisms of the inhibitory transition from acute to chronic pain of LDH by electroacupuncture)(82074529);Scientific Research Projects of Traditional Chinese Medicine Bureau of Guangdong Province(Based on the cAMP-PKA-HCN2 pathway the mechanism of electro-acupuncture to prevent the development of pain in lumbar disc herniation)(20211254)
Cite this article
QIN Qingguang, CHEN Zujiang, FAN Weimin, LI Junhua, LIAO Liqing, LI Yikai. Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated 2 contributes to electroacupuncture analgesia on lumbar disc herniation-induced radicular pain through activation of microglia in spinal dorsal horn[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 372-378.
share this article
| Gene | Sequence |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | Forward: CCTCGTCTCATAGACAAGATGGT |
| Reverse: GGGTAGAGTCATACTGGAACATG | |
| CX3CL1 | Forward: AGCAGTGACTGGATCGTCTC |
| Reverse: AAGTGGTGGACGCTTGAGTA; | |
| HCN2 | Forward: AGCAAGTGGAGCAGTACATG |
| Reverse: GCTGTCCTCGTCAAACATCT |
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| Gene | Sequence |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | Forward: CCTCGTCTCATAGACAAGATGGT |
| Reverse: GGGTAGAGTCATACTGGAACATG | |
| CX3CL1 | Forward: AGCAGTGACTGGATCGTCTC |
| Reverse: AAGTGGTGGACGCTTGAGTA; | |
| HCN2 | Forward: AGCAAGTGGAGCAGTACATG |
| Reverse: GCTGTCCTCGTCAAACATCT |
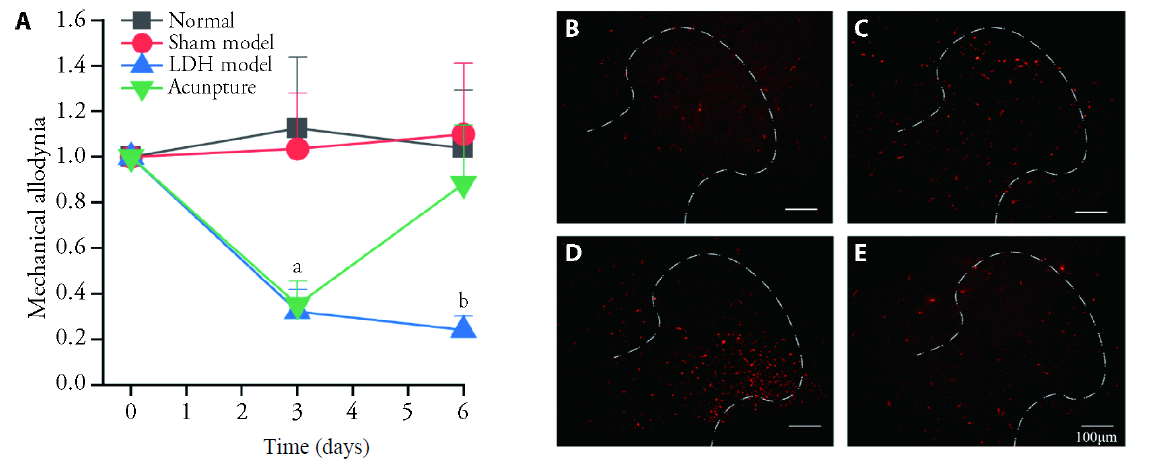
Figure 1 Electroacupuncture (EA) reduces mechanical allodynia thresholds and microglia activation in rats with lumbar disc herniation (LDH) EA was given on the 3rd day after modeling. A: the line graph shows the effect of EA on the mechanical allodynia threshold of the right plantar in model rats. The mechanical allodynia threshold before the intervention was identified as 1. Fluorescence image shows the expression of Iba1+ microglia of rat in the ipsilateral lumbar spinal dorsal horn at 6th day. B: normal group; C: the sham model group; D: model group; E: EA group. compared with normal group, bP < 0.05, compared with EA group, aP < 0.05 (n = 7).
