Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 1126-1139.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230517.003
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yangqing Chenfei formula (养清尘肺方) alleviates crystalline silica induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis by suppressing macrophage polarization
TIAN Xinrong1,2,3, HOU Runsu1,2,3, LIU Xinguang1,2,3, ZHAO Peng1,2,3, TIAN Yange1,2,3( ), LI Jiansheng4,5,6(
), LI Jiansheng4,5,6( )
)
- 1 Henan Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine for Respiratory Disease, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center for Chinese Medicine and Respiratory Diseases co constructed by Henan province and Education Ministry of P.R. China, Zhengzhou 450046, China
3 Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, China
4 Henan Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine for Respiratory Disease, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, China
5 Collaborative Innovation Center for Chinese Medicine and Respiratory Diseases co constructed by Henan province and Education Ministry of P.R. China, Zhengzhou 450046, China
6 Department of Respiratory Diseases, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, China
-
Received:2022-08-12Accepted:2022-11-23Online:2023-10-25Published:2023-05-17 -
Contact:Prof. LI Jiansheng, Henan Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine for Respiratory Disease, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, China. li_js8@163.com; Dr. TIAN Yange, Henan Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine for Respiratory Disease, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, China. yange0910@126.com. Telephone: +86-371-65676568; +86-13783656761 -
Supported by:Special Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Research of Henan Province(2021ZYZD01);Evaluation of the Therapeutic Effect and Characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine Dialectical Treatment for Coal Worker's Pneumoconiosis Based on A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel Controlled Trial; National Natural Science Fund of China(81973822);Exploring the Mechanism of Bufei Yishen Formula Inhibiting Inflammatory Response in the Treatment of COPD Based on Group Allocation Theory
Cite this article
TIAN Xinrong, HOU Runsu, LIU Xinguang, ZHAO Peng, TIAN Yange, LI Jiansheng. Yangqing Chenfei formula (养清尘肺方) alleviates crystalline silica induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis by suppressing macrophage polarization[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1126-1139.
share this article
| Group | n | 0W | 4W | 6W | 8W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 1.10±0.19 | 2.18±0.15 | 2.29±0.29 | 2.33±0.18 |
| Model | 6 | 1.08±0.20 | 1.75±0.19a | 1.87±0.29a | 1.89±0.19a |
| YCF | 6 | 1.09±0.10 | 1.84±0.21b | 2.20±0.13c | 2.25±0.14d |
| TET | 6 | 1.20±0.28 | 1.78±0.35a | 2.22±0.22c | 2.19±0.16d |
Table 1 Effect of YCF on TV of silicosis rats ( x - ± s)
| Group | n | 0W | 4W | 6W | 8W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 1.10±0.19 | 2.18±0.15 | 2.29±0.29 | 2.33±0.18 |
| Model | 6 | 1.08±0.20 | 1.75±0.19a | 1.87±0.29a | 1.89±0.19a |
| YCF | 6 | 1.09±0.10 | 1.84±0.21b | 2.20±0.13c | 2.25±0.14d |
| TET | 6 | 1.20±0.28 | 1.78±0.35a | 2.22±0.22c | 2.19±0.16d |
| Group | n | 0W | 4W | 6W | 8W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 0.39±0.09 | 0.51±0.06 | 0.48±0.07 | 0.48±0.05 |
| Model | 6 | 0.42±0.07 | 0.80±0.11a | 0.71±0.07a | 0.78±0.18a |
| YCF | 6 | 0.42±0.09 | 0.76±0.12a | 0.50±0.05b | 0.53±0.04b |
| TET | 6 | 0.53±0.30 | 0.80±0.12a | 0.57±0.07b | 0.60±0.11b |
Table 2 Effect of YCF on Penh of silicosis rats ( x - ± s)
| Group | n | 0W | 4W | 6W | 8W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 0.39±0.09 | 0.51±0.06 | 0.48±0.07 | 0.48±0.05 |
| Model | 6 | 0.42±0.07 | 0.80±0.11a | 0.71±0.07a | 0.78±0.18a |
| YCF | 6 | 0.42±0.09 | 0.76±0.12a | 0.50±0.05b | 0.53±0.04b |
| TET | 6 | 0.53±0.30 | 0.80±0.12a | 0.57±0.07b | 0.60±0.11b |
| Group | n | 0 W | 4 W | 6 W | 8 W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 0.55±0.20 | 0.94±0.14 | 1.06±0.10 | 1.16±0.19 |
| Model | 6 | 0.55±0.08 | 0.73±0.17a | 0.73±0.19b | 0.66±0.35b |
| YCF | 6 | 0.56±0.07 | 0.74±0.07a | 0.99±0.08c | 1.14±0.20c |
| TET | 6 | 0.51±0.08 | 0.77±0.18a | 1.02±0.12c | 1.01±0.09d |
Table 3 Effect of YCF on EF50 of silicosis rats ( x - ± s)
| Group | n | 0 W | 4 W | 6 W | 8 W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 0.55±0.20 | 0.94±0.14 | 1.06±0.10 | 1.16±0.19 |
| Model | 6 | 0.55±0.08 | 0.73±0.17a | 0.73±0.19b | 0.66±0.35b |
| YCF | 6 | 0.56±0.07 | 0.74±0.07a | 0.99±0.08c | 1.14±0.20c |
| TET | 6 | 0.51±0.08 | 0.77±0.18a | 1.02±0.12c | 1.01±0.09d |
| Group | n | 2W | 8W | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEV0.3 | FRC | MMEF | FEV0.3 | FRC | MMEF | ||||
| Normal | 6 | 9.7±1.3 | 3.2±0.7 | 80.3±6.9 | 10.4±0.6 | 4.0±0.1 | 68.3±7.7 | ||
