Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 417-425.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.03.008
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of phospholipid complex of flavonoids from persimmon leaves on atherosclerosis, and possible mechanism
CHEN Jinpeng1,2,3, ZHANG Kexia4, LIU Yi1,2,3, JIN Song5, GAI Xiaohong1,2,3, REN Tao1,2,3, TIAN Chengwang1,2,3( )
)
- 1 State Key Laboratory of Drug Delivery and Pharmacokinetics, Tianjin 300301, China
2 Tianjin Key Laboratory of TCM quality markers, Tianjin 300301, China
3 Tianjin Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, Tianjin 300301, China
4 Tianjin Pharmaceutial Research Institute Co. Ltd., Tianjin 300462, China
5 Sinopharm Group Tianjin Co. Ltd., Tianjin 300040, China
-
Received:2021-09-10Accepted:2021-11-15Online:2022-06-15Published:2022-05-20 -
Contact:TIAN Chengwang -
About author:TIAN Chengwang, State Key Laboratory of Drug Delivery and Pharmacokinetics, Tianjin 300301, China; Tianjin Key Laboratory of TCM quality markers, Tianjin 300301, China; Tianjin Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, Tianjin 300301, China. tiancw@tjipr.com,Telephone: +86-13672157582
-
Supported by:National Science and Technology Major Project of China (Research on Evaluation Technology of New Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on Big Data of Classical Prescription)(2019ZX09201005);International Cooperation Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine (China-Germany International Cooperation in Innovative Research and Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Botanical Medicine)(0610-2140NF020630)
Cite this article
CHEN Jinpeng, ZHANG Kexia, LIU Yi, JIN Song, GAI Xiaohong, REN Tao, TIAN Chengwang. Efficacy of phospholipid complex of flavonoids from persimmon leaves on atherosclerosis, and possible mechanism[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 417-425.
share this article
| Peak | tR | Formula | Calculated | Measured | Error (ppm) | Main fragment ions (m/z) | Identification | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | (min) | [M-H]-/[M+H]+ | [M-H]-/[M+H]+ | |||||||||||||
| 1 | 0.82 | C7H6O2 | --/123.0446 | --/123.0443 | -2.4 | Benzoic acid | ||||||||||
| 2 | 0.83 | C15H14O7 | 305.0661/-- | 305.0660 /-- | -0.3 | 179.0296[M-H-C6H5O3]- 125.0239[M-H-C9H7O4]- | Epigallocatechin15 | |||||||||