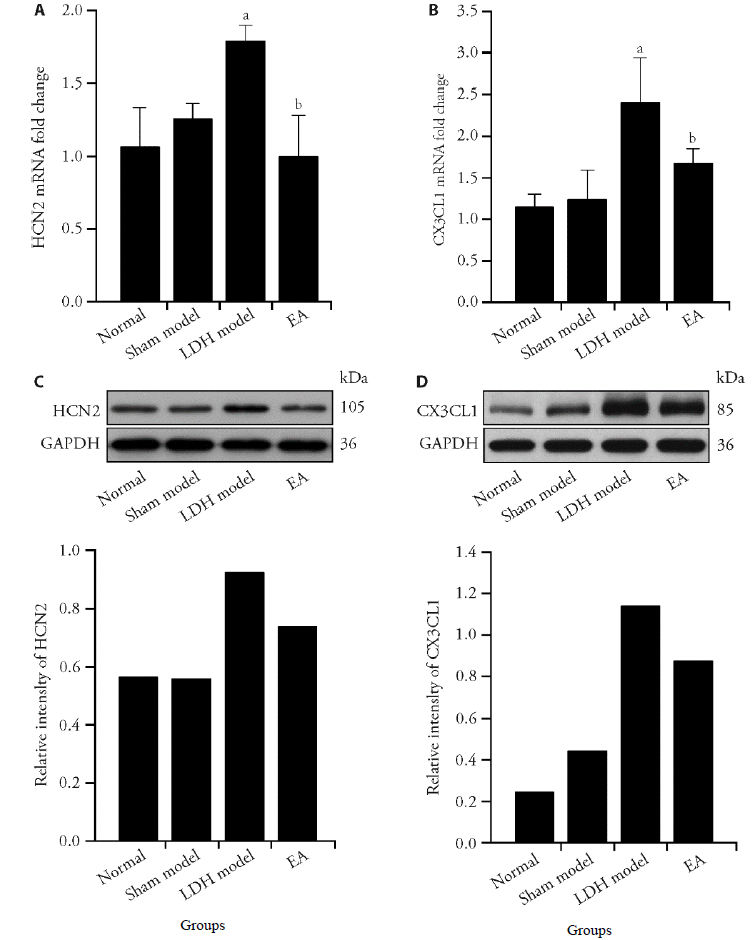
Figure 2 Electroacupuncture (EA) reduces the expression of HCN2 in ipsilateral dorsal root ganglia and CX3CL1 in ipsilateral spinal dorsal horn EA was given on the 3rd day after modeling, the expression of HCN2 and CX3CL1 was detected on the 6th day. A: the level of HCN2 mRNA in the right L5 dorsal root ganglion; B: the level of CX3CL1 mRNA in the ipsilateral spinal dorsal horn, separately; C, D: HCN2 protein and CX3CL1 protein expression (n = 3). Compared with normal group, aP < 0.05, compared with the acupuncture group, bP < 0.05 (n = 7).