| Model | 6 | 6.5±1.0a | 2.8±0.5 | 55.5±8.2a | 7.6±1.2a | 3.5±0.2a | 45.6±17.8a | ||
| YCF | 6 | 9.2±0.7b | 3.5±0.3c | 77.8±9.2b | 9.9±0.6b | 4.5±0.3b | 65.3±3.7c | ||
| TET | 6 | 8.9±2.3 | 3.1±0.3 | 73.9±11.9b | 8.6±1.7 | 3.9±0.4c | 57.7±15.1 | ||
Table 4 Effects of YCF on FEV 0.3, FRC, MMEF of silicosis rats ( x - ± s)
| Group | n | 2W | 8W | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEV0.3 | FRC | MMEF | FEV0.3 | FRC | MMEF | ||||
| Normal | 6 | 9.7±1.3 | 3.2±0.7 | 80.3±6.9 | 10.4±0.6 | 4.0±0.1 | 68.3±7.7 | ||
| Model | 6 | 6.5±1.0a | 2.8±0.5 | 55.5±8.2a | 7.6±1.2a | 3.5±0.2a | 45.6±17.8a | ||
| YCF | 6 | 9.2±0.7b | 3.5±0.3c | 77.8±9.2b | 9.9±0.6b | 4.5±0.3b | 65.3±3.7c | ||
| TET | 6 | 8.9±2.3 | 3.1±0.3 | 73.9±11.9b | 8.6±1.7 | 3.9±0.4c | 57.7±15.1 | ||

Figure 1 YCF enhanced pulmonary pathological changes and alleviated collagen deposition on silicosis A: HE staining of lung tissue on silicosis rats (× 200); A1-A4: the inflammatory cell infiltration of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 2; A5-A6: the inflammatory cell infiltration of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 8. B: MASSON staining of lung tissue on silicosis rats (× 200); B1-B4: the pulmonary pathological changes of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 2; B5-B6: the pulmonary pathological changes of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 8. C: expression level of COL-1 (× 200); C1-C4: the collagen type Ⅰ (Col Ⅰ) expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 2; C5-C6: the collagen type Ⅰ (Col Ⅰ) expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 8. D: expression level of COL-3 (× 200); D1-D4: the collagen type Ⅲ (Col Ⅲ) expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 2; D5-D6: the collagen type Ⅲ (Col Ⅲ) expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 8. Normal: healthy control rats; Model: silicosis rats; YCF: YCF treatment rats were intragastrically administered with 3.3663 g·kg-1·d-1 or 0.84 mL/100 g, once daily, from weeks 0-2 and 5-8; TET: tetrandrine treatment rats were intragastrically administered with 27 mg·kg-1·d-1 TET, from weeks 0-2 and 5-8 (n = 6). YCF: Yangqing Chenfei formula; TET: tetrandrine; HE: hematoxylin-eosin; COL-I: collage-1.
| Group | n | 2W | 8W | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | IL-1β | IL-6 | TNF-α | IL-1β | IL-6 | |||||
| Normal | 6 | 11.2±1.5 | 53.2±4.7 | 912.0±144.7 | 14.8±1.1 | 70.0±8.0 | 1229.8±70.3 | |||
| Model | 6 | 22.2±3.9a | 119.0±28.4a | 1445.2±198.3a | 21.8±2.3a | 131.5±22.2a | 1422.5±158.6a | |||
| YCF | 6 | 16.6±1.8b | 73.7±25.5b | 1166.6±135.0b | 17.2±2.9b | 83.8±2.9b | 1157.8±103.3b | |||
| TET | 6 | 16.8±1.6b | 82.5±23.4b | 1124.3±80.4b | 18.1±0.7b | 71.1±14.1b | 1074.3±73.9b | |||
Table 5 Levels of IL 1β, IL 6, and TNF ɑ in the lung tissue homogenate (pg/mg, x - ± s)
| Group | n | 2W | 8W | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | IL-1β | IL-6 | TNF-α | IL-1β | IL-6 | |||||
| Normal | 6 | 11.2±1.5 | 53.2±4.7 | 912.0±144.7 | 14.8±1.1 | 70.0±8.0 | 1229.8±70.3 | |||
| Model | 6 | 22.2±3.9a | 119.0±28.4a | 1445.2±198.3a | 21.8±2.3a | 131.5±22.2a | 1422.5±158.6a | |||
| YCF | 6 | 16.6±1.8b | 73.7±25.5b | 1166.6±135.0b | 17.2±2.9b | 83.8±2.9b | 1157.8±103.3b | |||
| TET | 6 | 16.8±1.6b | 82.5±23.4b | 1124.3±80.4b | 18.1±0.7b | 71.1±14.1b | 1074.3±73.9b | |||

Figure 2 YCF inhibited the macrophages polarization on silicosis rats A: expression level of CD68 (× 200) in silicosis rats on week 2 and 8; A1-A4: the CD68 expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 2; A5-A6: the CD68 expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 8. B: expression level of iNOS (× 200) in silicosis rats on week 2 and 8; B1-B4: the iNOS expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 2; B5-B6: the iNOS expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 8. C: expression level of CD206 (× 200) in silicosis rats on week 2 and 8; C1-C4: the CD206 expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 2; C5-C6: the CD206 expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 8. D: expression level of Arg-1 (× 200) in silicosis rats on week 2 and 8; D1-D4: the Arg-1 expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 2; D5-D6: the Arg-1 expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 8. E: expression level of TGF-β (× 200) in silicosis rats on week 8. E1-E4: the TGF-β expression of Normal, Model, YCF and TET in week 8. Normal: healthy control rats; Model: silicosis rats; YCF: YCF treatment rats were intragastrically administered with 3.3663 g·kg-1·d-1 or 0.84 mL/100 g, once daily, from weeks 5-8; TET: tetrandrine treatment rats were intragastrically administered with 27 mg·kg-1·d-1 TET, from weeks 5-8. n = 6. YCF: Yangqing Chenfei formula; TET: tetrandrine; Arg-1: Arginase-1; iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-beta.
