Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 881-890.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.04.018
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical evaluation of strengthening spleen and draining dampness in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a retrospective 10-year follow-up study
KE Tianxingjian1, CHEN Wanjia1( ), XIANG Ling2(
), XIANG Ling2( ), DENG Yueyi1, WANG Yiquan1, LIU Wangyi1, XING Yue1, LU Zhenzhen1, GAO Hongzhi1
), DENG Yueyi1, WANG Yiquan1, LIU Wangyi1, XING Yue1, LU Zhenzhen1, GAO Hongzhi1
- 1 Department of Nephrology, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China
2 Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine department, Shanghai Guangfulin Street Community Health Service Center Songjiang District, Shanghai 200000, China
-
Received:2024-03-22Accepted:2024-10-27Online:2025-07-25Published:2025-07-25 -
Contact:CHEN Wanjia,XIANG Ling -
About author:XIANG Ling, Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine department, Shanghai Guangfulin Street Community Health Service Center Songjiang District, Shanghai 200000, China. 18221717263@163.com
CHEN Wanjia, Department of Nephrology, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China. chenwanjia@vip.sina.com.
-
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Project, Clinical Study on the Treatment of Refractory Membranous Nephropathy with the Treatment of Strengthening Spleen and Draining Dampness in Method using Single Group Target Value Method(2019YFC1709403);Systematic Study on the Diagnosis and Treatment Rules of Membranous Nephropathy in Traditional Chinese Medicine(2023YFC35033501);Systematic Study on the Diagnosis and Treatment Rules of Membranous Nephropathy in Traditional Chinese Medicine(2023YFC35033503)
Cite this article
KE Tianxingjian, CHEN Wanjia, XIANG Ling, DENG Yueyi, WANG Yiquan, LIU Wangyi, XING Yue, LU Zhenzhen, GAO Hongzhi. Clinical evaluation of strengthening spleen and draining dampness in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a retrospective 10-year follow-up study[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 881-890.
share this article
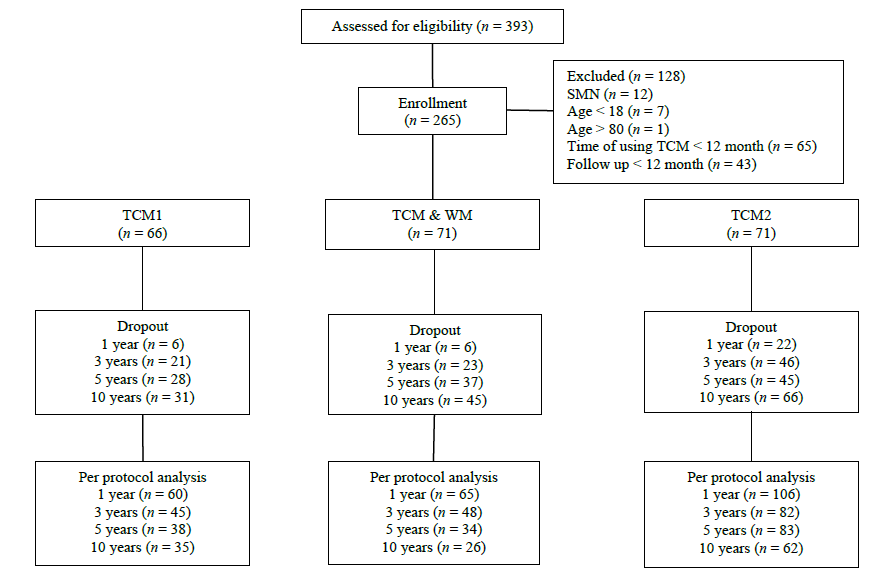
Figure 1 Follow-up flow chart TCM1: patients in this group received TCM treatment focusing on spleen strengthening and dampness drainage without prior exposure to conventional WM. TCM2: this group included patients who had received WM treatment, experienced treatment failure, and discontinued WM therapy for at least 6 months. Alternatively, it included patients who experienced relapse but were unwilling or unable to resume conventional WM. These patients subsequently received TCM therapy focused on spleen strengthening and dampness drainage at our center. TCM&WM: patients in this group received both TCM treatment and conventional WM as initial treatment at our center. TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine; WM: Western Medicine; SMN: Secondary membranous nephropathy.