| 3 | 0.94 | C7H6O5 | 169.0137/-- | 169.0133 /-- | -2.4 | 125.0230 [M-H-CO2]- | Gallic acid16 | |||||||||
| 4 | 0.99 | C15H14O7 | 305.0661/-- | 305.0660 /-- | -0.3 | 179.0295 [M-H-C6H5O3]- 125.0237 [M-H-C9H7O4]- | Gallocatechin15 | |||||||||
| 5 | 1.00 | C7H6O3 | --/139.0395 | --/ 139.0390 | -3.6 | 122.0846[M+2H-H2O]+ | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid16 | |||||||||
| 6 | 1.07 | C7H6O4 | 153.0188/-- | 153.0184 /-- | -2.6 | 109.0296 [M-H-CO2]- | 2,5-dihydroxyben-zoic acid16 | |||||||||
| 7 | 1.10 | C8H10O3 | 153.0552/-- | 153.0548 /-- | -2.6 | 125.0226 [M-H-CO]- | Hydroxytyrosol17 | |||||||||
| 8 | 1.35 | C15H14O6 | 289.0712/-- | 289.0713 /-- | 0.3 | 245.0804 [M-H-CO2]- 205.0503 [M-H-2C2H2O]- | Catechin | |||||||||
| 9 | 1.44 | C7H6O3 | --/139.0395 | --/ 139.0389 | 4.3 | 121.0328 [M+H-H2O]+ | 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid16 | |||||||||
| 10 | 2.63 | C21H20O13 | 479.0826/-- | 479.0842 /-- | 3.3 | 317.0219 [M-H-glc]- 121.0288 [M-H-glc-C7H4O4-CO2]- | Myricetin-3-O-glucopyranoside18 | |||||||||
| 11 | 2.96 | C15H10O8 | --/319.0454 | --/ 319.0439 | -4.7 | 303.0418 [M+H-H2O]+ 150.1165 [M+H-H2O-C7H4O4]+ | Myricetin18 | |||||||||
| 12 | 3.30 | C9H10O5 | 197.0450/-- | 197.0449 /-- | -0.5 | 153.0230 [M-H-CO2]- | Syringic acid16 | |||||||||
| 13* | 4.66 | C21H20O12 | 463.0877/-- | 463.0880 /-- | 0.6 | 301.0282 [M-H-glu]- 151.0073 [M-H-glu-C8H6O3]- | Hyperoside/isoquercetin19 | |||||||||
| 14* | 5.06 | C28H24O16 | 615.0986/-- | 615.0977 /-- | -1.5 | 463.0906 [M-H-C7H5O4]- 301.0331 [M-H-C7H5O4-glu]- | Quercetin 3-O-2”-galloylgalactoside/quercetin 3-O-2”- Galloylglucoside20 | |||||||||
| 15 | 5.62 | C20H18O11 | 433.0771/-- | 433.0742 /-- | -6.7 | 301.0318 [M-ara]- 151.0975 [M-ara-C8H6O3]- | Quercetin-3-O-arabinopyranoside21 | |||||||||
| 16 | 6.14 | C21H20O10 | --/433.1135 | --/ 433.1119 | -3.7 | 313.1023 [M+H-C4H9O4]+ | Vitexin | |||||||||
| 17* | 6.40 | C21H20O11 | 447.0927/-- | 447.0917 /-- | -2.2 | 301.0286 [M-H-rha]- | Quercitrin | |||||||||
| 18* | 7.02 | C21H20O11 | 447.0927/-- | 447.0937 /-- | 2.2 | 285.0392 [M-glu]-/[M-gal]- 151.0069 [M-H-C8H6O2-glu]- | Kaempferol-3-O-gl-ucopyranoside/Kae-mpferol-3-O-gal-actopyranoside | |||||||||
| 19 | 7.12 | C27H31O16 | 610.1534/-- | 610.1567 /-- | 5.4 | 447.0927 [M-H-glu]- 301.0321 [M-H-glu-rha]- | Quercetin-3-O-glucopyranosyl-(6→1)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside25 | |||||||||