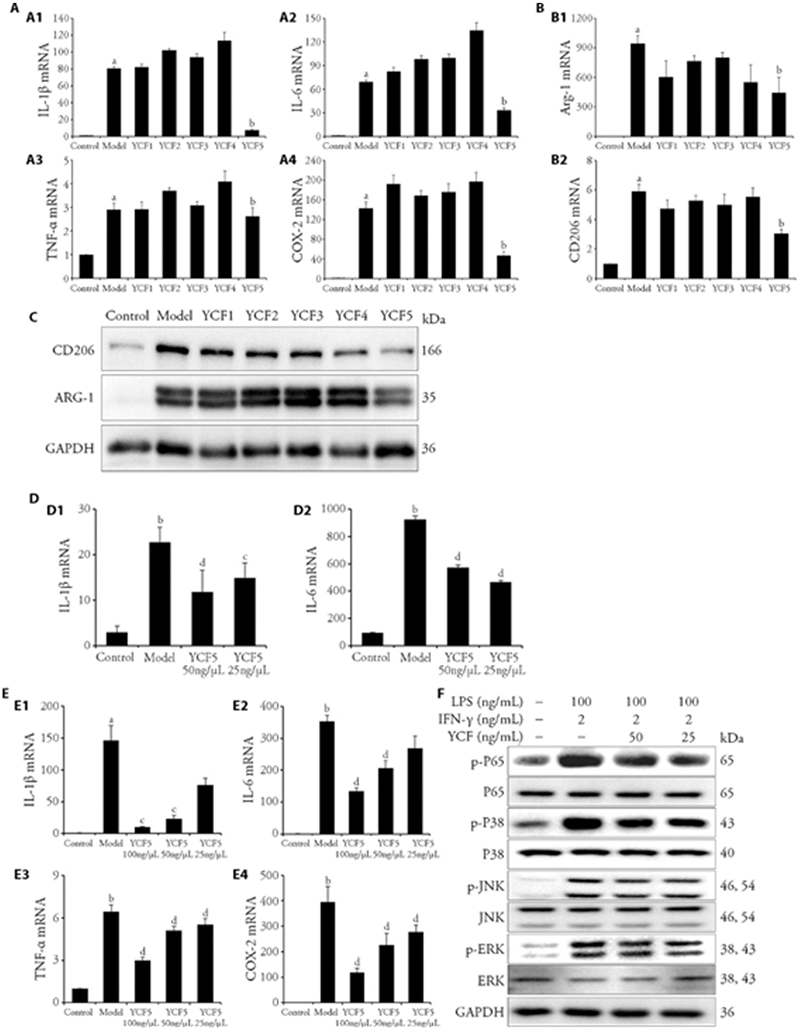
Figure 3 Effects of the substances of YCF and the effective segment of YCF (YCF5) suppressed macrophage polarization in MH-S MH-S were treated with different segments of YCF (100 μg/mL YCF1-5) for 3-6 h, and exposed to IFN-γ (2 ng/mL) + LPS (100 ng/mL) or IL-4 (20 ng/mL) for 12 h. A: RT-qPCR was applied to determine the mRNA expressions of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and COX-2 in M1 macrophages. MH-S were treated with different segments of YCF (100 μg/mL YCF1-5) for 3-6 h, and exposed to IFN-γ (2 ng/mL) + LPS (100 ng/mL) for 12 h. B: RT-qPCR was applied to determine the mRNA expressions of Arg-1 and CD206 in M2 macrophages; C: Protein expressions of CD206 and Arg-1 in M2 macrophages were detected by Western blotting; MH-S were treated with different segments of YCF (100 μg/mL YCF1-5) for 3-6 h, and exposed to IL-4 (20 ng/mL) for 12 h. GAPDH was used as the control. All data were showed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). aP < 0.01, vs control macrophages; bP < 0.01, vs model macrophages. D: protein levels of IL-1β and IL-6 in the culture medium were determined by ELISA; E: mRNA expressions of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and COX-2 in M1 macrophages. F: Western blotting assay was used to determine the protein expressions of p-JNK, JNK, p-ERK, ERK, p-P38, P38, p-P65, and P65 in M1 macrophages; MH-S were treated with different concentrations of YCF5 (100, 50, 25 μg/mL) for 3-6 h, and exposed to IFN-γ (2 ng/mL) + LPS (100 ng/mL) for 12 h. GAPDH was used as the control. Control: normal macrophages; Model: IFN-γ + LPS or IL-4 induced macrophages; YCF5 100, 50, 25 μg/mL: Macrophages treated with different concentrations of YCF5 (100, 50, 25 μg/mL). YCF: Yangqing Chenfei formula; TET: tetrandrine; MH-S: murine alveolar macrophage cell line; LPS: lipopolysaccharides; IFN-γ: interferon-gamma; IL-4: interleukin-4; RT-qPCR: real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase; ELISA: enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; p-JNK: phosphorylated C-Jun kinase enzyme; JNK: C-Jun kinase enzyme; p-ERK: phosphorylated extracellular signal regulated kinases; ERK: extracellular signal regulated kinases; IL-1β: interleukin-1 beta; IL-6: interleukin-6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; COX-2: cyclooxygenase-2. Arg-1: arginase-1; CD206: macrophage mannose receptor 1. All data were showed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vs Control macrophages; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, vs model macrophages.