| Item | Baseline | 1 year (n = 231) | 3 years (n = 175) | 5 years (n = 155) | 10 years (n = 123) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24-h urinary protein (g/d) | 4.3±2.7 | 2.6±2.5a | 1.8±2.1a | 1.9±1.9a | 1.7±2.7a |
| serum albumin (g/L) | 25.6±6.8 | 30.3±9.8a | 34.6±9.1a | 35.4±8.4a | 37.0±8.7a |
| Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 77.2±35.4 | 84.0±64.0 | 83.0±56.2 | 92.6±74.6 | 97.8±100.8 |
| eGFR (EPI formula) | 93.3±25.5 | 91.5±30.1 | 90.2±27.2 | 85.9±29.9 | 80.8±28.2a |
Table 1 Changes in key clinical indicators before and after treatment ($\bar{x} \pm s$)
| Item | Baseline | 1 year (n = 231) | 3 years (n = 175) | 5 years (n = 155) | 10 years (n = 123) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24-h urinary protein (g/d) | 4.3±2.7 | 2.6±2.5a | 1.8±2.1a | 1.9±1.9a | 1.7±2.7a |
| serum albumin (g/L) | 25.6±6.8 | 30.3±9.8a | 34.6±9.1a | 35.4±8.4a | 37.0±8.7a |
| Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 77.2±35.4 | 84.0±64.0 | 83.0±56.2 | 92.6±74.6 | 97.8±100.8 |
| eGFR (EPI formula) | 93.3±25.5 | 91.5±30.1 | 90.2±27.2 | 85.9±29.9 | 80.8±28.2a |
| Group | Time | n | 24-h urinary protein (g/d) | serum albumin (g/d) | Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | eGFR (EPI formula) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCM1 | 0 year | 66 | 4.3±2.2 | 26.3±6.5 | 67.3±19.2 | 100.1±18.4 |
| 1 year | 60 | 2.2±2.3 | 32.6±9.7 | 62.2±20.7 | 104.3±20.6 | |
| 3 years | 45 | 1.2±1.9 | 38.7±7.8 | 66.9±26.4 | 99.3±18.8 | |
| 5 years | 38 | 1.6±1.9 | 36.7±8.0 | 81.0±54.6 | 90.3±24.3 | |
| 10 years | 35 | 1.1±2.2 | 39.4±6.2 | 73.4±27.7 | 83.8±17.5 | |
| TCM2 | 0 year | 128 | 4.2±2.9 | 25.2±6.9 | 86.1±45.8 | 87.6±29.3 |
| 1 year | 106 | 2.8±2.0 | 29.4±9.3 | 97.6±86.1 | 85.9±33.1 | |
| 3 years | 82 | 1.8±1.7 | 33.7±9.4 | 87.5±60.4 | 87.7±29.3 | |
| 5 years | 83 | 1.9±2.0 | 35.1±8.4 | 90.3±63.6 | 86.0±29.6 | |
| 10 years | 62 | 2.3±3.2 | 34.7±8.3 | 104.4±120.4 | 80.1±29.2 | |
| TCM & WM | 0 year | 71 | 4.5±2.5 | 25.7±6.8 | 70.2±16.9 | 97.2±21.7 |
| 1 year | 65 | 2.8±3.4 | 29.7±10.5 | 81.2±36.0 | 89.3±29.1 | |
| 3 years | 48 | 2.1±2.6 | 32.5±8.9 | 90.5±66.7 | 85.8±28.9 | |
| 5 years | 34 | 2.3±1.9 | 34.7±8.6 | 110.1±110.0 | 81.3±36.0 | |
| 10 years | 26 | 1.0±1.5 | 39.8±10.7 | 105.9±96.7 | 79.6±34.7 |
Table 2 Changes in key clinical indicators before and after treatment ($\bar{x} \pm s$)