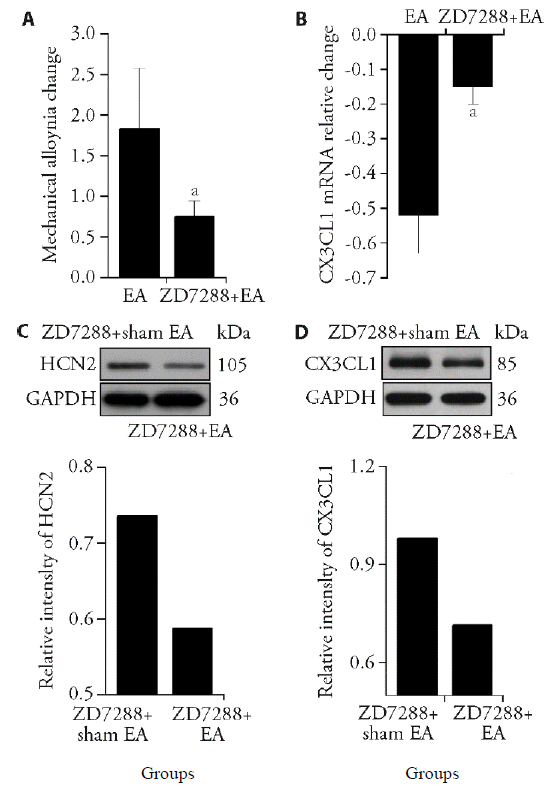
Figure 3 HCN2 antagonist reduces the analgesic effect of electroacupuncture (EA) on rats with lumbar disc herniation (LDH) HCN2 antagonist (50 μg of a rat) were injected into subarachnoid space of LDH model rats, per day for 3 d. A: the analgesic effect of EA on mechanical pain was significantly reduced; B: the expression of CX3CL1 in the spinal cord decreased; C, D: Western blot showed that HCN2 protein and CX3CL1 protein expression of the ZD7288 + sham EA group was higher than that of the ZD7288 + EA group, respectively (n = 3). Compared with EA group, aP < 0.05 (n = 7).
| 1 |
Kim YK, Kang D, Lee I, Kim SY. Differences in the incidence of symptomatic cervical and lumbar disc herniation according to age, sex and national health insurance eligibility: a pilot study on the disease's association with work. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2018; 15:2094.
DOI URL |
| 2 | Huang Y, Li Y, Zhong X, et al. Src-family kinases activation in spinal microglia contributes to central sensitization and chronic pain after lumbar disc herniation. Mol Pain 2017; 13:1-13. |
| 3 |
Sanzarello I, Merlini L, Rosa MA, et al. Central sensitization in chronic low back pain: a narrative review. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 2016; 29:625-33.
DOI URL |
| 4 |
Gore M, Sadosky A, Stacey BR, Tai KS, Leslie D. The burden of chronic low back pain: clinical comorbidities, treatment patterns, and health care costs in usual care settings. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012; 37:E668-77.
DOI URL |
| 5 |
Emery EC, Young GT, Berrocoso EM, Chen L, McNaughton PA. HCN2 ion channels play a central role in inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Science 2011; 333:1462-66.
DOI URL |
| 6 |
Ji RR, Nackley A, Huh Y, Terrando N, Maixner W. Neuroinflammation and central sensitization in chronic and widespread pain. Anesthesiology 2018; 129:343-66.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
Gu N, Peng JY, Murugan M, et al. Spinal microgliosis due to resident microglial proliferation is required for pain hypersensitivity after peripheral nerve injury. Cell Rep 2016; 16:605-14.
DOI URL |
| 8 |
Yabuki S, Igarashi T, Kikuchi S. Application of nucleus pulposus to the nerve root simultaneously reduces blood flow in dorsal root ganglion and corresponding hindpaw in the rat. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000; 25:1471-76.
DOI URL |
| 9 | Yang YQ, Yan C, Branford-White CJ, Hou XY. Biological values of acupuncture and chinese herbal medicine: impact on the life science. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 2014:593921. |
| 10 |
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 1994; 53:55-63.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Hou Y, Wang L, Gao J, Jin X, Ji F, Yang J. A modified procedure for lumbar intrathecal catheterization in rats. Neurol Res 2016; 38:725-32.
DOI URL |
| 12 | Wan Y. Involvement of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels in dorsal root ganglion in neuropathic pain. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2008; 60:579-80. |
| 13 |
Padmanabhan R, Singh S. Observations on the topographical relations of spinal nerve roots in the rat. Acta Anat (Basel) 1979; 105:378-80.