| Group | n | p-P65/GAPDH | p-P38/GAPDH | p-JNK/GAPDH | p-ERK/GAPDH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3 | 0.399±0.231 | 0.153±0.059 | 0.069±0.018 | 0.185±0.073 |
| Model | 3 | 1.375±0.358a | 0.743±0.107a | 0.832±0.123a | 0.787±0.074a |
| YCF5 50 μg/mL | 3 | 0.754±0.101b | 0.433±0.053b | 0.548±0.160c | 0.438±0.042b |
| YCF5 25 μg/mL | 3 | 0.892±0.254b | 0.477±0.075b | 0.584±0.116c | 0.403±0.016b |
Table 6 Protein expressions of p-JNK, p-ERK, p-P38, p-P6 in M1 macrophages( x - ± s)
| Group | n | p-P65/GAPDH | p-P38/GAPDH | p-JNK/GAPDH | p-ERK/GAPDH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3 | 0.399±0.231 | 0.153±0.059 | 0.069±0.018 | 0.185±0.073 |
| Model | 3 | 1.375±0.358a | 0.743±0.107a | 0.832±0.123a | 0.787±0.074a |
| YCF5 50 μg/mL | 3 | 0.754±0.101b | 0.433±0.053b | 0.548±0.160c | 0.438±0.042b |
| YCF5 25 μg/mL | 3 | 0.892±0.254b | 0.477±0.075b | 0.584±0.116c | 0.403±0.016b |

Figure 4 YCF attenuated IL-4-induced macrophage polarization in MH-S The MH-S cells were treated with different concentrations of YCF5 (50, 25 μg/mL) for 3-6 h, and exposed to IL-4 (20 ng/mL) for 12 h. A: immunofluorescence analysis of Arg-1 expression in M2 macrophages. A1: DAPI expression of Control group; A2: Arg-1 expression of Control group; A3: merged expression of Control group; A4: DAPI expression of Model group; A5: Arg-1 expression of Model group; A6: merged expression of Model group; A7: DAPI expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group; A8: Arg-1 expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group; A9: merged expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group. B: immunofluorescence analysis of CD206 expression in M2 macrophages. B1: DAPI expression of Control group; B2: CD206 expression of Control group; B3: merged expression of Control group; B4: DAPI expression of Model group; B5: CD206 expression of Model group; B6: merged expression of Model group; B7: DAPI expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group; B8: CD206 expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group; B9: Merged expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group. C: immunofluorescence analysis of p-STAT6 expression in M2 macrophages. C1: DAPI expression of Control group; C2: p-STAT6 expression of Control group; C3: merged expression of Control group; C4: DAPI expression of Model group; C5: p-STAT6 expression of Model group; C6: merged expression of Model group; C7: DAPI expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group; C8: p-STAT6 expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group; C9: merged expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group. D: immunofluorescence analysis of TGF-β expression in M2 macrophages. D1: DAPI expression of Control group; D2: TGF-β expression of Control group; D3: merged expression of Control group; D4: DAPI expression of Model group; D5: TGF-β expression of Model group; D6: Merged expression of Model group; D7: DAPI expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group; D8: TGF-β expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group; D9: merged expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group. E: immunofluorescence analysis of CTGF expression in M2 macrophages. E1: DAPI expression of Control group; E2: CTGF expression of Control group; E3: merged expression of Control group; E4: DAPI expression of Model group; E5: CTGF expression of Model group; E6: merged expression of Model group; E7: DAPI expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group; E8: CTGF expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group; E9: merged expression of 50 μg/mL YCF5 group. The images were taken at × 400 magnification. F: Western blot assay of Arg-1, CD206 and p-STAT6 protein expressions in M2 macrophages. GAPDH was used as control. Control: normal macrophages; Model: IL-4 induced macrophages; YCF5 50, 25 μg/mL: M2 macrophages treated with different concentrations of YCF5 (50, 25 μg/mL). Arg-1: Arginase-1; CD206: Macrophage mannose receptor 1; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-β; CTGF: connective tissue growth factor. YCF: Yangqing Chenfei formula; MH-S: murine alveolar macrophage cell line; IL-4: interleukin-4; RT-qPCR: real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; p-STAT6: phosphorylated signal transducers and activators of transcription 6; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase.