| Group | Time | n | 24-h urinary protein (g/d) | serum albumin (g/d) | Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | eGFR (EPI formula) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCM1 | 0 year | 66 | 4.3±2.2 | 26.3±6.5 | 67.3±19.2 | 100.1±18.4 |
| 1 year | 60 | 2.2±2.3 | 32.6±9.7 | 62.2±20.7 | 104.3±20.6 | |
| 3 years | 45 | 1.2±1.9 | 38.7±7.8 | 66.9±26.4 | 99.3±18.8 | |
| 5 years | 38 | 1.6±1.9 | 36.7±8.0 | 81.0±54.6 | 90.3±24.3 | |
| 10 years | 35 | 1.1±2.2 | 39.4±6.2 | 73.4±27.7 | 83.8±17.5 | |
| TCM2 | 0 year | 128 | 4.2±2.9 | 25.2±6.9 | 86.1±45.8 | 87.6±29.3 |
| 1 year | 106 | 2.8±2.0 | 29.4±9.3 | 97.6±86.1 | 85.9±33.1 | |
| 3 years | 82 | 1.8±1.7 | 33.7±9.4 | 87.5±60.4 | 87.7±29.3 | |
| 5 years | 83 | 1.9±2.0 | 35.1±8.4 | 90.3±63.6 | 86.0±29.6 | |
| 10 years | 62 | 2.3±3.2 | 34.7±8.3 | 104.4±120.4 | 80.1±29.2 | |
| TCM & WM | 0 year | 71 | 4.5±2.5 | 25.7±6.8 | 70.2±16.9 | 97.2±21.7 |
| 1 year | 65 | 2.8±3.4 | 29.7±10.5 | 81.2±36.0 | 89.3±29.1 | |
| 3 years | 48 | 2.1±2.6 | 32.5±8.9 | 90.5±66.7 | 85.8±28.9 | |
| 5 years | 34 | 2.3±1.9 | 34.7±8.6 | 110.1±110.0 | 81.3±36.0 | |
| 10 years | 26 | 1.0±1.5 | 39.8±10.7 | 105.9±96.7 | 79.6±34.7 |
| Item | 1 year (n = 231) | 3 years (n = 175) | 5 years (n = 155) | 10 years (n = 123) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | 40 (17.32) | 59 (33.71) | 54 (33.55) | 52 (42.28) |
| PR | 82 (35.50) | 63 (36.00) | 52 (34.84) | 37 (30.08) |
| Remission rate (%) (CR+PR) | 122 (52.81) | 122 (69.71) | 106 (68.39) | 89 (72.36) |
| RE | 0 (0.00) | 1 (2.50) | 6 (10.16) | 10 (18.52) |
Table 3 Overall efficacy analysis [n (%)]
| Item | 1 year (n = 231) | 3 years (n = 175) | 5 years (n = 155) | 10 years (n = 123) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | 40 (17.32) | 59 (33.71) | 54 (33.55) | 52 (42.28) |
| PR | 82 (35.50) | 63 (36.00) | 52 (34.84) | 37 (30.08) |
| Remission rate (%) (CR+PR) | 122 (52.81) | 122 (69.71) | 106 (68.39) | 89 (72.36) |
| RE | 0 (0.00) | 1 (2.50) | 6 (10.16) | 10 (18.52) |
| Group | Time | n | CR | PR | CR+PR | RE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCM1 | 1 year | 60 | 12 (20.0) | 22 (36.7) | 34 (56.7) | 0 (0.0) |
| 3 years | 45 | 23 (51.1) | 15 (33.3) | 38 (84.4) | 0 (0.0) | |
| 5 years | 38 | 18 (47.4) | 11 (29.0) | 29 (76.3) | 1 (4.4) | |
| 10 years | 35 | 20 (57.1) | 9 (25.7) | 29 (82.9) | 1 (5.6) | |
| TCM2 | 1 year | 106 | 13 (12.3) | 43 (40.6) | 56 (52.8) | 0 (0.0) |