PMID |
| 14 | Zhang ZJ, Jiang BC, Gao YJ. Chemokines in neuron-glial cell interaction and pathogenesis of neuropathic pain. Cell Mol Life Sci Sep 2017; 74:3275-91. |
| 15 |
Park HW, Ahn SH, Kim SJ, et al. Changes in spinal cord expression of fractalkine and its receptor in a rat model of disc herniation by autologous nucleus pulposus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011; 36:E753-60.
DOI URL |
| 16 | Liu Y, Zhao J, Tian Y. Efficacy and safety of electroacupuncture in treatment of lumbar disc herniation: a protocol for a cohort study. J Tradit Chin Med 2019; 39:127-32. |
| 17 |
Fernandes EC, Luz LL, Mytakhir O, Lukoyanov NV, Szucs P, Safronov BV. Diverse firing properties and Abeta-, Adelta-, and C-afferent inputs of small local circuit neurons in spinal lamina I. Pain 2016; 157:475-87.
DOI URL |
| 18 |
Braz J, Solorzano C, Wang X, Basbaum AI. Transmitting pain and itch messages: a contemporary view of the spinal cord circuits that generate gate control. Neuron 2014; 82:522-36.
DOI URL |
| 19 |
Kouranova EV, Strassle BW, Ring RH, Bowlby MR, Vasilyev DV. Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel mRNA and protein expression in large versus small diameter dorsal root ganglion neurons: correlation with hyperpolarization-activated current gating. Neuroscience 2008; 153:1008-19.
DOI PMID |
| 20 |
Song XJ, Hu SJ, Greenquist KW, Zhang JM, LaMotte RH, Mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia and ectopic neuronal discharge after chronic compression of dorsal root ganglia. J Neurophysiol 1999; 82:3347-58.
PMID |
| 21 |
He JT, Li XY, Zhao X, Liu X. Hyperpolarization-activated and cyclic nucleotide-gated channel proteins as emerging new targets in neuropathic pain. Rev Neurosci 2019; 30:639-49.
DOI URL |
| 22 |
Du L, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Zhu J, Yang Y, Zhang HL. Role of microglia in neurological disorders and their potentials as a therapeutic target. Mol Neurobiol 2017; 54:7567-84.
DOI URL |
| 23 |
Zhong Y, Huang YL, Hu YM, Zhu LR, Zhao YS. Puerarin alleviate radicular pain from lumbar disc herniation by inhibiting ERK-dependent spinal microglia activation. Neuropeptides 2018; 72:30-37.
DOI PMID |
| 24 |
Hanisch UK. Microglia as a source and target of cytokines. Glia 2002; 40:140-55.
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Chen G, Zhang YQ, Qadri YJ, Serhan CN, Ji RR. Microglia in pain: detrimental and protective roles in pathogenesis and resolution of pain. Neuron 2018; 100:1292-1311.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Blaszczyk L, Maitre M, Leste-Lasserre T, et al. Sequential alteration of microglia and astrocytes in the rat thalamus following spinal nerve ligation. J Neuroinflammation 2018; 15:349.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Hughes PM, Botham MS, Frentzel S, Mir A, Perry VH. Expression of fractalkine (CX3CL1) and its receptor, CX3CR1, during acute and chronic inflammation in the rodent CNS. Glia 2002; 37:314-27.
PMID |
| 28 |
Li T, Liu T, Chen X, et al. Microglia induce the transformation of A1/A2 reactive astrocytes via the CXCR7/PI3K/Akt pathway in chronic post-surgical pain. J Neuroinflammation 2020; 17:211.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Inoue K, Tsuda M. Microglia in neuropathic pain: cellular and molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Neurosci 2018; 19:138-52.