| Group | n | ARG-1 | CD206 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3 | 1.0±0.0 | 1.0±0.0 |
| Model | 3 | 227.7±11.7a | 9.3±2.1a |
| YCF5 100 μg/mL | 3 | 165.1±2.8b | 4.3±1.1c |
| YCF5 50 μg/mL | 3 | 195.2±14.3 | 6.0±1.4b |
| YCF5 25 μg/mL | 3 | 269.8±12.8 | 7.5±1.3 |
Table 7 mRNA expressions of Arg-1 and CD206 in M2 macrophages ( x - ± s)
| Group | n | ARG-1 | CD206 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3 | 1.0±0.0 | 1.0±0.0 |
| Model | 3 | 227.7±11.7a | 9.3±2.1a |
| YCF5 100 μg/mL | 3 | 165.1±2.8b | 4.3±1.1c |
| YCF5 50 μg/mL | 3 | 195.2±14.3 | 6.0±1.4b |
| YCF5 25 μg/mL | 3 | 269.8±12.8 | 7.5±1.3 |
| Group | n | CD206 /GAPDH | Arg-1/GAPDH | p-STAT6/GAPDH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3 | 0.21±0.07 | 0.15±0.12 | 0.00±0.00 |
| Model | 3 | 0.82±0.16a | 2.64±1.01a | 1.30±0.28a |
| YCF5 50 μg/mL | 3 | 0.44±0.09b | 1.77±0.72 | 1.29±0.11 |
| YCF5 25 μg/mL | 3 | 0.41±0.06b | 1.76±0.78 | 1.23±0.07 |
Table 8 Protein expressions of Arg-1, CD206 and p-STAT6 in M2 macrophage ( x - ± s)
| Group | n | CD206 /GAPDH | Arg-1/GAPDH | p-STAT6/GAPDH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3 | 0.21±0.07 | 0.15±0.12 | 0.00±0.00 |
| Model | 3 | 0.82±0.16a | 2.64±1.01a | 1.30±0.28a |
| YCF5 50 μg/mL | 3 | 0.44±0.09b | 1.77±0.72 | 1.29±0.11 |
| YCF5 25 μg/mL | 3 | 0.41±0.06b | 1.76±0.78 | 1.23±0.07 |
| 1. | Fernández Álvarez R, Martínez González C, Quero Martínez A, Blanco Pérez JJ, Carazo Fernández L, Prieto Fernández A. Guidelines for the diagnosis and monitoring of silicosis. Arch Bronconeumol 2015; 51: 86-93. |
| 2. |
Rimal B, Greenberg AK, Rom WN. Basic pathogenetic mechanisms in silicosis: current understanding. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2005; 11: 169-73.
PMID |
| 3. | Leung CC, Yu ITS, Chen W. Silicosis. Lancet Lond Engl 2012; 379: 2008-18. |
| 4. |
Reynolds K, Jerome J. Silicosis. Workplace Health Saf 2021; 69: 51.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Pollard KM. Silica, silicosis, and autoimmunity. Front Immunol 2016; 7: 97.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Lu Y, Li C, Du S, et al. 4-1BB signaling promotes alveolar macrophages-mediated pro-fibrotic responses and crystalline silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Front Immunol 2018; 9: 1848.
DOI PMID |
| 7. |
Adamcakova J, Mokra D. New insights into pathomechanisms and treatment possibilities for lung silicosis. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 4162.
DOI URL |
| 8. |
Liu T, Liu X, Li W. Tetrandrine, a Chinese plant-derived alkaloid, is a potential candidate for cancer chemotherapy. Oncotarget 2016; 7: 40800-15.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Song MY, Wang JX, Sun YL, et al. Tetrandrine alleviates silicosis by inhibiting canonical and non-canonical NLRP3 inflammasome activation in lung macrophages. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2022; 43: 1274-84.
DOI |
| 10. |
Li J, Zhao H, Xie Y, et al. Clinical efficacy of comprehensive therapy based on Traditional Chinese Medicine patterns on patients with pneumoconiosis: a pilot double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled study. Front Med 2022; 16: 736-44.
DOI |
| 11. |
Huaux F. New developments in the understanding of immunology in silicosis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 7: 168-73.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Zhao Y, Hao C, Bao L, et al. Silica particles disorganize the polarization of pulmonary macrophages in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2020; 193: 110364.
DOI URL |
| 13. |
Murray PJ. Macrophage polarization. Annu Rev Physiol 2017; 79: 541-66.
DOI PMID |
| 14. |
Du S, Li C, Lu Y, et al. Dioscin alleviates crystalline silica-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis through promoting alveolar macrophage autophagy. Theranostics 2019; 9: 1878-92.
DOI PMID |
| 15. | Greenberg MI, Waksman J, Curtis J. Silicosis: a review. Dis-Mon DM 2007; 53: 394-416. |
| 16. |
Yang M, Qian X, Wang N, et al. Inhibition of MARCO ameliorates silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Toxicol Lett 2019; 301: 64-72.