| 3 years | 82 | 21 ( (25.6) | 33 (40.2) | 54 (65.9) | 1 (7.7) | |
| 5 years | 83 | 24 (28.9) | 32 (38.6) | 56 (67.5) | 4 (19.1) | |
| 10 years | 62 | 19 (30.7) | 23 (37.1) | 42 (67.8) | 8 (33.3) | |
| TCM & WM | 1 year | 65 | 15 (23.1) | 17 (26.2) | 32 (49.2) | 0 (0.0) |
| 3 years | 48 | 15 (31.3) | 15 (31.3) | 30 (62.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| 5 years | 34 | 12 (35.3) | 9 (26.5) | 21 (61.8) | 1 (6.7) | |
| 10 years | 26 | 13 (50.0) | 5 (19.2) | 18 (69.2) | 1 (8.3) |
Table 4 Efficacy analysis across different treatment groups [n (%)]
| Group | Time | n | CR | PR | CR+PR | RE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCM1 | 1 year | 60 | 12 (20.0) | 22 (36.7) | 34 (56.7) | 0 (0.0) |
| 3 years | 45 | 23 (51.1) | 15 (33.3) | 38 (84.4) | 0 (0.0) | |
| 5 years | 38 | 18 (47.4) | 11 (29.0) | 29 (76.3) | 1 (4.4) | |
| 10 years | 35 | 20 (57.1) | 9 (25.7) | 29 (82.9) | 1 (5.6) | |
| TCM2 | 1 year | 106 | 13 (12.3) | 43 (40.6) | 56 (52.8) | 0 (0.0) |
| 3 years | 82 | 21 ( (25.6) | 33 (40.2) | 54 (65.9) | 1 (7.7) | |
| 5 years | 83 | 24 (28.9) | 32 (38.6) | 56 (67.5) | 4 (19.1) | |
| 10 years | 62 | 19 (30.7) | 23 (37.1) | 42 (67.8) | 8 (33.3) | |
| TCM & WM | 1 year | 65 | 15 (23.1) | 17 (26.2) | 32 (49.2) | 0 (0.0) |
| 3 years | 48 | 15 (31.3) | 15 (31.3) | 30 (62.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| 5 years | 34 | 12 (35.3) | 9 (26.5) | 21 (61.8) | 1 (6.7) | |
| 10 years | 26 | 13 (50.0) | 5 (19.2) | 18 (69.2) | 1 (8.3) |
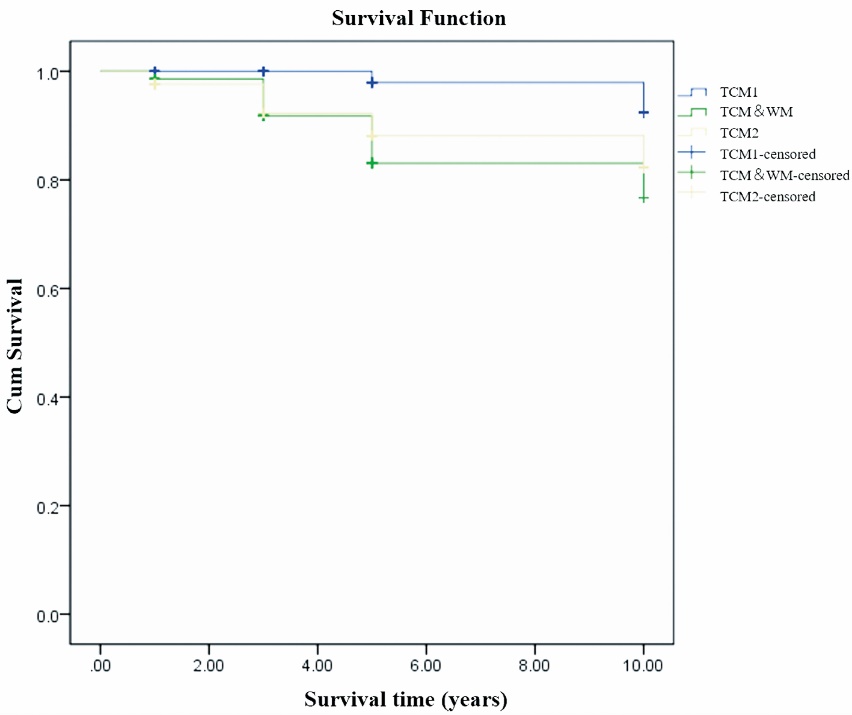
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier survival analysis comparing patients in different groups who did not reach the composite outcomes events TCM1: patients in this group received TCM treatment focusing on spleen strengthening and dampness drainage without prior exposure to conventional WM. TCM2: this group included patients who had received WM treatment, experienced treatment failure, and discontinued WM therapy for at least 6 months. Alternatively, it included patients who experienced relapse but were unwilling or unable to resume conventional WM. These patients subsequently received TCM therapy focused on spleen strengthening and dampness drainage at our center. TCM&WM: Patients in this group received both TCM treatment and conventional WM as initial treatment at our center. TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine; WM: Western Medicine.