DOI URL |
| [1] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [2] | SUN Qianhui, CHENG Kai, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, WU Xiaoling, XU Chang, QIU Xinghua, GAO Xiaofeng, LIU Daonan, YANG Qirui. Effect of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) at different time points on myocardial ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 113-121. |
| [3] | DU Zhongheng, CONG Wenjie, TANG Kejing, ZHENG Qiqi, SONG Zhiwei, CHEN Yong, YANG Su, ZHANG Chunwu, YE Tianshen. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) in mice with collagen-induced arthritis leads to adenosine A2A receptor-mediated alteration of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1103-1109. |
| [4] | JIANG Jianzhen, ZHANG Xin, LUO Zhenguo, SU Chengguo, ZHOU Haiyan, JIANG Yuqing, XIAO Xianjun, CHEN Yunfei, ZHU Jun. Efficacy of electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36) and Xuanzhong (GB39) on synovial angiogenesis in rats with adjuvant arthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 955-962. |
| [5] | LI Zhihao, HAN Wenjun, SONG Xiuling, LI Yan, CHEN Yuelai. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zhongji (CV3), Guanyuan (CV4), and bilateral Dahe (KI12) attenuates inflammation in rats with chronic nonbacterial prostatitis induced by estradiol through inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 963-972. |
| [6] | DING Luobin, WANG Huajun, LI Yao, LI Jia, LI Ling, GAO Yangping, GUAN Jian, GENG Weiqiang. Electroacupuncture stimulating Neixiyan (EX-LE5) and Dubi (ST35) alleviates osteoarthritis in rats induced by anterior cruciate ligament transaction via affecting DNA methylation regulated transcription of miR-146a and miR-140-5p [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 983-990. |
| [7] | SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, WANG Yuhang, XIN Chen, GU Dongmei, SUN Jianhua, PEI Lixia. Electroacupuncture alleviates water avoidance stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by improving intestinal barrier functions and suppressing the expression of inflammatory cytokines [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 494-500. |
| [8] | HAN Rui, CHANG Junzhao, LIU Qianqian, LIU Haitao, LI Junwei. Efficacy of electroacupunture at Zusanli (ST36) on jumping-injured muscle based on transcriptome sequencing and genes analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 322-328. |
| [9] | ZENG Hai, CAO Luxi, PANG Zhao, ZHAO Sisi, WANG Shiqi, LIN Zhuowen, CHEN Minan, LIN Shujun, ZHANG Yimin. Efficacy of acupuncture on repair of glial scars in rats with traumatic brain injury [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 329-336. |
| [10] | Minh Duc Nguyen, Thanh Van Tran, Quoc Vinh Nguyen, Ninh Khac Nguyen, Son Truong Vu, Luu Trong Nguyen, Linh Vu Phuong Dang. Effectiveness on post-stroke hemiplegia in patients: electroacupuncture plus cycling vs electroacupuncture alone [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 352-358. |
| [11] | XU Chang, LI Na, WU Xiaoling, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, SUN Qianhui, SHI Tianyu, CHAI Yemao, PANG Dandan, CHENG Kai. Effect of electroacupuncture on inflammatory signal expression in local tissues of rats with chronic pelvic pain syndrome based on purinergic 2X7 receptor/NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 signal pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 965-971. |
| [12] | SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, ZHAO Tingting, WANG Yuhang, PEI Lixia, SUN Jianhua. Electroacupuncture at Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) alleviates stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by modulating gut microbiota and corticotropin-releasing factor [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 732-740. |
| [13] | HU Xijiao, CHENG Yinglong, KANG Huanan, LI Shuoxi, WANG Yawen, LIU Jinzhe, SUN Yiming, LIU Li. Electroacupuncture attenuates chronic salpingitis via transforming growth factor-β1/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 781-787. |
| [14] | HUANG Yusi, YANG Jiju, LI Xinyi, HAO Huifeng, LI Chong, ZHANG Fan, LIN Haiming, XIE Xianfei, HE Ke, TIAN Guihua. Effectiveness and safety of electroacupuncture for the treatment of pain after laparoscopic surgery: a systematic review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 505-512. |
| [15] | Lakkana Rerksuppaphol, Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol. Efficacy of short duration versus conventional electroacupuncture in the treatment of obesity: a randomized crossover study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 256-263. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