DOI PMID |
| 17. |
Hamilton RF, Thakur SA, Holian A. Silica binding and toxicity in alveolar macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med 2008; 44: 1246-58.
DOI URL |
| 18. | Tan S, Chen S. Macrophage autophagy and silicosis: current perspective and latest insights. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: E453. |
| 19. | Fu R, Li Q, Fan R, et al. iTRAQ-based secretome reveals that SiO2 induces the polarization of RAW264.7 macrophages by activation of the NOD-RIP2-NF-κB signaling pathway. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2018; 63: 92-102. |
| 20. |
Hu S, Zhao H, Al-Humadi NH, Yin XJ, Ma JKH. Silica-induced apoptosis in alveolar macrophages: evidence of in vivo thiol depletion and the activation of mitochondrial pathway. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2006; 69: 1261-84.
DOI URL |
| 21. | Michalik M, Wójcik-Pszczoła K, Paw M, et al. Fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition in bronchial asthma. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 2018; 75: 3943-61. |
| 22. |
Chen S, Tan S, Yang S, et al. Nicotine induces apoptosis through exacerbation of blocked alveolar macrophage autophagic degradation in silicosis. Toxicol Lett 2020; 334: 94-101.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
Carneiro PJ, Clevelario AL, Padilha GA, et al. Bosutinib therapy ameliorates lung inflammation and fibrosis in experimental silicosis. Front Physiol 2017; 8: 159.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Huang R, Hao C, Wang D, et al. SPP1 derived from silica-exposed macrophage exosomes triggers fibroblast transdifferentiation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2021; 422: 115559.
DOI URL |
| 25. |
Kishore A, Petrek M. Roles of Macrophage polarization and macrophage-derived miRNAs in pulmonary fibrosis. Front Immunol 2021; 12: 678457.
DOI URL |
| 26. |
Cheng P, Li S, Chen H. Macrophages in lung injury, repair, and fibrosis. Cells 2021; 10: 436.
DOI URL |
| 27. |
Li J, Yao W, Zhang L, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis in lung fibroblasts co-cultured with silica-exposed alveolar macrophages. Respir Res 2017; 18: 91.
DOI URL |
| 28. |
Liu Y, Li Y, Xu Q, et al. Long non-coding RNA-ATB promotes EMT during silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by competitively binding miR-200c. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2018; 1864: 420-31.
DOI URL |
| 29. | Zhang ZQ, Tian HT, Liu H, Xie R. The role of macrophage-derived TGF-β1 on SiO2-induced pulmonary fibrosis: a review. Toxicol Ind Health 2021; 37: 240-50. |
| 30. |
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol 2018; 233: 6425-40.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Sica A, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 787-95.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Bashir S, Sharma Y, Elahi A, Khan F. Macrophage polarization: the link between inflammation and related diseases. Inflamm Res Off J Eur Histamine Res Soc Al 2016; 65: 1-11. |
| 33. |
Lai JL, Liu YH, Liu C, et al. Indirubin inhibits LPS-induced inflammation via TLR4 abrogation mediated by the NF-kB and MAPK signaling pathways. Inflammation 2017; 40: 1-12.
DOI URL |
| 34. | Jiménez-García L, Higueras MÁ, Herranz S, et al. A hispanolone-derived diterpenoid inhibits M2-Macrophage polarization in vitro via JAK/STAT and attenuates chitin induced inflammation in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol 2018; 154: 373-83. |
| 35. |
Wang N, Liang H, Zen K. Molecular mechanisms that influence the macrophage m1-m2 polarization balance. Front Immunol 2014; 5: 614.
DOI PMID |
| 36. | Bi Y, Chen J, Hu F, Liu J, Li M, Zhao L. M2 macrophages as a potential target for antiatherosclerosis treatment. Neural Plast 2019; 2019: 6724903. |
| 37. | Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD, Hunninghake GW, Crystal RG. Bleomycin-induced interstitial pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis 1979; 120: 893-9. |
| 38. |
Ashcroft T, Simpson JM, Timbrell V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J Clin Pathol 1988; 41: 467-70.
DOI PMID |
| 39. |
Liu L, Guo H, Song A, et al. Progranulin inhibits LPS-induced macrophage M1 polarization via NF-кB and MAPK pathways. BMC Immunol 2020; 21: 32.
DOI |
| 40. |
Kang HH, Kim IK, Lee HI, et al. Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces liver fibrosis in mice with diet-induced obesity via TLR4/MyD88/MAPK/NF-kB signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2017; 490: 349-55.
DOI URL |
| 41. |
Walford HH, Doherty TA. STAT6 and lung inflammation. JAK-STAT 2013; 2: e25301.
DOI URL |
| 42. |
Liew PX, Kubes P. The neutrophil’s role during health and disease. Physiol Rev 2019; 99: 1223-48.
DOI URL |
| 43. |
Thakur SA, Beamer CA, Migliaccio CT, Holian A. Critical role of MARCO in crystalline silica-induced pulmonary inflammation. Toxicol Sci Off J Soc Toxicol 2009; 108: 462-71.
DOI URL |
| 44. |
Bystrom J, Evans I, Newson J, et al. Resolution-phase macrophages possess a unique inflammatory phenotype that is controlled by cAMP. Blood 2008; 112: 4117-27.