| Item | Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95.0% CI) | P value | HR (95.0% CI) | P value | ||
| Incipient | 0.596 (0.378, 0.938) | 0.025 | - | - | |
| Use of immunosuppressants | 1.268 (0.838, 1.919) | 0.262 | - | - | |
| Use of ARB and / or ACEI drugs | 1.027 (0.695, 1.516) | 0.895 | - | - | |
| Treatment course of TCM | 0.843 (0.803, 0.884) | 0.000 | 0.826 (0.779, 0.876) | 0.000 | |
| Sex | 1.072 (0.721, 1.593) | 0.731 | - | - | |
| Age | 1.329 (1.035, 1.707) | 0.026 | - | - | |
| Hypertension | 1.565 (1.045, 2.344) | 0.030 | 1.912 (1.181, 3.094) | 0.008 | |
| Diabetes | 0.742 (0.447, 1.233) | 0.250 | - | - | |
| Proteinuria (g/d) | 1.023 (0.961, 1.089) | 0.474 | - | - | |
| Serum albumin(g/L) | 0.943 (0.916, 0.972) | 0.000 | 0.930 (0.894, 0.969) | 0.000 | |
| Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 1.008 (1.004, 1.012) | 0.000 | - | - | |
| eGFR (EPI) | 0.988 (0.981, 0.995) | 0.001 | - | - | |
| Urinary protein decline rate (1 year duration) | 0.917 (0.854, 0.986) | 0.018 | - | - | |
| Serum albumin rise rate (1 year duration) | 0.954 (0.931, 0.977) | 0.000 | 0.930 (0.909, 0.957) | 0.000 | |
Table 5 Factors influencing the efficacy of the TCM treatment plan (univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis, n = 265)
| Item | Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95.0% CI) | P value | HR (95.0% CI) | P value | ||
| Incipient | 0.596 (0.378, 0.938) | 0.025 | - | - | |
| Use of immunosuppressants | 1.268 (0.838, 1.919) | 0.262 | - | - | |