| 20* | 7.22 | C28H24O15 | 599.1037/-- | 599.1053 /-- | 2.7 | 417.0817 [M-H-C7H5O4]- 285.0393 [M-H-C7H5O4-glu]- | Kaempferol-3-O-2" -galloylgalactoside/ kaempferol-3-O-2”- galloylglucoside20 | |||||||||
| 21* | 7.35 | C20H18O10 | 417.0822/-- | 417.0824 /-- | 0.5 | 285.0349 [M-H-xyl]- 285.0349 [M-H-ara]- | Kaempferol-3-O-xylopyranoside/kaempferol-3-O- arabinopyranoside21 | |||||||||
| 22 | 7.44 | C22H22O12 | 477.1033/-- | 477.1030 /-- | 0.6 | 315.0492 [M-glu]- 300.0279 [M-glu-CH3]- | Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucopyranoside | |||||||||
| 23 | 7.45 | C15H10O7 | --/303.0505 | --/ 303.0499 | -2.0 | 153.0092 [M+H-C8H6O3]+ | Quercetin26 | |||||||||
| 24 | 7.47 | C15H10O6 | 285.0399/-- | 285.0392 /-- | -2.5 | 151.0068 [M-H-C8H6O2]- | Kaempferol26 | |||||||||
| 25 | 7.55 | C16H12O7 | --/317.0661 | --/ 317.0654 | -2.2 | 287.0463 [M+H-CH3O]+ 153.0085 [M+H-C9H8O3]+ | Isorhamnetin17 | |||||||||
| 26 | 8.64 | C16H12O8 | --/333.0610 | --/ 333.0591 | -5.7 | 318.0304 [M+H-CH3]+ 291.0779 [M+2H-CH3-CO]+ | Annulatin26 | |||||||||
| 27 | 10.41 | C15H10O5 | --/271.0606 | --/271.0601 | -1.8 | 153.0082 [M+H-C8H6O]+ 118.0236 [M+H-C7H4O4]+ | Apigenin17 | |||||||||
| Peak | tR | Formula | Calculated | Measured | Error | main fragment ions (m/z) | Identification | |||||||||
| No. | (min) | [M-H]-/[M+H]+ | [M-H]-/[M+H]+ | (ppm) | ||||||||||||
| 28* | 15.72 | C30H50O2 | 441.3733/-- | 441.3726 /-- | -1.6 | 304.9840 [M-H-C9H14O]- | Betulin/Uvaol27 | |||||||||
| 29 | 17.22 | C30H50O | 425.3783/-- | 425.3775 /-- | -1.9 | 217.0106 [M-H-C14H24O]- | β-amyrin28 | |||||||||
| 30 | 20.06 | C30H48O3 | 455.3525/-- | 455.3526/-- | 0.2 | 202.0042 [M-H-C14H24O-COOH]- 189.9268 [M-H-C16H24O2-H2O]- | Oleanolic acid28 | |||||||||
| 31 | 20.52 | C30H48O3 | 455.3525/-- | 455.3526/-- | 0.2 | 189.9282 [M-H-C16H24O2-H2O]- | Betulinic acid27 | |||||||||
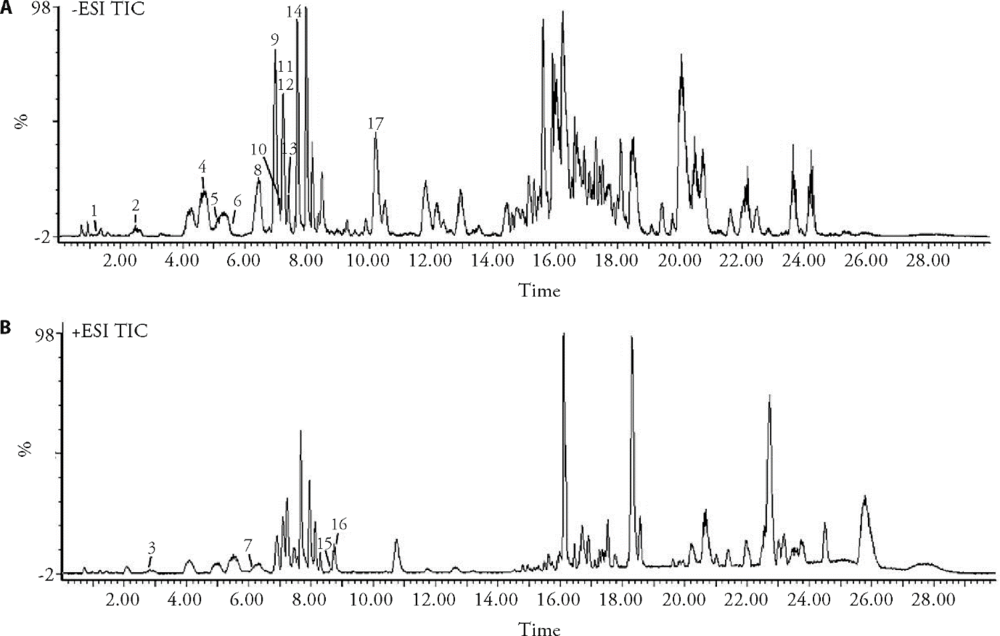
Table 1 List of the retention time and MS data (m/z) for each analyte identified in the PLF
| Peak | tR | Formula | Calculated | Measured | Error (ppm) | Main fragment ions (m/z) | Identification | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | (min) | [M-H]-/[M+H]+ | [M-H]-/[M+H]+ | |||||||||||||