DOI PMID |
| 45. |
Barbarin V, Xing Z, Delos M, Lison D, Huaux F. Pulmonary overexpression of IL-10 augments lung fibrosis and Th2 responses induced by silica particles. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2005; 288: L841-8.
DOI URL |
| 46. |
Dong J, Yu X, Porter DW, Battelli LA, Kashon ML, Ma Q. Common and distinct mechanisms of induced pulmonary fibrosis by particulate and soluble chemical fibrogenic agents. Arch Toxicol 2016; 90: 385-402.
DOI PMID |
| 47. |
Zhao H, Jiang Z, Lü R, et al. Transcriptome profile analysis reveals a silica-induced immune response and fibrosis in a silicosis rat model. Toxicol Lett 2020; 333: 42-8.
DOI PMID |
| 48. |
Driscoll KE, Lindenschmidt RC, Maurer JK, Perkins L, Perkins M, Higgins J. Pulmonary response to inhaled silica or titanium dioxide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1991; 111: 201-10.
DOI URL |
| 49. | Pu X, Wen H, Dou H, et al. Pathologic observation on animal model of silicosis. Zhong Hua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2011; 29: 761-5. |
| 50. |
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 2014; 41: 14-20.
DOI PMID |
| 51. |
Orecchioni M, Ghosheh Y, Pramod AB, Ley K. Macrophage polarization: different gene signatures in M1(LPS+) vs classically and M2(LPS-) vs alternatively activated macrophages. Front Immunol 2019; 10: 1084.
DOI PMID |
| 52. |
Zhai R, Ge X, Li H, Tang Z, Liao R, Kleinjans J. Differences in cellular and inflammatory cytokine profiles in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in bagassosis and silicosis. Am J Ind Med 2004; 46: 338-44.
PMID |
| 53. |
Liu H, Fang S, Wang W, et al. Macrophage-derived MCPIP mediates silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis via autophagy. Part Fibre Toxicol 2016; 13: 55.
DOI URL |
| 54. |
Zhou Z, Jiang R, Yang X, et al. circRNA mediates silica-induced macrophage activation via HECTD1/ZC3H12A-dependent ubiquitination. Theranostics 2018; 8: 575-92.
DOI URL |
| 55. | Wu LJ, He XY, Wang WX, et al. Dahuang Zhechong Pills suppress silicosis fibrosis progression via p 38 MAPK/TGF-β1/Smad pathway in vitro. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med ECAM 2021; 2021: 6662261. |
| 56. | Lawrence T. The nuclear factor NF-kappa B pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2009; 1: a001651. |
| 57. |
Necela BM, Su W, Thompson EA. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates cross-talk between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and nuclear factor-kappa B in macrophages. Immunology 2008; 125: 344-58.
DOI PMID |
| 58. |
Rayees S, Rochford I, Joshi JC, Joshi B, Banerjee S, Mehta D. Macrophage TLR4 and PAR2 signaling: role in regulating vascular inflammatory injury and repair. Front Immunol 2020; 11: 2091.
DOI PMID |
| 59. | Yu G, Yu H, Yang Q, et al. Vibrio harveyi infections induce production of proinflammatory cytokines in murine peritoneal macrophages via activation of p 38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways, but reversed by PI3K/AKT pathways. Dev Comp Immunol 2022; 127: 104292. |
| 60. |
Kim EK, Choi EJ. Compromised MAPK signaling in human diseases: an update. Arch Toxicol 2015; 89: 867-82.
DOI PMID |
| 61. |
Mendis E, Kim MM, Rajapakse N, Kim SK. Suppression of cytokine production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse macrophages by novel cationic glucosamine derivative involves down-regulation of NF-kappa B and MAPK expressions. Bioorg Med Chem 2008; 16: 8390-6.
DOI URL |
| 62. | An Y, Zhang H, Wang C, et al. Activation of ROS/MAPKs/NF-κB/NLRP3 and inhibition of efferocytosis in osteoclast-mediated diabetic osteoporosis. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 2019; 33: 12515-27. |
| 63. |
Ghosh S, Karin M. Missing pieces in the NF-kappa B puzzle. Cell 2002; 109 Suppl: S81-96.
DOI URL |
| 64. | Zhang Y, Gu X, Li D, Cai L, Xu Q. METTL3 regulates osteoblast differentiation and inflammatory response via smad signaling and MAPK signaling. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 21: E199. |
| 65. |
Gordon S, Plüddemann A, Martinez Estrada F. Macrophage heterogeneity in tissues: phenotypic diversity and functions. Immunol Rev 2014; 262: 36-55.
DOI PMID |
| 66. |
Zhang L, Wang Y, Wu G, Xiong W, Gu W, Wang CY. Macrophages: friend or foe in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Respir Res 2018; 19: 170.
DOI |
| 67. |
Tao H, Zhao H, Ge D, et al. Necroptosis in pulmonary macrophages promotes silica-induced inflammation and interstitial fibrosis in mice. Toxicol Lett 2022; 355: 150-9.
DOI URL |
| 68. |
Li C, Lu Y, Du S, et al. Dioscin exerts protective effects against crystalline silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Theranostics 2017; 7: 4255-75.