| Use of ARB and / or ACEI drugs | 1.027 (0.695, 1.516) | 0.895 | - | - | |
| Treatment course of TCM | 0.843 (0.803, 0.884) | 0.000 | 0.826 (0.779, 0.876) | 0.000 | |
| Sex | 1.072 (0.721, 1.593) | 0.731 | - | - | |
| Age | 1.329 (1.035, 1.707) | 0.026 | - | - | |
| Hypertension | 1.565 (1.045, 2.344) | 0.030 | 1.912 (1.181, 3.094) | 0.008 | |
| Diabetes | 0.742 (0.447, 1.233) | 0.250 | - | - | |
| Proteinuria (g/d) | 1.023 (0.961, 1.089) | 0.474 | - | - | |
| Serum albumin(g/L) | 0.943 (0.916, 0.972) | 0.000 | 0.930 (0.894, 0.969) | 0.000 | |
| Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 1.008 (1.004, 1.012) | 0.000 | - | - | |
| eGFR (EPI) | 0.988 (0.981, 0.995) | 0.001 | - | - | |
| Urinary protein decline rate (1 year duration) | 0.917 (0.854, 0.986) | 0.018 | - | - | |
| Serum albumin rise rate (1 year duration) | 0.954 (0.931, 0.977) | 0.000 | 0.930 (0.909, 0.957) | 0.000 | |
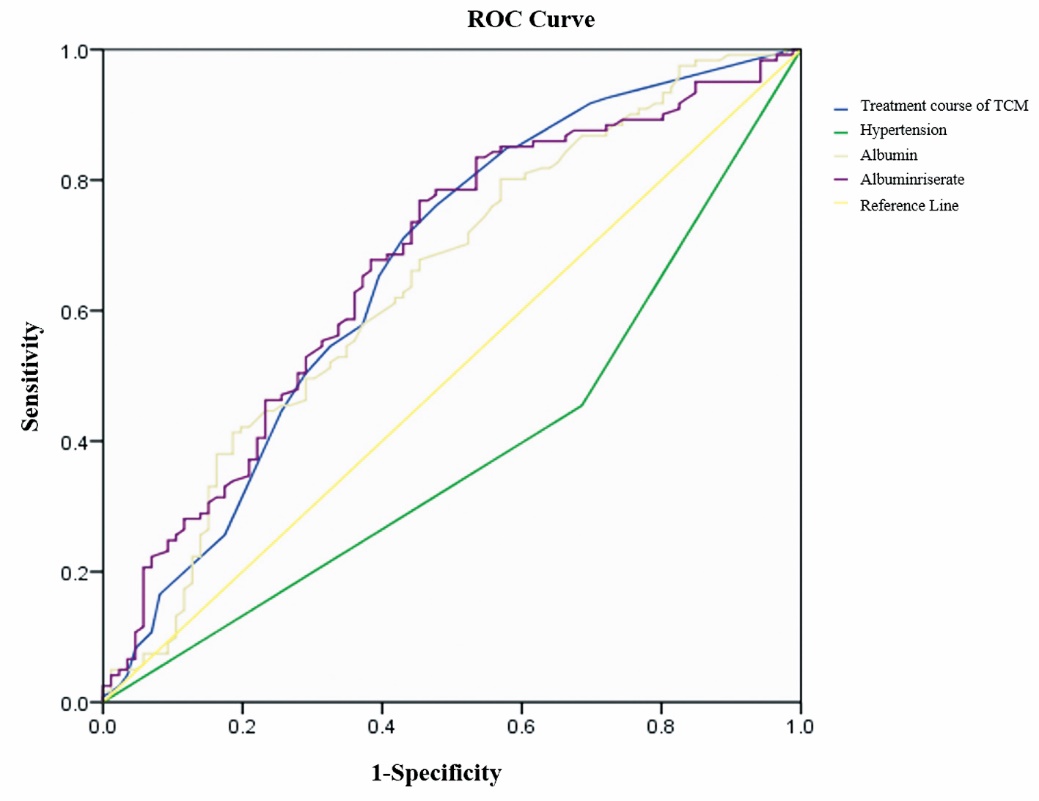
Figure 4 ROC curve for influencing factors of treatment efficacy in 265 patients TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine; ROC: receiver operating characteristic.
| 1. | Zhu P, Zhou FD, Wang SX, et al. Increasing frequency of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in primary glomerular disease: a 10-year renal biopsy study from a single Chinese nephrology centre. Nephrology (Carlton) 2015; 20: 560-6. |
| 2. |
Xu X, Wang G, Chen N, et al. Long-term exposure to air pollution and increased risk of membranous nephropathy in China. J Am Soc Nephrol 2016; 27: 3739-46.