| 1 | 0.82 | C7H6O2 | --/123.0446 | --/123.0443 | -2.4 | Benzoic acid | ||||||||||
| 2 | 0.83 | C15H14O7 | 305.0661/-- | 305.0660 /-- | -0.3 | 179.0296[M-H-C6H5O3]- 125.0239[M-H-C9H7O4]- | Epigallocatechin15 | |||||||||
| 3 | 0.94 | C7H6O5 | 169.0137/-- | 169.0133 /-- | -2.4 | 125.0230 [M-H-CO2]- | Gallic acid16 | |||||||||
| 4 | 0.99 | C15H14O7 | 305.0661/-- | 305.0660 /-- | -0.3 | 179.0295 [M-H-C6H5O3]- 125.0237 [M-H-C9H7O4]- | Gallocatechin15 | |||||||||
| 5 | 1.00 | C7H6O3 | --/139.0395 | --/ 139.0390 | -3.6 | 122.0846[M+2H-H2O]+ | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid16 | |||||||||
| 6 | 1.07 | C7H6O4 | 153.0188/-- | 153.0184 /-- | -2.6 | 109.0296 [M-H-CO2]- | 2,5-dihydroxyben-zoic acid16 | |||||||||
| 7 | 1.10 | C8H10O3 | 153.0552/-- | 153.0548 /-- | -2.6 | 125.0226 [M-H-CO]- | Hydroxytyrosol17 | |||||||||
| 8 | 1.35 | C15H14O6 | 289.0712/-- | 289.0713 /-- | 0.3 | 245.0804 [M-H-CO2]- 205.0503 [M-H-2C2H2O]- | Catechin | |||||||||
| 9 | 1.44 | C7H6O3 | --/139.0395 | --/ 139.0389 | 4.3 | 121.0328 [M+H-H2O]+ | 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid16 | |||||||||
| 10 | 2.63 | C21H20O13 | 479.0826/-- | 479.0842 /-- | 3.3 | 317.0219 [M-H-glc]- 121.0288 [M-H-glc-C7H4O4-CO2]- | Myricetin-3-O-glucopyranoside18 | |||||||||
| 11 | 2.96 | C15H10O8 | --/319.0454 | --/ 319.0439 | -4.7 | 303.0418 [M+H-H2O]+ 150.1165 [M+H-H2O-C7H4O4]+ | Myricetin18 | |||||||||
| 12 | 3.30 | C9H10O5 | 197.0450/-- | 197.0449 /-- | -0.5 | 153.0230 [M-H-CO2]- | Syringic acid16 | |||||||||
| 13* | 4.66 | C21H20O12 | 463.0877/-- | 463.0880 /-- | 0.6 | 301.0282 [M-H-glu]- 151.0073 [M-H-glu-C8H6O3]- | Hyperoside/isoquercetin19 | |||||||||
| 14* | 5.06 | C28H24O16 | 615.0986/-- | 615.0977 /-- | -1.5 | 463.0906 [M-H-C7H5O4]- 301.0331 [M-H-C7H5O4-glu]- | Quercetin 3-O-2”-galloylgalactoside/quercetin 3-O-2”- Galloylglucoside20 | |||||||||
| 15 | 5.62 | C20H18O11 | 433.0771/-- | 433.0742 /-- | -6.7 | 301.0318 [M-ara]- 151.0975 [M-ara-C8H6O3]- | Quercetin-3-O-arabinopyranoside21 | |||||||||
| 16 | 6.14 | C21H20O10 | --/433.1135 | --/ 433.1119 | -3.7 | 313.1023 [M+H-C4H9O4]+ | Vitexin | |||||||||
| 17* | 6.40 | C21H20O11 | 447.0927/-- | 447.0917 /-- | -2.2 | 301.0286 [M-H-rha]- | Quercitrin | |||||||||
| 18* | 7.02 | C21H20O11 | 447.0927/-- | 447.0937 /-- | 2.2 | 285.0392 [M-glu]-/[M-gal]- 151.0069 [M-H-C8H6O2-glu]- | Kaempferol-3-O-gl-ucopyranoside/Kae-mpferol-3-O-gal-actopyranoside | |||||||||