DOI PMID |
| 69. |
Duan J, Liu X, Wang H, Guo SW. The M2a macrophage subset may be critically involved in the fibrogenesis of endometriosis in mice. Reprod Biomed Online 2018; 37: 254-68.
DOI PMID |
| 70. |
Yao G, Bai Z, Niu J, et al. Astragalin attenuates depression-like behaviors and memory deficits and promotes M2 microglia polarization by regulating IL-4R/JAK1/STAT6 signaling pathway in a murine model of perimenopausal depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2022; 239: 2421-43.
DOI |
| [1] | CHEN Yunhu, YIN Moqing, FAN Lihua, JIANG Xuechun, ZHANG Tao, ZHU Xingyu, XU Hongfeng. Mirror-like tongue is an important predictor of acute heart failure: a cohort study of acute heart failure in Chinese patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1243-1251. |
| [2] | ZHU Lingyan, WEI Yihong, WANG Youhua, YANG Jianmei, LI Jiawei, CAO Min, ZHOU Duan. Protective efficacy of Shenge San (参蛤散) on mitochondria in H9c2 cardiomyocytes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 892-899. |
| [3] | ZHANG Jiaying, WEI Xiangxiang, LI Xuefeng, YUAN Yang, DOU Yinghuan, SHI Yanbin, XIE Ping, ZHOU Mengru, ZHAO Junnan, LI Miao, ZHANG Shuwen, ZHU Rui, TIAN Ying, TAN Hao, TIAN Feifei. Shunxin decoction (顺心组方) improves diastolic function in rats with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction induced by abdominal aorta constriction through cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase Signaling Pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 764-772. |
| [4] | CHEN Yunhu, FAN Lihua, ZHANG Tao, LIU Xueqian. Effectiveness of Zhuling decoction (猪苓汤) on diuretic resistance in patients with heart failure: a randomized, controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 439-445. |
| [5] | WANG Wei, LI Qingling, MA Qiang, XIA Ran, GAO Bing, WANG Yi, WANG Jing. Effects of moxibustion at bilateral Feishu (BL13) and Xinshu (BL15) combined with benazepril on myocardial cells apoptosis index and apoptosis-related proteins cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor in rats with chronic heart failure [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 227-233. |
| [6] | GU Xiaoli, CHEN Menglei, LIU Minghui, ZHANG Zhe, ZHAO Weiwei, CHENG Wenwu. Value of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome differentiation in predicting the survival time of patients with advanced cancer [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 636-641. |
| [7] | Fu Mingming, Wang Zhiqian, Liu Yan. Effects of Xinkeshu combined with levosimendan on perioperative heart failure in oldest-old patients with hip fractures [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 870-874. |
| [8] | Li Xiaoqian, Huang Pinxian, Wang Shijun, Cao Xuebin, He Jiancheng. Transforming growth factor β1 is a differentially expressed candidate protein of congestive heart failure with Qi-deficiency-blood-stasis syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(2): 311-316. |
| [9] | Yu Mei, Guo Hangyuan, Ye Lingling, Bian Jiaping, Ma Lijuan, Zheng Chunli. Effect of Jiawei Shenfu decoction on tumor necrosis factor-alpha and nuclear factor-kappa B in patients who have chronic heart failure with syndromes of deficiency of heart Yang [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(03): 418-424. |
| [10] | Gao Ling, Yang Ting, Zhu Jiaqi, Xu Lei, Su Li, Wang Di. Effect of Qiangxin Huoli decoction on rats with adriamycin-induced chronic heart failure [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(01): 81-88. |
| [11] | Liu Yaru, Zhao Jianxin, Tian Yuanxiang. Efficacy and safety of electroacupuncture in treatment of lumbar disc herniation: a protocol for a cohort study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(01): 127-132. |
| [12] | Gao Wulin, Dai Guohua, Zhang Tong, Bi Dongxue, Liu Chunhua, Shi Xiaojing, Zhao Fang, Zhao Chen. Tonifying Qi and activating blood circulation in terms of Traditional Chinese Medicine: their effects in patients with myocardial infarction [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(05): 726-732. |
| [13] | Guo Yuhong, Di Tingting, Zhao Jingxia, Xu Xiaolong, Li Ping, Huang Lijuan, Liu Qingquan. Fuxin decoction attenuates doxorubicin-induced heart failure in rats via oxidizing suppression and regulating immune responses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(04): 579-584. |
| [14] | Dai Guohua, Gao Wulin, Bi Dongxue, Liu Chunhua, Liu Yuhan, Wang Ning, Zhao Chen. Efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine in patients with acute myocardial infarction suffering from diabetes mellitus [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(03): 412-418. |
| [15] | Wang Xianliang, Hou Yazhu, Mao Jingyuan, Zhao Yingqiang, Niu Tianfu, Yuan Ruyu, Wang Yonggang, Cui Jinrong, Shi Le, Jia Xiuli, Fan Ruihong, Lin Qian, Zhang Yan, Li Zhijun, Shang Hongcai, Wang Baohe, Wang Hongwu, Wang Henghe, Cui Xiaolei, Soh Shanbin, Ruan Jishou, Zhang Boli. Western medication plus Traditional Chinese Medicine preparations in patients with chronic heart failure: a prospective, single-blind,randomized, controlled, and multicenter clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(06): 756-766. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