PMID |
| 3. | Köllner SMS, Seifert L, Zahner G, Tomas NM. Strategies towards antigen-specific treatments for membranous nephropathy. Front Immunol 2022; 13: 822508. |
| 4. |
Deng L, Xu G. Update on the application of monoclonal antibody therapy in primary membranous nephropathy. Drugs 2023; 83: 507-30.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Wang X, Cui Z, Zhang YM, et al. Rituximab for non-responsive idiopathic membranous nephropathy in a Chinese cohort. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2018; 33: 1558-63. |
| 6. | Fervenza FC, Appel GB, Barbour SJ, et al. Rituximab or cyclosporine in the treatment of membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2019; 381: 36-46. |
| 7. |
Gauckler P, Shin JI, Alberici F, et al. Rituximab in membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int Rep 2021; 6: 881-93.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Ronco P, Beck L, Debiec H, et al. Membranous nephropathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021; 7: 69.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | van de Logt AE, Fresquet M, Wetzels JF, et al. The anti-PLA2R antibody in membranous nephropathy: what we know and what remains a decade after its discovery. Kidney Int 2019; 96: 1292-302. |
| 10. |
Chen Y, Deng Y, Ni Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Shenqi particle) for patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Kidney Dis 2013; 62: 1068-76.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Wang YH, Sun LY, Li MM, Wang Y, Li XY, Liao X. Clinical evidence of oral Chinese patent medicines in treatment of chronic kidney disease: a scoping review. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2023; 29: 99-108. |
| 12. | Liu CY, Hu JF. The using of warming kidney and dredging collaterals in patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy, Guo Ji Zhong Yi Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2019; 41: 229-33. |
| 13. | Fernández-Juárez G, Rojas-Rivera J, Logt AV, et al. The STARMEN trial indicates that alternating treatment with corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide is superior to sequential treatment with tacrolimus and rituximab in primary membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 2021; 99: 986-98. |
| 14. | Storrar J, McDonnell T, Ragy O, et al. Time for a relook? An update on primary membranous nephropathy incidence in a large UK cohort. Clin Kidney J 2024; 17: 1-2. |
| 15. |
Ramachandran R, Kumar V, Bharati J, et al. Long-term follow-up of cyclical cyclophosphamide and steroids versus tacrolimus and steroids in primary membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int Rep 2021; 6: 2653-60.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Shi B, Zhang RR, Liang Y, et al. Efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine regimen Jianpi Qushi formula for refractory patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a retrospective case-series study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018; 2018: 5854710. |
| 17. | Shan W, Guan H, Gu H, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Heliyon 2024; 10: 1-13. |
| 18. |
Chen X, Chen Y, Shi K, et al. Comparison of prognostic, clinical, and renal histopathological characteristics of overlapping idiopathic membranous nephropathy and IgA nephropathy versus idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 11468.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Radice A, Trezzi B, Maggiore U, et al. Clinical usefulness of autoantibodies to M-type phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) for monitoring disease activity in idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN). Autoimmun Rev 2016; 15: 146-54.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Ronco P, Debiec H. Pathophysiological advances in membranous nephropathy: time for a shift in patient's care. Lancet 2015; 385: 1983-92.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Bally S, Debiec H, Ponard D, et al. Phospholipase A2 receptor-related membranous nephropathy and mannan-binding lectin deficiency. J Am Soc Nephrol 2016; 27: 3539-44.
PMID |
| 22. | du Buf-Vereijken PW, Branten AJ, Wetzels JF. Membranous nephropathy study group. cytotoxic therapy for membranous nephropathy and renal insufficiency: improved renal survival but high relapse rate. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2004; 19: 1142-8. |
| 23. |
Jha V, Ganguli A, Saha TK, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of steroids and cyclophosphamide in adults with nephrotic syndrome caused by idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007; 18: 1899-904.
DOI PMID |
| 24. | Lin S, Li HY, Zhou T, et al. Efficacy and safety of cyclosporine A in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in an Asian population. Drug Des Devel Ther 2019; 13: 2305-30. |
| 25. |
Yu X, Ruan L, Qu Z, et al. Low-dose cyclosporine in treatment of membranous nephropathy with nephrotic syndrome: effectiveness and renal safety. Ren Fail 2017; 39: 688-97.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Sato M, Takei T, Moriyama T, et al. Long-term outcomes of initial therapy for idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol 2017; 21: 842-51.