| 19 | 7.12 | C27H31O16 | 610.1534/-- | 610.1567 /-- | 5.4 | 447.0927 [M-H-glu]- 301.0321 [M-H-glu-rha]- | Quercetin-3-O-glucopyranosyl-(6→1)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside25 | |||||||||
| 20* | 7.22 | C28H24O15 | 599.1037/-- | 599.1053 /-- | 2.7 | 417.0817 [M-H-C7H5O4]- 285.0393 [M-H-C7H5O4-glu]- | Kaempferol-3-O-2" -galloylgalactoside/ kaempferol-3-O-2”- galloylglucoside20 | |||||||||
| 21* | 7.35 | C20H18O10 | 417.0822/-- | 417.0824 /-- | 0.5 | 285.0349 [M-H-xyl]- 285.0349 [M-H-ara]- | Kaempferol-3-O-xylopyranoside/kaempferol-3-O- arabinopyranoside21 | |||||||||
| 22 | 7.44 | C22H22O12 | 477.1033/-- | 477.1030 /-- | 0.6 | 315.0492 [M-glu]- 300.0279 [M-glu-CH3]- | Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucopyranoside | |||||||||
| 23 | 7.45 | C15H10O7 | --/303.0505 | --/ 303.0499 | -2.0 | 153.0092 [M+H-C8H6O3]+ | Quercetin26 | |||||||||
| 24 | 7.47 | C15H10O6 | 285.0399/-- | 285.0392 /-- | -2.5 | 151.0068 [M-H-C8H6O2]- | Kaempferol26 | |||||||||
| 25 | 7.55 | C16H12O7 | --/317.0661 | --/ 317.0654 | -2.2 | 287.0463 [M+H-CH3O]+ 153.0085 [M+H-C9H8O3]+ | Isorhamnetin17 | |||||||||
| 26 | 8.64 | C16H12O8 | --/333.0610 | --/ 333.0591 | -5.7 | 318.0304 [M+H-CH3]+ 291.0779 [M+2H-CH3-CO]+ | Annulatin26 | |||||||||
| 27 | 10.41 | C15H10O5 | --/271.0606 | --/271.0601 | -1.8 | 153.0082 [M+H-C8H6O]+ 118.0236 [M+H-C7H4O4]+ | Apigenin17 | |||||||||
| Peak | tR | Formula | Calculated | Measured | Error | main fragment ions (m/z) | Identification | |||||||||
| No. | (min) | [M-H]-/[M+H]+ | [M-H]-/[M+H]+ | (ppm) | ||||||||||||
| 28* | 15.72 | C30H50O2 | 441.3733/-- | 441.3726 /-- | -1.6 | 304.9840 [M-H-C9H14O]- | Betulin/Uvaol27 | |||||||||
| 29 | 17.22 | C30H50O | 425.3783/-- | 425.3775 /-- | -1.9 | 217.0106 [M-H-C14H24O]- | β-amyrin28 | |||||||||
| 30 | 20.06 | C30H48O3 | 455.3525/-- | 455.3526/-- | 0.2 | 202.0042 [M-H-C14H24O-COOH]- 189.9268 [M-H-C16H24O2-H2O]- | Oleanolic acid28 | |||||||||
| 31 | 20.52 | C30H48O3 | 455.3525/-- | 455.3526/-- | 0.2 | 189.9282 [M-H-C16H24O2-H2O]- | Betulinic acid27 | |||||||||
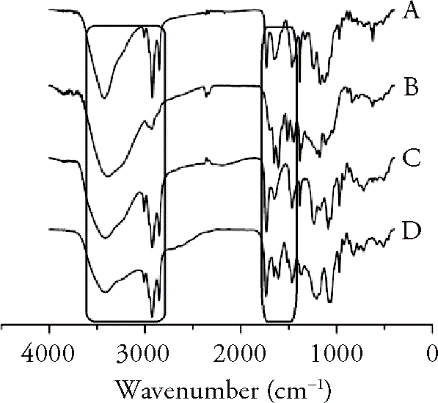
Figure 2 FTIR spectrum A: phospholipid; B: PLF; C: physical mixture; D: PLF-PC. FTIR: fourier transform infrared spectroscopy; PLF-PC: phospholipid complex of flavonoids from persimmon leaves.
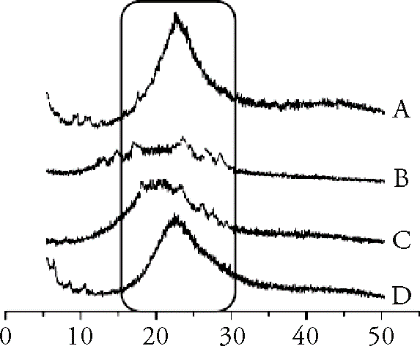
Figure 3 X-ray diffraction patterns A: phospholipid; B: PLF; C: physical mixture; D: PLF-PC. PLF-PC: phospholipid complex of flavonoids from per-simmon leaves.

Figure 4 SEM images A: phospholipid; B: PLF (B); C: physical mixture; D: PLF-PC. SEM: scanning electron microscopy; PLF-PC: phospholipid complex of flavonoids from persimmon leaves.
| 1 |
Mizuno Y, Jacob RF, Mason RP. Inflammation and the development of atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 2011; 18:351-8.
DOI URL |
| 2 |
Zhang SL, Guo CL, Chen ZG, et al. Vitexin alleviates ox-LDL-mediated endothelial injury by inducing autophagy via AMPK signaling activation. Mol Immunol 2017; 85:214-21.
DOI URL |
| 3 |
Xiao Y, Wang YC, Li LL, et al. Lactones from Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. Reduces atherosclerotic lesions in apoE-deficient mice via inhibiting over expression of NF-kB -dependent adhesion molecules. Fitoterapia 2014; 95:240-6.
DOI URL |
| 4 |
Chistiakov DA, Revin VV, Sobenin IA, et al. Vascular endothelium: functioning in norm, changes in atherosclerosis and current dietary approaches to improve endothelial function. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2015; 15:338-50.
PMID |
| 5 |
Zhang HP, Zheng FL, Zhao JH, et al. Genistein inhibits ox-LDL-induced VCAM-1, ICAM-1 and MCP-1 expression of HUVECs through heme oxygenase-1. Arch Med Res 2013; 44:13-20.
DOI URL |
| 6 | Takahashi Y, Zhu H, Yoshimoto T. Essential roles of lipoxygenases in LDL oxidation and development of atherosclerosis. Antioxid Redox Sign 2005; 7:425-31. |
| 7 | Pirillo A, Norata GD, Catapano AL. LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis. Mediat Inflamm 2013; 2013:15278-86. |
| 8 |
Deanfield JE, Halcox JP, Rabelink TJ. Endothelial function and dysfunction. Circulation 2007; 115:1285-95.
PMID |
| 9 |
Itabe H. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein as a biomarker of in vivo oxidative stress: from atherosclerosis to periodontitis. J Clin Biochem Nutr 2012; 51:1-8.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
Bei WJ, Peng WL, Ma Y, et al. NaoXinQing, an anti-stroke herbal medicine, reduces hydrogen peroxide-induced injury in NG108-15 cells. Neurosci Lett 2004; 363:262-5.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Akak CM, Djama CM, Nkengfack AE, et al. New coumarin glycosides from the leaves of Diospyros crassiflora (Hiern). Fitoterapia 2010; 81:873-7.
DOI URL |
| 12 |
Sun L, Zhang J, Fang K, et al. Flavonoids from persimmon (Diospyros kaki) leaves (FPL) attenuate H2O2-induced apoptosis in MC3T3-E1 cells via the NF-κB pathway. Food Funct 2014; 5:471-9.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Chen ZP, Sun J, Chen HX, et al. Comparative pharmacokinetics and bioavailability studies of quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin after oral administration of Ginkgo biloba extracts, Ginkgo biloba extract phospholipid complex and Ginkgo biloba extract solid dispersions in rats. Fitoterapia 2010; 81:1045-52.
DOI URL |
| 14 |
Zhang KX, Zhang YY, Zhang MY, et al. Effects of phospholipid complex of total flavonoids from Persimmon (Diospyros kaki L.) leaves on experimental atherosclerosis rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2016; 191:245-53.
DOI URL |
| 15 | Callemien D, Collin S. Use of RP-HPLC-ESI (-)-MS/MS to differentiate various proanthocyanidin isomers in lager beer extracts. J Am Soc Brew Chem 2008; 66:109-15. |
| 16 | Zhou XT, Wang L, Han L, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Diospyros kaki leaves. Chin Herb Med 2014; 45:3195-203. |
| 17 |
Ruth MLH, Paola QR, Ana A, et al. Polyphenolic profile of persimmon leaves by high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS). J Funct Foods 2016; 23:370-7.