DOI PMID |
| 27. |
Waldman M, Austin HA 3rd. Controversies in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 2009; 5: 469-79.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Schieppati A, Perna A, Zamora J, et al. Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults with nephrotic syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004; (4): CD004293. |
| 29. | Zhang XD, Cui Z, Zhang MF, et al. Clinical implications of pathological features of primary membranous nephropathy. BMC Nephrol 2018; 19: 215. |
| 30. | Couser WG. Primary membranous nephropathy [published correction appears in Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Sep 7; 12 (9):1528]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017; 12: 983-97. |
| 31. |
Kaneko K, Kimata T, Tsuji S, et al. Serum albumin level accurately reflects antioxidant potentials in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Clin Exp Nephrol 2012; 16: 411-4.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Qiu Y, Qiu Y, Yao GM, et al. Natural product therapies in chronic kidney diseases: An update. Nephrol Ther 2022; 18: 75-9. |
| 33. | Qiao L, Gao ZQ, Guo ZA, Jin Y. Mechanisms of active components of Astragalus membranaceus in regulating the NLRP3 inflammasome to attenuate diabetic nephropathy. Guo Ji Lao Nian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2025; 46: 360-4. |
| 34. |
Qin Q, Niu J, Wang Z, et al. Astragalus membranaceus inhibits inflammation via phospho-P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathways in advanced glycation end product-stimulated macrophages. Int J Mol Sci 2012; 13: 8379-87.
DOI PMID |
| 35. | Cao Y, Ruan Y, Shen T, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide suppresses doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by regulating the PI3k/Akt and p38MAPK pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014; 2014: 674219. |
| 36. |
Zhong Y, Deng Y, Chen Y, et al. Cijiang He J. Therapeutic use of traditional Chinese herbal medications for chronic kidney diseases. Kidney Int 2013; 84: 1108-18.
DOI PMID |
| 37. | Huang SH, Hu YF. Clinical effect of Wenyang Lishui decoction combined with Huangqi injection in the treatment of nephrotic syndrome patients. Yi Liao Zhuang Bei 2018; 31: 116-7. |
| 38. | Wang BZ, Zhao YJ, Hou YY. The effect of Huangqi injection on blood lipids and hemorheology in nephrotic syndrome. Heilongjiang Zhong Yi Yao 2020; 49: 11. |
| 39. | Nie RY, Xiong GL, Fu T, Pan MQ. Network Meta-analysis of Chinese medicine injections for the intervention of proteinuria in diabetic nephropathy. Guangzhou Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2025; 42: 518-30. |
| 40. |
Wen M, Küchle C, Sarkar O, et al. Plasmapheresis combined with rituximab for refractory idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Int Urol Nephrol 2014; 46: 847-8.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | TIAN Xinrong, HOU Runsu, LIU Xinguang, ZHAO Peng, TIAN Yange, LI Jiansheng. Yangqing Chenfei formula (养清尘肺方) alleviates crystalline silica induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis by suppressing macrophage polarization [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1126-1139. |
| [2] | CHEN Yunhu, YIN Moqing, FAN Lihua, JIANG Xuechun, ZHANG Tao, ZHU Xingyu, XU Hongfeng. Mirror-like tongue is an important predictor of acute heart failure: a cohort study of acute heart failure in Chinese patients [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1243-1251. |
| [3] | GUO Zhuang, WANG Junwen, LI Zhonglong, CHEN Zhongjie, CHEN Li, YAN Shiyan, LU Hongrong, LI Zhigeng, LI Guanying. Protocol to establish auxiliary diagnostic model for knee osteoarthritis functional testing equipment [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 379-385. |
| [4] | Zhao Xiao Feng , Su Shi Jun , Guo Yun Hong , Wang Shu. Mortality and recurrence of vascular disease among stroke patients treated with combined TCM therapy [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012, 32(02): 173-178. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||