DOI URL |
| 18 |
Chen G, Xue J, Xu SX, et al. Chemical constituents of the leaves of Diospyros kaki and their cytotoxic effects. J Asian Nat Prod Res 2007; 9:347-53.
PMID |
| 19 |
Xie CY, Xie ZS, Xu XJ, et al. Persimmon (Diospyros kaki L.) leaves: a review on traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties. J Ethnopharmacol 2015; 163:229-40.
DOI URL |
| 20 | Kawakami K, Nishida H, Tatewaki N, et al. Persimmon leaf extract inhibits the ATM activity during DNA damage response induced by doxorubicin in A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells. Biosci Biotech Bioc 2011; 75:650-5. |
| 21 | Chen G, Xu SX, Sha Y. Studies on the constituents of Diospyros kaki leaves. Chinese Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. J Med Chem 2000; 10:298-9. |
| 22 |
Chen G, Xu SX, Wang HZ, et al. Note: Kakispyrol, a new biphenyl derivative from the leaves of Diospyros kaki. J Asian Nat Prod Res 2005; 7:265-8.
DOI URL |
| 23 |
Ganfer F, Chapuis JC, Msonthi JD, et al. Cytotoxic naphthoquinones, molluscicidal saponins and flavonols from Diospyros zombensis. Phytochemistry 1987; 26:2501-3.
DOI URL |
| 24 |
Xue YL, Miyakawa T, Hayashi Y, et al. Isolation and tyrosinase inhibitory effects of polyphenols from the leaves of persimmon, Diospyros kaki. J Agric Food Chem 2011; 59:6011-7.
DOI URL |
| 25 | Chen G, Lu H, Wang C, et al. Effect of five flavonoid compounds isolated from leaves of Diospyros kaki on stimulus-induced superoxide generation and tyrosyl phosphorylation of proteins in human neutrophils. Clin Chim Acta 2002; 362:169-75. |
| 26 |
Chen G, Wei SH, Huang J, et al. A novelC-glycosylflavone from the leaves of Diospyros kaki. J Asian Nat Prod Res 2009; 11:503-7.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Uc-Cachon AH, Molina SGM, Said FS, et al. A new dimeric naphthoquinone from Diospyros anisandra. Nat Prod Res 2013; 27:1174-8.
DOI PMID |
| 28 |
Higa M, Ogihara K, Yogi S. Bioactive naphthoquinone derivatives from Diospyros maritime Blume. Chem Pharm Bull 1998; 46:1189-93.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Cai H, Harrison DG. Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: the role of oxidant stress. Circ Res 2000; 87:840-4.
PMID |
| 30 |
Vallance P, Chan N. Endothelial function and nitric oxide: clinical relevance. Heart 2001; 85:342-50.
PMID |
| 31 |
Wheatcroft SB, Williams IL, Shah AM, et al. Pathophysiological implications of insulin resistance on vascular endothelial function. Diabet Med 2003; 20:255-68.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Pober JS. Endothelial activation: intracellular signaling pathways. Arthritis Res 2002; 4:109-18.
DOI URL |
| 33 |
Steffens S, Mach F. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Herz 2004; 29:741-8.
PMID |
| 34 | Sena MC, Pereira AM, Seiça R. Endothelial dysfunction-a major mediator of diabetic vascular disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013; 1832:2216-31. |
| 35 |
Libby P, Theroux P. Pathophysiology of coronary artery disease. Circulation 2005; 111:3481-8.
DOI URL |
| [1] | REN Hui, ZHAO Lintao, GAO Kai, YANG Yuanyuan, CUI Xiaomin, HU Jing, CHEN Zhiyong, LI Ye. Deciphering the chemical profile and pharmacological mechanism of Jinlingzi powder (金铃子散) against bile reflux gastritis using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with Q exactive focus mass spectrometry, network pharmacology, and molecular docking [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1209-1218. |
| [2] | LIU Xueling, MA Kun, TAO Wenhua, XU Zhongkun, LIU Gang, HU Chunyan, MAO Weiwei, GU Chang, GUO Qi. Natural products for treatment of premature ovarian failure: a narrative review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 606-617. |
| [3] | Esma Anissa Trad Khodja, Abd El Hamid Khabtane, Rabah Arhab, Djamila Benouchenne, Mohamed Sabri Bensaad, Chawki Bensouici, Ramazan Erenler. In vitro assessment of antioxidant, neuroprotective, anti-urease and anti-tyrosinase capacities of Tamarix africana leaves extracts [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 252-264. |
| [4] | HENG Xianpei, LI Liang, YANG Liuqin, WANG Zhita. Efficacy of Dangua Fang (丹瓜方) on endothelial cells damaged by oxidative stress [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 900-907. |
| [5] | ZHU Guohua, SUN Xipeng, DING Cuntao, ZHAO Huan, LI Jing, HUA Qi. Effect of Songlingxuemaikang(松龄血脉康) on mild essential hypertension in patients: a randomized parallel-controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 799-805. |
| [6] | CHEN Qi;QI Xu;FU Yu;JI Tingting;CHAO Ying;LI Jun;MENG Qinghai;BIAN Huimin;LI Yu;. Liuwei Dihuang formula(六味地黄方)protect endothelial cells from apoptosis by up-regulating expression of estrogen receptor-α [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(2): 227-235. |
| [7] | ?nder Aybast?er;. Efficacy of methanol-water extract of Inula helenium root against oxidative DNA damage [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(2): 293-300. |
| [8] | TONG Hengli, ZHU Jing, GONG Feipeng, ZHONG Lingyun, XU Ting. Relationship between cardiotonic activity of Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) and its fingerprint determined by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(1): 140-149. |
| [9] | Deng Zhihao, Yan Yan, Zhao Baoming, Wang Rui, Wang Xiaofeng, Chen Haoxuan, Wen Binyu. Identification of the active ingredients from Guangtongxiao decoction in rat bile based on ultra-performance liquid chromatography/Synapt G2 quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(6): 999-1006. |
| [10] | Wang Qiang, Yang Jing, Lei Yan, Xiu Chengkui, Huo Yanming, Shi Hang. Effects of extracts from Renshen(Radix Ginseng), Sanqi(Radix Notoginseng), and Chuanxiong(Rhizoma Chuanxiong) on F-actin in senescent microvascular endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(3): 376-385. |
| [11] | Lin Shujun, Zhu Mingmin, Chen Weihao, Zhang Yujuan, Lin Jihuan, Pu Liu, Chen Shulian, Zhang Yimin, Liu Xin. Acupuncture stimulation of Yamen(GV 15), Fengfu(GV 16), Baihui(GV 20), Shuigou(GV 26) and Hegu(LI 4) reduces brain microglia activation in a traumatic brain injury rat model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(2): 267-274. |
| [12] | Wang Ying, Li Ming, Yu Xuesong, He Sheng, Wu Xinrong, Wang Yan. Mulberry leaf flavonoids protect against glucotoxicity-induced INS-1 cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(02): 153-159. |
| [13] | Bao Xiaoxia, Li Liuye, Xue Xiaoou. Flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata inhibit activation of tumor-associated macrophages by blocking the Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(02): 160-165. |
| [14] | Jung Joo Yoon, Byung Hyuk Han, Eun Sik Choi, Seung Namgung, Da Hye Jeong, Song Nan Jin, Yun Jung Lee, Dae Gill Kang, Ho Sub Lee. Involvement of heme oxygenase-1 induction in anti-vascular inflammation effects of Xanthoceras sorbifolia in human umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(06): 803-814. |
| [15] | Feng Yu, Zhang Junxiu, Li Shaodan, Liu Yi, Zhang Yin, Guo Yunxia, Yang Minghui. Changes in nitric oxide, angiotensin Ⅱ, angiopoietin-like protein 4 mRNA, neuregulin 1 mRNA, and platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 in rats with acute blood stasis induced by high-molecular-weight dextran [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(06): 846-853. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||